Medical billing and coding are integral components of the healthcare industry, ensuring efficient and accurate financial transactions between healthcare providers and insurance companies. This process involves translating medical procedures, diagnoses, and treatments into alphanumeric codes, which are then used to create invoices and claim forms. Additionally, medical billers and coders verify patient insurance coverage, submit claims to insurance companies, and follow up on any outstanding payments. The complex and vital nature of this role requires individuals with strong attention to detail, knowledge of medical terminology, and familiarity with insurance guidelines and regulations.
Medical Billing
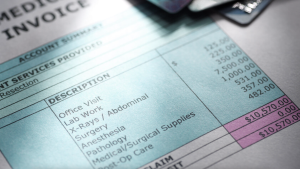
Medical billing is the process of submitting and following up on claims with health insurance companies in order to receive payment for services rendered by a healthcare provider. It involves translating medical procedures and diagnoses into a standardized code format, preparing invoices, and managing accounts receivable.
Importance
Accurate and efficient medical billing is crucial for healthcare facilities and providers to receive timely reimbursement for their services. It ensures financial stability by maximizing revenue and minimizing payment delays. Additionally, proper medical billing enhances overall patient satisfaction by reducing billing errors and ensuring transparency in healthcare costs.
Process
The medical billing process begins with gathering patient information and verifying insurance coverage. The healthcare provider then assigns appropriate codes to the services provided, including diagnosis codes, procedure codes, and modifiers, which accurately reflect the medical treatment received. These codes are then entered into the billing software system, along with patient demographics and billing details. The claim is then submitted electronically to the insurance company for review and payment.
Coding Systems
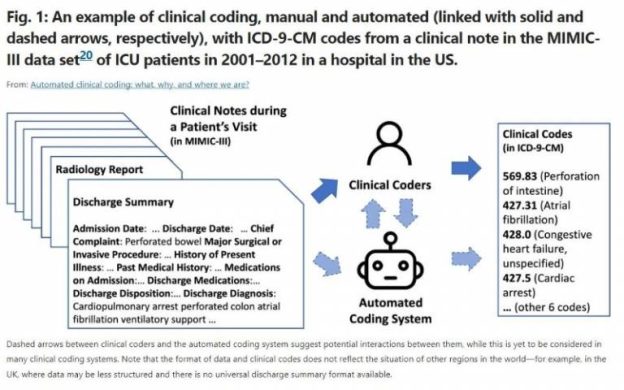
Medical billing relies on various coding systems, including the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) and Current Procedural Terminology (CPT). The ICD system provides codes for diagnosing health conditions, while the CPT system assigns codes to medical procedures and services. These coding systems ensure uniformity and accuracy in healthcare documentation, billing, and reimbursement processes.
Types of Medical Bills
There are different types of medical bills that can be generated depending on the healthcare setting and services provided. These may include hospital bills, physician bills, laboratory bills, radiology bills, and pharmacy bills. Each type of bill requires specific coding and billing processes tailored to the services rendered in that particular department.
Key Skills
Professionals involved in medical billing must possess a range of key skills to perform their roles effectively. These include knowledge of medical terminology, coding systems, and billing guidelines. Attention to detail, analytical thinking, and problem-solving skills are also essential to ensure accurate and timely claims submission. Additionally, proficiency in using billing software and understanding insurance processes is crucial for successful medical billing operations.
