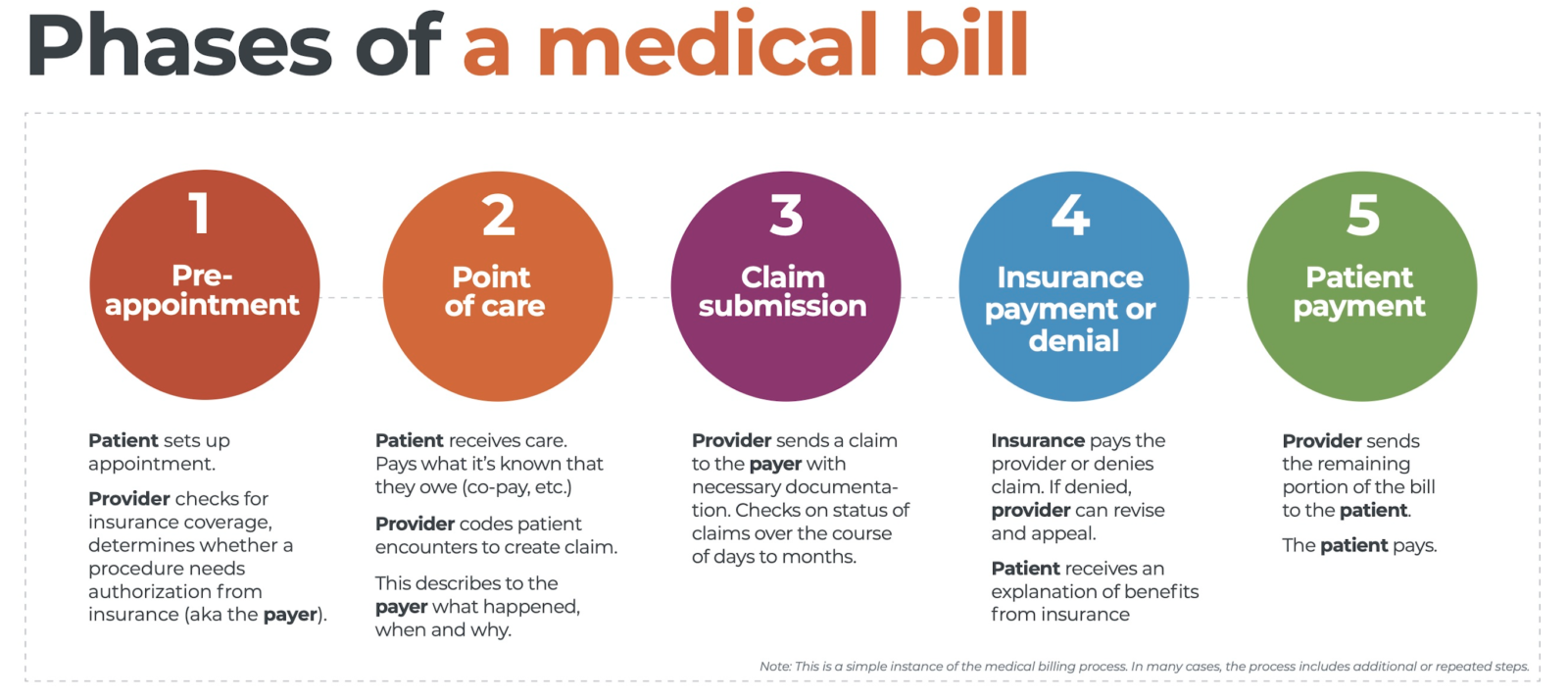
When considering the medical billing process, understanding the initial step is crucial. To begin the journey of medical billing, one must first ascertain the primary step. This essential aspect sets the foundation for a smooth and efficient billing procedure. Consequently, identifying and comprehending the initial step in the medical billing process is of utmost importance.
In an intricate process such as medical billing, the first step holds significant significance. This critical starting point serves as a vital cornerstone for accurate and effective billing. Nevertheless, investigating and comprehending the initial step within the medical billing process is vital for professionals operating within this field. By delving into this fundamental stage, healthcare providers, administrators, and billers can establish a robust framework that ensures the billing process adheres to the necessary guidelines and regulations.
Overall, grasping the initial step in the medical billing process is crucial to comprehending the intricacies of this integral procedure. A deep understanding of this first phase allows healthcare professionals to embark on a successful journey toward efficient medical billing practices. By diving into the nuances and complexities of the medical billing process, one can achieve greater clarity and proficiency in this essential aspect of the healthcare industry.
Understanding the Medical Billing Process

