In the field of medical billing, understanding the various types of plans is essential for accurately processing patients’ claims. This article explores the different types of plans commonly encountered in medical billing, covering insurance plans such as Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), Point of Service (POS) plans, and Medicare/Medicaid. By gaining insight into these plans, you will be better equipped to navigate the complexities of medical billing and ensure proper reimbursement for healthcare services provided.
Types of Plans in Medical Billing
Medical billing is an essential part of the healthcare system, ensuring that healthcare providers receive payment for the services they render to patients. Within the realm of medical billing, there are various types of plans that individuals may have, each with its own set of rules and requirements. In this article, we will explore the different types of plans in medical billing, their features, and how they impact both healthcare providers and patients.
Private Insurance Plans
Private insurance plans are typically obtained through an employer or purchased individually. These plans are provided by private companies and offer a range of coverage options depending on the policy selected. Private insurance plans often have a network of preferred healthcare providers, commonly known as in-network providers. When seeking medical services from in-network providers, the plan usually covers a larger portion of the cost, while visiting out-of-network providers may result in higher out-of-pocket expenses.
Government Sponsored Plans
Government-sponsored plans are designed to provide healthcare coverage for specific segments of the population. The most well-known government-sponsored plans in the United States are Medicare and Medicaid. Medicare is available to individuals aged 65 and older, as well as those with certain disabilities. Medicaid, on the other hand, is a joint federal and state program that provides healthcare coverage for low-income individuals and families. These plans have specific guidelines and requirements for eligibility and coverage, and medical billing for government-sponsored plans follows unique processes..
Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) Plans
HMO plans are a type of managed care plan that focuses on preventive care and cost control. Under an HMO plan, individuals must select a primary care physician (PCP) who serves as the main point of contact for all healthcare needs. PCPs coordinate care and refer patients to specialists or hospitals within the HMO network. HMO plans typically require individuals to obtain a referral from their PCP before seeking specialized care. This system aims to control costs by directing individuals to specific providers and ensuring a coordinated approach to care.
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) Plans
PPO plans, also known as managed care plans, offer a larger degree of flexibility compared to HMO plans. These plans allow individuals to seek care from both in-network and out-of-network providers. While individuals can see any healthcare provider they choose, visiting in-network providers typically results in lower out-of-pocket costs due to negotiated rates. PPO plans do not require individuals to obtain a referral before seeing a specialist, providing greater freedom and convenience in accessing healthcare services.

This image is property of i.ytimg.com.
Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO) Plans
EPO plans combine characteristics of both HMO and PPO plans. Similar to HMO plans, EPO plans require individuals to select a primary care physician and obtain referrals for specialized care within the network. However, like PPO plans, EPO plans do not cover services rendered by out-of-network providers, except in cases of emergencies. EPO plans aim to strike a balance between cost control and flexibility, ensuring that individuals receive coordinated care while still having the option to seek specialized services.
Point of Service (POS) Plans
POS plans are a hybrid of HMO and PPO plans, combining aspects of both. Individuals under a POS plan are required to select a primary care physician and obtain referrals for specialist care within the network. However, individuals also have the option to seek care outside the network without a referral, although this usually results in higher out-of-pocket costs. POS plans offer greater flexibility than HMO plans while still maintaining some cost control measures.
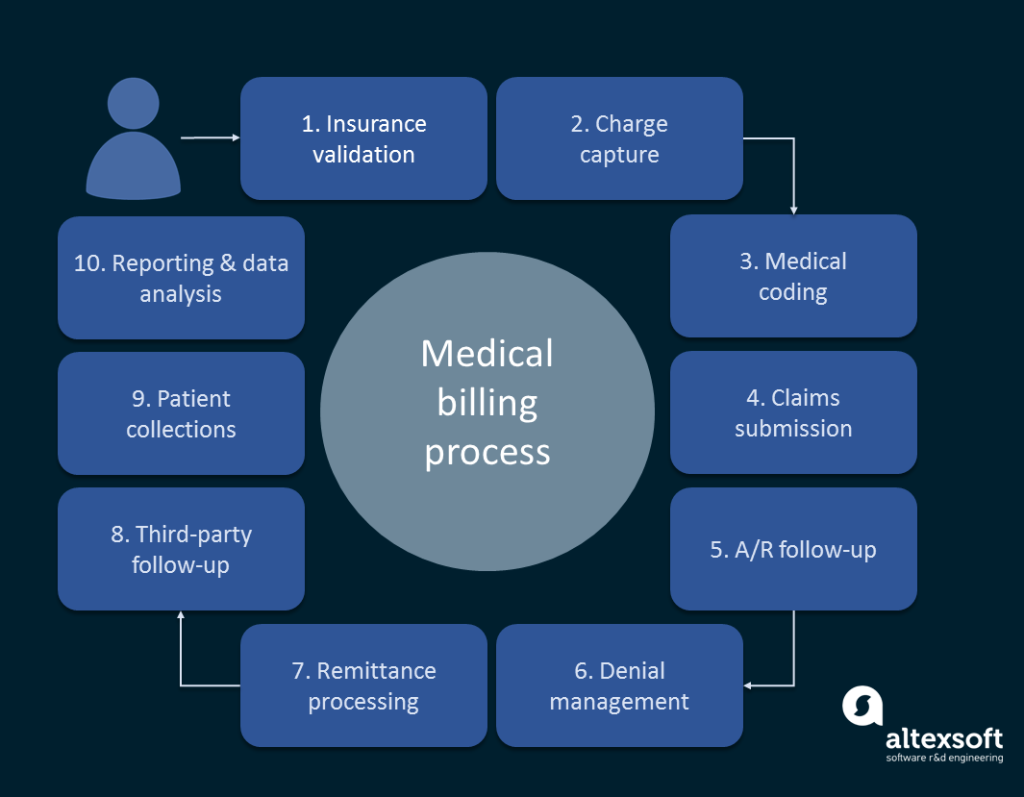
This image is property of www.altexsoft.com.
