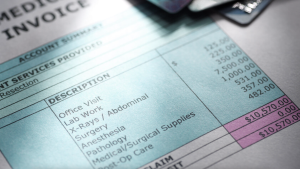
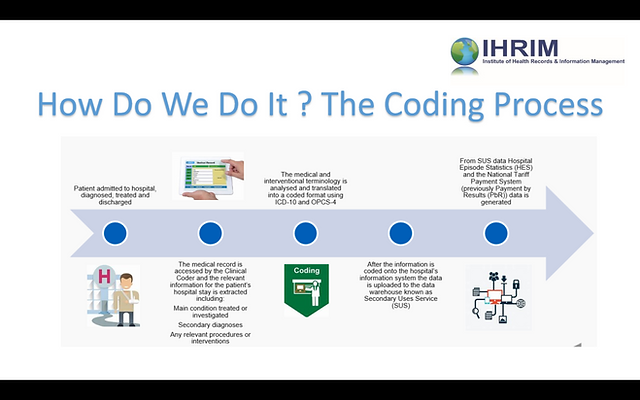
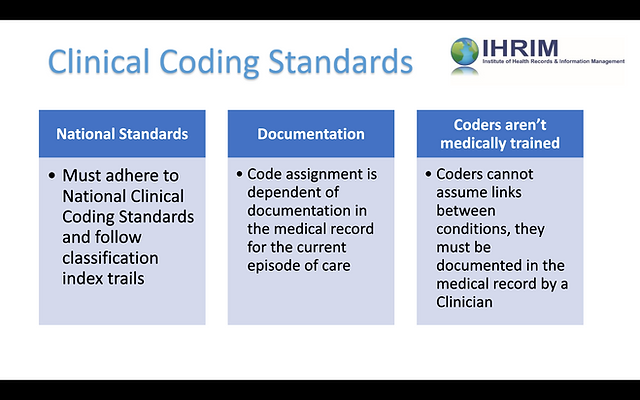
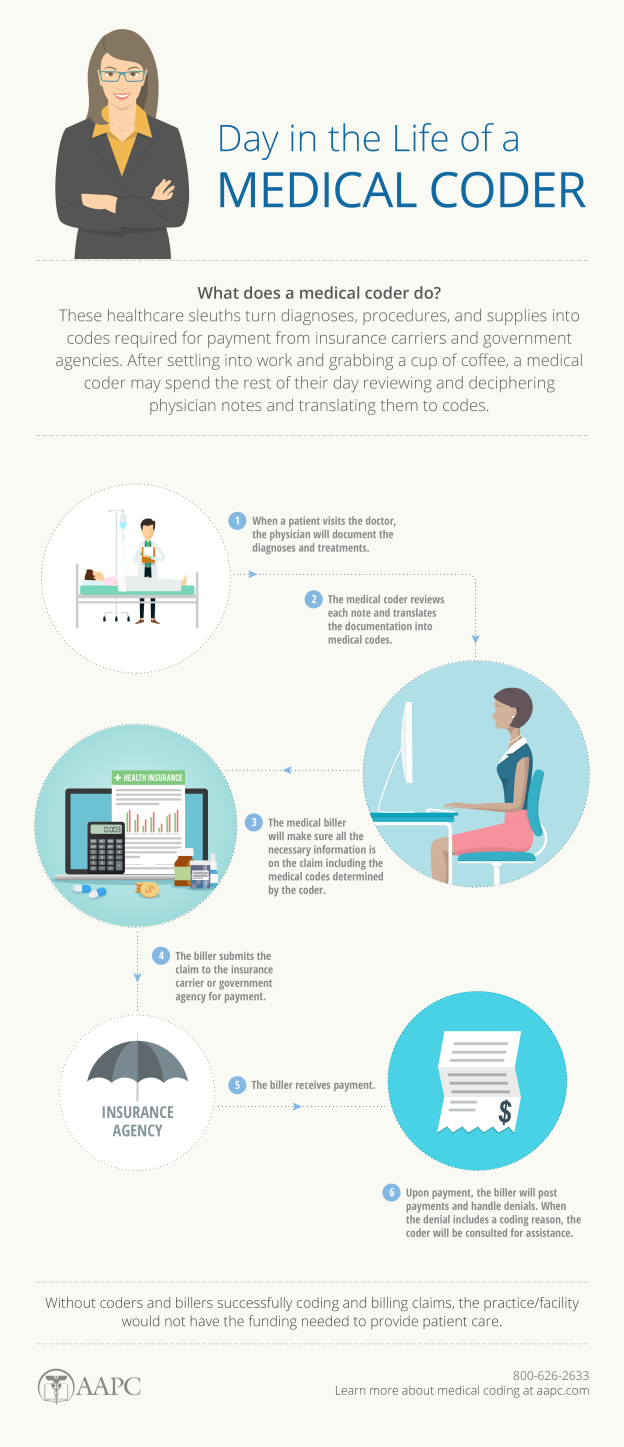
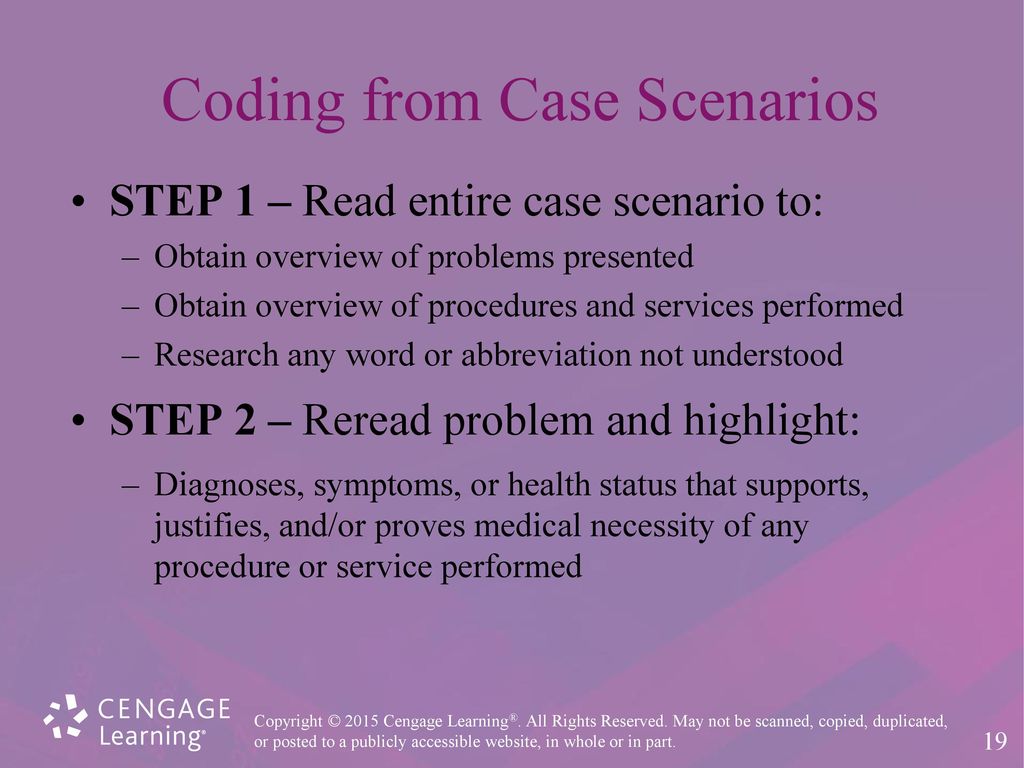
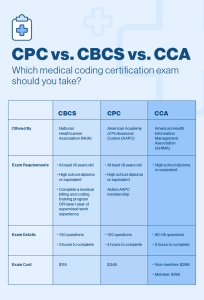
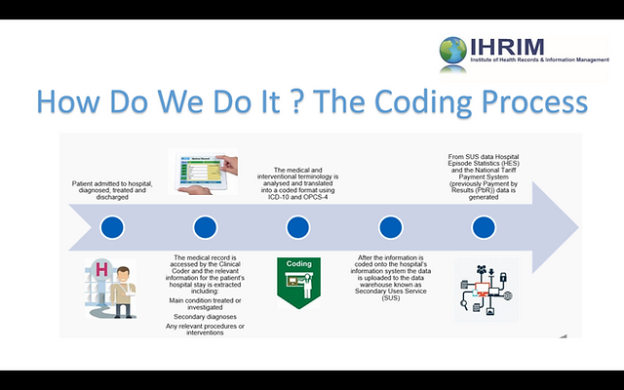
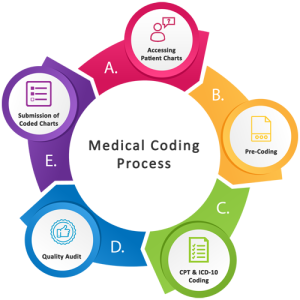
