In today’s fast-paced and highly advanced technological era, the question of whether medical billing can be automated has become a subject of great interest and discussion. The potential benefits of streamlining the medical billing process through automation are immense, promising increased accuracy, efficiency, and cost savings for healthcare providers. This article explores the possibilities and challenges associated with automating medical billing, shedding light on the potential impact it can have on the healthcare industry as a whole.
Overview
What is medical billing?
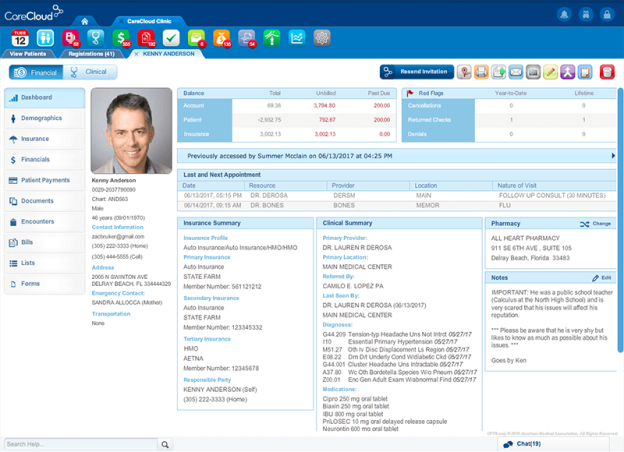
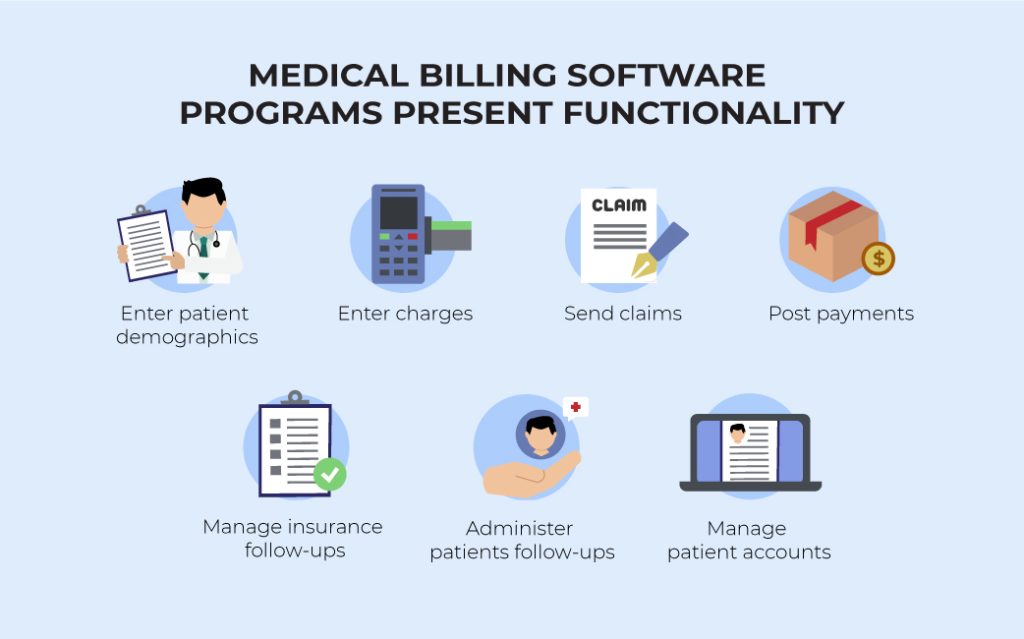
Medical billing refers to the process of submitting and following up on claims with health insurance companies in order to receive payment for the services provided by healthcare providers. It involves translating medical procedures, diagnoses, and treatments into standardized codes, preparing claims, and submitting them to insurance companies for reimbursement. Medical billing is a critical aspect of healthcare revenue management and plays a crucial role in the financial stability of healthcare organizations.
The complexity of medical billing
Medical billing is a complex and intricate process that requires a deep understanding of medical procedures, coding systems, insurance policies, and regulatory standards. It involves navigating through a labyrinth of rules and regulations set by both government agencies and private insurance companies. The complexity arises from various factors, including the evolving nature of medical treatments, specialized coding systems, varying insurance policies, and the need for meticulous attention to detail.
Importance of accurate medical billing
Accurate medical billing is of utmost importance for several reasons. Firstly, it ensures that healthcare providers receive timely payments for the services they provide. This is crucial for the financial viability of healthcare organizations, as it directly impacts their ability to provide quality care to patients. Secondly, accurate billing minimizes errors in insurance claims, reducing the likelihood of claim denials and delays in reimbursement. Finally, accurate medical billing helps in maintaining the integrity of healthcare data and ensures compliance with regulatory standards.