Fee-for-Service (FFS) Plans
Fee-for-Service plans, also known as traditional indemnity plans, provide the highest level of freedom when it comes to healthcare provider choice. Under an FFS plan, individuals can see any provider they want without the need for referrals. However, this freedom comes at a cost, as FFS plans often have higher premiums and deductibles compared to other types of plans. Additionally, individuals may need to submit claims themselves to receive reimbursement for covered services. FFS plans can be attractive for individuals who prioritize provider choice and are willing to pay higher costs.
High Deductible Health Plans (HDHP)
High Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs) are designed to lower monthly premiums in exchange for higher out-of-pocket costs. These plans feature a higher deductible than other types of plans, meaning individuals must pay a certain amount out of their own pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in. HDHPs are often paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), which allow individuals to save pre-tax dollars to pay for qualified medical expenses. These plans can be a cost-effective option for individuals who are generally healthy and do not anticipate regular high-cost medical services.
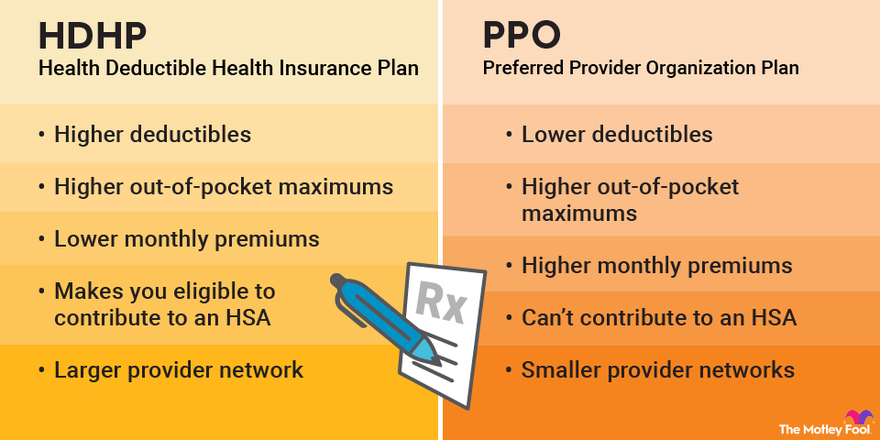
This image is property of m.foolcdn.com.
Medicare Advantage Plans
Medicare Advantage plans, also known as Medicare Part C, are offered by private insurance companies approved by Medicare. These plans combine the benefits of Original Medicare (Part A and B) with additional coverage options, such as prescription drug coverage (Part D) and sometimes even additional benefits like dental or vision care. Medicare Advantage plans may have different rules and costs compared to Original Medicare, and individuals must continue paying their Medicare Part B premium in addition to any premium associated with the Medicare Advantage plan.
Medicaid and State Programs
Medicaid is a government-sponsored program that provides healthcare coverage for low-income individuals and families. Each state has its own Medicaid program, and eligibility requirements and coverage options may vary. Medicaid covers a wide array of medical services, including doctor visits, hospital stays, and prescription medications, among others. Enrollment in Medicaid is based on income and other factors, and individuals must meet certain criteria to qualify. State programs may also offer additional healthcare coverage options or assistance programs that complement Medicaid benefits.
In conclusion, understanding the different types of plans in medical billing is crucial for both healthcare providers and patients. The variety of plans available offers individuals the flexibility to choose the type of coverage that suits their needs and preferences. Healthcare providers must be well-versed in the intricacies of each plan to ensure accurate and timely billing, while patients must familiarize themselves with the specific guidelines, requirements, and costs associated with their chosen plan. By navigating the complex landscape of medical billing plans effectively, both healthcare providers and patients can work together to ensure quality care while maintaining financial stability.
