RCM, also known as Revenue Cycle Management, plays a crucial role in the field of medical billing. It encompasses the entire process of tracking patient information, verifying insurance eligibility, submitting claims, and collecting payment for healthcare services. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of RCM and how it ensures a streamlined and efficient financial workflow for healthcare providers. Discover the inner workings of RCM and its significance in maximizing revenue and minimizing administrative burdens in the medical billing sector.
Definition of RCM in Medical Billing
Explanation of RCM
Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) is a crucial process in the healthcare industry that focuses on optimizing the financial aspects of a medical practice. It involves the management of all administrative and clinical functions that contribute to the capture, management, and collection of patient service revenue.
In simpler terms, RCM is the end-to-end process of ensuring that healthcare providers receive proper compensation for the services they render to patients. It involves various steps, from patient registration to claim submission, payment posting, and accounts receivable management.
Importance of RCM
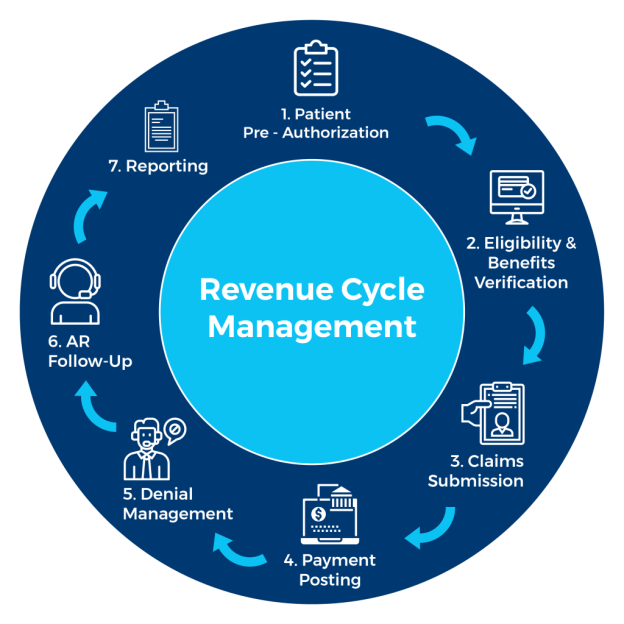
This image is property of www.imagineteam.com.
Efficient RCM practices are essential for the financial well-being of medical practices and healthcare organizations. It ensures that medical providers receive accurate and timely reimbursement for their services, minimizing revenue leakage and improving overall financial stability.
Without effective RCM, healthcare providers may face widespread billing and collection errors, delayed payments, increased denials, and revenue loss. This can have a significant impact on the ability of medical practices to meet their financial obligations, invest in new technologies, and provide quality patient care.
Components of RCM
