In the field of healthcare, the role of a medical coder is indispensable when it comes to ensuring accurate and efficient recording of medical diagnoses, procedures, and treatments. A good medical coder possesses a unique set of qualities that contribute to the effective management of medical data, meticulous attention to detail, proficiency in coding systems and guidelines, and a strong ethical commitment. They play a critical role in healthcare organizations by ensuring proper reimbursement, maintaining data integrity, and supporting effective communication between healthcare providers, insurance companies, and patients. Understanding what makes a good medical coder is essential for healthcare professionals seeking to optimize their coding processes and uphold the highest standards of quality and accuracy.
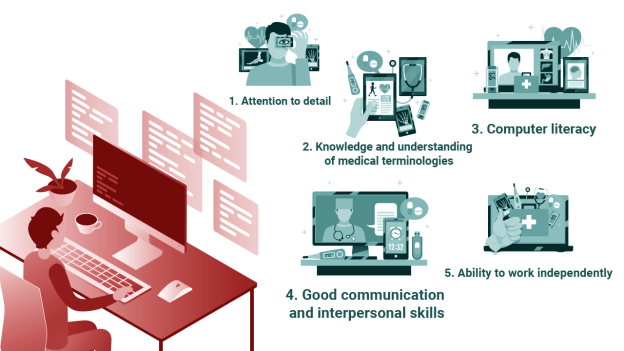
Required Skills

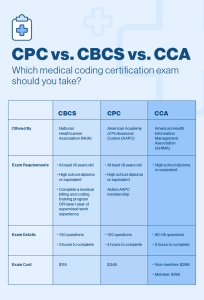
This image is property of cache.aapc.com.
Knowledge of Medical Terminology
A good medical coder possesses a strong knowledge of medical terminology. This involves understanding the specific language used in the healthcare field, such as medical procedures, diseases, and anatomical terms. By having a comprehensive understanding of medical terms, coders are able to accurately assign the appropriate codes to patient records.
Understanding of Anatomy and Physiology
In addition to medical terminology, a good medical coder must have a solid understanding of anatomy and physiology. This means having a clear comprehension of the human body, its systems, and how they function. This knowledge is crucial for accurately coding medical procedures and diagnoses, as it helps coders identify the specific area or organ of the body that is affected by a particular condition.
Proficiency in Medical Coding Systems
Proficiency in medical coding systems is an essential skill for any medical coder. It involves a deep understanding of the different coding systems used in healthcare, such as the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), Current Procedural Terminology (CPT), and Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS). A good medical coder is able to navigate these systems effectively, ensuring that the correct codes are assigned to each patient encounter.
Attention to Detail

Accurate Data Entry
Attention to detail is critical in the role of a medical coder, especially when it comes to accurate data entry. Coders must carefully review and transcribe information from medical records into the coding software or system. Any errors or omissions in this process can result in incorrect coding, leading to potential billing issues or improper patient care. A good medical coder takes the time to meticulously enter data, double-checking for accuracy and completeness.
Thorough Documentation
Thorough documentation is another important aspect of attention to detail in medical coding. Coders must ensure that all relevant details of a patient’s medical record are captured and documented accurately. This includes recording the patient’s medical history, diagnoses, treatments, and any other pertinent information. By providing comprehensive documentation, coders support the accuracy and integrity of the coding process, enabling healthcare providers to make informed decisions.
Precise Code Application
The application of codes requires a high level of precision to ensure accurate reimbursement and appropriate patient care. A good medical coder understands the nuances of coding guidelines and is able to accurately assign the most appropriate codes based on the provided documentation. This involves carefully reviewing the medical record, interpreting the diagnosis and procedures, and selecting the relevant codes. Precision in code application is crucial for providing accurate and reliable data for billing and statistical purposes.
Analytical Abilities

Ability to Interpret Medical Records
Interpreting medical records is a key analytical skill for a medical coder. Coders must be able to comprehend complex medical documentation, including physician notes, lab results, and imaging reports. By carefully analyzing these records, coders can accurately assign the appropriate codes that reflect the diagnoses and treatments provided to the patient. This requires the ability to recognize key information and apply coding guidelines effectively.
Identifying Relevant Information
Being able to identify relevant information within medical records is essential for accurate coding. A good medical coder has the ability to sift through extensive amounts of documentation and focus on the details that impact coding decisions. They can distinguish between significant and insignificant information, ensuring that the correct codes are assigned based on the relevant details provided in the patient record.
Problem-Solving Skills
Problem-solving skills are crucial in medical coding, as coders often encounter challenging cases that require thoughtful analysis and decision-making. A good medical coder has the ability to solve complex coding puzzles by applying their knowledge of coding guidelines, consulting coding resources, and seeking clarification from healthcare providers when needed. Effective problem-solving ensures that accurate codes are assigned, leading to appropriate reimbursement and optimal patient care.
Ethical Conduct