Medical Coding
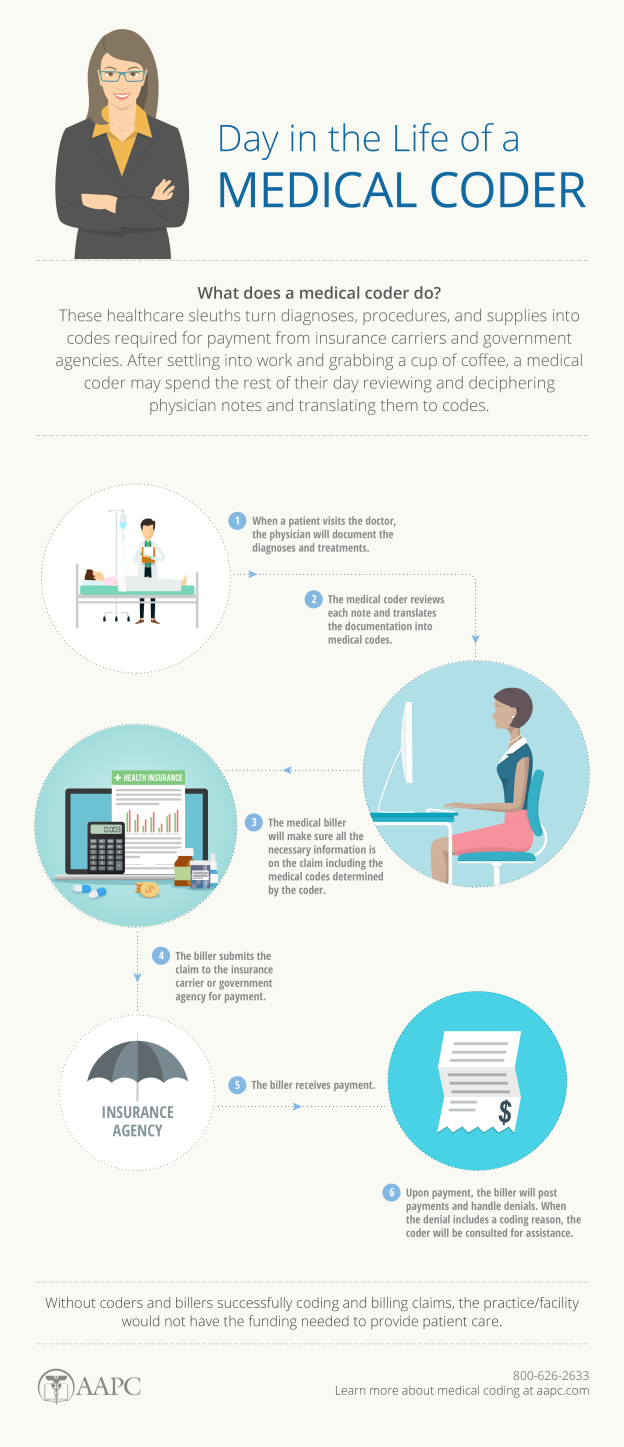
Medical coding is the process of translating medical procedures, diagnoses, and treatments into alphanumeric codes. These codes are used for various purposes, including medical billing, insurance claims processing, and healthcare data analysis. Accurate medical coding ensures that each patient’s medical history is documented properly and can be accessed when needed.
Importance
Medical coding is integral to healthcare operations as it enables consistent documentation, analysis, and reimbursement. It facilitates the exchange of medical information among healthcare providers, insurance companies, and regulatory organizations. Proper coding ensures that healthcare services are appropriately categorized and billed for, leading to accurate reimbursement and improved quality of care.
