Medical coding plays a crucial role in the healthcare industry, providing a standard system for documenting and classifying diseases, diagnoses, procedures, and treatments. As a crucial link between healthcare providers, insurance companies, and government agencies, medical coding ensures accurate and efficient communication and reimbursement processes. This essential function allows for streamlined healthcare operations, improved patient care, and effective healthcare analytics. Without medical coding, the complexities of healthcare data would remain inaccessible, hindering both the quality and efficiency of healthcare services. Medical coding plays a crucial role in the healthcare industry, serving as the backbone of various processes and activities. It involves the transformation of healthcare diagnosis, procedures, medical services, and equipment into universal medical alphanumeric codes. These codes are used for a variety of purposes, including documentation, claim submission, reimbursement, research, and statistical analysis. Understanding medical coding and its significance is essential for healthcare professionals, as it directly impacts patient safety, effective communication, revenue cycle management, and overall healthcare delivery.
Coding and Documentation

This image is property of www.rasmussen.edu.
One of the primary functions of medical coding is to ensure accurate and standardized documentation of patient encounters, medical services, and procedures. Medical coders meticulously review medical records, physician notes, and other relevant documentation to extract the necessary information and assign appropriate codes. This coding process helps to maintain a comprehensive and organized record of patient care, enabling healthcare providers to track and analyze patient outcomes, monitor treatment effectiveness, and assess the quality of care provided. Proper coding and documentation also facilitate communication among healthcare professionals involved in a patient’s care, ensuring that accurate and up-to-date information is readily available.
Claim Submission and Reimbursement
Accurate medical coding is essential for the successful submission of insurance claims and reimbursement. When healthcare services are provided to patients, medical coders assign specific codes to each service or procedure performed and submit these codes along with the relevant patient information to insurance companies or government agencies. These codes serve as a standardized language that allows payers to understand the nature and extent of the services provided. By ensuring that the codes accurately reflect the services rendered, healthcare providers can optimize their chances of receiving timely and appropriate reimbursement for their services, reducing the risk of payment denials or delays.
Research and Statistical Analysis
Medical coding also plays a critical role in healthcare research and statistical analysis. By using standardized codes to categorize and classify diseases, medical procedures, and healthcare encounters, researchers can analyze large datasets to identify trends, patterns, and outcomes. Medical coding enables the production of reliable and valid statistical information, helping researchers, policymakers, and public health officials make informed decisions regarding patient care, resource allocation, and healthcare policy. Additionally, medical coding is instrumental in monitoring disease prevalence, tracking the effectiveness of interventions, and assessing population health outcomes, ultimately contributing to advancements in medical knowledge and improved patient care.
Definition and Purpose of Medical Coding
Medical coding is the process of transforming healthcare diagnosis, procedures, medical services, and equipment into universally recognized alphanumeric codes. The purpose of medical coding is to ensure standardized documentation, facilitate effective communication, streamline revenue cycle management, and support research and statistical analysis. By assigning specific codes to various healthcare activities, medical coding enables the collection and sharing of accurate and consistent information among healthcare providers, payers, researchers, and policymakers. These codes serve as a common language that allows for seamless data exchange, decision-making, and quality improvement across the healthcare continuum.
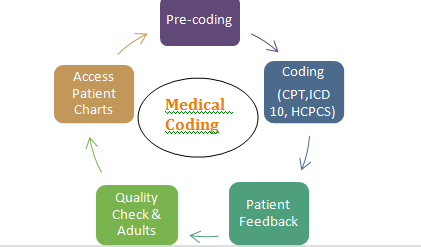
This image is property of lifepronow.com.
Categories of Medical Codes
Medical codes are categorized into different code sets based on their purpose and usage. The two main categories of medical codes are:
- International Classification of Diseases (ICD) Codes: These codes are used to classify diseases, injuries, symptoms, and other health conditions. The current version of the ICD is the ICD-10, which provides a standardized system for documenting and reporting conditions and diagnoses. ICD codes are crucial for epidemiological studies, healthcare planning, resource allocation, and reimbursement.
- Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) Codes: CPT codes are used to describe medical procedures and services provided by healthcare professionals. Developed and maintained by the American Medical Association (AMA), CPT codes are widely used in the United States and are essential for accurate billing, claim submission, and reimbursement. CPT codes are regularly updated to reflect changes in medical technology, procedures, and guidelines.
Other categories of medical codes include Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) codes, which are used for additional non-physician services and supplies, and National Drug Codes (NDC), which identify specific pharmaceutical products.
Medical Coding Systems
Medical coding systems provide a structured framework for assigning codes to medical diagnoses, procedures, and services. These systems ensure uniformity, consistency, and accuracy in medical coding, facilitating effective communication and data exchange among different stakeholders. The main coding systems used in medical coding include:
- ICD Coding System: The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) coding system is used for classifying diseases, injuries, and other health conditions. It is maintained by the World Health Organization (WHO) and widely adopted worldwide. The most recent version, ICD-10, provides a detailed and comprehensive set of codes for accurate disease documentation and reporting.
- CPT Coding System: The Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) coding system is used for describing and reporting medical procedures and services provided by healthcare professionals. Developed and maintained by the American Medical Association (AMA), CPT codes are regularly updated to reflect changes in medical practice and technology.
- HCPCS Coding System: The Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) is used for additional non-physician services, supplies, and equipment not included in the CPT coding system. HCPCS codes are essential for accurate billing, claim submission, and reimbursement.
Medical coding systems ensure that healthcare professionals use standardized codes for accurate and consistent documentation, billing, and reporting, thereby facilitating efficient healthcare delivery, insurance claims processing, and research activities.
Ensuring Patient Safety
Accurate medical coding plays a significant role in ensuring patient safety by providing a reliable and standardized system for documenting and communicating healthcare encounters. By assigning specific codes to diagnoses, procedures, and services, medical coders contribute to the accuracy and completeness of medical records, reducing the risk of errors, omissions, or misinterpretations. Accurate coding allows healthcare providers to have a comprehensive view of a patient’s medical history and treatment, enabling them to make informed clinical decisions, identify potential risks or complications, and provide appropriate care. Inaccurate or inconsistent coding can result in medication errors, misdiagnosis, delayed treatment, or adverse events, posing a significant threat to patient safety. Therefore, maintaining the highest level of accuracy and adherence to coding guidelines is paramount for ensuring patient safety and quality healthcare delivery.
Facilitating Effective Communication
Medical coding serves as a standardized language that enables effective communication among healthcare professionals, payers, researchers, and policymakers. By using universally recognized codes to represent diagnoses, procedures, and services, healthcare providers can easily share and exchange information, improving care coordination and continuity. Consistent coding allows for accurate and reliable data transfer between different healthcare settings, such as hospitals, clinics, and laboratories, ensuring that all relevant information is available whenever needed. Effective communication facilitated by medical coding minimizes the possibility of miscommunication, misunderstandings, or discrepancies, enhancing healthcare efficiency, collaboration, and patient outcomes.
Streamlining Revenue Cycle Management
Accurate and timely medical coding is essential for streamlining revenue cycle management and ensuring financial sustainability for healthcare organizations. The use of standardized codes allows healthcare providers to accurately capture and document the services performed, supporting proper billing and claim submission. Medical coders play a crucial role in translating complex medical procedures and services into codes that accurately represent the resources utilized. By ensuring accurate coding, healthcare providers can optimize their revenue cycle processes, reduce claim denials or rejections, and minimize the risk of auditing or compliance issues. Proper coding also helps healthcare organizations manage their accounts receivable, negotiate contracts with payers, and maximize reimbursement for services rendered, ultimately contributing to their financial stability and sustainability.
Certified Professional Coder (CPC)
The Certified Professional Coder (CPC) certification is one of the most recognized and sought-after certifications in the field of medical coding. Offered by the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC), the CPC certification validates the expertise and proficiency of medical coders in assigning accurate codes for diagnoses, procedures, and services. To obtain the CPC certification, candidates must pass a comprehensive examination that tests their knowledge of medical coding guidelines, healthcare regulations, anatomy, and medical terminology. CPC-certified professionals demonstrate a high level of competency in medical coding, enabling them to contribute effectively to accurate documentation, revenue cycle management, and overall healthcare quality.
