In the realm of medical billing, denial codes serve as essential indicators of claim rejections and payment discrepancies. Familiarizing yourself with the most prevalent denial codes can significantly impact your healthcare organization’s revenue cycle management. By understanding these codes, you can effortlessly navigate through the complex world of medical billing, streamline the claims process, and ensure efficient reimbursement. This article will provide you with valuable insights into the various denial codes commonly encountered in medical billing, equipping you with the knowledge necessary to identify and address payment denials effectively.
Introduction
In the complex world of medical billing, denial codes play a crucial role in the reimbursement process. As a healthcare provider, it is important to understand denial codes and their significance in order to minimize claim rejections and maximize revenue. This article will provide an overview of denial codes in medical billing, discuss the different types of denial codes, highlight some of the most common denial codes, and present steps to reduce denials. Additionally, we will emphasize the importance of clear communication in the medical billing process.
Overview of Denial Codes in Medical Billing

Explanation of Denial Codes
Denial codes are standardized codes used by insurance companies to communicate reasons for claim rejections or denials. These codes provide a clear and concise explanation for why a claim was not paid or partially paid. Denial codes contain alphanumeric characters and are assigned by insurance payors based on the specific reason for the denial.
Importance of Denial Codes
Denial codes serve as a valuable tool for healthcare providers, enabling them to identify and address billing issues promptly. By understanding the reasons behind claim denials, healthcare organizations can implement necessary changes to improve their billing processes, reduce denials, and ultimately increase revenue. Denial codes also facilitate communication between healthcare providers and insurance companies, allowing for easier resolution of payment disputes.
How Denial Codes are Used in Medical Billing
Denial codes are used throughout the medical billing process, from claim submission to claim resolution. When a claim is denied, the denial code is included in the Explanation of Benefits (EOB) or remittance advice sent by the insurance company to the healthcare provider. This code serves as a reference for the provider to investigate the reason for the denial and take appropriate action, such as correcting errors, appealing the denial, or resubmitting the claim.
Types of Denial Codes
Front-end Denial Codes
Front-end denial codes are typically related to demographic or eligibility issues, such as invalid patient information, missing or incorrect insurance details, or expired coverage. These denials occur at the initial stage of claim submission and can often be resolved by verifying and updating patient and insurance information.
Back-end Denial Codes
Back-end denial codes are related to issues that arise after claim submission, such as coding errors, lack of medical necessity, or missing documentation. These denials require further investigation and intervention to address the underlying issues and rectify the claim.
Claim Denial Codes
Claim denial codes are specific to the nature of the claim and provide information regarding the services billed, such as duplicate claims, services not covered by the insurance plan, or lack of authorization. These denials require careful review and follow-up to determine the necessary steps for resolution.
Medical Necessity Denial Codes
Medical necessity denial codes indicate that the services provided were not deemed medically necessary by the insurance company. These denials often require additional documentation or a detailed explanation from the healthcare provider to justify the need for the services rendered.
Authorization Denial Codes
Authorization denial codes indicate that the services provided were not pre-authorized by the insurance company. This can result in claim denials and may require the healthcare provider to submit a retroactive authorization request or seek an appeal if the services were deemed medically necessary.
Coding Denial Codes
Coding denial codes indicate errors or discrepancies in the coding of medical procedures or diagnoses. These denials typically require a review of the documentation and correction of any coding errors before the claim can be resubmitted for reimbursement.
Common Denial Codes in Medical Billing
Understanding the most common denial codes can help healthcare providers identify recurring issues and take proactive steps to avoid these denials. Some of the most common denial codes in medical billing include:
Insufficient Documentation (Denial Code: CO4)
Insufficient documentation denial codes are often issued when the supporting documentation for a claim is incomplete or does not provide enough evidence to justify the services billed. This denial code highlights the importance of thorough and accurate documentation in the medical billing process.
Non-covered Charges (Denial Code: CO50)
Non-covered charges denial codes indicate that certain charges or services are not covered under the patient’s insurance plan. This denial code can be avoided by verifying insurance coverage and benefits prior to providing services and informing patients of any potential out-of-pocket expenses.
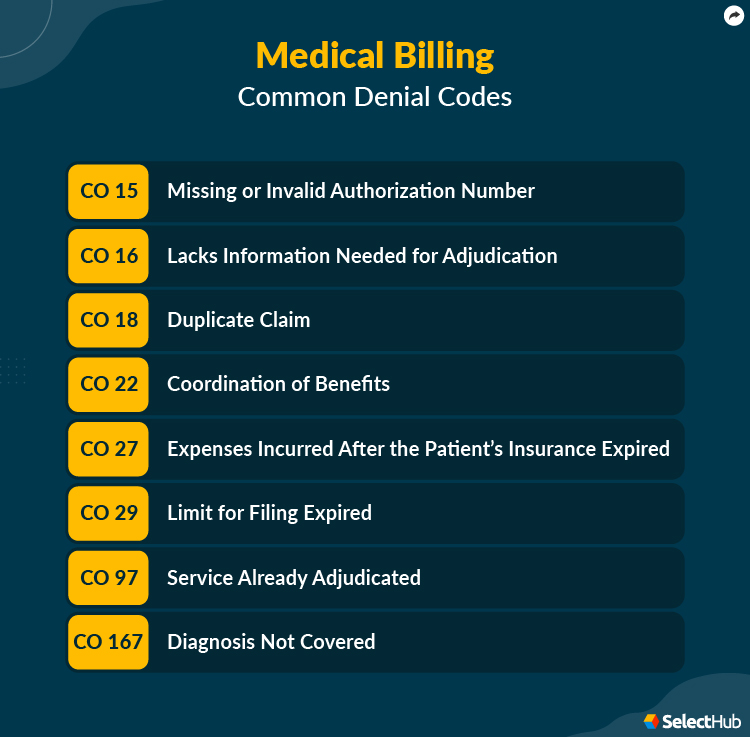
Duplicate Claim (Denial Code: CO19)
Duplicate claim denial codes are issued when a claim for the same services has already been submitted and processed by the insurance company. This code highlights the importance of maintaining accurate and up-to-date records to avoid duplicate claim submissions.