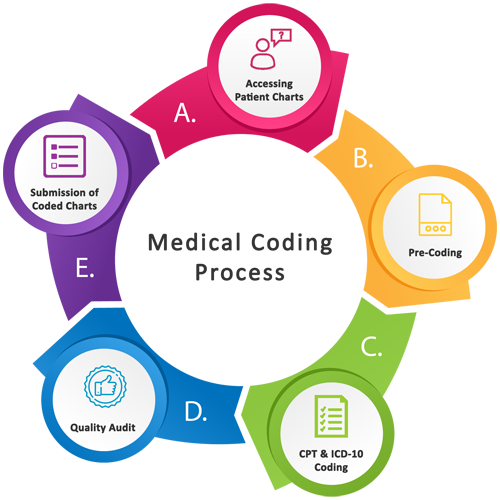
Process
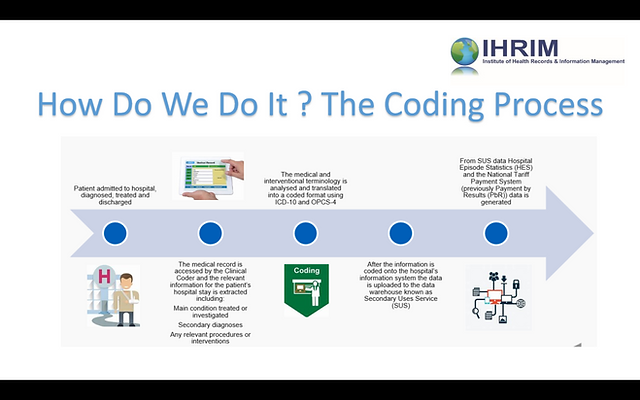
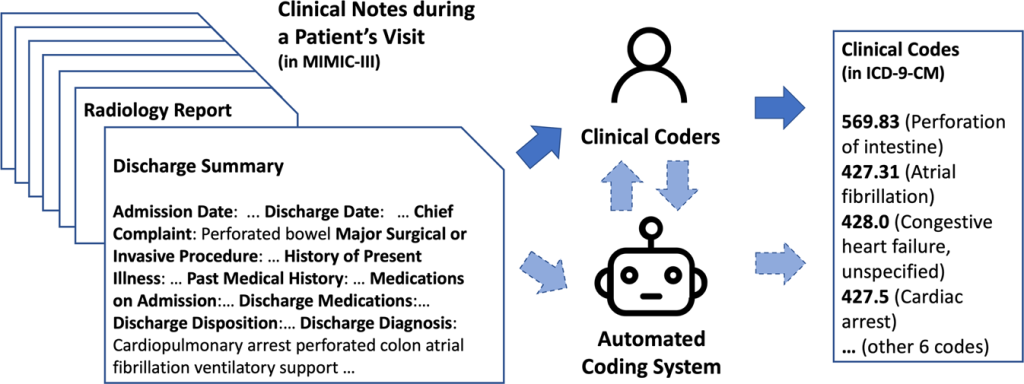
The medical coding process starts by reviewing medical records, such as physician notes, laboratory results, and radiology reports. The coder then assigns diagnostic codes based on the provided documentation and translates the services rendered into appropriate procedural codes. These codes are utilized to generate bills, submit insurance claims, and maintain comprehensive patient records.
Types of Medical Codes
There are several types of medical codes used in the coding process. Diagnosis codes, primarily based on the ICD system, identify the patient’s medical condition. Procedure codes, such as CPT codes, describe the specific services provided during a medical encounter. Additionally, there are codes for pharmaceuticals, durable medical equipment, and other healthcare products.
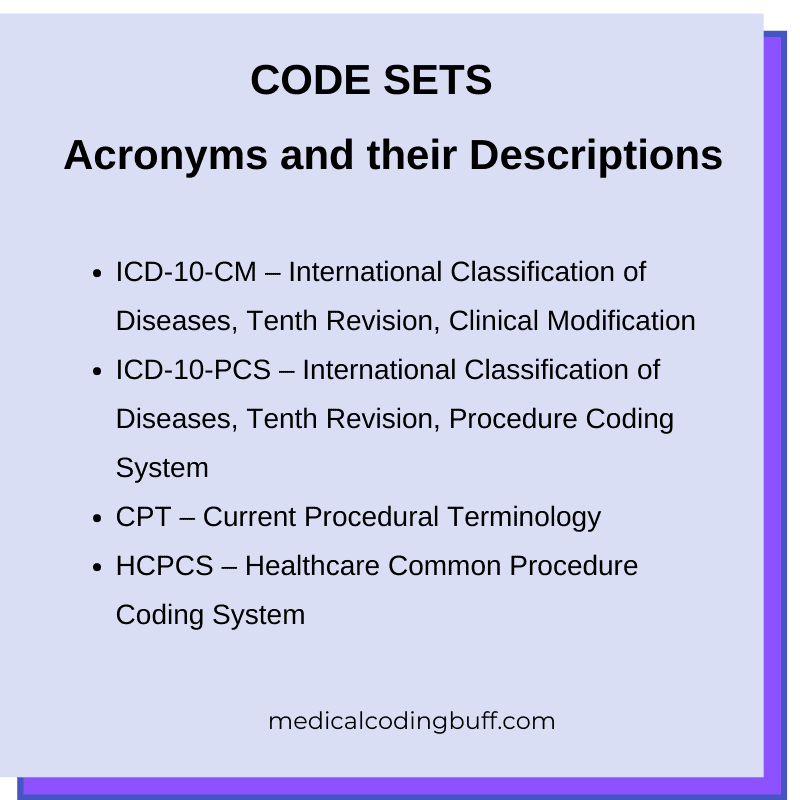
Code Sets
Code sets are comprehensive collections of codes that are used to represent medical information in a standardized manner. Common code sets used in medical coding include ICD-10-CM (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification) for diagnoses, ICD-10-PCS (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Procedure Coding System) for inpatient procedures, and HCPCS (Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System) for outpatient services and supplies.
