In the field of healthcare, clinical codes play a crucial role in organizing and categorizing medical information. By assigning specific codes to different diagnoses, procedures, medications, and other healthcare components, these classification systems ensure consistency and facilitate accurate data management. In this article, we will explore the various types of clinical codes used in medical practice, examining their significance and providing examples to shed light on their practical applications.
This image is property of www.medicalcodingbuff.com.
Introduction
Clinical codes are essential tools used in healthcare to classify and categorize medical diagnoses, procedures, treatments, and substances. These codes serve as a common language for healthcare professionals, researchers, and insurance providers, ensuring accurate and standardized documentation of patient information. The use of clinical codes enables efficient healthcare management, billing, and research analysis. In this article, we will explore the different types of clinical codes and their significance in healthcare.
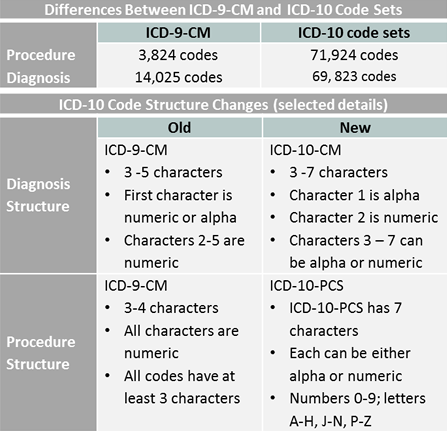
International Classification of Diseases (ICD)
The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) is the most widely used and internationally recognized clinical coding system. It provides a standardized framework for classifying diseases, injuries, and other health conditions. The ICD system is regularly updated to reflect advances in medical knowledge and capture evolving healthcare practices.
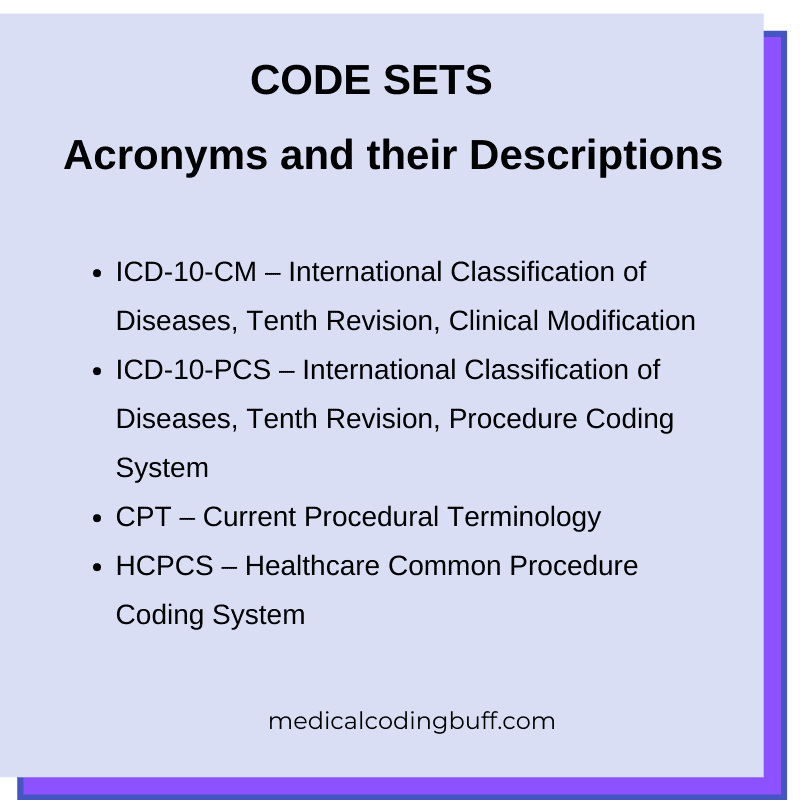
ICD-10-CM
ICD-10-CM (Clinical Modification) is the current version of the ICD classification system used in the United States. It consists of alphanumeric codes that represent different diseases, symptoms, and abnormal findings. The codes in ICD-10-CM provide a detailed description of a patient’s health condition, allowing healthcare professionals to accurately diagnose and treat various diseases.
