Clinical coding is the backbone of the healthcare industry, ensuring accurate and efficient documentation of patient medical records. It involves the systematic assignment of codes to medical diagnoses, procedures, and treatments to enable billing, statistical analysis, and research. Clinical coders possess extensive knowledge of medical terminology, anatomy, and coding guidelines to meticulously decipher patient information and accurately translate it into standardized codes. With the increasing importance of data analysis in healthcare, the role of clinical coding has become indispensable in ensuring the provision of high-quality care, proper reimbursement, and advancement in medical research.
What Is Clinical Coding?
This image is property of media.springernature.com.
Overview of Clinical Coding
Clinical coding is a fundamental process in healthcare institutions that involves translating medical diagnoses and procedures into a standardized language. It plays a crucial role in the management of patient information, medical billing, and statistical analysis. By assigning specific codes to medical conditions and treatments, clinical coders ensure accurate documentation, communication, and retrieval of healthcare data.
Role and Importance of Clinical Coding
Clinical coding serves as the backbone of healthcare data management. It bridges the gap between healthcare providers, insurance companies, and government agencies by providing a universal language that accurately represents medical services. This standardized coding system enables efficient communication, ensures accurate billing and reimbursement, facilitates research and quality improvement initiatives, and supports decision-making processes in healthcare organizations.
Without clinical coding, the process of sharing medical information between different healthcare stakeholders would be highly inefficient and prone to errors. The use of standardized codes not only improves data accuracy but also enhances patient safety by minimizing the risk of misinterpretation or confusion regarding medical procedures and diagnoses.
Clinical Coding Process
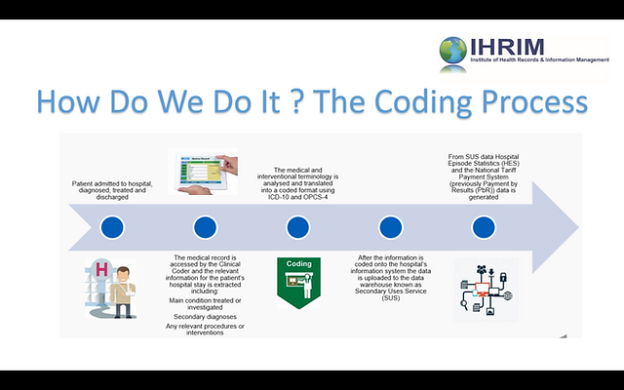
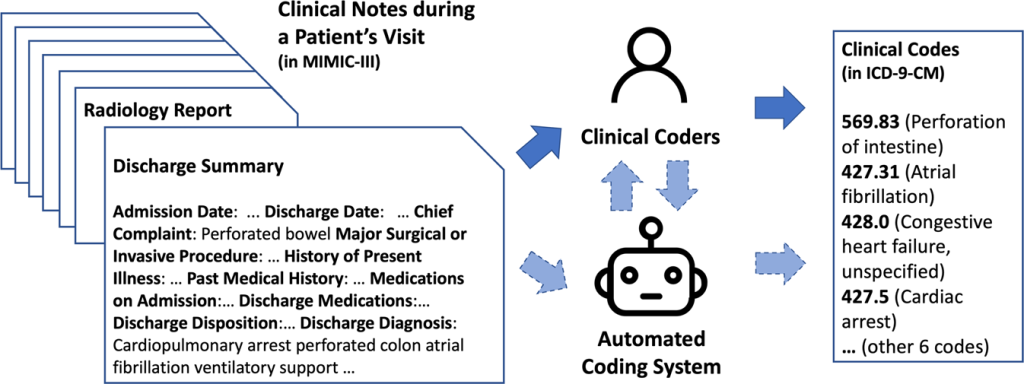
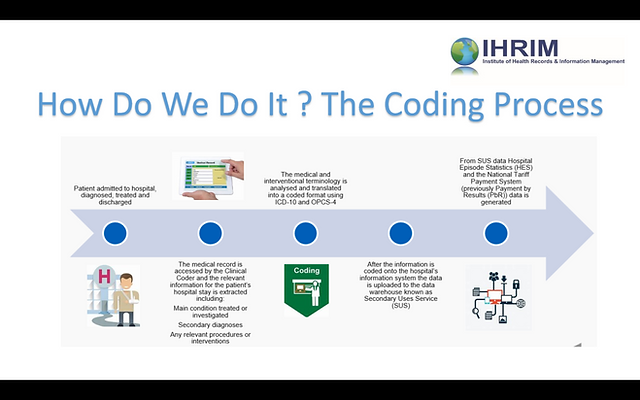
The clinical coding process involves several steps to accurately capture and categorize medical data. It typically starts with the identification of the relevant medical information from patient records, including diagnoses, procedures, medications, and laboratory results. Clinical coders then assign specific codes to each piece of information based on established coding systems such as ICD-10-CM/PCS, CPT, or HCPCS Level II.