Diagnostic Coding Systems
Diagnostic coding systems, such as the ICD-10-CM, provide a standardized method of classifying diseases, injuries, and health conditions. These codes aid in accurate communication, research, and data analysis, ensuring the consistency and comparability of health information. Diagnostic codes establish a common language between healthcare providers, payers, and researchers.
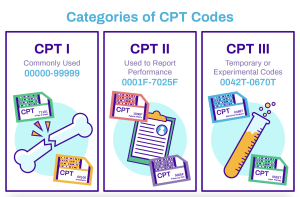
Procedural Coding Systems
Procedural coding systems, such as the CPT system, describe the specific services and treatments provided during a medical encounter. Procedural codes enable accurate billing, reimbursement, and statistical reporting. They provide a standardized format for documenting the procedures performed, ensuring clarity and consistency in healthcare documentation.
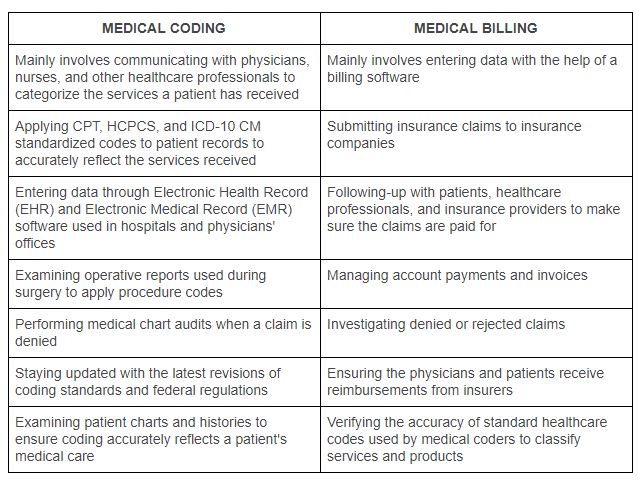
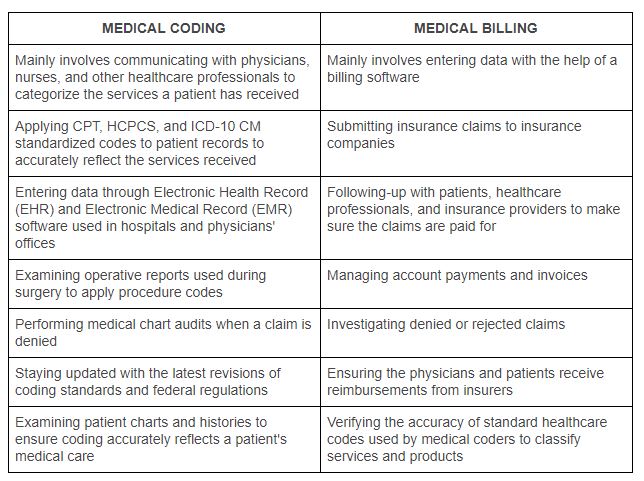
Similarities Between Medical Billing and Coding

Collaboration
Both medical billing and coding require collaboration between healthcare providers, billing specialists, and coders. Effective communication is essential to ensure accurate coding and billing, as coders rely on medical documentation from healthcare providers to assign appropriate codes. Collaborative efforts between these two roles are essential for successful claims processing and timely reimbursement.