Advantages of Automated Medical Billing
Efficiency and time-saving
Automated medical billing systems streamline the billing process, saving significant time and effort for healthcare providers and their administrative staff. These systems automate repetitive tasks such as data entry, claim submission, and payment processing, allowing staff to focus on other essential tasks. Additionally, automated systems can handle a large volume of claims more efficiently, reducing the time required for processing and increasing overall workflow efficiency.
Reduced errors and improved accuracy
Manual medical billing processes are prone to human errors, resulting in costly mistakes and claim denials. Automated medical billing systems minimize errors by eliminating manual data entry and relying on standardized coding and billing rules. By reducing errors and improving accuracy, healthcare providers can enhance their revenue collection and decrease the need for time-consuming claim resubmissions and appeals.
Streamlined claims processing
Automated medical billing systems streamline the claims processing workflow by automating various steps, from data capture to claim submission. These systems can automatically verify patient insurance eligibility, generate accurate and complete claims, and electronically submit them to insurance companies. This eliminates the need for paper-based processes and reduces the time and effort required for claims processing. Additionally, automated systems can track the progress of claims, flagging any potential issues or delays for quick resolution.
Improved revenue cycle management
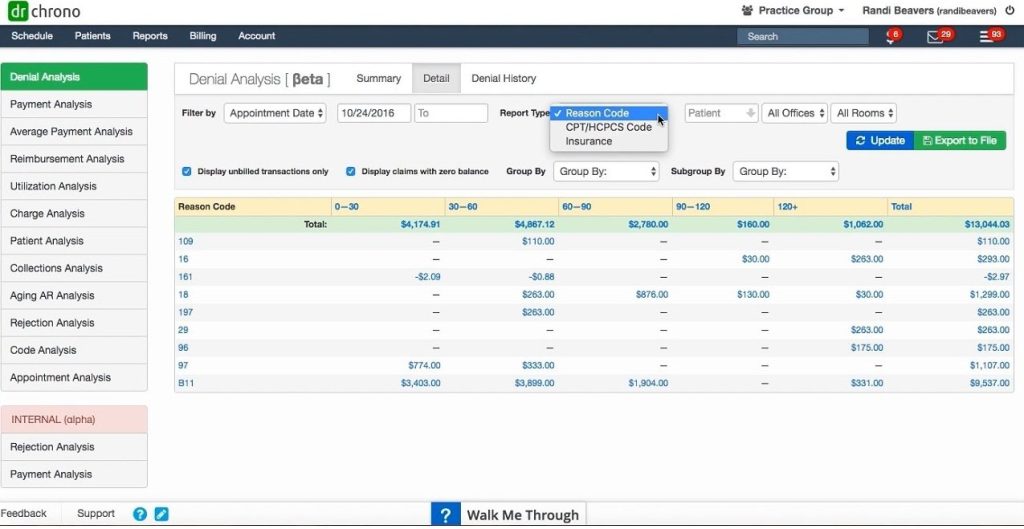
Automated medical billing systems provide valuable tools for managing the revenue cycle of healthcare organizations. These systems can generate detailed reports and analytics, allowing providers to monitor their financial performance and identify potential revenue leakage points. By having real-time insights into their revenue cycle, healthcare organizations can proactively address issues and optimize their revenue collection process.
Enhanced data confidentiality and security
Automated medical billing systems ensure the confidentiality and security of patient information by implementing robust data encryption and access controls. These systems comply with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) regulations, ensuring that patient data remains protected and only accessible to authorized personnel. By enhancing data security, healthcare providers can build trust with their patients and maintain compliance with regulatory standards.
Challenges in Automating Medical Billing
Lack of standardized processes and data
One of the significant challenges in automating medical billing is the lack of standardized processes and data across healthcare organizations. Each healthcare provider may have its own unique workflow and data management system, making it challenging to develop a one-size-fits-all automated solution. Additionally, data quality and consistency issues can arise when integrating data from various sources, further complicating the automation process.
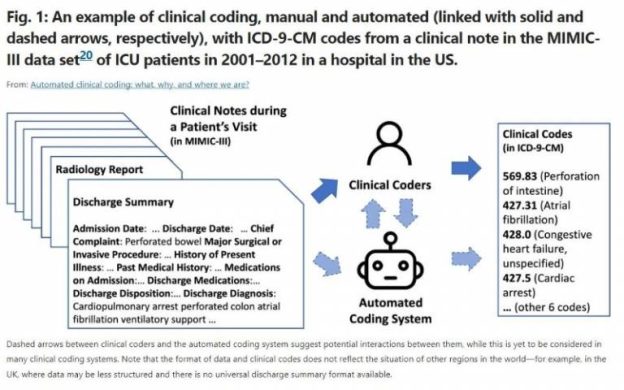
Complexities in coding and reimbursement rules
Medical coding and reimbursement rules are complex and subject to constant updates and changes. The transition from paper-based coding systems to electronic systems has brought about its own set of challenges. Automated medical billing systems need to stay up-to-date with the latest coding standards and reimbursement rules to ensure accurate claim submission. This requires continuous monitoring and maintenance, which can be demanding for healthcare organizations.