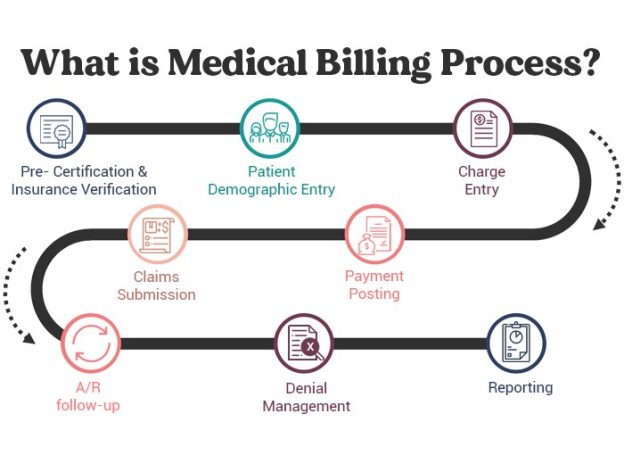
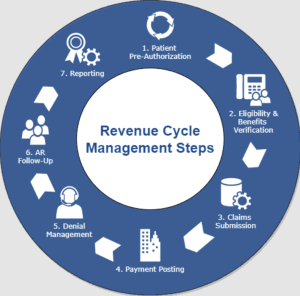
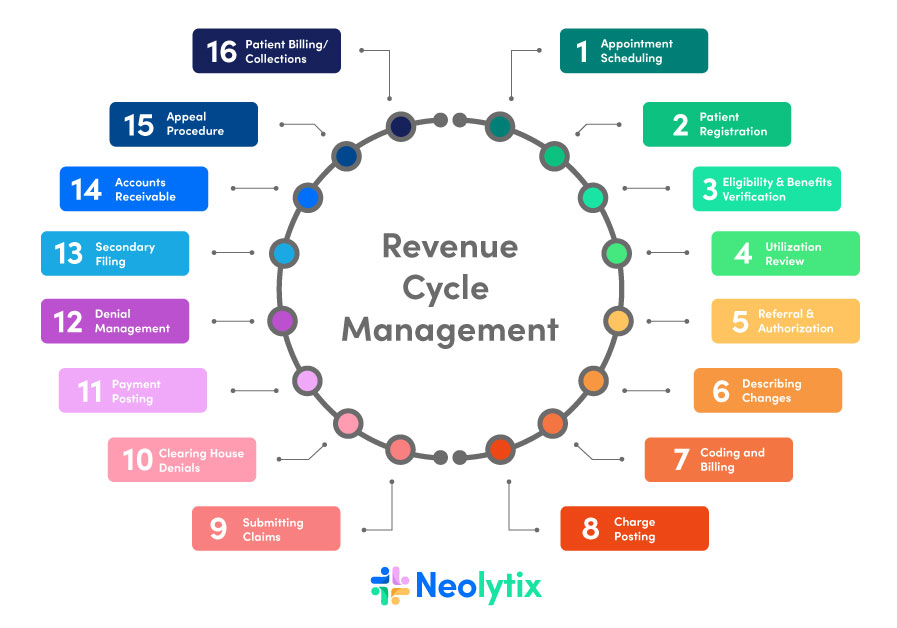
The Revenue Cycle Management process consists of several key components that work together to ensure the smooth flow of financial transactions in medical billing. It involves stages such as patient registration, insurance verification, charge capture, coding and documentation, claim submission, payment posting, accounts receivable management, denial management, appeals and follow-up, and reporting and analytics.
Each component plays a crucial role in the overall revenue cycle, and any inefficiencies or errors in these areas can have a detrimental effect on the financial health of a healthcare organization.

This image is property of neolytix.com.
Understanding RCM Process
To fully comprehend the revenue cycle, it is essential to delve deeper into each stage of the RCM process and understand how they contribute to the overall financial operations of a medical practice.
Patient Registration
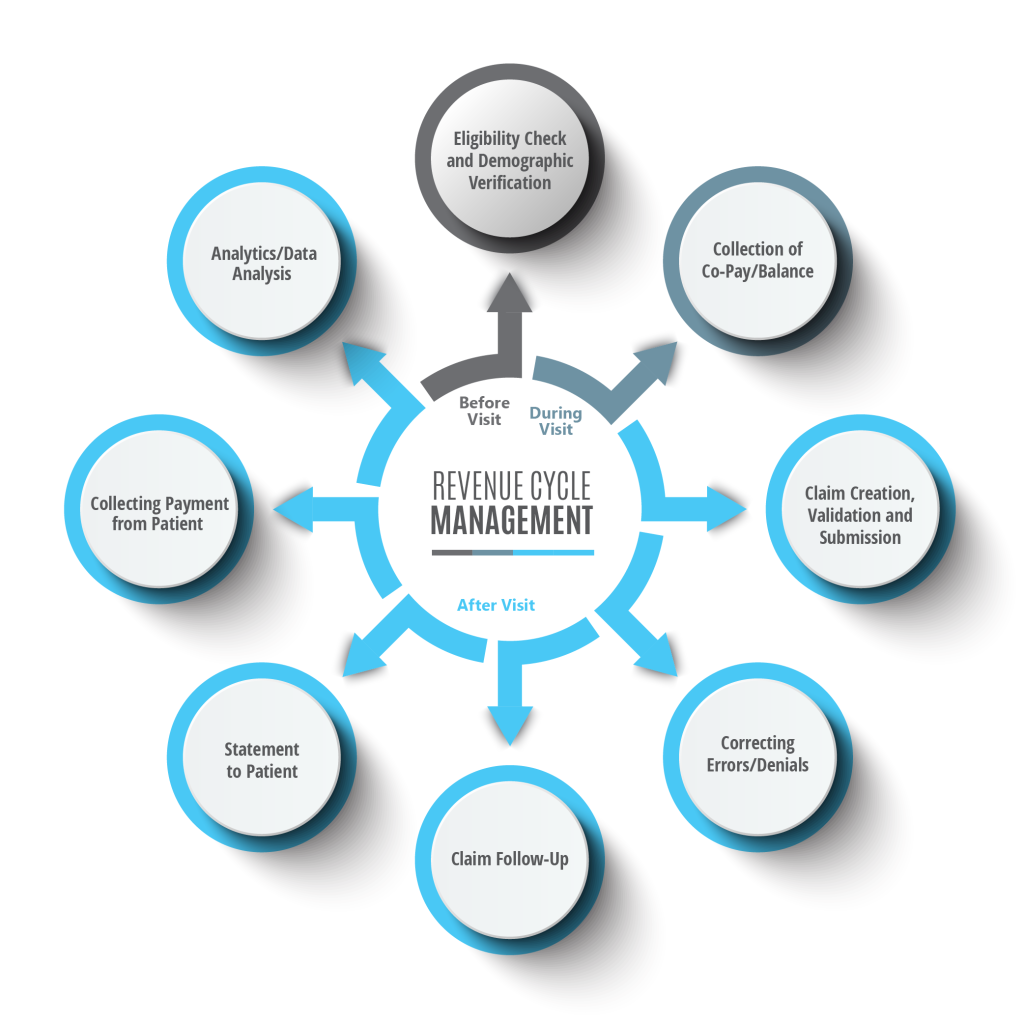
Patient registration is the first step in the revenue cycle and involves collecting accurate demographic and insurance information from patients. This data is crucial for verifying insurance coverage, determining patient eligibility, and accurately billing for services rendered.
It is important to ensure that patient information is captured correctly to avoid billing errors and delays in claim processing.
Insurance Verification
Insurance verification is a critical step in the revenue cycle that validates the patient’s insurance coverage and determines the extent of benefits available. It involves verifying the patient’s eligibility, identifying any pre-authorization requirements, and understanding the patient’s financial responsibilities.
By conducting thorough insurance verification, medical providers can avoid claim denials and reduce the risk of non-payment for services rendered.
Charge Capture