Certified Coding Specialist (CCS)
The Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) certification is offered by the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA) and is geared towards medical coders working in hospital settings. The CCS certification validates the knowledge and skills required to accurately assign codes for diagnoses, procedures, and services within the inpatient hospital setting. Candidates for the CCS certification must pass an examination that assesses their understanding of coding guidelines, medical terminology, anatomy, pharmacology, and healthcare regulations specific to hospital coding. CCS-certified professionals possess the expertise necessary to accurately code complex medical cases, contribute to accurate reimbursement, and support effective data analysis and research in the hospital setting.
Certified Coding Associate (CCA)
The Certified Coding Associate (CCA) certification is also offered by AHIMA and is designed for entry-level medical coders or individuals seeking to enter the field of medical coding. The CCA certification validates foundational knowledge and skills in medical coding, providing a stepping stone for further career growth and advancement. To obtain the CCA certification, candidates must pass an examination that covers the basics of medical coding, including coding guidelines, anatomy, medical terminology, and healthcare regulations. CCA-certified professionals possess the fundamental knowledge needed to accurately assign codes, contribute to documentation accuracy, and support revenue cycle management in healthcare settings.

This image is property of www.sonayukti.com.
Health Information Technician
A career opportunity in medical coding is to become a health information technician. Health information technicians play a critical role in managing and maintaining patient health information, including medical records, diagnostic test results, and treatment plans. These professionals are responsible for ensuring the accuracy, completeness, and accessibility of patient information, utilizing their knowledge of medical coding, privacy regulations, and health information systems. Health information technicians often work alongside medical coders to ensure the proper coding and documentation of patient encounters, supporting effective communication, research, and healthcare planning. A degree or certification in health information management is typically required for a career as a health information technician.
Medical Coder
A medical coder is a specialized professional who assigns codes to medical diagnoses, procedures, and services. Medical coders are responsible for reviewing medical records, physician notes, and other relevant documentation to extract the necessary information and assign appropriate codes. They meticulously follow coding guidelines, ensure documentation accuracy, and keep up with changes in coding systems and regulations. Medical coders play a crucial role in accurate billing, claim submission, and reimbursement, supporting revenue cycle management and healthcare financial sustainability. A strong understanding of medical terminology, anatomy, coding guidelines, and healthcare regulations is essential for a successful career as a medical coder.
Medical Billing Specialist
Medical billing specialists are responsible for the accurate and timely submission of insurance claims and the management of healthcare billing processes. Although medical coding and medical billing are distinct roles, they often overlap, and many professionals perform both functions. Medical billing specialists utilize the codes assigned by medical coders to process claims, verify insurance coverage, and ensure proper reimbursement from insurance companies or government programs. They must have a deep understanding of coding systems, insurance policies, revenue cycle processes, and billing regulations. Medical billing specialists play a crucial role in healthcare revenue cycle management, ensuring the financial viability of healthcare organizations and facilitating the timely payment of healthcare services.
Complexity of Coding Guidelines
One of the main challenges in medical coding is navigating the complexity of coding guidelines and systems. Medical coders must have a detailed understanding of coding principles, guidelines, and conventions to accurately assign codes that reflect the services provided and the medical terminology used. The various code sets, such as ICD, CPT, and HCPCS, have their own specific rules and guidelines, requiring continuous learning and staying up-to-date with changes and revisions. Additionally, the interpretation and application of coding guidelines can be subjective at times, leading to potential discrepancies in coding practices. It is crucial for medical coders to undergo comprehensive training, gain practical experience, and regularly participate in continuing education to ensure accurate and compliant coding practices.