Introduction to Medical Billing
Medical billing is a crucial aspect of the healthcare industry, playing a vital role in ensuring that healthcare providers receive proper reimbursement for the services they render to patients. It involves the systematic processing of patient information, coding, claim submission, and follow-up to facilitate the timely and accurate payment of medical services. Without an efficient medical billing process, healthcare providers may face financial challenges and encounter difficulties in sustaining their operations.
Importance of Medical Billing
Medical billing serves as the backbone of the revenue cycle management for healthcare providers. It plays a critical role in translating medical services into monetary transactions, making it possible for providers to receive payment from insurance companies, government entities, or directly from patients. Effective medical billing helps providers maintain financial stability, meet operational costs, and continue delivering quality care to patients. Additionally, thorough and accurate medical billing ensures compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of audits or penalties.
Overview of the Medical Billing Process
The medical billing process comprises several interrelated steps that begin from gathering patient information and extends to payment collection and managing denials. Understanding each stage of the medical billing process is crucial to ensure a smooth and efficient revenue cycle. Let us explore each step in detail.
Gathering Patient Information

Collecting Patient Demographics
The first step in the medical billing process involves collecting extensive patient demographic information. This includes personal details such as name, address, contact information, date of birth, and social security number. Accurate patient identification is crucial for proper insurance verification, claim submission, and subsequent correspondence with insurance companies or other payers. Providers must ensure the privacy and security of patient information, adhering to strict HIPAA regulations to maintain confidentiality.
Verifying Insurance Details
After collecting patient demographics, healthcare providers must verify the patient’s insurance coverage. This step helps determine the patient’s eligibility for specific medical services and provides essential information for claim submission. Insurance verification involves verifying the insurance company, policy number, coverage effective dates, copayments, deductibles, and any pre-authorization requirements. Accurate and up-to-date insurance details are imperative to avoid claim denials or payment delays.
Obtaining Medical History
In addition to demographic and insurance information, healthcare providers might need to obtain the patient’s medical history. Gathering comprehensive medical records, including previous diagnoses, procedures, and treatments, helps in determining appropriate codes for billing purposes. The medical history also aids in assessing medical necessity and ensuring proper documentation to support the services provided.
Coding and Documentation
Importance of Medical Coding
Medical coding plays a crucial role in the medical billing process as it involves translating medical diagnoses, procedures, and services into standardized codes. These codes are essential for claim submission, reimbursement determination, and statistical analysis. Accurate and detailed coding ensures proper payment for services rendered while maintaining compliance with coding guidelines and regulations.
Assigning Appropriate Diagnosis Codes
