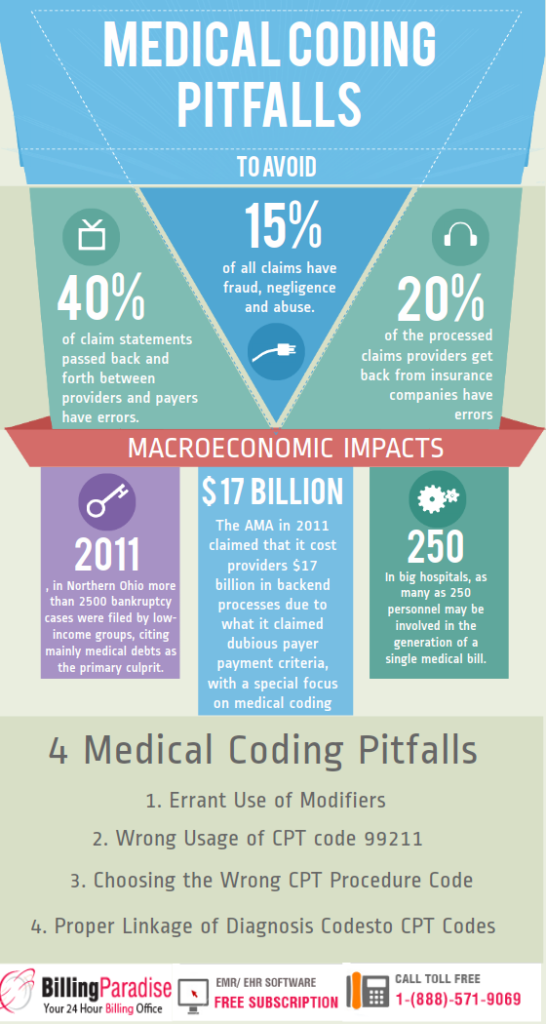
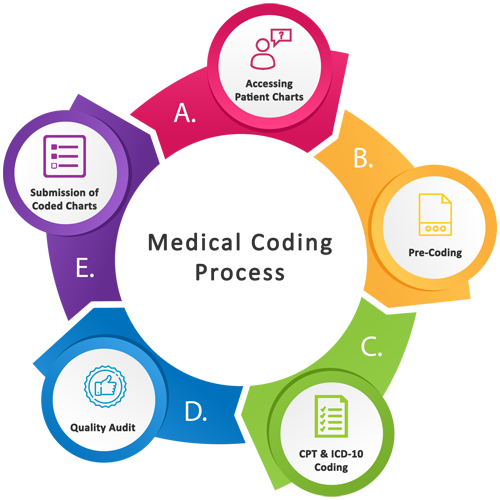
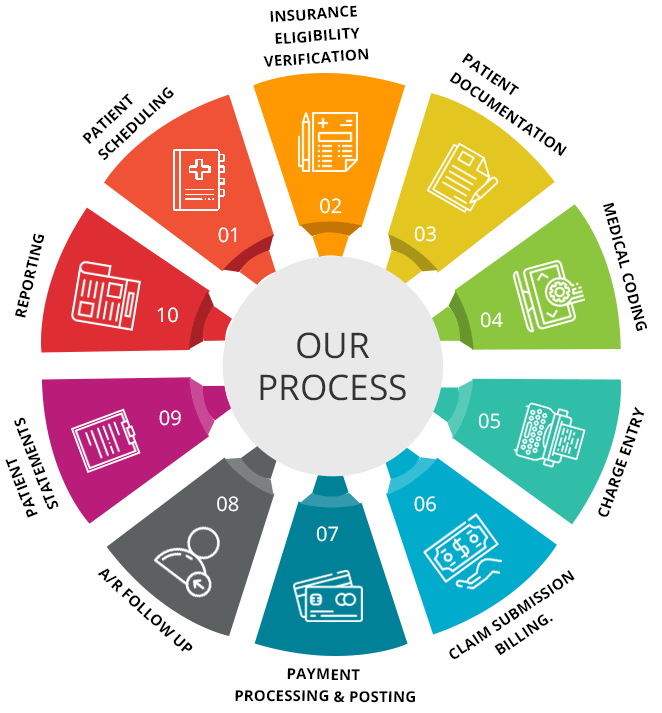
In the evolving field of healthcare, the question arises: Can a medical coder work for themselves? With the rising demand for medical coding professionals and the increasing number of healthcare practices, many coders are exploring the possibility of working independently. This article examines the factors that determine whether a medical coder can successfully establish their own business and navigate the intricacies of the industry. From exploring the necessary skills and qualifications to understanding the challenges and rewards, this article offers valuable insights for those considering this career path.