Maintaining Confidentiality
One of the fundamental ethical responsibilities of a medical coder is maintaining patient confidentiality. Coders work with sensitive medical information and must adhere to strict confidentiality protocols to protect patient privacy. This includes handling patient records with care, following HIPAA guidelines, and ensuring that only authorized individuals have access to patient data. A good medical coder understands the importance of preserving patient confidentiality and takes the necessary steps to safeguard sensitive information.
Adhering to Coding Guidelines
Adhering to coding guidelines is an ethical obligation for medical coders. These guidelines ensure consistency and accuracy in coding practices across healthcare settings. A good medical coder is well-versed in the coding guidelines established by organizations such as the American Medical Association (AMA) and the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). By following these guidelines, coders ensure that the codes assigned reflect the documented conditions and procedures accurately, promoting ethical coding practices.
Avoiding Fraudulent Practices
Maintaining ethical conduct also involves avoiding fraudulent practices in medical coding. Fraudulent coding can include intentionally misrepresenting services provided, upcoding to receive higher reimbursements, or unbundling services to increase billing amounts. A good medical coder is committed to honesty and integrity in their coding practices, ensuring that codes accurately represent the documented medical services and that coding is performed in accordance with the law and regulatory standards.
Continuing Education

Staying Updated with Coding Changes
Staying updated with coding changes is crucial for a medical coder to maintain proficiency in their role. The field of medical coding is constantly evolving, with updates and revisions to coding guidelines, new codes being introduced, and changes in reimbursement policies. A good medical coder takes the initiative to stay informed about these changes, whether through attending conferences, participating in webinars, or subscribing to coding publications. This commitment to continuing education ensures that coders are equipped with the most up-to-date knowledge and skills.
Participating in Professional Development
Participating in professional development activities is another way good medical coders enhance their skills and stay current in the field. This can include pursuing continuing education courses specifically tailored to medical coding, attending workshops or seminars, or joining professional organizations related to coding. These opportunities provide coders with opportunities to network with peers, learn from industry experts, and further their knowledge and expertise.
Pursuing Certification Programs
Obtaining professional certification demonstrates a commitment to excellence in medical coding. Certifications, such as the Certified Professional Coder (CPC) or Certified Coding Specialist (CCS), validate an individual’s knowledge and proficiency in medical coding. A good medical coder recognizes the value of these certifications and pursues them as a means of professional growth and advancement. Certification programs often require ongoing education and recertification, further emphasizing the importance of continuing education for medical coders.
Communication Skills

Effective Interpersonal Communication
Effective interpersonal communication is essential for medical coders to collaborate effectively with healthcare professionals. Coders often need to clarify documentation or seek additional information from physicians or nurses to ensure accurate coding. A good medical coder possesses strong communication skills, which include active listening, asking pertinent questions, and clearly conveying information to facilitate effective communication with the medical staff.
Clear Written and Verbal Skills
Clear written and verbal skills are equally important for effective communication in medical coding. Coders must be able to articulate their thoughts clearly when discussing coding-related matters with colleagues or healthcare providers. They also need to accurately document their coding decisions in written reports or patient records. A good medical coder is able to communicate in a concise and precise manner, ensuring that coding-related information is effectively conveyed and understood.
Collaboration with Medical Staff
Collaboration with medical staff is a key aspect of successful medical coding. Coders work closely with physicians, nurses, and other healthcare professionals to ensure accurate documentation and coding. A good medical coder actively collaborates with the medical staff by seeking clarification, providing feedback on documentation practices, and fostering a cooperative working relationship. This collaboration contributes to the accuracy and completeness of medical records, ultimately improving patient care and billing accuracy.
Organizational Skills

Ability to Prioritize Tasks
The ability to prioritize tasks is essential for medical coders, as they often face multiple assignments and deadlines. Coders must assess the urgency and importance of coding tasks and allocate their time and resources accordingly. This involves effectively managing their workload, understanding the impact of delayed coding, and ensuring that high-priority cases are addressed promptly. A good medical coder demonstrates strong organizational skills by effectively prioritizing tasks to meet deadlines and maintain productivity.
Managing Deadlines
Meeting deadlines is crucial in the fast-paced environment of medical coding. Healthcare providers rely on timely and accurate coding to facilitate billing and reimbursement processes. A good medical coder understands the importance of meeting deadlines and takes proactive measures to manage their time effectively. This may involve setting personal deadlines to ensure timely completion of coding assignments, effectively organizing their work schedule, and anticipating potential bottlenecks to avoid delays.
Keeping Records Organized
Organized record-keeping is vital for efficient medical coding. A good medical coder maintains a systematic approach to organizing and storing patient records, coding references, and other relevant documentation. This includes utilizing electronic health record systems effectively, maintaining a well-organized filing system, and ensuring that coding resources are easily accessible. By keeping records organized, the coder can quickly retrieve information when needed, minimize errors, and streamline the coding workflow.
Time Management