charge capture involves accurately recording the services provided to patients, along with relevant codes and charges. This step ensures that all services rendered are properly documented and can be billed to insurance companies or patients.
Accurate charge capture is crucial for proper reimbursement and compliance with coding and billing guidelines.
Coding and Documentation
Coding and documentation play a pivotal role in the revenue cycle as they determine the accuracy of billing and the level of reimbursement. Healthcare providers must ensure that medical records are accurately coded to reflect the services provided, diagnoses, and procedures performed.
Proper documentation and coding not only facilitate accurate billing but also mitigate the risk of audits and non-compliance.
Claim Submission
Claim submission involves transmitting the medical claims to insurance companies or government payers for reimbursement. It is crucial to submit clean claims that adhere to all coding, billing, and formatting requirements to expedite the payment process.
Submitting accurate and complete claims reduces the risk of claim denials and delays in reimbursement.
Payment Posting
Payment posting involves recording and reconciling payments received from insurance companies, patients, or other payers. This step ensures that all payments are properly allocated and tracked, enabling accurate financial reporting and analysis.
Efficient payment posting practices minimize discrepancies and assist in identifying any outstanding balances, denials, or underpayments.
Accounts Receivable Management
Accounts Receivable (AR) management involves tracking and managing outstanding balances owed by payers or patients. It includes activities such as following up on unpaid claims, identifying and resolving payment discrepancies, and managing collections.
Effective AR management is crucial for reducing outstanding balances, optimizing cash flow, and improving the financial performance of a medical practice.