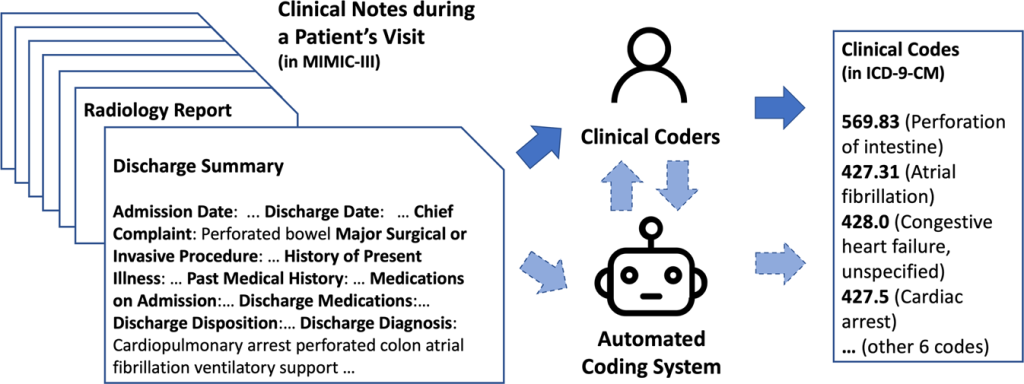
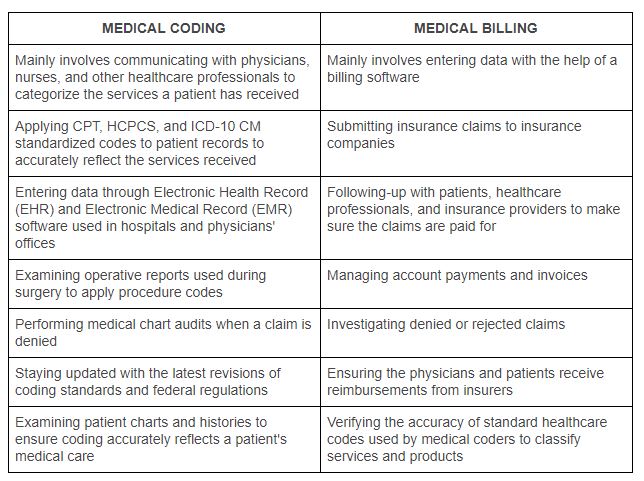
As a nurse seeking to expand your skillset and advance your career, you may have considered learning medical coding. Medical coding plays a crucial role in healthcare, ensuring accurate documentation and reimbursement for services provided. However, navigating the world of medical coding can seem complex and overwhelming. In this article, we will explore the best approach for nurses to learn medical coding, providing you with actionable steps to acquire the necessary knowledge and skills in this field. By following these guidelines, you can confidently embark on a rewarding journey towards becoming a proficient medical coder.
