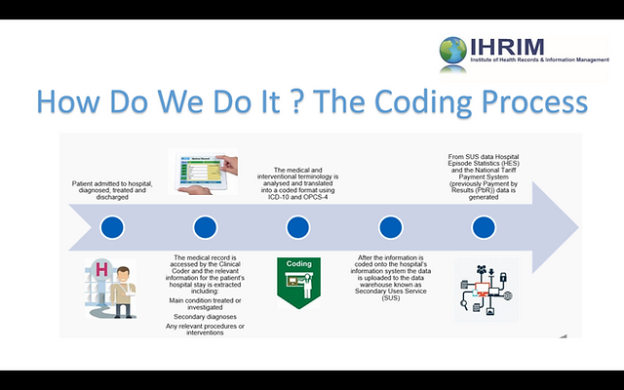
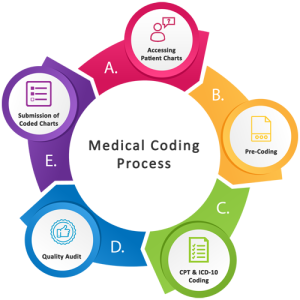
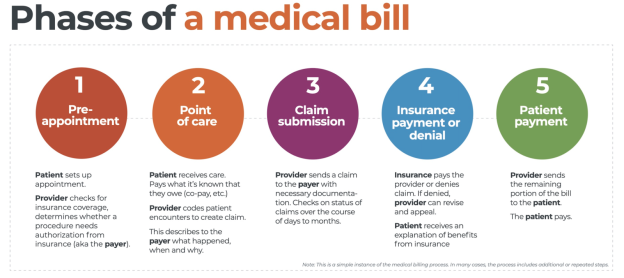
In the realm of medical billing, the utilization of modifiers plays a vital role in accurately documenting and categorizing procedures and services. These modifiers act as additional codes that provide crucial information about various factors, such as the extent of a procedure or the circumstances surrounding a patient’s condition. By incorporating modifiers, healthcare professionals ensure that insurance companies, healthcare providers, and patients all have a comprehensive understanding of the medical services provided, leading to efficient billing processes and accurate reimbursement.
What is a Modifier in Medical Billing?
Definition of a Modifier
In medical billing, a modifier is a two-character code that is added to a CPT code or a HCPCS code to provide additional information about a service or procedure. Modifiers are used to indicate that a procedure or service has been altered in some way, such as the time, location, or circumstances under which it was performed. These codes help to ensure accuracy and specificity in medical billing and play a crucial role in determining reimbursement rates.
Types of Modifiers
There is a wide range of modifiers used in medical billing, each serving a specific purpose and providing unique information about a procedure or service. Some common types of modifiers include:
- Modifier 25: Signifies a significant, separately identifiable evaluation and management (E/M) service provided on the same day as another service or procedure.
- Modifier 59: Indicates a distinct procedural service that is not typically considered part of the primary service.
- Modifier 26: Specifies the professional component of a specific service or procedure that was provided by the physician.
- Modifier 51: Identifies multiple procedures performed during the same session or on the same day by the same provider.
- Modifier 76: Indicates a repeat procedure or service performed on the same day.
- Modifier 22: Highlights an increased level of complexity or time spent on a particular service or procedure.
- Modifier 32: Denotes that a service or procedure was mandated by a federal, state, or local regulation or law.
- Modifier 50: Represents a bilateral procedure performed on both sides of the body or site(s).
- Modifier 62: Indicates the involvement of two surgeons in performing a specific procedure.
Purpose of Modifiers in Medical Billing
Modifiers play a crucial role in medical billing by providing additional information and ensuring accuracy in the claims submission process. They serve the following purposes:
-
Ensuring Accurate Reimbursement: Modifiers provide detailed information about the services or procedures performed, allowing payers to accurately assess the complexity and value of the care provided. This information helps ensure that healthcare providers are reimbursed appropriately.
-
Facilitating Proper Documentation: By using modifiers, medical professionals can clearly communicate any variations or modifications to the usual procedure. This facilitates proper documentation, ensuring that the medical record reflects the specific circumstances under which a service or procedure was performed.
-
Preventing Denials and Audits: Proper use of modifiers helps prevent claim denials and audits by providing transparency and supporting the medical necessity of services. Modifiers allow payers to identify and understand any unique aspects of a procedure or service, reducing the likelihood of claim rejection or post-payment audits.