Denial Management
Denial management refers to the process of identifying and resolving claim denials. It involves analyzing denied claims, identifying the root causes, taking corrective actions, and resubmitting them for reconsideration.
By implementing an effective denial management process, healthcare organizations can minimize financial losses due to claim denials and streamline their revenue flow.
Appeals and Follow-up
Appeals and follow-up play a crucial role in the revenue cycle by addressing denied claims and pursuing payment reconsiderations. Timely and strategic appeals can help overturn claim denials and maximize reimbursement.
Proactive follow-up with insurance companies and patients ensures that outstanding claims are pursued diligently, minimizing the risk of revenue loss.
Reporting and Analytics
Reporting and analytics provide valuable insights into the financial health and performance of a medical practice. By analyzing key metrics and trends, such as days in accounts receivable, denial rates, and collection rates, healthcare organizations can identify areas of improvement and implement effective strategies to enhance revenue cycle performance.
Regular reporting and analytics enable data-driven decision-making and help optimize financial outcomes for medical practices.
Benefits of Implementing RCM in Medical Billing
Implementing an effective RCM strategy in medical billing offers numerous benefits that positively impact the financial strength and operational efficiency of healthcare organizations.
Increased Revenue
Efficient RCM practices ensure accurate and timely reimbursement, resulting in increased revenue for medical practices. By minimizing claim denials, reducing billing errors, and optimizing collections, healthcare organizations can maximize their revenue potential.
Improved Cash Flow
Efficient RCM practices optimize the cash flow of medical practices by reducing the time between service delivery and payment receipt. Faster reimbursements enable medical practices to meet their financial obligations, invest in growth opportunities, and provide better patient care.
Reduced Billing Errors
Implementing robust RCM processes helps minimize billing errors, ensuring accurate claims submission and reimbursement. This reduces the risk of claim denials, rework, and revenue leakage, resulting in improved financial stability for medical practices.
Enhanced Efficiency
Effective RCM practices streamline administrative and clinical processes, reducing manual interventions and redundancy. This increases operational efficiency, allowing healthcare providers to focus more on patient care and practice growth.
Better Compliance
Strong RCM processes ensure compliance with coding, billing, and regulatory guidelines. By adhering to industry standards and regulations, healthcare organizations can mitigate the risk of audits, penalties, and legal issues.
Streamlined Workflow
Implementing RCM practices involves streamlining various financial and administrative processes, creating a more efficient workflow. This leads to better coordination between departments, improved communication, and reduced delays in claim processing and payment posting.
Access to Real-Time Data
Effective RCM systems provide access to real-time financial data and reports, enabling healthcare organizations to monitor their revenue cycle performance. By analyzing key metrics and trends, medical practices can identify areas of improvement and implement proactive strategies to optimize financial outcomes.
Greater Control and Transparency
Implementing RCM practices provides healthcare organizations with greater control and transparency over their financial operations. By having a clear understanding of the revenue cycle, medical practices can make informed decisions, implement effective strategies, and ensure financial stability and growth.