Enroll in a Medical Coding Certification Program
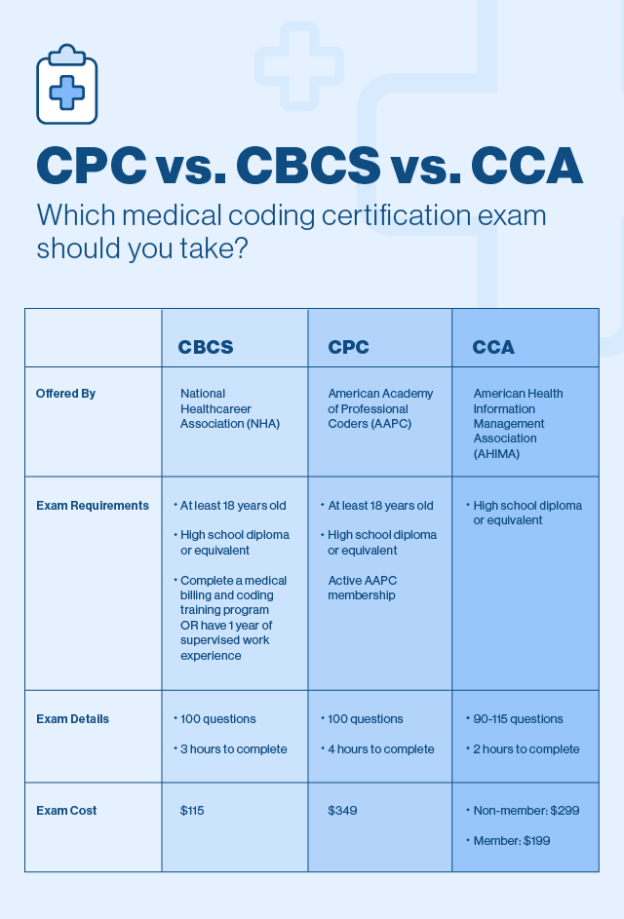
When embarking on a career in medical coding, one of the foundational steps is to research and select a suitable certification program. Choosing the right program can significantly impact your career prospects and job opportunities in the field of medical coding. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate this process:
Research available certification programs
When considering a career in medical coding, it is essential to start by researching available certification programs. Look for programs that are accredited and recognized within the healthcare industry. This will ensure that the certification you earn is respected and valued by employers. Take the time to explore different programs and gather information on their curriculum, requirements, and reputation.
Choose a reputable program
A reputable medical coding certification program is crucial for your career development. Look for programs that have been endorsed or accredited by recognized organizations, such as the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC) or the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA). These organizations have established standards for medical coding education and can help you identify a reputable program.
Determine the program’s structure and requirements
Once you have identified potential programs, carefully review their structure and requirements. Consider factors such as the duration of the program, the flexibility of the schedule, and the mode of delivery (e.g., online or in-person). Evaluate your own availability and learning preferences to select a program that aligns with your needs. Additionally, pay attention to any prerequisites or prerequisite courses that may be required for enrollment.
Apply for the certification program
After thoroughly researching and considering various certification programs, it is time to apply. Follow the application instructions provided by the program of your choice. Be sure to submit all required documents and meet any application deadlines. Keep in mind that competition for enrollment in reputable programs can be high, so it is essential to complete the application process accurately and promptly.
Take Online Medical Coding Courses

Explore online learning platforms
With the advancement of technology, online learning platforms have become a popular and convenient option for acquiring new skills. Take the time to explore different platforms that offer medical coding courses. Look for platforms that are reputable and offer comprehensive courses taught by experienced instructors. Examples of well-known online learning platforms include Udemy, Coursera, and edX.
Research and compare online medical coding courses
Once you have identified online learning platforms, dive deeper into their course offerings. Research and compare the medical coding courses available on each platform. Pay attention to course syllabi, instructor credentials, and student reviews. Look for courses that cover foundational topics in medical coding, such as Anatomy and Physiology, medical terminology, and ICD-10 coding systems.
Read reviews and testimonials
To ensure the quality and effectiveness of online medical coding courses, take the time to read reviews and testimonials from past students. These firsthand accounts can provide valuable insights into the course content, delivery, and overall learning experience. Look for courses that have positive reviews, with students highlighting the practicality and relevance of the course material.
Enroll in a suitable online course
After careful consideration, select an online medical coding course that suits your learning needs and preferences. Enroll in the course and follow the instructions provided by the online learning platform. Take advantage of the flexibility offered by online courses to set a schedule and allocate dedicated time for studying and completing course assignments.
Attend Medical Coding Workshops and Seminars

Look for local or national workshops and seminars
Attending workshops and seminars can provide valuable opportunities to enhance your medical coding knowledge. Look for local or national workshops and seminars that offer specialized training or focus on specific coding topics. These events often feature expert speakers and industry professionals who can provide insights and share their expertise.