In the medical billing process, assigning appropriate diagnosis codes is crucial to accurately represent the patient’s medical condition. Healthcare providers must document the patient’s diagnoses, symptoms, and related information to determine the correct codes from the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) coding system. These codes provide a universally accepted language to communicate and classify medical conditions, facilitating effective communication between healthcare providers and insurance companies.
Assigning Procedure Codes
Alongside diagnosis codes, healthcare providers must also assign procedure codes to accurately represent the medical services provided. Procedure codes are obtained from coding systems such as the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) or Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS). These codes provide information about the specific services rendered, including diagnostic tests, treatments, surgeries, or other medical procedures. Accurate procedure coding ensures appropriate reimbursement for the services performed.
Preparing and Submitting Claims
Creating an Itemized Bill
After coding and documentation, the next step involves creating an itemized bill or claim. An itemized bill provides a detailed breakdown of the services provided, including the associated codes, unit costs, and quantities. It is crucial to include all relevant services rendered during the patient’s visit to ensure accurate reimbursement. Providers must maintain proper documentation to support the items included in the claim and provide clarity in case of any audits or reviews.
Completing Claim Forms
Alongside the itemized bill, healthcare providers must complete claim forms specific to each payer, such as the CMS-1500 form for Medicare or the UB-04 form for institutional claims. These claim forms capture essential information about the patient, services provided, billing codes, and costs. It is crucial to accurately complete these forms, ensuring that all required fields are filled, and the codes match the documentation. Any errors or missing information can lead to claim denials or payment delays.
Including Supporting Documentation
Supporting documentation is vital to validate the services billed and provide evidence of medical necessity. It includes medical reports, test results, surgical notes, or any other relevant documentation supporting the services billed. Accurate and complete supporting documentation strengthens the claim’s validity, reduces the risk of denials, and assists in resolving potential audits or reviews.
Claim Submission Methods
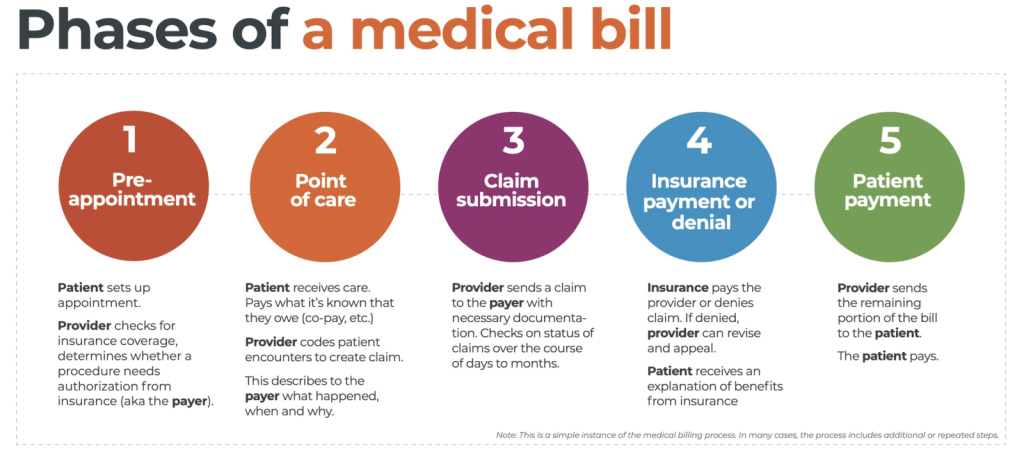
Electronic Claims Submission
One common method of claim submission is through electronic means. Electronic claims submission involves using specialized billing software or electronic data interchange systems to transmit claims directly to insurance companies or clearinghouses. This method offers numerous advantages, including faster claim processing, reduced errors through automated checks, and improved tracking and reporting capabilities.
Paper Claims Submission
Although electronic claims submission is prevalent, some healthcare providers still utilize paper claims submission. Paper claims involve printing out the necessary claim documents and manually mailing them to the designated insurance companies. While this method is generally slower and less efficient compared to electronic submission, it may be necessary in certain situations where electronic submission is not feasible or practical.
Claim Submission through Clearinghouses
Many healthcare providers use clearinghouses to streamline the claims submission process. Clearinghouses act as intermediaries between healthcare providers and insurance companies, processing and formatting claims before transmitting them to the appropriate payers. This helps ensure compliance with specific payer requirements and minimizes errors or rejections. Clearinghouses can also provide valuable real-time claim validation and status updates.
Claim Adjudication and Processing