ICD-10-PCS
ICD-10-PCS (Procedure Coding System) is another component of the ICD-10 classification. Unlike ICD-10-CM, which focuses on diagnoses, ICD-10-PCS is used to code medical procedures and interventions. This system enables the precise documentation of surgical procedures, making it valuable for surgical planning, billing, and statistical analysis.
ICD-11
ICD-11 is the upcoming revision of the International Classification of Diseases, which is expected to be implemented worldwide in the near future. ICD-11 incorporates significant changes, such as improved integration with electronic health records and an expanded range of diagnostic codes. This update aims to enhance the accuracy of clinical coding and provide a more comprehensive understanding of diseases and health conditions.
Current Procedural Terminology (CPT)
Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) is a coding system developed and maintained by the American Medical Association (AMA). It is widely used in the United States to report medical procedures and services to insurance companies for reimbursement purposes. CPT codes cover a broad range of medical specialties and are regularly updated to reflect advancements in medical technology and procedures.
Evaluation and Management Codes
Evaluation and Management (E/M) codes are a subset of CPT codes that are used to document patient encounters, including office visits, hospital visits, consultations, and telemedicine services. E/M codes provide a structured approach to recording the complexity and nature of the medical encounter, facilitating accurate reimbursement and reflecting the level of medical decision-making involved.
Anesthesia Codes
Anesthesia codes in the CPT system are used to classify different types and levels of anesthesia administered during surgical procedures. These codes consider factors such as the patient’s age, health status, and the procedure’s complexity to accurately represent the anesthesia services provided.
Surgery Codes
CPT surgery codes enable the precise documentation of surgical procedures, including both invasive and non-invasive techniques. These codes provide detailed descriptions of specific surgeries, facilitating accurate billing, tracking surgical outcomes, and supporting research and analysis.
Radiology Codes
Radiology codes in the CPT system cover a wide range of diagnostic imaging procedures, such as X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds. These codes capture the specific type of imaging procedure performed, the body part examined, and the complexity of the test, ensuring accurate reimbursement and tracking of imaging services.
Pathology and Laboratory Codes
Pathology and Laboratory codes in the CPT system are used to classify laboratory tests, pathology procedures, and other diagnostic services. These codes capture the specific test performed, the specimen type, and the methodology used, enabling accurate billing and analysis of laboratory services.
Medicine Codes
Medicine codes in the CPT system encompass a broad range of services, such as non-surgical treatments, vaccinations, and administration of medications. These codes provide a standardized way of documenting medical services not covered by other CPT code categories, ensuring accurate reimbursement and tracking of medical treatments.
Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS)
The Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) is a coding system used in the United States to identify and categorize medical services, supplies, and equipment not covered by CPT codes. HCPCS is divided into two levels: Level I and Level II.
Level I HCPCS Codes
Level I HCPCS codes comprise the subset of CPT codes used to report services provided by physicians, non-physician practitioners, and medical facilities. These codes are integrated into the broader HCPCS system and are primarily used for billing and reimbursement purposes.
Level II HCPCS Codes
Level II HCPCS codes cover a wide range of medical supplies, durable medical equipment, and other healthcare services not included in CPT codes. These codes are used by non-physician providers, such as ambulance services, home healthcare agencies, and medical suppliers, to accurately document and bill for their services.
SNOMED CT
SNOMED CT (Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine – Clinical Terms) is a comprehensive clinical coding system used globally to support the electronic exchange of clinical health information. It consists of a vast collection of medical concepts, their descriptions, and relationships, providing a standardized terminology for clinical documentation and data exchange.
Concepts
SNOMED CT includes a broad range of concepts representing various diseases, procedures, symptoms, anatomical structures, and substances. Each concept is assigned a unique code and standardized name, enabling precise and consistent communication across healthcare systems and settings.