Check for workshops offered by professional associations
Professional associations, such as the AAPC or AHIMA, regularly organize workshops and seminars for their members. These events are designed to provide additional training and education opportunities for medical coders. Check the websites of these associations for upcoming workshops and seminars that may be beneficial to your professional development.
Consider attending virtual workshops and webinars
In addition to in-person workshops and seminars, there are also virtual options available. Virtual workshops and webinars allow you to participate in professional development activities from the comfort of your own home. Look for virtual events that cover topics of interest and align with your learning goals. Take advantage of interactive features, such as live Q&A sessions, to further enhance your learning experience.
Gain Practical Experience Through Internships

Research hospitals, clinics, and healthcare facilities offering internships
Practical experience is crucial in medical coding, as it allows you to apply your knowledge in real-world settings. Research hospitals, clinics, and healthcare facilities in your area that offer internships to aspiring medical coders. These internships provide opportunities to work alongside experienced professionals and gain hands-on coding experience.
Apply for medical coding internships
Once you have identified suitable internships, prepare your application materials and apply accordingly. Pay attention to any specific requirements or qualifications outlined in the internship postings. Highlight relevant skills and experiences in your application documents to increase your chances of being selected. Consider reaching out to your professional network for any potential internship opportunities.
Take advantage of hands-on training opportunities
During your internship, make the most of the hands-on training opportunities provided. Actively engage with the medical coding tasks assigned to you, ensuring accuracy and attention to detail. Seek guidance and feedback from experienced coders, as their insights can enhance your learning and skill development. Embrace the challenges and learning opportunities that arise during your internship.
Learn from experienced medical coders
One of the most significant benefits of interning is the opportunity to learn from experienced medical coders. Take advantage of the knowledge and expertise they have gained through years of practice. Ask questions, seek clarification, and observe their coding workflows. Building a mentoring relationship with experienced coders can greatly contribute to your professional growth and development.
Seek Mentoring from Experienced Medical Coders

Connect with medical coding professionals
Seeking mentorship from experienced medical coders can provide valuable guidance and support in your journey to become a skilled coder. Connect with professionals who have extensive experience in the field through networking events or professional associations. Reach out to them via email or social media platforms such as LinkedIn and express your interest in receiving mentorship.
Request mentorship or guidance
Clearly communicate your goals and the areas in which you would like guidance or mentorship. Explain the reasons why you believe their expertise would be beneficial to your professional development. Be respectful of their time and understand that not all professionals may be available or willing to provide mentorship. However, many professionals are passionate about sharing their knowledge and may be open to mentoring.
Learn from their expertise and practical knowledge
Once you have established a mentorship relationship, make the most of the opportunity to learn from their expertise and practical knowledge. Be receptive to their feedback and suggestions, and actively seek their guidance in challenging coding scenarios. Regularly communicate with your mentor, update them on your progress, and seek their advice on how to further enhance your skills and knowledge.
Join Professional Associations and Networks
Explore medical coding professional associations
Joining professional associations dedicated to medical coding can offer numerous benefits. Explore associations such as the AAPC and AHIMA, which offer memberships to medical coders. These associations provide access to resources, educational opportunities, and networking events specifically tailored to the needs of medical coders.
Consider becoming a member
Carefully evaluate the benefits and costs associated with membership in professional associations. Review the resources, tools, and support provided to members. Determine if the membership fees are an investment worth making based on the value you anticipate receiving. Joining a professional association can enhance your professional credibility and provide opportunities for career advancement.
Attend networking events and conferences
Professional associations often organize networking events and conferences where members can interact with industry professionals, engage in knowledge sharing, and expand their professional network. Take advantage of these events to connect with other medical coders, learn from their experiences, and possibly even discover new career opportunities. Actively participate in discussions and engage with industry leaders to maximize your networking experience.
Utilize Online Resources and Reference Materials
To excel in the field of medical coding, it’s crucial to continually expand your knowledge and stay up-to-date with industry practices. Here are some strategies to help you enhance your skills and expertise:
Access online medical coding forums and communities
Online forums and communities dedicated to medical coding can be valuable resources for knowledge-sharing and support. Join reputable online forums and actively participate in discussions. Ask questions, share your experiences, and seek advice from more experienced coders. These online communities can be a source of ongoing learning and a platform to stay updated with the latest industry trends and developments.
