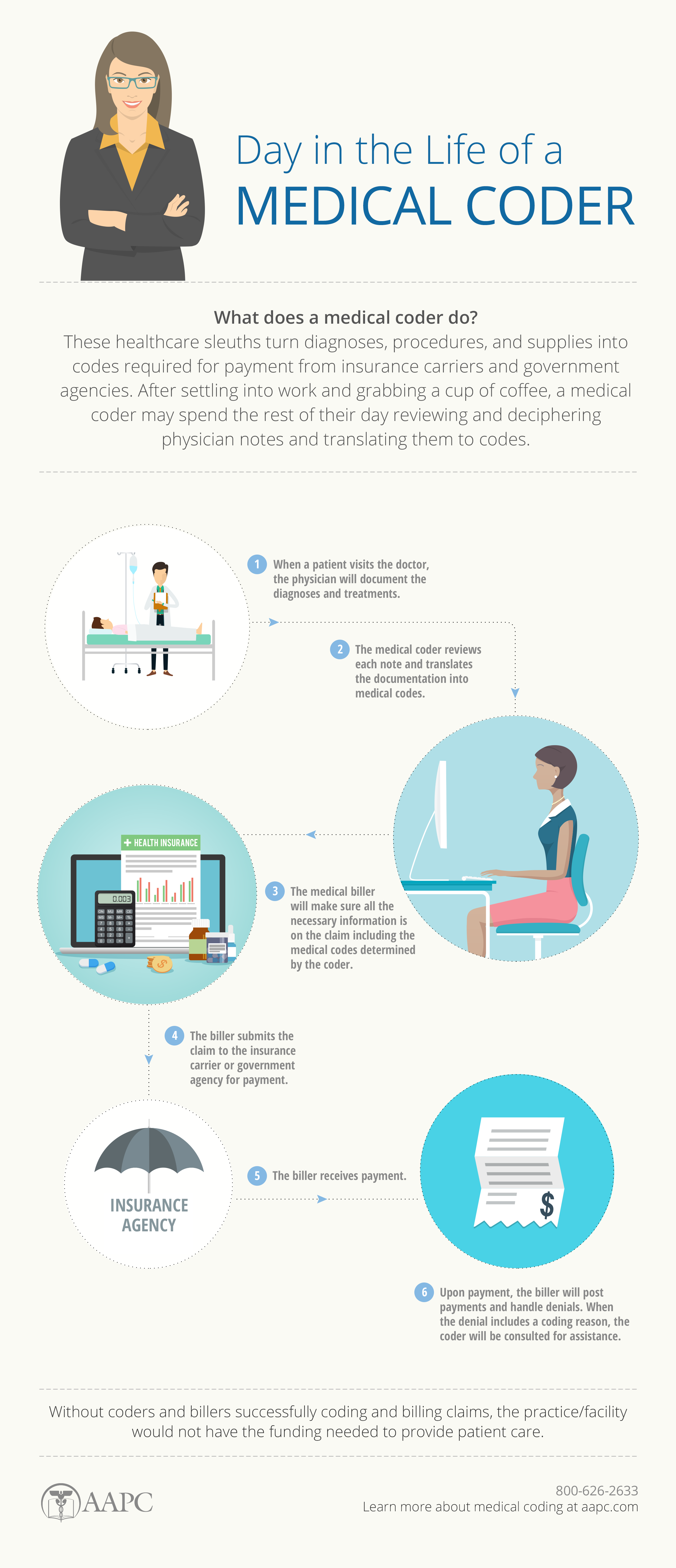
Medical billing and coding is a crucial aspect of healthcare administration, responsible for ensuring accurate billing and coding of medical procedures and services. To excel in this field, you need a diverse set of skills. An eye for detail is essential, as you will be working with complex medical codes and patient records. The ability to interpret and follow guidelines and regulations is also crucial, as compliance with healthcare laws is paramount. Additionally, strong computer and communication skills are necessary to effectively navigate electronic health record systems and collaborate with healthcare professionals. A comprehensive understanding of medical terminology and anatomy is also fundamental to accurately assign codes. In this article, we will explore the essential skills needed to succeed in medical billing and coding.