What is a medical coder?

Definition of a medical coder
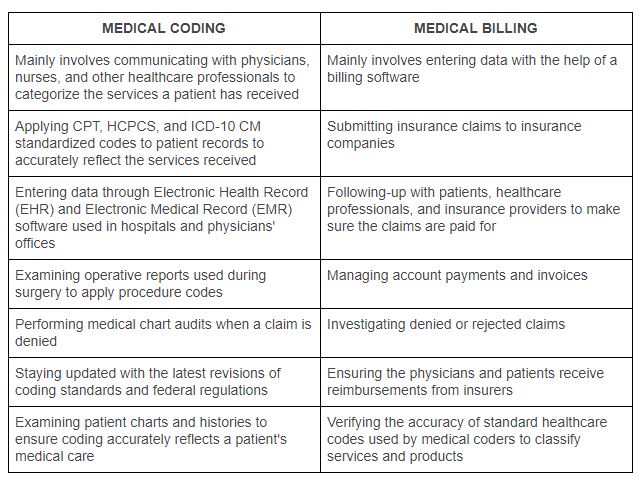
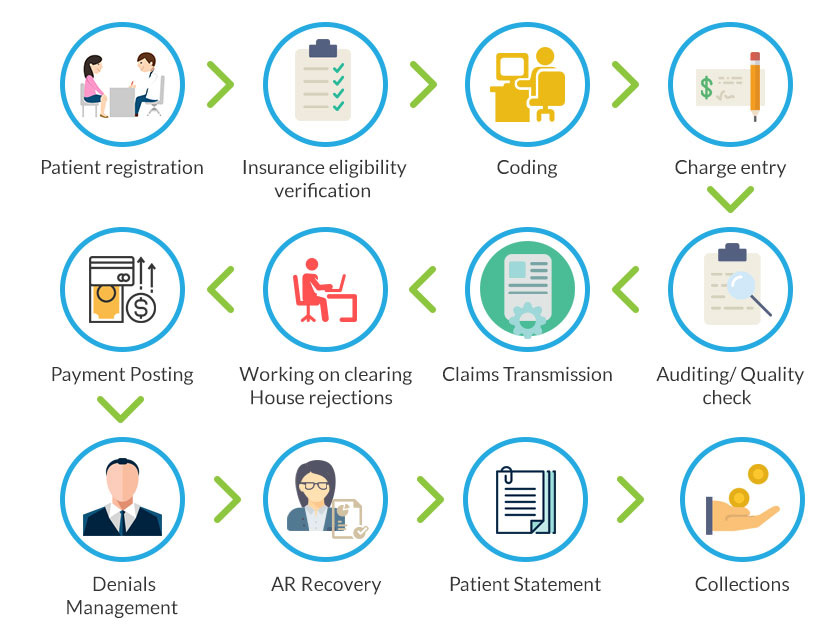
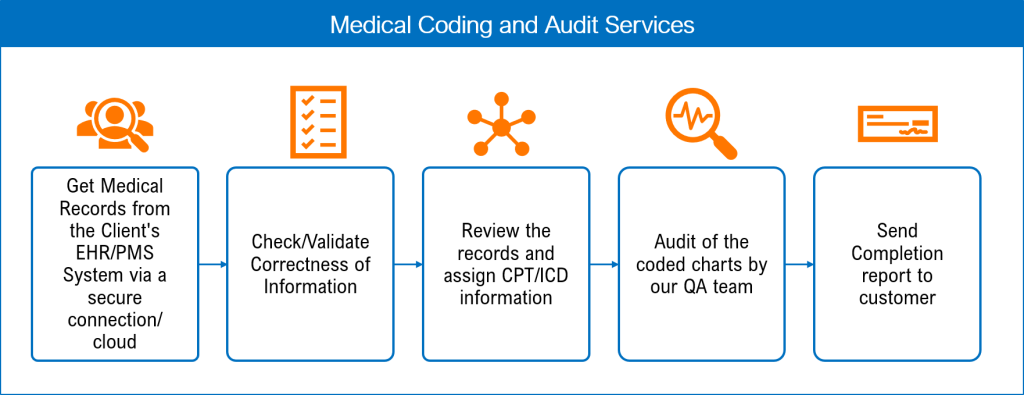
A medical coder is a healthcare professional responsible for translating medical diagnoses, procedures, and treatments into standardized codes. These codes are used for reimbursement purposes by insurance companies, government healthcare programs, and other healthcare providers. Medical coders play a crucial role in maintaining accurate and complete medical records, ensuring proper billing, and facilitating effective communication between healthcare providers and payers.
Role and responsibilities of a medical coder
The role of a medical coder is to analyze patient medical records, such as doctor’s notes, lab results, and surgical reports, and assign appropriate codes to each procedure, diagnosis, and treatment. This coding process requires a strong understanding of medical terminology, anatomy, and physiology, as well as knowledge of various coding systems, such as the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) and Current Procedural Terminology (CPT). Medical coders must adhere to industry coding guidelines and regulations to ensure accuracy and compliance.
Qualifications and certifications
Required education for a medical coder
While a specific degree is not always required to become a medical coder, most employers prefer candidates with formal education in medical coding or a related field. Many community colleges and vocational schools offer certificate programs and associate degrees in medical coding, which provide comprehensive training in coding principles, anatomy, and healthcare documentation. Some employers may also require a minimum level of education, such as a high school diploma or equivalent, along with relevant work experience.
Certifications for medical coding
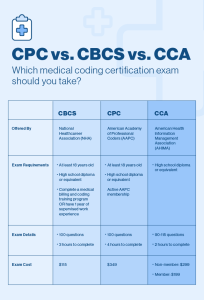
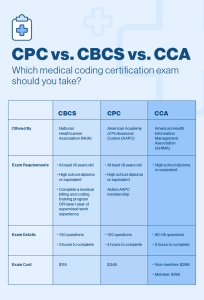
