In the realm of healthcare administration, it is critical to discern between medical billing and medical coding, as they serve distinct yet interconnected functions. While both involve handling patient data and ensuring proper reimbursement, medical billing focuses on the financial aspect of healthcare services while medical coding focuses on translating medical procedures and diagnoses into standardized codes. This article will explore three key differences between medical billing and medical coding, shedding light on their unique roles and responsibilities.
Definition and Purpose of Medical Billing and Medical Coding
Medical Billing
Medical billing is a crucial administrative process in the healthcare industry that involves submitting and following up on claims with insurance companies to ensure the timely and accurate reimbursement for healthcare services rendered to patients. The purpose of medical billing is to facilitate the financial transactions between healthcare providers and insurance companies or patients, ultimately ensuring that the healthcare organizations receive the appropriate payment for their services.
Medical Coding
On the other hand, medical coding is the process of assigning standardized codes to the diagnoses, procedures, and treatments documented in patient medical records. These codes, such as the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) codes and the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes, ensure uniformity and consistency in recording medical information for various purposes, including reimbursement, research, and healthcare analytics. The primary purpose of medical coding is to translate the details of healthcare services into universally recognized alphanumeric codes that can be used for various purposes, with reimbursement being one of the key aspects.
Education and Training

Medical Billing Education and Training
To pursue a career in medical billing, individuals typically need a high school diploma or equivalent. However, some employers may prefer candidates with additional education or training, such as an associate’s degree or a certification program in medical billing. These programs provide individuals with a comprehensive understanding of medical terminology, insurance regulations, billing software usage, and various coding systems. Additionally, staying updated with the evolving healthcare regulations and technologies is essential for medical billing professionals.
Medical Coding Education and Training
Unlike medical billing, a career in medical coding often requires specialized training and certification. In order to become a medical coder, individuals can complete a coding program or earn a degree in health information management. These education programs typically cover anatomy and physiology, medical terminology, coding guidelines, and the use of coding systems. It is crucial for medical coders to have a strong attention to detail and a deep understanding of the various coding classification systems and guidelines, such as the ICD-10-CM and the Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS).
This image is property of www.parkmedicalbilling.com.
Job Responsibilities
In the world of healthcare administration, medical billing and coding professionals shoulder distinct yet interconnected responsibilities.
Medical Billing Job Responsibilities
As a medical billing professional, your primary responsibility is to ensure accurate and timely submission of claims for reimbursement. This involves verifying patient insurance coverage, collecting necessary documentation, and accurately entering patient information and services provided into billing software. You will also be responsible for reviewing and correcting any coding or billing errors, addressing denied claims, and following up with insurance companies or patients to resolve payment discrepancies or outstanding balances. In addition, it is important to maintain patient confidentiality and adhere to relevant legal and ethical guidelines.
Medical Coding Job Responsibilities
As a medical coder, your main responsibility is to translate the details of medical procedures, diagnoses, and treatments into appropriate alphanumeric codes. This involves reviewing patient medical records, extracting relevant information, and assigning the correct codes according to the established coding systems and guidelines. Accuracy and attention to detail are crucial to ensure that the coded information accurately represents the services provided. Medical coders also play a crucial role in auditing and reviewing coded data for compliance purposes and providing feedback to healthcare providers to improve documentation practices.
Skills Required

Medical Billing Skills Required
To excel in medical billing, strong organizational and administrative skills are essential. You need to effectively manage patient records, insurance claims, and billing processes. Proficiency in using billing software and electronic health record (EHR) systems is also important. Additionally, you must have excellent communication skills to interact with insurance companies, patients, and healthcare providers. Detail-oriented skills are crucial for accurately entering data and identifying discrepancies. It is also necessary to stay updated on insurance regulations and coding guidelines.
Medical Coding Skills Required
In the field of medical coding, attention to detail and analytical thinking are vital. You must possess a sound knowledge of anatomy, medical terminology, and coding classification systems. Strong computer skills, including proficiency in coding software, are necessary for accurately assigning codes. Additionally, problem-solving skills are valuable when navigating complex medical documentation and resolving coding discrepancies. Continuous learning and staying updated with coding system changes and industry updates is crucial for maintaining accurate and up-to-date coding practices.
Coding Systems Utilized
Medical Billing Coding System
In medical billing, the coding system primarily used is the Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS). HCPCS includes two levels of codes: Level I codes, which are identical to the American Medical Association’s CPT codes and are used for reporting medical procedures and services, and Level II codes, which are alphanumeric codes used for reporting supplies, equipment, and non-physician services.
Medical Coding Classification Systems
Medical coding professionals utilize various coding classification systems to assign codes to diagnoses and procedures. The most commonly used systems include the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), which is currently in its 10th edition (ICD-10), and the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT), which is maintained by the American Medical Association. The ICD-10-CM is used for coding diagnoses, while the CPT codes are used to document medical procedures and services.
Reimbursement and Revenue Generation
Medical Billing Reimbursement Process
In medical billing, the reimbursement process involves submitting claims to insurance companies or patients for the services rendered. The claims include the appropriate coding information, patient demographics, and details of the services provided. The insurance company or payer reviews the claims and determines the reimbursement amount based on the patient’s insurance coverage and the services’ medical necessity. Upon approval, the insurance company releases payment to the healthcare provider. Efficient medical billing ensures timely reimbursement, reducing potential revenue losses.
Medical Coding and Revenue Generation
While medical coding itself does not directly generate revenue, accurate and thorough coding plays a critical role in revenue generation for healthcare organizations. Proper coding ensures that healthcare providers can accurately bill for the services they have provided. Accurate coding also helps prevent coding errors or fraudulent practices that could result in denied claims or potential legal issues. Optimizing revenue requires a collaborative effort between medical coders, billers, and healthcare providers to ensure accurate documentation and coding that reflects the value of the services rendered.
Compliance and Documentation