Technical Skills
To excel in the field of medical billing and coding, you must possess a strong foundation in technical skills. One crucial skill is a comprehensive knowledge of medical terminology. An in-depth understanding of medical terms and vocabulary is necessary to accurately assign the correct codes and ensure proper documentation.
In addition to medical terminology, you should also have a firm grasp of medical codes. These codes, such as the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) and Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes, are essential for accurately documenting and billing for medical procedures and services. Familiarity with these codes and their application is crucial to ensure compliance with insurance requirements and government regulations.
Proficiency in using coding software is another essential technical skill for medical billing and coding professionals. Various coding software programs are commonly used in healthcare settings to streamline the coding and billing process. Being adept at utilizing these software applications will increase your efficiency and accuracy, contributing to effective medical coding and billing practices.
Furthermore, the ability to analyze medical records is a vital technical skill in medical billing and coding. Analyzing medical records allows you to identify and extract the necessary information for coding and billing purposes accurately. This skill involves reviewing patient histories, diagnoses, treatments, and procedures, ensuring that all relevant details are recorded appropriately.
Computer Skills
In today’s digital age, computer skills are indispensable for medical billing and coding professionals. Proficiency in using electronic health records (EHR) systems is essential for efficient and accurate documentation. EHR systems enable healthcare providers to store and access patient information electronically, streamlining the coding and billing process. Familiarity with EHR systems allows you to navigate through patient records, update information, and retrieve relevant data quickly.
Additionally, a basic understanding of billing software is necessary for medical billing and coding professionals. Billing software enables you to generate invoices, process payments, and manage financial transactions related to medical services. Being familiar with such software applications allows you to handle billing tasks efficiently, ensuring prompt and accurate processing of medical claims.
Knowledge of spreadsheet applications is another valuable computer skill in the field of medical billing and coding. Spreadsheet software, such as Microsoft Excel, can be utilized for various purposes, including organizing and analyzing data, creating reports, and tracking financial information. Proficiency in using spreadsheet functions and formulas facilitates the management and analysis of billing and coding data.
Communication Skills
Effective communication skills are vital for medical billing and coding professionals. The ability to communicate verbally and in writing with clarity and precision is essential for accurate documentation and efficient information exchange.
In terms of verbal communication, the ability to effectively convey information to patients, colleagues, and other healthcare professionals is crucial. Clear and concise verbal communication ensures that patients understand the medical codes and billing processes, helping to address any concerns or questions they may have. Additionally, effective verbal communication allows for seamless collaboration with physicians and other healthcare professionals, facilitating accurate coding and billing practices.
Written communication skills are equally important in medical billing and coding. The ability to document codes, procedures, and billing information accurately in medical records and claims is a fundamental aspect of the job. Attention to detail and clarity in written communication is necessary to prevent errors, ensure accurate record-keeping, and facilitate smooth billing processes.
Active listening skills are also crucial for medical billing and coding professionals. By actively listening to patients, colleagues, and healthcare professionals, you can gather important information, clarify doubts, and address any concerns or questions effectively. Active listening enhances the accuracy of coding and billing by enabling you to capture and comprehend critical details and instructions.
Moreover, the ability to explain complex medical codes to patients in a simple and accessible manner is essential. Patient education is an important aspect of medical billing and coding, as it empowers patients to understand the billing process, their responsibilities, and any potential implications for their healthcare coverage. Being able to convey complex information in a patient-friendly manner is essential for providing quality service and ensuring patient satisfaction.
Attention to Detail
Attention to detail is a crucial skill for medical billing and coding professionals, as the accuracy of coding and documentation directly impacts healthcare reimbursement, patient care, and legal compliance.