Certifications in medical coding are voluntary but highly recommended for medical coders. The two most widely recognized certifications for medical coding are the Certified Professional Coder (CPC) credential, offered by the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC), and the Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) credential, offered by the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA). These certifications demonstrate proficiency in medical coding and enhance job prospects, earning potential, and professional credibility.
Importance of qualifications and certifications
Obtaining the necessary education and certifications is essential for medical coders. Employers often prefer candidates with formal training and certifications, as they demonstrate a commitment to professional development and a high level of competence in medical coding. In addition, qualifications and certifications can help medical coders stay up to date with the latest coding guidelines and regulations, which are constantly evolving in the healthcare industry. These credentials also provide a competitive edge when seeking employment or pursuing self-employment opportunities.
Employment options for medical coders

Working for a healthcare facility
Many medical coders work directly for healthcare facilities, such as hospitals, clinics, and physician practices. These coders are typically employed on a full-time or part-time basis and work collaboratively with other healthcare professionals, such as physicians, nurses, and administrative staff. Working within a healthcare facility offers stability, a structured work environment, and opportunities for professional growth and advancement. Medical coders in this setting may have access to additional benefits, such as health insurance and retirement plans.
Working as a freelancer or independent contractor
Medical coders also have the option to work as freelancers or independent contractors. This allows for more flexibility and autonomy in terms of choosing clients, setting rates, and managing workloads. Freelance medical coders can work from home or any location of their choice, using their own equipment and software. They are responsible for acquiring and maintaining clients, handling billing and collections, and managing their own business operations. Working as a freelancer requires self-discipline, self-motivation, and strong business and marketing skills.