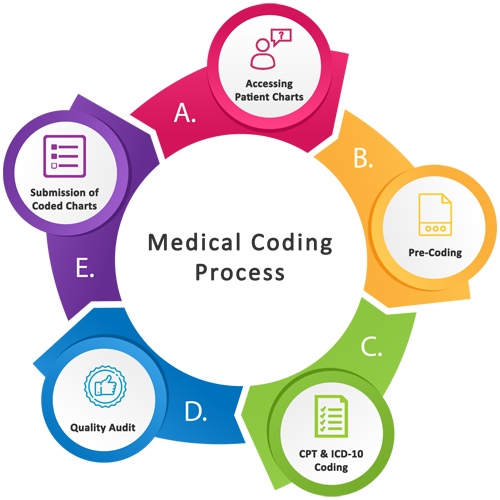
This image is property of healthteqservices.com.
Keeping Up with Constant Changes
The field of medical coding is constantly evolving, with regular updates and revisions to coding systems, guidelines, and regulations. Medical coders must stay abreast of these changes to ensure accurate and compliant coding. Changes to coding systems, such as the transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10, can necessitate significant updates to coding practices, requiring medical coders to relearn and adapt to new coding rules and conventions. Additionally, new medical procedures, technologies, and treatments are continually being developed, requiring corresponding code additions or modifications. It is essential for medical coders to actively engage in professional development activities, such as attending conferences, participating in workshops, and pursuing continuing education, to stay current with the latest coding updates and industry trends.
Potential for Coding Errors
Despite the best efforts of medical coders, coding errors can occur due to various factors, including human error, misinterpretation of documentation, inadequate training, or lack of clarity in coding guidelines. These errors can have significant consequences, ranging from claim denials and payment delays to inappropriate treatment or reimbursement for healthcare services. Coding errors can also impact the accuracy of healthcare statistics, research studies, and quality improvement initiatives, leading to uninformed decision-making and compromised patient care. To minimize the potential for coding errors, healthcare organizations should implement regular coding audits, provide ongoing training and education to coders, and promote a culture of accuracy and accountability in coding practices.
Advancements in Artificial Intelligence
The future of medical coding is shaped by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning technologies. AI has the potential to revolutionize the medical coding process by automating repetitive tasks, enhancing accuracy, and improving efficiency. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of medical records and coding data, identify patterns, and generate accurate code suggestions, reducing the burden on human coders and minimizing the risk of errors. AI-powered coding systems can continuously learn and adapt to changes in coding guidelines and regulations, ensuring compliance and consistency in coding practices. As AI technology continues to evolve and mature, it is expected to play an increasingly prominent role in medical coding, offering enhanced productivity, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness.
Increased Automation in Coding Processes
Automation is becoming more prevalent in various aspects of healthcare, and medical coding is no exception. Technological advancements have enabled the development of computer-assisted coding (CAC) systems, which can automate certain coding tasks. CAC systems use natural language processing and machine learning algorithms to analyze medical documentation and suggest appropriate codes. While human coders still play a crucial role in reviewing and validating the suggested codes, CAC systems can significantly expedite the coding process and improve coding accuracy. Automation in coding processes can help healthcare organizations streamline their coding operations, reduce the dependence on manual coding, and allocate coding resources more efficiently.
Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHR)
The integration of medical coding with electronic health records (EHR) systems is another significant development in the field. Electronic health records provide a digital platform for capturing, storing, and exchanging patient health information. When medical coding is seamlessly integrated with EHR systems, it allows for real-time coding, automated documentation, and immediate access to coding data. Coding professionals can instantly review and assign codes based on the information entered into the EHR, reducing delays and ensuring accurate coding. Integration with EHR systems also facilitates interoperability and seamless data exchange between different healthcare organizations, improving care coordination and patient outcomes. Additionally, joint efforts in standardization and interoperability among coding and EHR systems contribute to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare delivery.
Confidentiality and Privacy
Medical coders have an ethical responsibility to maintain patient confidentiality and privacy. In the course of their work, coders have access to sensitive and confidential patient health information, including medical records, diagnostic test results, and treatment plans. It is crucial for coders to strictly adhere to privacy regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, and ensure the secure handling and protection of patient information. Coders must maintain the confidentiality of patient data, only access information necessary for coding purposes, and avoid any unauthorized disclosure or misuse of patient information. Upholding patient confidentiality and privacy fosters trust between patients and healthcare providers, protecting patients’ rights and promoting ethical coding practices.