Utilize reputable medical coding websites
There are numerous reputable websites that provide comprehensive information, resources, and tools for medical coders. Utilize these websites to access coding guidelines, reference materials, and coding software. Examples of reputable medical coding websites include the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) website and the AAPC website. Regularly visit these websites to stay informed about coding updates and changes.
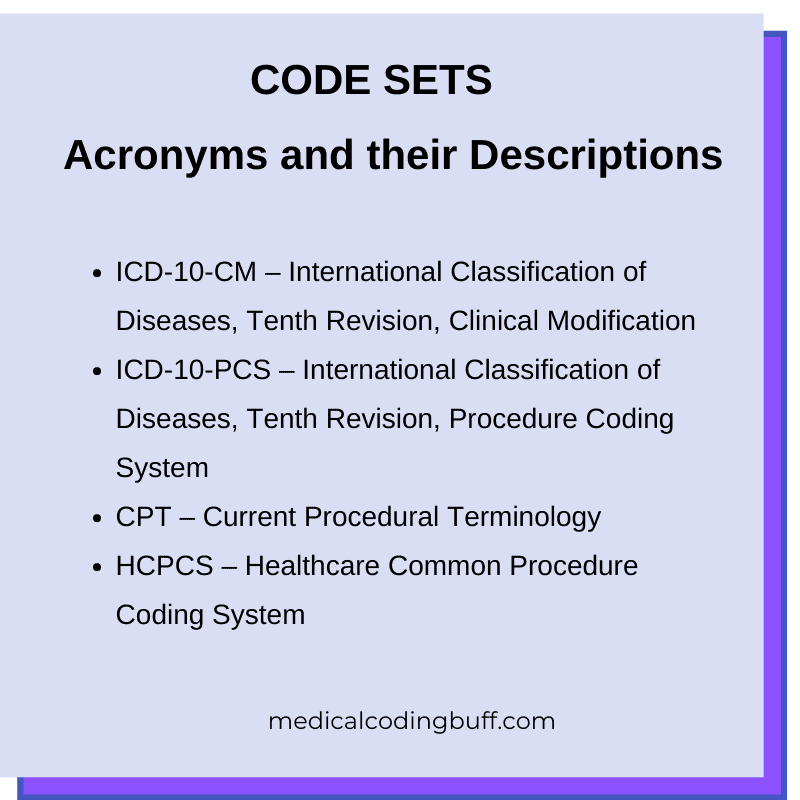
Refer to coding guidelines and manuals
Coding guidelines and manuals serve as essential references for medical coders. Familiarize yourself with industry-standard coding guidelines, such as the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) guidelines and the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) manual. Regularly refer to these resources to ensure accurate and compliant coding. Stay updated with any revisions or updates to the guidelines to maintain coding accuracy.
Practice Hands-on Coding Exercises and Case Studies
To enhance your proficiency in medical coding, it’s essential to actively seek out coding practice resources and engage in regular practice. Here are some strategies to help you improve your coding skills:
Look for coding practice resources
To reinforce your coding skills and improve proficiency, look for coding practice resources. These resources often include coding exercises, case studies, and scenarios designed to simulate real-world coding scenarios. Practice coding different types of medical records to enhance your ability to apply coding guidelines accurately.
Complete coding exercises and case studies
Allocate dedicated time to complete coding exercises and case studies regularly. Treat these exercises as opportunities to apply your knowledge, refine your coding skills, and identify areas for improvement. Pay attention to the coding guidelines and documentation provided, and strive for accuracy and consistency in your coding assignments.
Seek feedback and review your work
After completing coding exercises and case studies, seek feedback from experienced coders or instructors. Request a review of your work to identify any coding errors or areas where improvement is needed. Actively evaluate your own performance and compare your coding assignments with the provided reference answers. Learn from any mistakes made and use them as opportunities for growth and improvement.