Accuracy
Accurate medical coding and billing are paramount to avoid claim denials and ensure proper reimbursement. Both processes require attention to detail and adherence to coding guidelines and regulations. Coders must accurately translate medical information into codes, while billing specialists ensure that claims are submitted with correct patient and billing details. Both disciplines play a crucial role in maintaining the accuracy of healthcare documentation and claims.
Confidentiality
Both medical billing and coding involve handling sensitive patient data, such as medical records and insurance information. Professionals in both fields must adhere to strict confidentiality and privacy regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Maintaining patient confidentiality is essential to protect patient rights and ensure the security of medical information.
Differences Between Medical Billing and Coding

Role and Responsibility
Medical billers are responsible for preparing and submitting insurance claims, verifying insurance coverage, and managing accounts receivable. They work closely with insurance companies and patients to resolve billing issues and ensure timely reimbursement. On the other hand, medical coders assign diagnostic and procedural codes to the services provided by healthcare providers. They analyze medical documentation and apply coding guidelines to accurately represent patient diagnoses and treatments.
Skills and Training
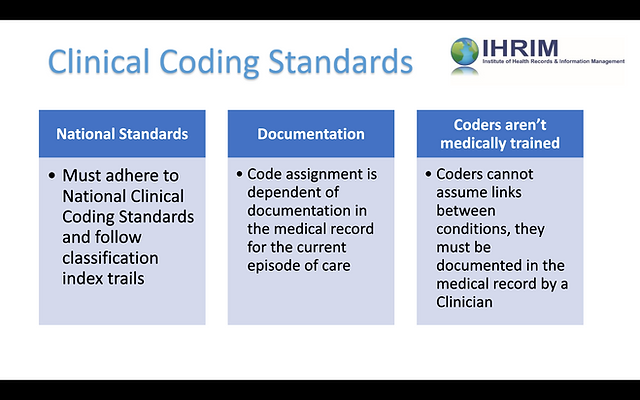
Medical billing and coding require different skill sets and training. Billing specialists need excellent organizational skills, knowledge of insurance guidelines, and proficiency in billing software. They must also possess strong communication and problem-solving abilities to effectively navigate insurance claim processes. Medical coders, on the other hand, require in-depth knowledge of coding systems, anatomy, and medical terminology. They undergo specialized training and certification programs to develop proficiency in coding guidelines and conventions.
Software Usage
While medical billers heavily rely on billing software for claims submission and accounts management, medical coders primarily utilize coding software to assign codes accurately. Billing software automates the claim submission process, streamlines accounts receivable management, and provides analytics for revenue cycle management. Coding software assists coders in maintaining coding accuracy, providing code suggestions, and organizing coding data.
Challenges in Medical Billing and Coding

Coding Errors
One of the significant challenges in medical billing and coding is the potential for coding errors. Mistakes in code assignment can lead to claim denials, payment delays, and legal repercussions. Coders must be vigilant in understanding coding guidelines and accurately translating medical documentation into codes to minimize the risk of coding errors.
Denied Claims
Denied claims are a major hurdle in medical billing and coding. Insurance companies may deny claims for various reasons, such as incorrect coding, lack of medical necessity, or missing information. Medical billers need to proactively resolve claim denials by making necessary corrections, providing additional documentation, or appealing the decision. Timely resolution of denied claims is crucial to maintain steady cash flow for healthcare organizations.
