In the world of medical billing, modifiers play a crucial role in accurately documenting and coding procedures. Effective utilization of modifiers can significantly impact the reimbursement process and minimize coding errors. This article aims to shed light on the different types of modifiers used in medical billing, their purpose, and how they enhance the accuracy and transparency of healthcare claims. Understanding these modifiers is essential for healthcare providers and billing professionals to ensure precise coding, streamline the billing process, and optimize reimbursement rates.
Modifiers in Medical Billing
modifiers play a crucial role in the realm of medical billing. They serve as additional codes that can be appended to a healthcare service or procedure to provide further clarification or information to the payer. These modifiers help in accurately conveying the nature of the service provided, any special circumstances, or any variations from the usual billing practices. By understanding the definition, purpose, and importance of modifiers, healthcare professionals can ensure accurate and efficient reimbursement for the services they provide.
Definition of Modifiers
Modifiers are two-character alphanumeric codes that are added to the primary procedure code in medical billing. These codes help to modify the way a service or procedure is identified and reimbursed. Modifiers provide additional information about the service to the payer, such as the method, extent, or circumstances of the procedure. They allow healthcare providers to communicate any significant changes or variations that may impact the billing and coding process.
Purpose of Modifiers
The primary purpose of modifiers in medical billing is to provide additional information and clarification to the payer. These codes enable healthcare professionals to accurately describe the services they provide, ensuring that the submitted claims reflect the complex nature of the procedures performed. Modifiers serve to eliminate ambiguities and facilitate accurate billing by indicating any special circumstances or variations that may affect reimbursement. Additionally, modifiers help prevent claim denials, delays, or incorrect payments by providing the necessary context for the billed services.
Importance of Modifiers in Medical Billing
The importance of modifiers in medical billing cannot be overstated. Proper use of modifiers ensures accurate reimbursement for the services rendered by healthcare providers. By effectively communicating any special circumstances or variations, modifiers help to justify the need for specific services and facilitate proper payment from insurance payers. Moreover, modifiers help in fulfilling the requirements of insurance companies, maintaining compliance with billing regulations, and reducing the likelihood of billing errors or fraudulent claims. Overall, modifiers play a vital role in ensuring streamlined medical billing processes and improved financial outcomes for healthcare practitioners.
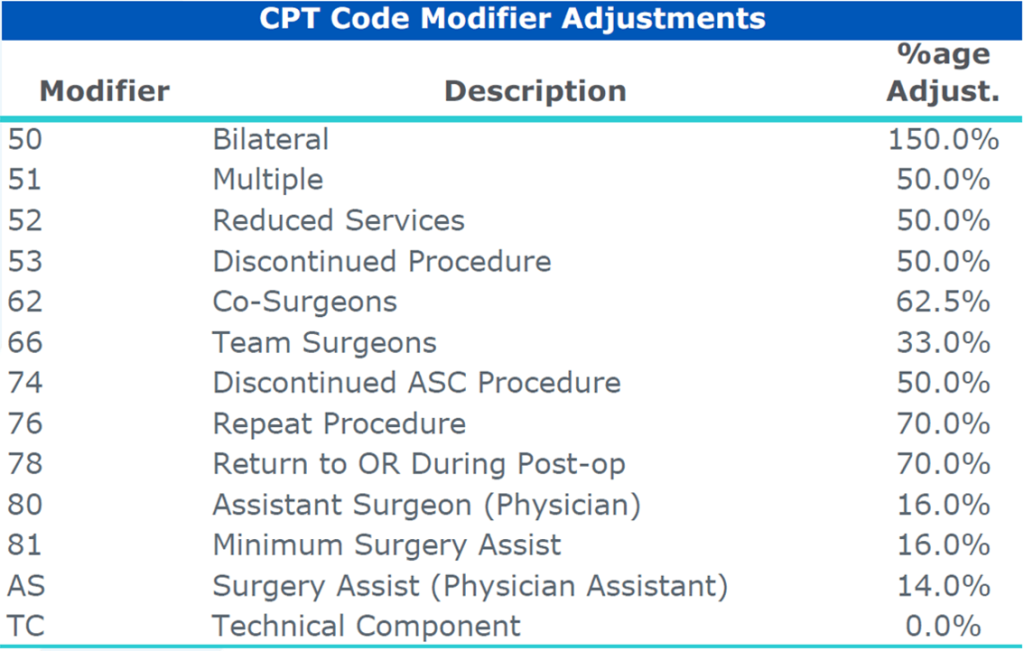
This image is property of www.veralon.com.