Honest and Accurate Coding
Ethical medical coders prioritize honesty and accuracy in their coding practices. The codes assigned by medical coders reflect the nature and extent of healthcare services provided, directly impacting patient care, reimbursement, and statistical analysis. Coders must assign codes that accurately represent the documentation provided, avoiding any intentional manipulation or misrepresentation of patient encounters. Ethical coding practices require coders to continuously update their knowledge, seek clarification when documentation is ambiguous, and consult coding guidelines and relevant resources. Accurate coding promotes transparency, ensures appropriate reimbursement, and contributes to reliable healthcare data, research, and decision-making. Upholding honest and accurate coding practices is essential for maintaining the integrity of the healthcare system and upholding professional standards.
Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Medical coders must comply with regulatory standards and guidelines set forth by various governing bodies and organizations. These standards include coding guidelines, privacy regulations, billing and reimbursement rules, and healthcare industry best practices. Coders must stay informed about changes and updates to these standards and ensure their coding practices align with the most current regulations. Compliance with regulatory standards helps healthcare organizations maintain their legal and ethical obligations, avoid penalties or legal issues, and safeguard the overall integrity of the coding and billing processes. Regular training and education on coding compliance and adherence to industry standards are essential for medical coders to fulfill their professional responsibilities and maintain high standards of practice.
Formal Education Programs
Formal education programs play a vital role in providing aspiring medical coders with the necessary knowledge and skills to excel in their careers. Many colleges, universities, and vocational schools offer programs in health information management, medical coding, or medical billing and coding. These programs typically include coursework in medical terminology, anatomy, coding guidelines, healthcare regulations, and health information systems. Some programs also provide hands-on training in coding software and real-world coding scenarios. Graduating from a formal education program in medical coding can demonstrate a candidate’s commitment to the field and provide a solid foundation for pursuing professional certifications or entering the job market.
Professional Coding Associations
Professional coding associations, such as the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC) and the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA), offer resources and support to medical coders at all stages of their careers. These associations provide opportunities for networking, professional development, and continuing education. They offer coding workshops, webinars, conferences, and online courses to help coders stay updated on coding guidelines, industry trends, and best practices. Membership in professional coding associations can provide access to coding resources, career opportunities, and a community of coding professionals, promoting growth, mentorship, and professional recognition.
Continuing Education Requirements
Continuing education is essential for medical coders to maintain their knowledge and skills and stay abreast of changes in coding practices, regulations, and guidelines. Professional certifications, such as the CPC, CCS, and CCA, require certified coders to fulfill continuing education requirements to maintain their certification status. Continuing education may include attending coding seminars, participating in webinars or workshops, completing online courses, or pursuing advanced coding certifications or specialization. Continuous learning and professional development enhance a coder’s competency, expand their career opportunities, and ensure they remain up-to-date with the latest coding practices, regulations, and advancements in the field.
In conclusion, medical coding plays a vital role in healthcare by supporting documentation, claim submission, reimbursement, research, and statistical analysis. Accurate coding is essential for ensuring patient safety, facilitating effective communication, and streamlining revenue cycle management. Certified medical coders, such as CPCs, CCSs, and CCAs, are highly skilled professionals who contribute to the accuracy and efficiency of coding processes. Career opportunities in medical coding include health information technician, medical coder, and medical billing specialist. While medical coding presents challenges such as coding complexity, keeping up with changes, and the potential for errors, advancements in technology, automation, and integration with electronic health records are shaping the future of coding. To uphold ethical coding practices, medical coders must prioritize patient confidentiality, accurate coding, compliance with regulatory standards, and ongoing training and education. Formal education programs, professional coding associations, and continuing education opportunities are available to support and enhance the knowledge and skills of medical coders. Overall, the role of medical coding continues to be critical in healthcare delivery, ensuring accurate documentation, efficient revenue cycle management, and the generation of reliable health data for research and decision-making.