Insurance Complexity
Navigating the complexities of insurance policies and reimbursement processes can pose challenges in medical billing and coding. Each insurance company may have different coverage rules, reimbursement rates, and prior authorization requirements. Billers must stay updated with insurance guidelines and policies to ensure accurate billing and successful claims processing. The complexity of insurance systems can create delays and confusion in the billing and coding workflow.
Future Trends in Medical Billing and Coding

Automation
Advancements in technology are driving automation in medical billing and coding. Automated billing software and artificial intelligence (AI) solutions are streamlining the claims submission process, reducing manual errors, and enhancing efficiency. Automation also improves data accuracy, enabling faster reimbursement and reducing administrative burden on healthcare providers.
Telehealth Integration
The increasing popularity of telehealth services has necessitated updates in medical billing and coding practices. Telehealth encounters require proper documentation and accurate coding to ensure appropriate reimbursement. Integration of telehealth-specific coding guidelines and billing processes into existing systems is crucial for efficient reimbursement and successful implementation of remote healthcare services.
Data Analytics
Data analytics is playing an increasingly significant role in medical billing and coding. Analyzing claims data and coding patterns provides valuable insights for improving billing accuracy, identifying areas of improvement, and optimizing revenue cycle management. Predictive analytics and advanced reporting tools help healthcare organizations make informed decisions to enhance financial performance and streamline billing and coding operations.
Benefits of Medical Billing and Coding
Financial Stability
Effective medical billing and coding practices contribute to the financial stability of healthcare organizations. Accurate and timely billing ensures that healthcare providers receive appropriate reimbursement for services rendered. By minimizing claim denials and optimizing revenue cycle management, medical billing and coding practices enhance the overall financial health of healthcare facilities.
Improved Patient Care
Proper medical billing and coding directly impact patient care. Accurate coding and billing processes lead to transparent communication between healthcare providers, insurance companies, and patients. Timely reimbursement ensures that healthcare providers can invest in advanced treatments, equipment, and resources, ultimately improving the quality of patient care and outcomes.
Career Opportunities
The field of medical billing and coding offers numerous career opportunities. Qualified professionals can work in various healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, private practices, and insurance companies. With the growing demand for skilled billers and coders, individuals in this field can pursue diverse career paths, such as medical coding auditing, practice management, and revenue cycle consulting.
Career Path in Medical Billing and Coding

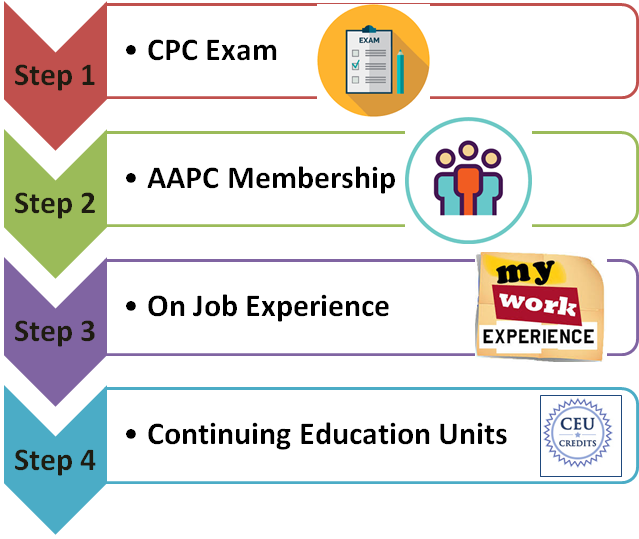
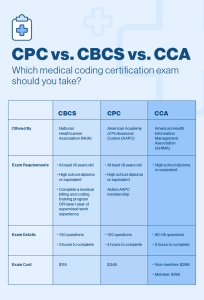
Education and Certification
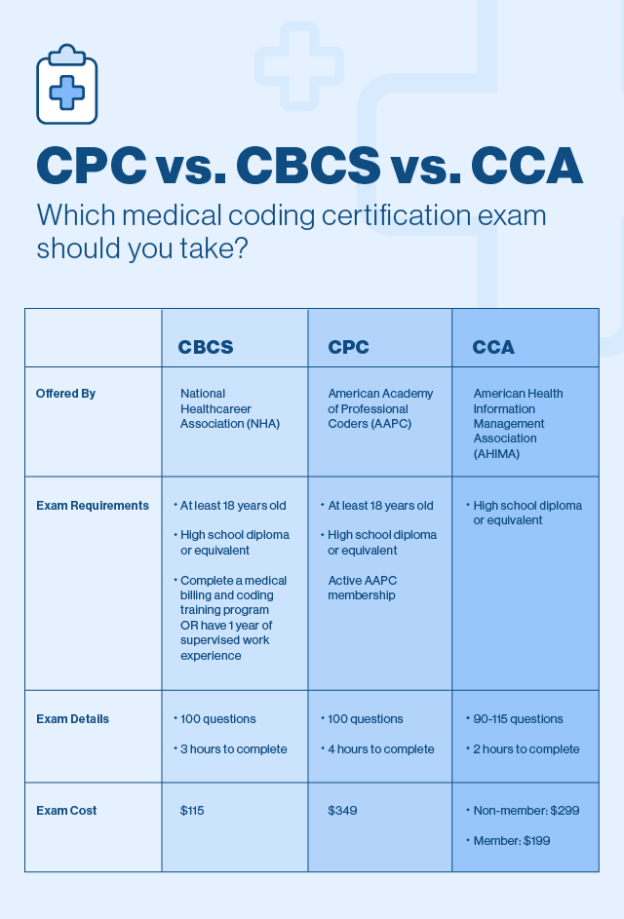