Stay Updated with Industry Changes and Regulations

Follow industry news and updates
Medical coding is a field that continually evolves and undergoes changes. It is crucial to stay updated with industry news and updates to ensure that you are practicing coding in accordance with the latest guidelines and regulations. Follow reputable industry news sources, such as professional association websites, coding journals, and healthcare publications. Stay informed about changes in coding systems, regulatory requirements, and industry trends.
Subscribe to medical coding journals and publications
Subscribing to medical coding journals and publications can provide you with ongoing access to in-depth articles, case studies, and expert insights. These resources often cover a wide range of coding topics and offer a deeper understanding of complex coding scenarios. Subscribe to reputable publications such as “Coding Edge,” “Journal of AHIMA,” or “AAPC Healthcare Business Monthly” to receive regular updates and valuable educational content.
Attend webinars and workshops on new coding guidelines
As coding guidelines evolve, attending webinars and workshops on new coding guidelines can help you stay informed and up-to-date. Professional associations, healthcare organizations, and coding experts often offer these educational sessions to provide guidance on changes to coding systems or regulations. Actively participate in these webinars and workshops to enhance your coding knowledge and ensure compliance with the latest coding guidelines.
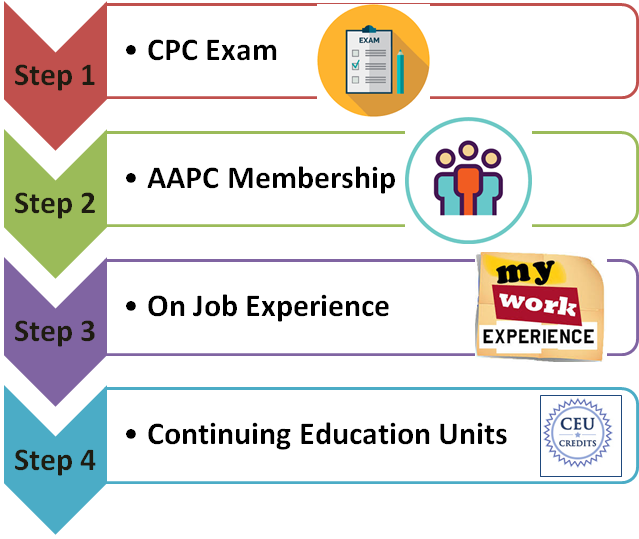
Prepare for Medical Coding Certification Exams
Becoming a skilled medical coder is a multi-faceted journey that requires dedication, continuous learning, and thorough preparation for certification exams. Here are the steps to help you prepare effectively:
Identify certification exam requirements
Upon completion of your medical coding education and training, you may choose to pursue a certification to enhance your professional credibility. Identify the requirements for the certification exam you intend to take. This may include specific educational prerequisites, experience requirements, and knowledge of coding guidelines and systems. Take the time to understand the exam format, content, and scoring criteria.
Review study materials and practice exams
To prepare for your certification exam, gather study materials and resources specific to the exam you will be taking. This may include textbooks, study guides, or online courses specifically tailored to the certification exam. Additionally, practice exams can help you familiarize yourself with the exam format and assess your readiness. Seek out reputable study materials and practice exams from recognized sources.
Create a study schedule and dedicate time for preparation
Creating a study schedule is crucial to ensure adequate preparation for your certification exam. Dedicate regular blocks of time specifically for studying and review. Break down your study sessions into manageable chunks, focusing on different areas of the exam content. Consistency and discipline in following your study schedule will increase your chances of success on the certification exam.
Take mock exams for self-assessment
As your exam date approaches, take advantage of mock exams to assess your knowledge and readiness. Mock exams can simulate the actual exam experience and provide a gauge of your progress. Analyze your performance on mock exams and identify areas that require further study or revision. Review any incorrect answers and seek clarification on concepts or coding guidelines that you find challenging.
In conclusion, becoming a skilled medical coder requires a comprehensive approach to education and professional development. By enrolling in a reputable medical coding certification program, pursuing online courses, attending workshops, gaining practical experience, seeking mentoring, joining professional associations, utilizing online resources, practicing coding exercises, staying updated with industry changes, and preparing for certification exams, you can enhance your knowledge and skillset. Remember to dedicate time, effort, and a commitment to lifelong learning to excel in the field of medical coding.