Coding and Modifiers in Medical Billing
Using Modifiers with CPT Codes
Modifiers are typically added to Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes to provide additional information about the services or procedures performed. The use of modifiers with CPT codes allows healthcare providers to accurately describe any variations or modifications to a standard procedure, ensuring proper reimbursement and documentation.
For example, if a patient undergoes a comprehensive eye examination that includes both a refraction and a dilated fundus examination, the CPT code for the comprehensive eye examination would be modified with modifier 59 to indicate that the refraction and dilated fundus examination were distinct procedural services.
Associating Modifiers with Diagnosis Codes
In addition to being used with CPT codes, modifiers can also be associated with diagnosis codes in medical billing. When a modifier is added to a diagnosis code, it provides additional information about the condition being treated or the circumstances of the patient’s condition.
For instance, if a patient undergoes a surgical procedure due to complications or exacerbations of a pre-existing condition, a modifier may be added to the diagnosis code to indicate the relationship between the procedure and the underlying condition.
Combining Modifiers in Medical Bill Claims
In some cases, multiple modifiers may be necessary to accurately describe a service or procedure. When combining modifiers, it is essential to follow specific rules and guidelines to avoid confusion or denials.
For example, if a patient requires an extended consultation that is both complex and performed after hours, the appropriate modifiers may be 22 and 57. Modifier 22 highlights the increased complexity, while modifier 57 indicates that the decision to perform the surgery was made during the consultation.
Commonly Used Modifiers in Medical Billing
Modifier 25: Significant, Separately Identifiable Evaluation and Management (E/M) Service
Modifier 25 is used to indicate that an evaluation and management (E/M) service is separately identifiable from another procedure or service performed on the same day. This modifier is typically used when a physician provides a separate and significant E/M service in addition to a procedure, such as a minor surgery or a diagnostic test.
For example, if a patient visits a physician’s office for a routine check-up and during the same visit, the physician also performs a minor procedure, such as removing a benign skin lesion, modifier 25 would be added to the E/M code to indicate that the evaluation and management service was distinct and separately identifiable from the procedure.
Modifier 59: Distinct Procedural Service
Modifier 59 is one of the most commonly used modifiers in medical billing. It is used to indicate that a service or procedure is distinct or independent from another service or procedure performed on the same day. This modifier helps to identify procedures that are not typically reported together but may be warranted under certain circumstances.
For example, if a patient undergoes a knee arthroscopy for the treatment of a meniscal tear and, during the same operative session, the surgeon also performs a chondroplasty on a different compartment of the knee, modifier 59 would be added to the chondroplasty code to indicate that it is a distinct procedural service.
Modifier 26: Professional Component
Modifier 26 is used to identify the professional component of a service or procedure that is performed by the physician. This modifier is commonly used for services or procedures that have both a professional and a technical component.
For instance, when a physician interprets and reports the results of a radiological study such as an x-ray, the professional component is billed separately from the technical component. In this case, the professional component is identified by adding modifier 26 to the appropriate CPT or HCPCS code.
Modifier 51: Multiple Procedures
Modifier 51 is used to indicate that multiple procedures were performed during the same session or on the same day by the same provider. This modifier is necessary to avoid the inappropriate reduction in reimbursement when multiple procedures are performed.
For example, if a surgeon performs both a primary and a secondary repair during the same surgical session, modifier 51 would be added to the secondary repair code to indicate that it is a separate and additional procedure performed by the same provider.
Modifier 76: Repeat Procedure or Service
Modifier 76 is used to indicate that a procedure or service was repeated by the same provider on the same day. This modifier is necessary to distinguish between a repeated procedure and a separate procedure performed at a later time.
For instance, if a patient requires a repeat chest radiograph after a few hours due to a change in clinical condition, modifier 76 would be added to indicate that the subsequent radiograph is a repeat of the initial procedure.
Modifier 22: Increased Procedural Services
Modifier 22 is used to indicate that a specific service or procedure required significantly increased work by the physician or surgeon. This modifier is reported to reflect the additional time, effort, and complexity involved in performing a procedure.
For example, if a surgeon encounters unexpected difficulties or obstacles during a procedure, resulting in the procedure taking longer than usual or requiring more extensive work, modifier 22 would be added to indicate the increased procedural services provided.
Modifier 32: Mandated Services
Modifier 32 is used to indicate that a service or procedure was mandated by a federal, state, or local regulation or law. This modifier is typically used when a payer requires a healthcare provider to perform a specific service or procedure.
For instance, if a government program mandates that all newborns receive a particular screening test shortly after birth, modifier 32 would be added to indicate that the service was mandated.