Verifying Claims Accuracy
Upon receiving claims, insurance companies or payers engage in the process of claim adjudication. This involves reviewing the submitted claims for accuracy, completeness, and compliance with coding and documentation guidelines. Claims undergo thorough scrutiny to ensure that the services billed are valid, supported by appropriate medical records, and adhere to specific payer policies.
Reviewing for Medical Necessity
One key aspect of claim adjudication is reviewing the medical necessity of the billed services. Insurance companies assess whether the provided services align with established medical guidelines and are deemed necessary for the patient’s condition. This evaluation helps determine whether payment should be approved or denied. Reviewers assess the medical records and supporting documentation to ensure that the services meet the required criteria.
Determining Coverage and Reimbursement
After claim adjudication, insurance companies determine the coverage and reimbursement amounts for approved claims. Reimbursement amounts may vary depending on factors such as the contracted fee schedule, policy coverage limits, deductibles, copayments, or coinsurance percentages. The insurance company issues an Explanation of Benefits (EOB) or Remittance Advice (RA) to communicate the payment details to the healthcare provider.
Follow-up on Claims

Tracking Claim Status
Following claim submission, healthcare providers must actively track the status of their claims. This involves monitoring claim progress, ensuring timely processing, and identifying any potential delays or issues. Tracking claim status allows providers to take appropriate actions promptly, such as following up with insurance companies, addressing claim rejections, or resubmitting corrected claims.
Identifying and Resolving Claim Errors
Throughout the claim adjudication process, errors or discrepancies may arise, potentially leading to claim denials. Healthcare providers need to identify and address these claim errors promptly. Common reasons for claim errors include inaccurate coding, missing information, incomplete documentation, or non-compliance with payer policies. Resolving claim errors requires careful review, coordination with relevant departments, and communication with insurance companies to rectify the issues.
Appealing Denied Claims
In cases where claims are denied, healthcare providers have the right to appeal the decision. Claim denials can occur due to various reasons, including incomplete documentation, lack of medical necessity, or disputes with insurance policy coverage. Providers must thoroughly review the denial reason, gather necessary supporting documentation, and submit an appeal with a well-constructed argument to dispute the denial and seek reimbursement.
Payment Collection

Follow-up on Outstanding Balances
After successful adjudication and reimbursement, healthcare providers must follow up on outstanding patient balances. This involves keeping track of patient payments or unpaid portions after insurance coverage. Providers may send out invoices, statements, or reminders to patients regarding their outstanding balances. Timely payment collection helps ensure financial stability and sustains the healthcare provider’s operations.
Coordination with Insurance Providers
In some instances, healthcare providers may need to coordinate directly with insurance providers to address any payment discrepancies or unresolved issues. This may involve re-submission of claims, clarification of coding or documentation, or negotiation of payment amounts. Effective coordination between the provider’s billing department and insurance company representatives helps resolve payment-related concerns efficiently.
Handling Patient Payments
Aside from insurance reimbursements, healthcare providers also collect payments directly from patients. This includes copayments, deductibles, or services not covered by insurance. Providers must clearly communicate payment expectations to patients, offer various payment methods, and ensure proper documentation of the payment received. Accurate and efficient management of patient payments contributes to the financial stability of healthcare providers.
Managing Denials and Appeals

Understanding Denial Reasons
To effectively manage claim denials, healthcare providers must understand the reasons behind them. Denial reasons can vary, such as coding errors, lack of medical necessity, non-covered services, or policy-specific exclusions. By analyzing denial patterns and identifying common reasons for denials, providers can implement measures to minimize future denials and improve claim submission accuracy.
Appealing Denied Claims
As mentioned earlier, appealing denied claims is a critical step in maximizing revenue and ensuring proper reimbursement for healthcare services. Providers need to review the denial reason, gather additional supporting documentation if necessary, and outline a strong argument to support the appeal. Timely and comprehensive appeals increase the chances of overturning claim denials and acquiring the rightful reimbursement.
Resubmitting Corrected Claims
In cases where claim errors or discrepancies are identified, providers may need to resubmit corrected claims. This requires careful review of the initial denial reason, revision of coding or documentation, and ensuring compliance with payer requirements. Accurate resubmission of corrected claims aims to rectify errors and facilitate successful claim adjudication.
Ensuring Compliance and Legal Requirements

Medical Billing Compliance
Compliance with legal and regulatory requirements is essential in the medical billing process. Healthcare providers must adhere to various regulations, including those set by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and other federal and state regulations. Compliance encompasses areas such as patient privacy, claims documentation, proper coding practices, and billing accuracy.
HIPAA Regulations
As patient privacy and data security are paramount, healthcare providers must strictly adhere to the regulations laid out by HIPAA. These regulations govern the handling of patient health information, including the collection, storage, transmission, and disclosure of such information. Providers must maintain secure systems, train employees on privacy protocols, and implement measures to safeguard patient data.
Anti-Fraud Measures
To combat fraudulent activities, healthcare providers must be vigilant in implementing anti-fraud measures in their billing processes. This involves conducting periodic internal audits, implementing fraud detection mechanisms, and educating employees on identifying potential fraudulent activities. Compliance with anti-fraud regulations helps maintain the integrity of the medical billing process and protects both providers and patients from fraudulent behaviors.
In conclusion, understanding the medical billing process is vital for healthcare providers to ensure accurate and timely reimbursement for services rendered. From gathering patient information to claim submission, adjudication, and payment collection, each step plays a pivotal role in maintaining the financial viability of healthcare practices. By adhering to coding guidelines, complying with legal requirements, and staying updated with insurance policies, healthcare providers can navigate the complex landscape of medical billing successfully.