Entry into the field of medical billing and coding typically requires completion of a training program or associate degree in medical coding or health information management. Professional certifications, such as Certified Professional Coder (CPC) or Certified Professional Biller (CPB), are highly regarded and may enhance job prospects. Continuing education and staying updated with coding guidelines and industry trends are essential for career advancement in this field.
Job Opportunities
Qualified medical billers and coders can find employment opportunities in various healthcare settings. These include hospitals, physician practices, nursing homes, insurance companies, and third-party billing companies. With the increasing demand for skilled professionals, job prospects in this field are expected to remain favorable.
Salary Potential
The salary potential in medical billing and coding can vary based on factors such as education, experience, and location. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for medical records and health information technicians, which includes medical billers and coders, was $44,090 as of May 2020. However, professionals with advanced certifications and specialized skills may earn higher salaries.
Technological Advancements in Medical Billing and Coding
Electronic Health Records
The adoption of electronic health records (EHRs) has revolutionized medical billing and coding practices. EHR systems provide a centralized digital platform for efficient documentation, coding, and claims processing. Integration of EHRs with billing software automates coding processes, reduces error rates, and enhances the overall efficiency and accuracy of medical billing and coding operations.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming medical billing and coding by automating time-consuming tasks and improving accuracy. AI algorithms can assist coders in identifying appropriate codes based on medical documentation, reducing the risk of coding errors. AI-powered billing software can analyze claim data and automatically detect potential issues, enhancing claims accuracy and reducing claim denials.
Mobile Applications
Mobile applications are emerging as a convenient tool for medical billing and coding processes. These applications enable access to coding resources, insurance guidelines, and coding updates on mobile devices. Coders and billers can easily refer to coding manuals, search for coding information, and stay updated with industry trends, even while on the go, enhancing productivity and efficiency.
Conclusion
Medical billing and coding are integral components of the healthcare system, ensuring accurate documentation, efficient claims processing, and optimal reimbursement. These professions require specialized knowledge, attention to detail, and collaboration between healthcare providers, billing specialists, and coders. Despite their distinct roles and responsibilities, medical billing and coding share common goals of accuracy, collaboration, and maintaining patient confidentiality. Technological advancements, such as automation and AI, are transforming these fields, streamlining operations, and improving overall efficiency. With the increasing demand for skilled professionals, medical billing and coding offer promising career paths with opportunities for financial stability, improved patient care, and career growth.