Services Not Medically Necessary (Denial Code: CO50)
Services not medically necessary denial codes indicate that the services provided were not deemed necessary or appropriate for the patient’s condition by the insurance company. This denial code often requires additional documentation or an appeal to justify the medical necessity of the services rendered.
Claim filed too late (Denial Code: CO29)
Claim filed too late denial codes indicate that the claim was not submitted within the designated timeframe specified by the insurance company. Healthcare providers must be aware of the timely filing requirements of each insurance plan and submit claims in a timely manner to avoid this denial.
Lack of Authorization (Denial Code: CO4)
Lack of authorization denial codes indicate that the services provided were not pre-authorized by the insurance company, resulting in claim denial. To avoid this denial, healthcare providers must obtain proper authorization prior to providing services, especially for procedures or treatments that require pre-authorization.
Service Not Covered by Payor (Denial Code: CO97)
Service not covered by payor denial codes indicate that the specific service or procedure is not covered under the patient’s insurance plan. Healthcare providers must verify the coverage and benefits for each patient to ensure that the services provided are eligible for reimbursement.
Incorrect Coding (Denial Code: CO16)
Incorrect coding denial codes indicate errors or discrepancies in the coding of medical procedures or diagnoses. These denials can often be avoided by ensuring accurate coding practices and proper documentation to support the assigned codes.
Claim Lacks Information (Denial Code: CO16)
Claim lacks information denial codes indicate that the claim submitted is missing essential information or is incomplete. This denial code emphasizes the importance of submitting complete and accurate claims to avoid claim rejections or denials.
Invalid or Missing Claim/Service Date (Denial Code: CO16)
Invalid or missing claim/service date denial codes indicate that the claim or service date provided on the claim form is incorrect or missing. Healthcare providers must ensure that the claim forms are accurately completed and include all necessary information, including the date of service.

Steps to Reduce Denials
Minimizing claim denials requires proactive measures and attention to detail. Here are some steps healthcare providers can take to reduce denials:
Verify Patient Information
Double-checking patient information, such as name, date of birth, insurance details, and contact information, can help prevent front-end denials caused by incorrect or outdated information. Maintaining an accurate patient database and verifying information prior to claim submission is key to reducing denials.
Ensure Accurate Documentation
Thorough and accurate documentation is essential to support the services billed and justify medical necessity. Healthcare providers must ensure that all relevant information, such as patient history, examination findings, procedures performed, and treatment plans, are clearly and accurately documented.
Verify Insurance Coverage and Benefits
Verifying insurance coverage and benefits prior to providing services can help identify potential coverage limitations or exclusions. By informing patients of any out-of-pocket expenses and obtaining proper pre-authorization when required, healthcare providers can minimize denials related to coverage issues.
Submit Clean Claims
Submitting clean claims that are accurately coded, complete, and include all necessary documentation is crucial to avoid claim denials. Conducting thorough internal reviews and quality checks before claim submission can help identify and correct any potential errors or omissions.
Follow up on Denials
Promptly following up on denied claims is essential to identify the reasons for denial and take appropriate action. This may involve providing additional documentation, appealing the denial, or correcting any coding errors. Proactive denial management can improve claim resolution rates and reduce revenue loss.
Implement Denial Management Processes
Developing and implementing effective denial management processes can help healthcare providers identify trends, address underlying issues, and prevent recurring denials. This may involve analyzing denial data, conducting staff training on coding and documentation, and regularly reviewing and updating billing policies and procedures.
Importance of Clear Communication
Clear communication is paramount in the medical billing process to ensure accurate claim submission and timely reimbursement. Here are some areas where clear communication is crucial:
Clear Documentation
Clear and concise documentation of patient encounters, procedures performed, and treatment plans is essential to support the services billed and justify medical necessity. Healthcare providers must ensure that their documentation is comprehensive, legible, and follows established guidelines and coding rules.
Precise Coding
Accurate and precise coding is crucial to ensure that the services rendered are properly identified and billed. Healthcare providers should stay updated on coding guidelines, use the most specific and appropriate codes, and document any additional details or modifiers necessary to accurately reflect the services provided.
Effective Claim Submission
Submitting claims electronically using standardized formats and following payor-specific guidelines can improve the efficiency and accuracy of claim submission. Prompt and accurate claim submission increases the chances of timely reimbursement and reduces the likelihood of denials.
Proper Appeals Process
In cases where a denial occurs, having a well-defined appeals process is essential. Clear communication and documentation of the reasons for the appeal, along with any supporting evidence, can significantly improve the chances of a successful appeal.
Conclusion
Understanding denial codes and their implications is crucial for healthcare providers to navigate the complex landscape of medical billing successfully. By comprehending different denial code categories, recognizing common denial codes, and implementing effective denial management processes, providers can minimize claim denials, optimize revenue, and improve overall billing efficiency. Clear communication through accurate documentation, precise coding, effective claim submission, and a well-defined appeals process is essential to ensure maximum reimbursement and streamline the medical billing process. Sound knowledge of denial codes combined with proactive measures can lead to improved financial outcomes and enhanced patient satisfaction.