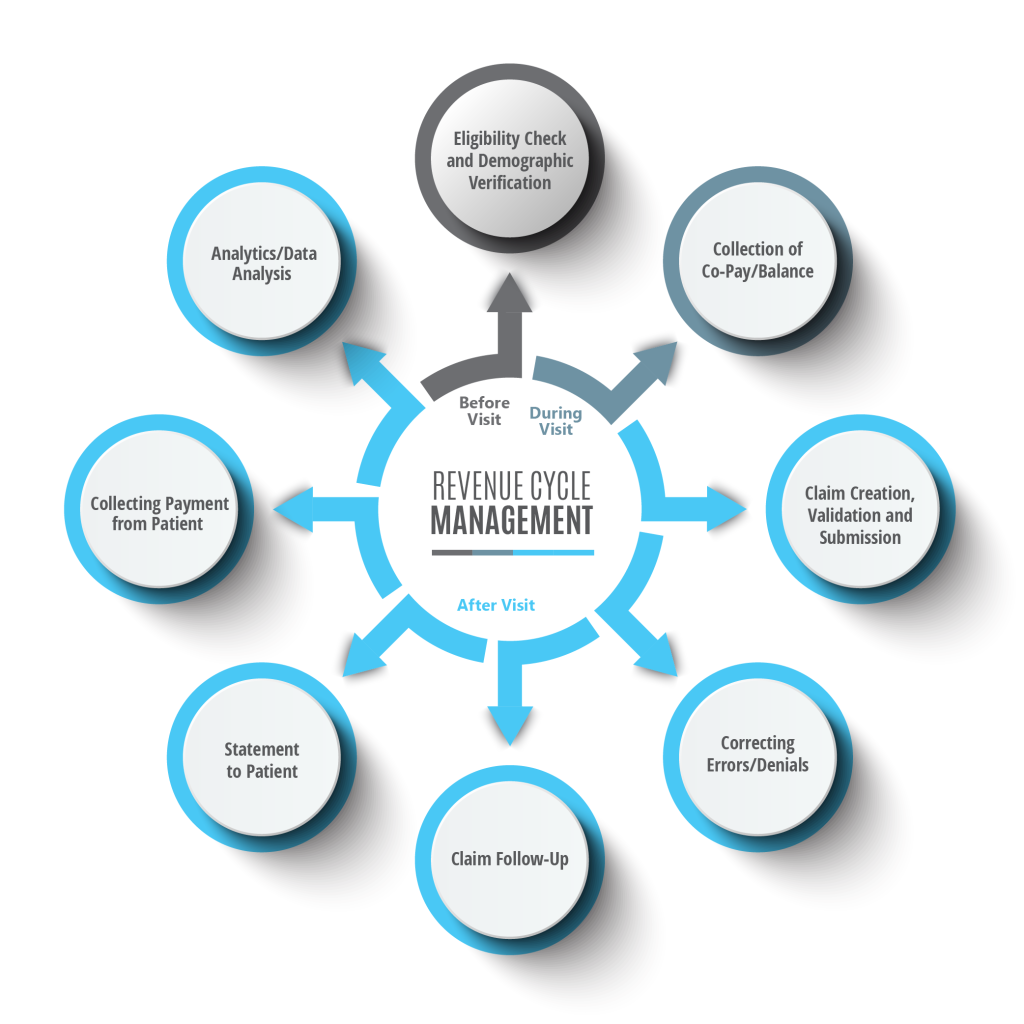
This image is property of usercontent.one.
Role of Technology in RCM
Technology plays a vital role in improving the efficiency and effectiveness of revenue cycle management. It enables healthcare organizations to automate various tasks, enhance data accuracy, and streamline processes.
Automation and Electronic Health Records
Automation tools and electronic health records (EHR) systems simplify and streamline the revenue cycle by automating repetitive tasks and reducing manual interventions. This improves accuracy, saves time, and minimizes errors in patient registration, charge capture, claims submission, and payment posting.
Medical Billing Software and Tools
Specialized medical billing software and tools are designed to streamline and optimize the billing and collection processes. These tools automate tasks such as coding, claims submission, payment posting, denial management, and reporting, improving overall RCM efficiency and accuracy.
Integration and Interoperability
Integration and interoperability between various healthcare systems, such as EHR, practice management systems, and billing software, enable seamless data exchange and collaboration. This enhances efficiency, reduces data entry errors, and improves the accuracy of financial transactions in the revenue cycle.
Data Security and Privacy
As technology advances, the importance of data security and privacy in RCM becomes increasingly critical. Healthcare organizations must implement robust security measures to protect patient information, comply with regulations, and safeguard sensitive financial data.
Challenges in Implementing RCM
While RCM offers numerous benefits, healthcare organizations often face several challenges when implementing and maintaining effective revenue cycle management practices.
Complex and Changing Regulations
The ever-changing nature of regulations and coding guidelines in the healthcare industry presents a significant challenge for healthcare organizations. Medical practices must invest in ongoing education and training to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and prevent revenue loss due to non-compliance.
Staff Training and Education
Implementing effective RCM practices requires skilled and knowledgeable staff who understand the complexities of the revenue cycle. Staff training and education programs are essential to equip employees with the necessary skills to navigate the RCM process effectively.