Integration with existing healthcare systems
Integrating an automated medical billing system with existing healthcare systems, such as electronic health records (EHR) and practice management software, can be a complex and resource-intensive task. Compatibility issues and data migration challenges may arise during the integration process, necessitating careful planning and coordination between different stakeholders. Additionally, staff training may be required to ensure smooth adoption and utilization of the automated system.
Resistance to change and lack of training
Resistance to change and lack of training among healthcare providers and administrative staff can pose significant challenges in the implementation of automated medical billing systems. Some individuals may be hesitant to adopt new technologies or may lack the necessary skills to navigate and utilize the automated system effectively. To overcome these challenges, comprehensive training programs and ongoing support should be provided to facilitate the smooth transition to automated medical billing.
Technologies Used in Automated Medical Billing
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning are revolutionizing the field of healthcare and medical billing. These technologies are used to automate repetitive tasks, analyze large volumes of data, and detect patterns and anomalies. AI and machine learning algorithms can help identify coding errors, predict claim denials, and optimize the billing process by learning from historical data and trends.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) involves the use of software robots to automate manual and rule-based tasks in the medical billing process, such as data entry, claim validation, and payment posting. RPA systems can mimic human actions, interact with various systems, and perform tasks with speed and accuracy, reducing the need for manual intervention.
Electronic Health Records (EHR)
Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems play a crucial role in automated medical billing. These systems store and manage patient health information electronically, allowing healthcare providers to access and share patient data seamlessly. Integrated EHR and billing systems enable automatic capture and transfer of relevant billing data, minimizing manual data entry and reducing the risk of errors.
Practice Management Software
Practice Management Software is specifically designed to manage the administrative and financial functions of healthcare practices. These software solutions automate various tasks, such as appointment scheduling, patient registration, billing, and claims management. By integrating with other healthcare systems, practice management software can streamline the billing process and improve overall practice efficiency.
Clearinghouses and Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
Clearinghouses and Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) systems facilitate the electronic exchange of claim data between healthcare providers and insurance companies. Clearinghouses act as intermediaries, receiving electronic claims from healthcare providers, validating them for accuracy and completeness, and forwarding them to the appropriate insurance companies. EDI standardizes the format and content of claim data, ensuring seamless communication and reducing the likelihood of errors.
Benefits for Healthcare Providers
Reduced administrative burdens
Automated medical billing systems alleviate the administrative burden on healthcare providers and their staff. By automating routine tasks, such as data entry, eligibility verification, and claim submission, staff can focus on more value-added activities, such as patient care and revenue optimization. This leads to improved staff satisfaction and increased productivity.
Faster and more accurate claims processing
Automated medical billing systems significantly reduce the time required for claims processing. By eliminating manual processes and relying on standardized coding and billing rules, these systems can generate accurate and complete claims quickly. Faster claims processing leads to reduced accounts receivable days and quicker reimbursement, improving the financial health of healthcare providers.
Improved revenue collection
Automated medical billing systems improve revenue collection by reducing billing errors, minimizing claim denials, and accelerating reimbursement cycles. These systems can flag potential issues or discrepancies in claims, allowing providers to resolve them promptly. By optimizing the revenue collection process, healthcare providers can enhance their cash flow and financial stability.
Better financial management and reporting
Automated medical billing systems provide healthcare providers with real-time financial insights and analytics. By generating detailed reports and dashboards, these systems enable providers to track their financial performance, identify revenue leakage points, and make informed decisions. This improves financial management and allows providers to proactively address any financial challenges.
Increased staff productivity
By automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, automated medical billing systems increase staff productivity. Administrative staff can focus on more strategic activities, such as patient engagement, revenue optimization, and process improvement. By leveraging technology, healthcare providers can maximize their staff’s potential and enhance overall practice efficiency.
Benefits for Patients
Faster and more accurate claim submissions
Automated medical billing systems expedite the claim submission process, allowing patients to receive timely reimbursement for their healthcare expenses. These systems generate accurate and complete claims, minimizing the chances of claim denials and delays. Faster claim submissions result in quicker payment processing, reducing the financial burden on patients.
Reduced billing errors and disputes
Automated medical billing systems minimize billing errors and disputes, ensuring that patients are billed accurately for the services they receive. By relying on standardized coding systems and automated processes, these systems reduce the likelihood of incorrect charges, duplicate billing, or billing for services not rendered. This leads to improved patient satisfaction and trust in the billing process.
Improved transparency and understanding of medical costs
Automated medical billing systems provide patients with increased transparency and a better understanding of their medical costs. These systems can generate itemized bills, detailing the specific services rendered and the corresponding charges. This helps patients understand the breakdown of their healthcare expenses and make more informed decisions regarding their care.