Types of Modifiers
Modifiers are classified into various categories based on the specific nature of the service or procedure. These categories include Evaluation and Management (E/M) modifiers, Anatomic modifiers, Global Surgery modifiers, Surgical modifiers, Radiology modifiers, Pathology and Laboratory modifiers, Durable Medical Equipment (DME) modifiers, Ambulance modifiers, Preventive Services modifiers, and Mental Health Services modifiers. Let’s explore each category in detail:
Evaluation and Management (E/M) Modifiers
Evaluation and Management modifiers are commonly used in medical billing to indicate specific circumstances or variations related to E/M services. These modifiers are added to the E/M codes to provide detailed information about the complexity, location, or other unique aspects of the service. For example, Modifier 25 is used to indicate that an E/M service was separately identifiable from a procedure performed on the same day.
Anatomic Modifiers
Anatomic modifiers are used to indicate a specific anatomical site upon which a procedure is performed. These modifiers help in specifying the exact location of the service, thereby providing additional details for proper reimbursement. An example of an anatomic modifier is Modifier F1, which indicates that a procedure was performed on the left hand.
Global Surgery Modifiers
Global Surgery modifiers are used to identify specific circumstances related to procedures with global surgical periods. These modifiers help in distinguishing between pre-operative, intra-operative, and post-operative services provided by the surgeon. Modifier 24 is an example of a global surgery modifier that indicates a separately identifiable evaluation and management service performed during the post-operative period.
Surgical Modifiers
Surgical modifiers are used to provide additional information about surgical procedures. These modifiers help in indicating specific circumstances or variations related to the surgical service provided. For instance, Modifier 51 indicates that multiple procedures were performed during the same surgical session.
Radiology Modifiers
Radiology modifiers are used to provide further details about radiological services or imaging studies. These modifiers help in indicating different aspects of the radiology service, such as the number of views, multiple procedures performed, or the use of specific equipment. An example is Modifier 26, which indicates that only the professional component of a radiological service was performed.
Pathology and Laboratory Modifiers
Pathology and Laboratory modifiers are used to provide details about laboratory services or diagnostic tests. These modifiers help in specifying circumstances that may impact the billing and coding of these services, such as site-specific or technical components. Modifier 90, for example, indicates that a laboratory test was performed outside the usual reference range.
Durable Medical Equipment (DME) Modifiers
Durable Medical Equipment modifiers are used to identify specific circumstances related to the use of durable medical equipment. These modifiers help in providing further details about the equipment used or any necessary accessories. An example of a DME modifier is Modifier RR, which indicates rental equipment.
Ambulance Modifiers
Ambulance modifiers are used to indicate specific circumstances related to ambulance services. These modifiers help in providing additional information about the transportation or level of service provided during an ambulance transport. Modifier RH, for instance, indicates that a physician was present during a medical emergency transport.
Preventive Services Modifiers
Preventive Services modifiers are used to identify specific circumstances related to preventive healthcare services. These modifiers help in indicating additional information about the preventive services provided or specific aspects related to preventive care. Modifier 33 is an example of a preventive services modifier that indicates a preventive service was performed.
Mental Health Services Modifiers
Mental Health Services modifiers are used to specify certain aspects of mental health services. These modifiers help in indicating details about the type of service provided or specific circumstances related to mental health care. Modifier GT, for example, indicates that telehealth services were provided for mental health care.
In conclusion, modifiers serve as vital components in medical billing, providing additional information and clarification to ensure accurate reimbursement for healthcare services. Understanding the different types of modifiers and their specific purposes enables healthcare professionals to effectively communicate the complexities of the services they provide. By utilizing modifiers correctly, healthcare providers can streamline their billing processes and ensure proper payment for the care they deliver.