Efficient Workflow
Efficient workflow is key to maximizing productivity in medical coding. A good medical coder establishes effective workflow processes that allow for smooth and timely completion of coding tasks. This involves mapping out the coding process, identifying areas for improvement, and streamlining repetitive tasks. By optimizing their workflow, medical coders can minimize inefficiencies, reduce errors, and enhance productivity.
Meeting Productivity Targets
Medical coders often have productivity targets to meet, which require them to code a certain number of records within a given timeframe. Striving to meet these targets demonstrates a commitment to efficiency and high-quality work. A good medical coder understands their productivity goals and develops strategies to achieve them, such as implementing time-saving techniques, utilizing coding resources effectively, and maintaining focus and attention to detail while working.
Handling Multiple Assignments
The ability to handle multiple assignments simultaneously is a valuable skill for medical coders. Coders often work on several coding projects at once and must effectively manage their time and resources to meet deadlines. This requires the ability to prioritize tasks, effectively delegate when appropriate, and maintain focus and attention to detail across different assignments. A good medical coder demonstrates strong time management skills by effectively juggling multiple assignments without compromising the quality and accuracy of their coding.
Problem-Solving
This image is property of www.rasmussen.edu.
Identifying and Resolving Coding Errors
Identifying and resolving coding errors is an important problem-solving skill for medical coders. Errors in coding can have significant consequences, ranging from incorrect billing to improper patient care. A good medical coder possesses the ability to identify coding errors through careful review and analysis of medical records and coding guidelines. They then take the necessary steps to correct the errors, such as consulting with healthcare providers, seeking additional documentation, or appealing coding denials when appropriate.
Troubleshooting Billing Issues
Billing issues can arise in medical coding due to various factors, such as coding errors, incorrect documentation, or insurance-related discrepancies. A good medical coder has problem-solving skills that enable them to troubleshoot and resolve these billing issues effectively. This may involve investigating the root cause of the issue, coordinating with billing or finance departments, or engaging in constructive communication with insurance companies to rectify the problem and ensure accurate reimbursement.
Finding Solutions to Complex Cases
Complex cases often require advanced problem-solving skills from medical coders. These cases may involve rare or unusual conditions, extensive medical procedures, or conflicting information in the medical record. A good medical coder demonstrates resilience and critical thinking in such situations, researching coding guidelines, consulting coding experts, and collaborating with healthcare providers to find solutions. By approaching complex cases with a problem-solving mindset, coders can accurately assign codes that reflect the complexity and uniqueness of each case.
Professionalism

Maintaining a Positive Attitude
Maintaining a positive attitude is an important aspect of professionalism for medical coders. The field of medical coding can be challenging and demanding, but a good medical coder approaches their work with optimism and enthusiasm. They understand the value of maintaining a positive work environment, both for themselves and their colleagues. By exhibiting a positive attitude, medical coders can enhance productivity, foster teamwork, and promote a culture of professionalism in the workplace.
Ethical Decision-Making
Ethical decision-making is a key characteristic of a good medical coder. Coders often encounter situations that require ethical judgment, such as coding ambiguous documentation or handling confidential patient information. A good medical coder consistently makes ethical decisions by adhering to coding guidelines, maintaining patient confidentiality, and avoiding fraudulent practices. They prioritize accuracy, honesty, and integrity in their coding practices, ensuring that they uphold ethical standards in their daily work.
Teamwork and Collaboration
Teamwork and collaboration are essential for a harmonious and efficient work environment in medical coding. A good medical coder understands the importance of working collaboratively with colleagues, healthcare providers, and other members of the healthcare team. They actively contribute to team discussions, share knowledge and expertise, and support their colleagues when needed. By fostering teamwork and collaboration, medical coders contribute to a positive and productive work environment, ultimately benefiting patient care and the overall success of the organization.
In conclusion, being a good medical coder requires a combination of technical skills, attention to detail, analytical abilities, ethical conduct, continuing education, communication skills, organizational skills, time management, problem-solving, and professionalism. By possessing these skills and traits, medical coders can effectively contribute to the accuracy and integrity of medical coding, supporting optimal patient care and reimbursement processes within the healthcare industry.