Cost of Implementation
Implementing robust RCM practices often requires significant investments in technology, staff training, and process improvement initiatives. The upfront costs associated with implementing RCM can pose a challenge for small and mid-sized medical practices, potentially delaying the realization of financial benefits.
Resistance to Change
Resistance to change can be a significant barrier to implementing effective RCM practices. Healthcare organizations must address any resistance among staff members to ensure successful adoption of new processes, technologies, and workflows.
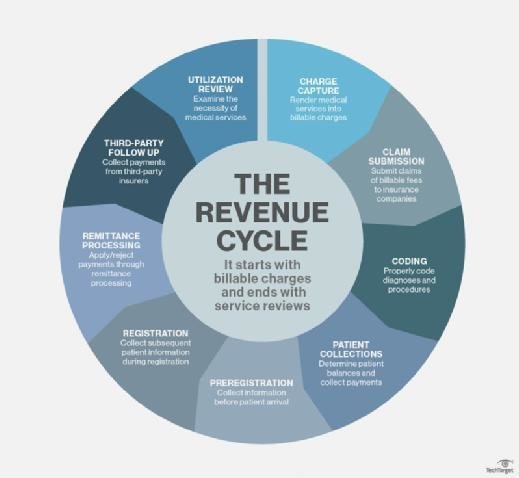
This image is property of cdn.ttgtmedia.com.
Best Practices for Successful RCM
To ensure successful revenue cycle management, healthcare organizations should follow best practices that optimize financial outcomes and operational efficiency.
Clear Communication and Collaboration
Clear communication and collaboration between departments, such as front desk staff, billing and coding teams, and clinical staff, are crucial for efficient RCM. Effective communication ensures accurate capture of patient information, timely claims submission, and streamlined billing processes.
Regular Staff Training and Education
Regular training and education programs help staff stay updated with the latest coding and billing guidelines, regulations, and technological advancements. This ensures that employees understand their roles and responsibilities in the revenue cycle and can adapt to changing industry requirements.
Streamlining Processes
Streamlining processes, eliminating redundancies, and optimizing workflows can significantly improve RCM efficiency. By identifying and eliminating bottlenecks and unnecessary steps, medical practices can reduce errors, minimize delays, and speed up claims processing.
Continuous Monitoring and Analysis
Continuous monitoring and analysis of key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics enable healthcare organizations to identify areas of improvement and implement proactive strategies to enhance revenue cycle performance. Regular analysis helps detect potential issues early, leading to timely interventions and improved financial outcomes.
Investing in Technology
Investing in robust technology solutions, such as medical billing software, automation tools, and secure data management systems, can significantly enhance RCM efficiency. Technology streamlines processes, improves accuracy, and provides real-time insights, contributing to better financial performance.
Outsourcing vs. In-House RCM
When considering revenue cycle management, healthcare organizations have the choice between outsourcing RCM services or managing them in-house. Both options have their advantages and should be carefully evaluated based on the specific needs and resources of the medical practice.
Advantages of Outsourcing RCM
Outsourcing RCM offers several benefits, including specialized expertise, reduced operational costs, scalability, and access to the latest technologies. Outsourcing allows medical practices to focus on patient care while benefiting from the expertise and efficiency of professional RCM service providers.
Advantages of In-House RCM
In-house RCM provides greater control and customization options, allowing medical practices to tailor their revenue cycle processes to their specific needs. It also enables tighter integration with other internal systems and departments, facilitating seamless communication and collaboration.
Factors to Consider in Decision-Making
When deciding between outsourcing and in-house RCM, healthcare organizations should consider factors such as resource availability, cost-effectiveness, expertise requirements, scalability, and the ability to manage regulatory compliance. A thorough assessment of these factors will help determine the best fit for the medical practice.

This image is property of www.mdsolbilling.com.
Future Trends in RCM
As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, several emerging trends in revenue cycle management are shaping the future of medical billing.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are revolutionizing the healthcare industry, including revenue cycle management. AI-powered algorithms analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make predictions, enhancing coding accuracy, streamlining claims processing, and improving revenue outcomes.