Working for a medical coding company
Another employment option for medical coders is to work for a medical coding company or consulting firm. These organizations specialize in providing coding services to healthcare facilities, helping them navigate the complex coding and billing processes. Medical coders working for coding companies may have a hybrid role, where they have the flexibility of working remotely but are still employed by the company. This arrangement offers the benefits of working from home while providing the support and structure of an established organization.
Advantages of working for themselves

Flexibility in schedule
One of the main advantages of working for themselves as a medical coder is the flexibility in schedule. Freelance coders can choose when and where they work, allowing for a better work-life balance. They have the freedom to set their own hours, take breaks as needed, and accommodate personal commitments or responsibilities. This flexibility is particularly appealing to individuals who prefer non-traditional work hours or have other obligations, such as caregiving or pursuing further education.
Work-life balance
Working for themselves as a medical coder also enables individuals to achieve a better work-life balance. By having control over their schedule, freelancers can allocate time for personal activities, hobbies, and family responsibilities. They can more easily manage their work commitments around personal priorities, reducing stress and enhancing overall well-being. This can lead to increased job satisfaction and improved mental and physical health.
Ability to choose clients and projects
Another significant advantage of working for themselves is the ability to choose clients and projects. Freelance medical coders have the freedom to determine which clients they want to work with, based on their interests, expertise, and ethical considerations. This allows for professional growth and the opportunity to work on a variety of interesting and challenging coding assignments. Freelancers can also select projects that align with their desired workload, ensuring a manageable and sustainable caseload.
Higher earning potential
Working for themselves as a medical coder can also offer higher earning potential compared to traditional employment. Freelance coders have the opportunity to set their own rates and negotiate project fees based on their skills, experience, and market demand. They can benefit from direct client relationships and avoid sharing their earnings with an employer. Additionally, as they gain experience and develop a strong reputation, they may attract higher-paying clients and more lucrative projects, leading to increased income over time.
Challenges of working for themselves

Finding and securing clients
One of the main challenges of working for themselves as a medical coder is finding and securing clients. Freelancers need to actively market their services and build a client base to sustain their business. This requires networking, creating professional relationships, and developing a strong online presence. Building a reputation and attracting clients can be time-consuming and may involve a period of financial uncertainty, especially for those starting their self-employment journey.
Managing finances and billing
Another challenge faced by self-employed medical coders is managing finances and billing. Freelance coders are responsible for their own bookkeeping, invoicing, and tax filings. They must keep track of income and expenses, ensure timely payments from clients, and comply with tax regulations. This requires financial organization and knowledge of business accounting practices. Seeking professional assistance from an accountant or bookkeeper may be necessary to ensure accurate financial management.
Marketing and self-promotion
Working for themselves requires medical coders to actively market their services and engage in self-promotion. This involves creating a professional website, utilizing social media platforms, and networking with potential clients and industry professionals. Effective marketing and self-promotion strategies are crucial to attracting clients, building credibility, and establishing a strong professional presence. Developing marketing skills and adopting a proactive approach to promoting services are essential for self-employed medical coders.
Dealing with administrative tasks
As self-employed medical coders, individuals must handle various administrative tasks that may not be directly related to coding. This includes client communication, project coordination, record keeping, and maintaining business documentation. These administrative responsibilities can be time-consuming and may divert focus from coding-related activities. Developing efficient systems and utilizing technology tools can help streamline administrative tasks, allowing medical coders to allocate more time and energy to their coding work.
Setting up as a self-employed medical coder

Obtaining necessary licenses and permits
Before starting a self-employed medical coding business, it is important to understand and comply with all relevant licensing and permit requirements. Different jurisdictions may have specific regulations and guidelines for operating a medical coding business. Researching and obtaining the necessary licenses and permits ensures legal compliance and protects the self-employed medical coder’s business and reputation.