After assigning the codes, the coded data is entered into electronic health records (EHR) or specialized coding software. This information is then used for various purposes, such as billing, reporting, research, and quality improvement. Regular audits and reviews are conducted to ensure the accuracy and integrity of the coded data, as well as to identify opportunities for coding improvement.
Types of Clinical Coding Systems
There are several coding systems used in clinical coding, each with its own specific purpose and scope. The three main coding systems are ICD-10-CM/PCS, CPT, and HCPCS Level II.
ICD-10-CM/PCS Coding System
ICD-10-CM/PCS (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification/Procedure Coding System) is the primary coding system used for classifying and documenting medical diagnoses and procedures in the United States. It consists of two parts: ICD-10-CM for diagnoses coding and ICD-10-PCS for procedures coding.
ICD-10-CM codes are alphanumeric and provide detailed information about a patient’s medical condition. They are used for clinical, research, and administrative purposes. On the other hand, ICD-10-PCS codes are strictly used for inpatient hospital procedures and provide specific details about the surgical techniques used and the body parts involved.
CPT Coding System
CPT (Current Procedural Terminology) is a coding system developed and maintained by the American Medical Association (AMA). It is used to accurately describe and identify medical services and procedures performed by healthcare providers. CPT codes are numeric and alphanumeric, and they provide a standardized method for reporting healthcare services for reimbursement purposes.
CPT codes are widely used by healthcare professionals, insurance companies, and governmental agencies for various purposes, including billing, reimbursement, and quality reporting. They provide a uniform language for communicating medical procedures and services across different healthcare settings.
HCPCS Level II Coding System
HCPCS (Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System) Level II is a coding system used primarily for products, supplies, and services not covered by CPT codes. HCPCS Level II codes are alphanumeric and are used for billing purposes, particularly for certain durable medical equipment, prosthetics, orthotics, and supplies.
The HCPCS Level II coding system complements the CPT coding system by providing additional specificity and granularity for certain types of healthcare items and services. It is widely used by healthcare providers, suppliers, and payers to ensure accurate billing and reimbursement for these specific categories of products and services.
This image is property of static.wixstatic.com.
Clinical Coding in Healthcare Institutions
Clinical coding is an integral part of the daily operations in healthcare institutions, including hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare facilities. Proper coding ensures accurate billing, facilitates data analysis and research, supports quality improvement initiatives, and enables effective communication among healthcare professionals and stakeholders.
In hospitals, Clinical coders work closely with medical and nursing staff to translate medical reports, charts, and other documentation into standardized codes. These codes are then used for billing purposes, reimbursement claims, research projects, and public health reporting. Accurate coding also helps hospitals track patient outcomes, identify trends, and evaluate the performance of different clinical departments.
In outpatient clinics and physician practices, clinical coding is equally important. Coders review medical records, encounter forms, and other relevant documentation to accurately assign codes for diagnoses, procedures, and other services rendered. This ensures proper billing and reimbursement while supporting accurate data analysis and research efforts.
Clinical Coding Certification and Training
Clinical coding requires specialized knowledge and skills, which are typically acquired through formal education and certification programs. Many countries have established professional organizations and certification bodies that offer training and certification programs for clinical coders.
These programs cover in-depth knowledge of medical terminology, anatomy, and physiology, as well as an understanding of coding guidelines, regulations, and best practices. Clinical coders also need proficiency in using coding software and electronic medical records systems, as well as strong analytical and problem-solving skills.
Certification in clinical coding serves as proof of expertise and can enhance job prospects and career advancement opportunities. It provides employers and healthcare organizations with confidence in the coder’s ability to accurately assign codes and maintain the integrity of healthcare data.

This image is property of static.wixstatic.com.
Current Trends and Challenges in Clinical Coding
As healthcare continues to evolve, clinical coding faces several trends and challenges. One significant trend is the ongoing transition from ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM/PCS coding systems. This transition allows for more detailed and specific coding but requires coders to adapt to the new coding guidelines and conventions.
Another trend is the increasing use of electronic health records (EHR) and coding software. These technological advancements have improved coding efficiency and accuracy, but they also require clinical coders to be proficient in using these systems effectively and to adapt to new software updates.
Furthermore, the rise of value-based reimbursement and quality-based initiatives has added complexity to the coding process. Clinical coders now need to accurately capture not only the medical diagnoses and procedures but also additional data related to patient outcomes and quality metrics.
Challenges in clinical coding include the ongoing need for coder education and training to keep up with coding updates and changes, as well as ensuring the accuracy and integrity of coded data. Additionally, the use of multiple coding systems, each with its own rules and requirements, can create confusion and complexity for coders and stakeholders.
In conclusion, clinical coding is a vital and complex process in healthcare institutions. It serves as a universal language for accurately representing medical diagnoses and procedures, facilitating efficient communication, accurate billing, and data analysis. Clinical coders play a crucial role in ensuring the integrity and accuracy of coded data and must keep up with evolving coding systems and technologies to meet the demands of the ever-changing healthcare landscape.