Timely and accurate insurance processing
Automated medical billing systems streamline the insurance processing for patients. These systems can verify insurance eligibility in real-time and ensure accurate processing of insurance claims. Patients can have confidence that their insurance claims will be handled promptly and accurately, reducing the need for prolonged follow-up and claim resubmission.
Enhanced patient experience
Ultimately, automated medical billing systems contribute to an enhanced patient experience. By reducing billing errors, accelerating claims processing, and providing greater transparency, these systems create a more seamless and positive billing experience for patients. This improves patient satisfaction, loyalty, and trust in the healthcare provider.
Case Studies
Case Study 1: XYZ Hospital’s Implementation of Automated Medical Billing
XYZ Hospital, a large healthcare organization, faced challenges in its manual medical billing process, including inaccuracies, delays, and a high volume of claim denials. To address these issues, the hospital implemented an automated medical billing system that integrated with its EHR and practice management software. The system streamlined the billing workflow, automated claim submissions, and improved coding accuracy. As a result, the hospital experienced a significant reduction in billing errors and claim denials, leading to improved revenue collection and financial stability.
Case Study 2: ABC Clinic’s Success with Streamlined Claims Processing
ABC Clinic, a multi-specialty clinic, struggled with inefficiencies and delays in its claims processing. This impacted the clinic’s cash flow and strained relationships with insurance companies. To overcome these challenges, the clinic implemented a robotic process automation (RPA) solution that automated claim validation, submission, and payment posting. The RPA system seamlessly integrated with the clinic’s existing practice management software, eliminating the need for manual intervention. The implementation resulted in streamlined claims processing, faster reimbursement, and improved relationships with insurance companies.
Regulatory Considerations
HIPAA compliance
Automated medical billing systems must comply with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) regulations. These regulations set standards for the security and privacy of protected health information (PHI) and impose strict penalties for non-compliance. Automated systems should incorporate robust data encryption, access controls, and audit trails to protect patient data and maintain compliance with HIPAA regulations.
Healthcare reimbursement policies and regulations
Automated medical billing systems need to stay updated with healthcare reimbursement policies and regulations. These policies govern the reimbursement rates, coverage criteria, and billing requirements for various services and procedures. Compliance with these policies is essential to ensure accurate claim submission and avoid potential penalties or legal issues.
Medical coding standards and updates
Automated medical billing systems rely on standardized coding systems, such as ICD-10 and CPT, to translate medical procedures and diagnoses into codes for billing purposes. These systems need to stay current with the latest coding updates and revisions to ensure accurate claim submission. Regular updates and training are necessary to adapt to changes in medical coding standards.
Future of Medical Billing Automation
Advancements in AI and machine learning
The future of medical billing automation lies in advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize the accuracy, speed, and efficiency of medical billing processes. AI algorithms can learn from vast amounts of data, identify patterns and anomalies, and make intelligent decisions. Machine learning can optimize workflows, automate claim validation, and improve revenue cycle management.
Integration of blockchain technology
Blockchain technology holds promise in enhancing the security, transparency, and integrity of medical billing processes. By leveraging the decentralized nature of blockchain, healthcare providers can ensure the immutability and traceability of billing data, minimizing the risk of tampering or fraud. Blockchain-enabled smart contracts can automate claims processing, reducing the need for intermediaries and speeding up reimbursement.
Enhanced interoperability and data exchange
The future of medical billing automation will witness enhanced interoperability and seamless data exchange between healthcare systems. Integrated systems, such as EHR, practice management software, and automated billing systems, will allow for the seamless transfer of data, eliminating the need for manual data entry and reducing errors. Improved interoperability will streamline the billing process and enhance overall efficiency.
Industry-wide standardization efforts
Standardization efforts in medical billing will play a significant role in shaping the future of automation. Streamlining coding systems, reimbursement rules, and billing processes across healthcare organizations will simplify the automation process. Industry-wide collaboration and the establishment of common standards will enable automated systems to function seamlessly and improve the accuracy and efficiency of medical billing.
Conclusion
Automated medical billing presents numerous advantages for healthcare providers and patients alike. The efficiency, accuracy, and streamlined claims processing provided by automated systems alleviate administrative burdens, reduce billing errors, and improve revenue collection for healthcare providers. Patients benefit from faster claim submissions, reduced billing errors, enhanced transparency, and improved insurance processing. However, challenges such as lack of standardization, coding complexities, integration issues, and resistance to change must be addressed in the implementation of automated medical billing systems. As technologies continue to evolve and regulatory standards advance, the potential for automation in medical billing will grow. A balanced approach, considering the benefits and challenges of automation, is crucial to ensure successful adoption and utilization of automated medical billing systems.