Setting up a home office
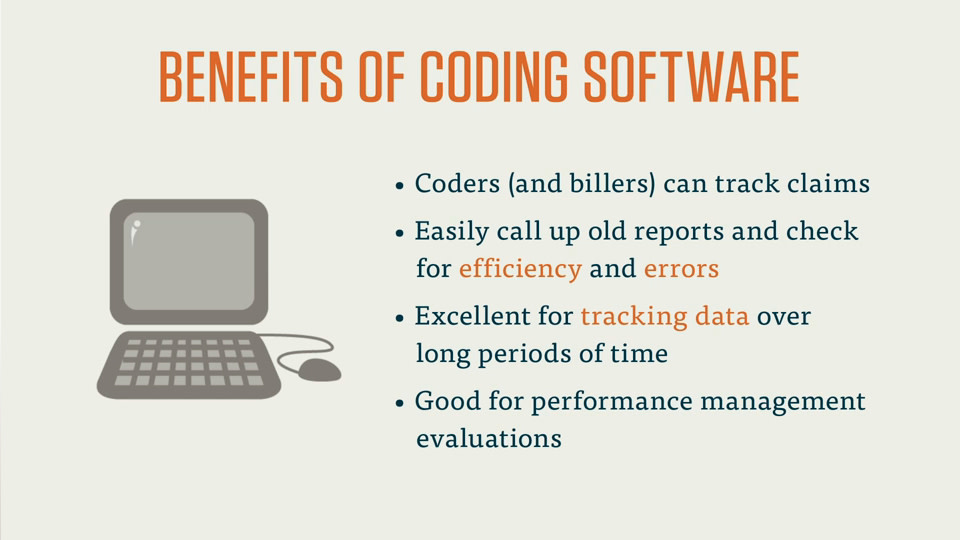
Creating a suitable workspace is an essential aspect of setting up as a self-employed medical coder. This typically involves setting up a home office with the necessary equipment, such as a computer, reliable internet connection, and appropriate coding software. The home office should be comfortable, well-organized, and free from distractions to facilitate concentration and productivity.
Establishing professional relationships
Building professional relationships is crucial for self-employed medical coders. This includes establishing connections with potential clients, industry professionals, and fellow coders. Networking can be done through attending industry conferences and events, joining professional organizations, and engaging in online communities. Maintaining professional relationships can lead to referrals, collaboration opportunities, and access to industry updates and resources.
Creating a business plan
A well-defined business plan is essential for self-employed medical coders. It outlines the goals, strategies, and financial projections for the business. A comprehensive business plan addresses aspects such as target market, marketing strategies, pricing structure, financial projections, and contingency plans. It serves as a guide to ensure the business operates efficiently and effectively.
Marketing and networking

Creating a professional website
A professional website is an important marketing tool for self-employed medical coders. It serves as an online portfolio, showcasing qualifications, certifications, and previous work experience. The website should have clear and concise information about the coder’s services, rates, and contact details. Including testimonials or client reviews can help build credibility and attract potential clients.
Utilizing social media for promotion
Social media platforms offer valuable opportunities for self-employed medical coders to promote their services and engage with clients. Creating professional profiles on platforms such as LinkedIn, Facebook, and Twitter allows coders to share industry updates, demonstrate expertise, and connect with potential clients. Engaging regularly with relevant healthcare communities and utilizing targeted advertising can further enhance visibility and reach a wider audience.
Attending industry conferences and events
Attending industry conferences and events provides self-employed medical coders with valuable networking opportunities. These events often bring together coding professionals, industry leaders, and potential clients. Participating in workshops, panel discussions, and educational sessions can expand knowledge, make connections, and stay updated with industry trends. Active involvement in industry events can help build a strong professional network and increase visibility within the medical coding community.
Joining professional organizations
Membership in professional organizations, such as the AAPC or AHIMA, provides self-employed medical coders with numerous benefits. These organizations offer access to resources, educational opportunities, and networking platforms specifically tailored to medical coders. Being part of a professional organization demonstrates a commitment to continuous learning and professional development, enhancing credibility and providing opportunities for growth and advancement.