Medical Billing Compliance and Documentation
In medical billing, compliance with laws, regulations, and ethical guidelines is of utmost importance. This includes adhering to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), which protects patients’ privacy and security of health information. Medical billing professionals must also ensure accurate documentation of patient information, services provided, and coding details. Proper documentation supports the reimbursement process, protects against potential audit issues, and maintains transparency in healthcare transactions.
Medical Coding Compliance and Documentation
Similar to medical billing, medical coding requires strict adherence to compliance and documentation standards. Accurate coding is essential for proper reimbursement, billing integrity, and healthcare analytics. It ensures that healthcare organizations provide services that meet medical necessity requirements and are appropriately reimbursed. Proper documentation practices, including clear and concise medical records, play a crucial role in supporting accurate coding. Compliance with coding guidelines and ethical standards ensures that the coded information accurately reflects the healthcare services provided.
Workflow and Collaboration

Medical Billing Workflow
In the medical billing workflow, timely and efficient coordination between various stakeholders is essential. This includes collaboration with healthcare providers, medical coders, and insurance companies. The workflow typically involves verifying patient insurance coverage, collecting patient information, accurately coding the services provided, submitting claims to insurance companies, and diligently following up on unpaid or denied claims. Clear communication and effective collaboration ensure smoother billing processes, reduced errors, and improved revenue cycle management.
Medical Coding and Collaboration
Medical coding professionals often collaborate closely with healthcare providers, medical billers, and other administrative staff. Collaboration starts with the accurate documentation of patient medical records to ensure appropriate coding. Coders may work closely with healthcare providers to clarify documentation ambiguities or request additional information. Concurrently, collaboration with medical billers helps ensure accurate coding for optimal reimbursement. Effective teamwork and communication between all stakeholders are crucial for maintaining accurate and compliant coding practices.
Industry Certification
Medical Billing Certification
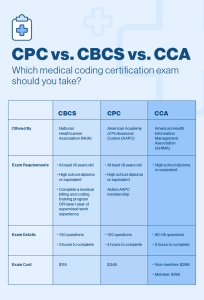
While certification is not always a requirement for medical billing professionals, it can enhance job prospects and demonstrate competence in the field. Several organizations, such as the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC) and the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA), offer certifications specific to medical billing. These certifications typically require passing an examination that assesses knowledge of medical terminology, coding systems, billing regulations, and ethical standards.
Medical Coding Certification
Unlike medical billing, medical coding certifications are widely recognized and often preferred by employers. Certifications such as the Certified Professional Coder (CPC) offered by the AAPC and the Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) offered by AHIMA validate the coder’s proficiency in various coding systems, guidelines, and ethical practices. These certifications require passing rigorous examinations that assess coding knowledge and skills. Earning a certification enhances job opportunities, provides professional recognition, and demonstrates a commitment to ongoing education and best practices.
Salary and Job Outlook

Medical Billing Salary and Job Outlook
The salary range for medical billing professionals varies depending on factors such as education, experience, geographical location, and the size of the organization. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for medical records and health information technicians, which includes medical billers, was $44,090 as of May 2020. The job outlook for medical billing professionals remains favorable, with a projected growth rate of 8% from 2019 to 2029, driven by an increasing demand for healthcare services and the growing complexity of medical billing regulations and insurance requirements.
Medical Coding Salary and Job Outlook
Similarly, the salary for medical coding professionals can vary based on similar factors such as experience, certifications, and geographic location. According to the BLS, the median annual wage for medical records and health information technicians, which includes medical coders, was $48,370 as of May 2020. The job outlook for medical coding professionals also remains positive, with a projected growth rate of 8% from 2019 to 2029. The demand for accurate coding and quality data is expected to continue increasing as the healthcare industry evolves and relies more heavily on data analytics and information management.
In conclusion, while medical billing and medical coding have distinct roles and responsibilities within the healthcare industry, they are closely interconnected and essential for revenue cycle management and accurate documentation. Medical billing ensures timely reimbursement for healthcare services, while medical coding provides the foundational element of accurate coding for proper reimbursement and healthcare data analysis. By understanding the differences and synergies between these two vital functions, healthcare organizations can optimize their financial operations, improve patient care, and maintain compliance with industry standards.