Modifier 50: Bilateral Procedure
Modifier 50 is used to indicate that a procedure or service was performed on both sides of the body or site(s). This modifier is reported when a procedure is performed bilaterally, and there is no specific bilateral code available.
For example, if a patient requires a bilateral knee replacement, modifier 50 would be added to the appropriate procedure code to indicate that the procedure was performed on both knees.
Modifier 62: Two Surgeons
Modifier 62 is used to indicate that two surgeons performed a specific procedure. This modifier is necessary when two surgeons each contribute a significant and separate portion to the procedure.
For instance, if a complex surgical procedure requires the expertise of two surgeons working together, modifier 62 would be added to indicate the involvement of both surgeons.
Guidelines for Proper Modifier Usage
Understanding Modifier Documentation Requirements
To ensure proper use of modifiers, healthcare providers should adhere to documentation requirements set by payers and coding guidelines. Documentation should clearly support the use of modifiers and provide essential details about the service or procedure.
Providers should include detailed information that justifies the use of the modifier, such as the specific circumstances, complications, or complexity of the service. Proper documentation is crucial to support the medical necessity and accuracy of the claim.
Adhering to Medicare Modifier Guidelines
In addition to understanding payer-specific guidelines, it is essential to adhere to the Medicare modifier guidelines. Medicare, as a major healthcare payer, has specific rules and regulations regarding modifiers, and non-compliance may result in claim denials or audits.
Healthcare providers should refer to the Medicare Claims Processing Manual for comprehensive guidance on modifier usage. Staying informed about Medicare’s guidelines can help ensure compliance and accurate reimbursement.
Avoiding Overuse or Misuse of Modifiers
One common challenge in modifier usage is the overuse or misuse of modifiers. Using modifiers incorrectly or without proper justification can lead to claim denials or investigations.
Healthcare providers must exercise caution and avoid using modifiers inappropriately to maximize reimbursement. Overuse or misuse of modifiers can raise red flags and invite payer scrutiny, potentially triggering audits or investigations.
To mitigate the risk of overuse or misuse, providers should educate themselves and their staff on proper documentation, coding guidelines, and payer-specific requirements. Education and training can help ensure that modifiers are used appropriately and accurately in medical billing.
Documentation and Reporting for Modifiers
Maintaining Detailed Patient Records
Accurate and detailed patient records are vital in supporting the use of modifiers in medical billing. Providers should maintain thorough documentation that includes the rationale for using each modifier, the circumstances surrounding the service or procedure, and any other relevant details.
By documenting the specific circumstances under which a modifier is used, providers can provide evidence of medical necessity and support reimbursement claims. Detailed patient records also aid in communication with payers and auditing entities.
Including Modifier Information in Claims
When submitting claims for reimbursement, it is crucial to include explicit information about the modifiers used. This allows payers to accurately process the claims and assess the appropriateness of the modifiers used.
In addition to including the appropriate modifier codes, providers should provide supporting documentation to justify the use of the modifier. This may include operative reports, progress notes, or other relevant medical records that establish medical necessity.
Communicating with Payers and Auditors
Proper communication with payers and auditors is essential to ensure that the use of modifiers is understood and appropriately assessed. Providers should be prepared to explain the reasoning behind the use of modifiers and provide any necessary documentation to support their claims.
Engaging in open and transparent communication with payers and auditors can help resolve any questions or concerns about the use of modifiers and prevent unnecessary claim denials or audits. Prompt and accurate responses to payer inquiries can also expedite the reimbursement process.
Common Challenges in Modifier Usage
Confusing Modifier Rules and Guidelines
One of the common challenges in modifier usage is the confusion surrounding the rules and guidelines associated with each modifier. Providers and billing staff must remain up-to-date with the latest coding guidelines and payer requirements to ensure accurate and compliant use of modifiers.
Regular education and training on modifier usage can help minimize confusion and ensure adherence to coding guidelines. Consulting coding resources, attending coding seminars, or participating in webinars can provide valuable insights and updates on modifier rules and guidelines.
Keeping up with Modifier Updates and Changes
Modifiers and their associated rules are subject to updates and changes over time. New modifiers may be introduced, and existing ones may be revised or retired. Staying informed about these updates can be challenging but crucial to maintaining accurate billing practices.
Providers should regularly review updates from coding organizations, medical billing associations, and payers to stay abreast of any modified or new modifier guidelines. Subscribing to industry newsletters or joining relevant professional associations can provide access to the latest updates and resources.