Maintaining professional development

Continuing education and training
Continuing education and training are vital for self-employed medical coders to stay updated with coding guidelines and best practices. Various online courses, webinars, and workshops are available to enhance coding skills and expand knowledge in specialty areas. Engaging in continuing education not only ensures coding accuracy and compliance but also allows coders to adapt to changing regulations and industry advancements.
Staying updated with coding guidelines and regulations
As coding guidelines and regulations often change, self-employed medical coders need to stay informed and updated. Following industry news, subscribing to coding newsletters, and participating in coding forums can provide valuable insights into the latest coding updates and changes. Regular review of coding manuals, such as the ICD and CPT guidelines, is essential for accurate and up-to-date coding practices.
Participating in coding workshops and seminars
Participating in coding workshops and seminars offers self-employed medical coders the opportunity to deepen their coding knowledge, gain new skills, and stay current with industry trends. These events often feature expert speakers, case studies, and interactive sessions that facilitate learning and professional growth. Attending coding workshops and seminars also allows for networking with industry professionals and exchanging experiences and insights.
Networking with other medical coders
Networking with fellow medical coders is valuable for self-employed coders as it provides opportunities for collaboration, knowledge sharing, and professional support. Joining online forums, social media groups, or local coding associations can create connections and foster a community of like-minded professionals. Collaborating and networking with other coders can lead to joint projects, referrals, and ongoing professional relationships.
Managing clients and projects

Establishing clear communication channels
Effective communication is essential when working with clients as a self-employed medical coder. Establishing clear communication channels, such as email, phone, or project management tools, ensures that both parties have a shared understanding of project requirements, timelines, and expectations. Responding promptly to client inquiries, providing regular progress updates, and establishing mutual trust and transparency contribute to successful client relationships.
Setting project timelines and deadlines
Setting realistic project timelines and meeting deadlines are crucial for self-employed medical coders. Clear project timelines allow for effective planning and resource allocation, ensuring that projects are completed in a timely manner. Adhering to agreed-upon deadlines demonstrates professionalism and reliability, helping to build a positive reputation and maintain client satisfaction.
Handling client expectations
Managing client expectations is an important aspect of working with clients as a self-employed medical coder. This involves clearly defining project scope, deliverables, and limitations upfront. It is important to set realistic expectations regarding turnaround times, availability for client communication, and project outcomes. By managing expectations effectively, self-employed medical coders can avoid misunderstandings, maintain client satisfaction, and build long-term relationships.
Providing quality coding services
Delivering high-quality coding services is essential for self-employed medical coders to maintain a positive reputation and attract repeat business. This requires accurate and thorough coding, adherence to industry guidelines, and attention to detail. Continuous self-assessment, quality assurance processes, and professional ethics contribute to providing coding services that meet or exceed client expectations.
Conclusion

Summary of advantages and challenges
Working for themselves as a medical coder offers numerous advantages, including flexibility in schedule, work-life balance, the ability to choose clients and projects, and higher earning potential. However, there are also challenges to overcome, such as finding clients, managing finances and billing, marketing and self-promotion, and handling administrative tasks.
Importance of proper planning and preparation
To successfully work for themselves as a medical coder, individuals need to engage in proper planning and preparation. This includes obtaining necessary education and certifications, setting up a home office, establishing professional relationships, and creating a business plan. By investing time and effort in these areas, self-employed medical coders can position themselves for success.
Success stories of self-employed medical coders
Numerous success stories exist of self-employed medical coders who have thrived in their entrepreneurial journey. These individuals have built thriving businesses, earned a reputation for excellence, and achieved financial stability. Their stories serve as inspiration and motivation for aspiring self-employed medical coders.
Final thoughts on working for themselves
Working for themselves as a medical coder offers the opportunity for professional growth, autonomy, and a fulfilling career. It requires dedication, self-discipline, and ongoing commitment to professional development. With the right qualifications, certifications, and business acumen, self-employed medical coders can enjoy the advantages of flexible work arrangements and reap the rewards of their expertise and hard work.