Accurate data entry is a fundamental aspect of attention to detail in medical billing and coding. Ensuring that codes, diagnoses, treatments, and other pertinent information are entered correctly into the system helps prevent errors and inaccuracies in the billing process. A single mistake in data entry can have significant consequences, such as delayed payments or denied claims.
Thoroughness in reviewing medical records is another aspect of attention to detail. Carefully examining medical records allows you to identify any missing or incomplete information that may impact coding accuracy or billing reimbursement. By conducting thorough reviews, you can ensure the completeness and accuracy of medical records, minimizing the risk of coding errors and maximizing reimbursement.
Precision in assigning codes is paramount in medical billing and coding. Each code represents a specific procedure, diagnosis, or treatment, and assigning the correct code is vital for accurate billing and reimbursement. Having an eye for detail and precision ensures that the appropriate codes are assigned, preventing potential claim denials and ensuring compliance with insurance requirements.
Analytical Skills
Analytical skills are indispensable for medical billing and coding professionals. The ability to analyze medical charts and records plays a crucial role in accurately coding and billing for healthcare services.
One aspect of analytical skills is the ability to identify discrepancies in documentation. Analyzing medical records allows you to notice any inconsistencies, missing information, or conflicting data that may impact coding accuracy or billing compliance. Recognizing these discrepancies is essential for prompt resolution and preventing potential errors in coding and billing.
Critical thinking is vital in code assignment. As a medical billing and coding professional, you will encounter various medical procedures, diagnoses, and treatments. Applying critical thinking skills allows you to interpret complex medical information accurately, correlate it with the relevant codes, and assign the most appropriate code to ensure accurate billing. Critical thinking helps you navigate the intricacies of medical coding, enabling you to make sound decisions and deliver high-quality healthcare reimbursement services.
Organizational Skills
Organizational skills are essential for medical billing and coding professionals to ensure efficiency and effectiveness in their work. The ability to manage time efficiently allows you to prioritize tasks, meet deadlines, and maintain productivity.
Efficient time management is crucial in the fast-paced world of medical billing and coding. There are often numerous tasks to handle simultaneously, such as reviewing medical records, assigning codes, and processing claims. Being able to prioritize these tasks based on urgency and importance ensures that deadlines are met and patient care is not compromised. Effective time management also helps prevent backlogs and delays in the billing process, contributing to the overall efficiency of healthcare operations.
Maintaining organized records is another key aspect of organizational skills in medical billing and coding. Accurate and well-organized records ensure that coding and billing information can be easily retrieved whenever required. Organized records facilitate smooth communication with insurance companies, auditors, and healthcare providers, ensuring prompt and accurate reimbursement. By keeping records in order, you contribute to the integrity and efficiency of the billing process.
Customer Service Skills
Medical billing and coding professionals often interact with patients, insurance companies, and healthcare providers. Therefore, possessing excellent customer service skills is crucial to ensure a positive and professional experience for all parties involved.
Empathy and compassion towards patients are essential qualities for medical billing and coding professionals. Dealing with medical codes, procedures, and billing can be overwhelming for patients. Demonstrating empathy, understanding, and compassion helps alleviate their concerns and build trust. By approaching patients with kindness and patience, you contribute to their overall satisfaction and well-being.
Resolving billing and coding inquiries is an integral part of customer service in this field. Patients, insurance companies, and healthcare providers may have questions or concerns regarding the billing process, claims, or codes. Being able to address these inquiries efficiently, accurately, and courteously enhances the overall customer experience. Timely and effective resolution of inquiries contributes to patient satisfaction, efficient reimbursement, and positive relationships with insurers and providers.
Patient advocacy is another facet of customer service in medical billing and coding. Advocating for patients’ rights and navigating the complexities of insurance coverage help ensure that patients receive the appropriate care and reimbursement. By actively working towards patients’ best interests, you contribute to their overall well-being and satisfaction.