Handling Modifier Denials and Appeals
Despite providers’ best efforts, modifier denials can still occur due to various reasons, such as coding errors or lack of supporting documentation. When faced with a modifier denial, it is important to thoroughly review the denial reason and take appropriate action.
Providers should carefully examine the claims and associated documentation for any discrepancies or missing information. If the denial is unjustified, an appeal can be filed with the payer, providing additional documentation and supporting evidence for the use of the modifier.
Following up with payers during the appeals process and maintaining clear lines of communication can help resolve modifier denials and ensure accurate reimbursement for services provided.
Impact of Modifier Usage on Reimbursement
Effect on Reimbursement Rates
Proper and accurate usage of modifiers can significantly impact reimbursement rates for healthcare providers. By providing additional information about the services or procedures performed, modifiers ensure that providers are appropriately compensated for the work performed.
When used correctly, modifiers can help increase reimbursement rates by accurately reflecting the level of complexity and additional work involved in a service or procedure. Conversely, improper or inaccurate usage of modifiers may result in lower reimbursement rates or claim denials.
Influence on Claim Approval and Denial
Modifiers play a crucial role in the approval or denial of claims by payers. When used appropriately, modifiers provide additional information that helps payers assess the medical necessity and appropriateness of services rendered.
Accurate use of modifiers ensures that claims are reviewed and processed accurately, increasing the likelihood of approval. Conversely, improper use or lack of modifiers may raise red flags, leading to claim denials or delays in the reimbursement process.
Financial Implications for Healthcare Providers
The use of modifiers in medical billing has significant financial implications for healthcare providers. Accurate and compliant use of modifiers ensures that providers are reimbursed fairly and appropriately for the services provided to patients.
By effectively communicating the specific circumstances surrounding a service or procedure, modifiers can help maximize reimbursement rates and prevent financial losses for healthcare providers. Conversely, incorrect or inappropriate use of modifiers may result in decreased revenue, claim denials, or even legal consequences.
It is crucial for providers to prioritize proper training and education on modifier usage to mitigate financial risks and ensure accurate reimbursement for the services they provide.
Training and Education for Modifier Usage
Modalities for Medical Billing and Coding Training
Training and education play a crucial role in ensuring accurate and compliant use of modifiers in medical billing. There are various modalities available to healthcare providers and billing staff to enhance their understanding and proficiency in modifier usage.
Formal education programs, such as medical coding and billing courses, offer comprehensive training on coding guidelines and modifier usage. These programs provide in-depth knowledge of coding systems, rules, and regulations, enabling individuals to apply modifiers accurately.
Several online platforms also offer coding and billing courses, allowing individuals to learn at their own pace. These courses provide interactive lessons, practical exercises, and assessments to reinforce understanding and retention of modifier usage principles.
Continuing Education for Modifier Knowledge
Continuing education is essential to stay up-to-date with the ever-evolving field of medical billing and coding. Ongoing professional development allows healthcare providers and billing staff to expand their knowledge and improve their proficiency in modifier usage.
Continuing education options include attending coding conferences, webinars, and workshops. These events often provide updates on coding guidelines, changes to modifiers, and opportunities to engage in discussions and case studies to enhance understanding.
Engaging in networking opportunities with other coding and billing professionals can also be valuable for staying informed about industry best practices and sharing experiences related to modifier usage.
Industry Resources for Guideline Updates
To facilitate accurate modifier usage, healthcare providers and billing staff should leverage industry resources for guideline updates and other relevant information. These resources can provide the latest information on coding guidelines, payer-specific requirements, and best practices.
Organizations such as the American Medical Association (AMA), the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), and professional coding associations offer comprehensive resources, including coding manuals, newsletters, and online portals with updated information on modifiers.
Providers should also regularly review payer-specific guidelines and policies to ensure compliance with their specific requirements. Payers often provide documentation and education materials to help providers understand their modifier expectations.
Conclusion
Modifiers play a critical role in medical billing, ensuring accurate reimbursement, facilitating proper documentation, and reducing denials and audits. Healthcare providers must familiarize themselves with the various types of modifiers and their associated guidelines to ensure accurate and compliant reporting of services.
By understanding the purpose and appropriate usage of modifiers, providers can maximize their reimbursement rates, maintain thorough documentation, and avoid unnecessary claim denials or audits. Through ongoing training and staying informed about coding updates, providers can ensure accurate reimbursement while upholding the highest standards of coding and billing integrity in healthcare.