Telehealth and Virtual Care
The rapid growth of telehealth and virtual care services has introduced new challenges and opportunities in revenue cycle management. As healthcare delivery models evolve, medical practices need to adapt their RCM processes to accommodate remote service delivery, automated claims processing, and reimbursement for virtual care services.
Value-Based Care and Alternative Payment Models
The shift towards value-based care and alternative payment models, such as bundled payments and accountable care organizations, is driving changes in revenue cycle management. Healthcare organizations must implement RCM strategies that align with these models, emphasizing outcomes, quality of care, and cost efficiency.
Data Analytics and Predictive Models
Data analytics and predictive modeling are becoming increasingly important in revenue cycle management. By analyzing large datasets, healthcare organizations can identify trends, predict payment behaviors, and optimize financial outcomes. Predictive models assist in identifying potential payment risks, fraud, and improving overall revenue cycle efficiency.
Case Studies: Successful RCM Implementation
To illustrate the benefits and impact of implementing effective revenue cycle management, let us examine three case studies.
Healthcare Organization A
Healthcare Organization A, a large multi-specialty clinic, implemented streamlined RCM processes and integrated technology solutions. By centralizing billing functions and automating claims processing, they reduced billing errors by 30% and increased clean claim rate by 20%. These improvements led to a 15% increase in revenue and improved overall cash flow.
Medical Practice B
Medical Practice B, a small primary care clinic, outsourced their RCM services to a specialized provider. By leveraging the expertise of the RCM provider, they experienced a 25% reduction in claim denials, improved collection rates by 15%, and increased revenue by 20%. Outsourcing RCM allowed the medical practice to focus more on patient care and practice growth.
Hospital C
Hospital C, a large healthcare system, invested in advanced analytics tools for their revenue cycle. By leveraging data analytics and predictive modeling, they identified key areas for improvement, optimized their billing processes, and reduced their average days in accounts receivable by 20%. These improvements resulted in significant cost savings and improved financial performance.
Conclusion
Revenue cycle management is an essential component of medical billing that ensures accurate and timely reimbursement for healthcare services. By implementing efficient RCM practices, healthcare organizations can optimize financial outcomes, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient care.
The revenue cycle involves various stages, from patient registration to claim submission, payment posting, denial management, and reporting. Each stage plays a vital role in the overall financial health of a medical practice and requires careful attention to detail and adherence to regulations.
Implementing RCM practices offers numerous benefits, including increased revenue, improved cash flow, reduced billing errors, enhanced efficiency, better compliance, streamlined workflow, increased control and transparency, and access to real-time data. These advantages contribute to the overall financial stability and growth of medical practices.
Technology plays a crucial role in RCM, enabling automation, secure data management, integration, and interoperability. By leveraging technology solutions, healthcare organizations can streamline processes, improve accuracy, and gain valuable insights into their revenue cycle performance.
While implementing RCM, healthcare organizations face challenges such as complex regulations, staff training requirements, implementation costs, and resistance to change. Overcoming these challenges requires clear communication, regular training, process streamlining, continuous monitoring, and strategic investment in technology.
The decision between outsourcing and in-house RCM depends on factors such as resource availability, expertise requirements, cost-effectiveness, scalability, and regulatory compliance. Medical practices must carefully evaluate these factors to determine the optimal approach for their revenue cycle management.
Looking ahead, future trends in RCM include the integration of artificial intelligence, telehealth, value-based care, alternative payment models, data analytics, and predictive modeling. These trends will shape the future of revenue cycle management, driving innovation and operational improvements in medical billing.
Successful RCM implementations, as demonstrated by case studies, highlight the positive impact of optimized processes, technology adoption, and strategic decision-making. Healthcare organizations can learn from these experiences to improve their own revenue cycle management practices and achieve better financial outcomes.
In conclusion, with the ever-changing healthcare landscape, effective revenue cycle management is becoming increasingly important. By embracing best practices, leveraging technology, and staying ahead of emerging trends, healthcare organizations can optimize their revenue cycle, enhance financial performance, and provide better patient care.