Ethical Behavior
Ethical behavior is of utmost importance in the field of medical billing and coding. As a healthcare professional dealing with sensitive information, adherence to patient confidentiality laws, legal and ethical standards, and maintaining integrity is non-negotiable.
Adhering to patient confidentiality laws is a fundamental ethical obligation. Protecting patient information and ensuring its confidentiality is critical for maintaining trust and complying with privacy regulations. Respecting patient confidentiality helps foster a safe and secure environment for patients, encouraging open communication and ensuring the integrity of medical records and billing practices.
Compliance with legal and ethical standards is another essential aspect of ethical behavior in medical billing and coding. Staying up to date with healthcare regulations, laws, and ethical guidelines ensures that coding and billing practices align with industry standards. By adhering to these standards, you safeguard patient well-being, protect healthcare reimbursement integrity, and maintain compliance with legal requirements.
Maintaining integrity in handling sensitive information is a core value in medical billing and coding. Healthcare professionals are entrusted with sensitive patient data involving medical conditions, treatments, and finances. Demonstrating honesty, confidentiality, and professionalism in handling this information strengthens patient trust, protects patient rights, and upholds the ethical principles of the medical field.
Medical Knowledge
Having a solid foundation of medical knowledge is vital for medical billing and coding professionals. A comprehensive understanding of medical procedures, treatments, diseases, and guidelines is necessary to accurately assign the appropriate codes and ensure compliance with insurance requirements and legal regulations.
Understanding medical procedures and treatments allows you to effectively translate pertinent clinical information into accurate codes. Knowledge of these procedures and treatments enables you to comprehend the significance of the documentation, ensuring accurate coding and appropriate reimbursement for healthcare services rendered.
Knowledge of disease processes is equally important in medical billing and coding. Understanding the underlying conditions and their impact on patients’ health enables you to assign the correct codes accurately. Gaining familiarity with disease processes allows for proper documentation and billing, ensuring accurate reimbursement and appropriate funding for patient care.
Awareness of medical guidelines and regulations is essential for medical billing and coding professionals. Medical coding and billing practices must align with industry standards, insurance requirements, and legal regulations. Keeping updated with the ever-evolving guidelines and regulations helps maintain compliance, prevent claim denials, and safeguard the integrity of the coding and billing process.
Teamwork
The ability to work effectively in a team setting is crucial for medical billing and coding professionals. Collaborating with physicians, nurses, and other healthcare professionals is necessary to ensure accurate and timely coding and billing processes.
Collaborating with physicians and other healthcare professionals allows you to obtain accurate and complete medical documentation for coding purposes. By actively engaging with the healthcare team, you can clarify any discrepancies, seek clarification, and gather the necessary information to assign appropriate codes. Effective collaboration ensures accurate billing and reimbursement, while also enhancing the overall quality of patient care.
Working in multidisciplinary teams is common in the healthcare industry. Medical billing and coding professionals often must collaborate with colleagues from various departments, such as finance, compliance, and administration. Embracing teamwork and constructive communication within these multidisciplinary teams contributes to overall operational efficiency and ensures accurate coding, billing, and reimbursement.
Sharing knowledge and insights is crucial for teamwork in medical billing and coding. By actively participating in knowledge-sharing initiatives, such as team meetings, seminars, or relevant training sessions, you can stay updated with coding and billing practices, industry changes, and regulatory updates. Sharing your insights and experiences with colleagues fosters a collaborative environment, facilitates continuous learning, and elevates the collective knowledge and skills of the team.
In conclusion, medical billing and coding require a diverse set of skills encompassing technical proficiencies, computer skills, communication abilities, attention to detail, analytical capabilities, organizational skills, customer service aptitude, ethical behavior, medical knowledge, and teamwork. By developing and honing these skills, you can excel in the field of medical billing and coding, contributing to efficient healthcare reimbursement, accurate documentation, and the delivery of high-quality patient care.