Description Logic
SNOMED CT incorporates description logic, a formal logic system, to support advanced reasoning capabilities and semantic precision. This allows healthcare professionals and computer systems to accurately interpret and analyze the meaning of coded clinical information, enhancing the accuracy and interoperability of healthcare data.
Relationships
SNOMED CT facilitates the representation of complex relationships between different clinical concepts. These relationships capture various aspects, such as anatomical structure hierarchies, disease classifications, and procedures’ dependencies, enabling more comprehensive and nuanced clinical documentation, research, and analysis.
Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes (LOINC)
The Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes (LOINC) is a widely used coding system for identifying laboratory and clinical observations. LOINC codes enable the standardization and interoperability of laboratory and clinical data, allowing healthcare professionals and researchers to compare and analyze results across different healthcare organizations and systems.
Universal Code System
LOINC provides a universal code system for identifying and exchanging laboratory and clinical observations, such as laboratory tests, vital signs, and clinical assessments. These codes ensure consistency and comparability in documenting and sharing patient information, supporting improved patient care and research outcomes.
Component and Property
LOINC codes consist of two main components: a component code and a property code. The component code represents the type of observation, while the property code defines the specific characteristic being measured or observed. This dual-component structure enables precise identification and classification of a wide range of laboratory and clinical observations.
Units of Measure
LOINC codes also include standard units of measure for laboratory and clinical observations. These units provide a consistent and unambiguous representation of measurement values, facilitating accurate interpretation and comparison of data across different healthcare systems and settings.
This image is property of cdn.sketchbubble.com.
RxNorm
RxNorm is a standardized terminology and drug vocabulary developed by the National Library of Medicine in the United States. It encompasses a comprehensive collection of medication-related concepts, facilitating the exchange of medication information and supporting medication management across different healthcare systems.
Unique Ingredient Identifier (UNII)
RxNorm incorporates the Unique Ingredient Identifier (UNII) system, which assigns a unique code to each active ingredient found in medication products. This enables precise identification and linkage of medication ingredients, supporting accurate medication management, adverse event reporting, and medication reconciliation.
Prescribable Names
RxNorm includes prescribable names for medication products, representing the names used in clinical practice when prescribing medications. These names align with national drug formularies, product monographs, and drug compendia, ensuring consistent and standardized medication prescribing across healthcare settings.
Semantic Clinical Drugs
RxNorm’s Semantic Clinical Drugs (SCD) subset provides a refined representation of medication concepts, focusing on clinically relevant drug information. SCD concepts encompass aspects such as drug ingredients, strengths, dosage forms, and routes of administration, enabling accurate and precise medication documentation, analysis, and decision support.
Current Dental Terminology (CDT)
Current Dental Terminology (CDT) is a coding system developed by the American Dental Association (ADA) to document dental procedures and services. CDT codes provide a standardized approach to dental coding, facilitating accurate billing, communication, and analysis of dental treatments.
Veterinary Classification of Procedures (VetCPT)
Veterinary Classification of Procedures (VetCPT) is a coding system used in veterinary medicine to classify and document veterinary procedures and services. VetCPT codes provide a structured framework for veterinary coding, allowing for accurate billing, tracking of veterinary treatments, and analysis of animal health outcomes.
Conclusion
Clinical codes play a pivotal role in healthcare by providing a standardized language for classifying medical diagnoses, procedures, treatments, and substances. The various coding systems, such as ICD, CPT, HCPCS, SNOMED CT, LOINC, RxNorm, CDT, and VetCPT, enable healthcare professionals, researchers, and insurance providers to accurately capture and communicate vital healthcare information. These codes facilitate efficient healthcare management, billing, research analysis, and interoperability, ultimately leading to improved patient care and outcomes. By understanding the different types of clinical codes and their significance, healthcare professionals can effectively utilize these coding systems to enhance healthcare delivery and advance medical knowledge.