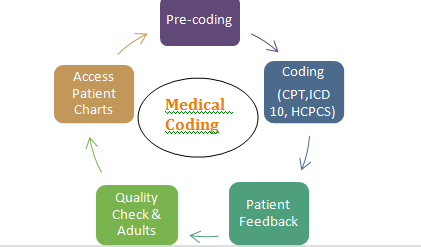
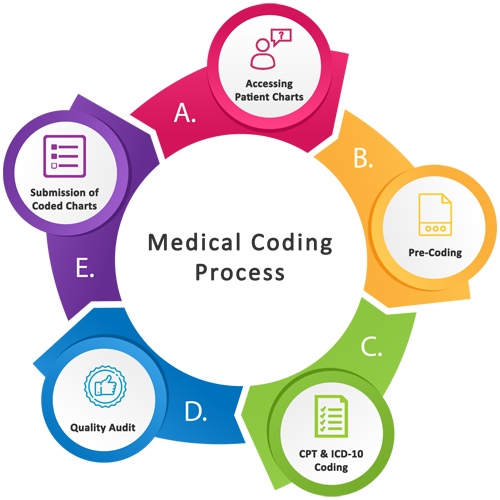
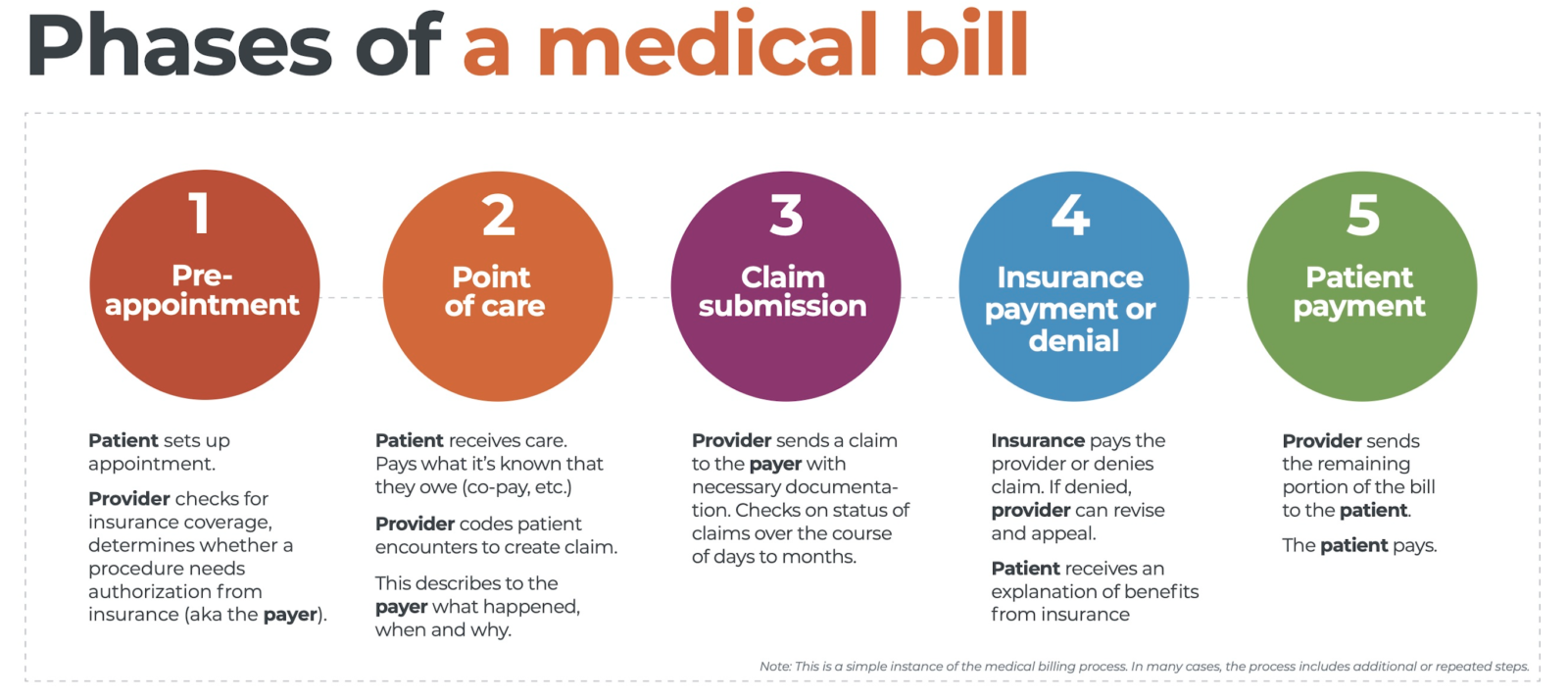
In the complex realm of healthcare, navigating the landscape of medical billing poses numerous challenges. From ever-evolving regulations to reimbursement complications, the intricacies of this process can be overwhelming. This article sheds light on the key obstacles faced by healthcare providers in the realm of medical billing, offering insights into the hurdles they must overcome to ensure efficient and accurate financial transactions. By understanding these challenges, both healthcare professionals and patients can work towards a more streamlined and transparent billing experience.
Technological Challenges
Outdated Systems
One of the biggest challenges faced in medical billing is the use of outdated systems. Many healthcare organizations still rely on legacy software and hardware that may not have the capabilities to efficiently handle the increasing complexities of medical billing. These outdated systems often lack important features such as real-time claim tracking, electronic remittance advice, and automated coding verification. As a result, medical billing processes become slow, prone to errors, and require manual intervention that introduces additional delays and inefficiencies.
Integration Issues
Integrating different systems and software is another technological challenge in medical billing. Healthcare organizations often have multiple systems for different functions, such as electronic health records (EHRs), scheduling, and billing. However, these systems may not integrate seamlessly, leading to information silos and data discrepancies. This lack of integration can hinder the seamless flow of information between departments and result in delays and errors in the billing process.
Lack of Automation
Manual and paper-based processes not only slow down medical billing operations but also increase the risk of errors. With the lack of automation, administrative staff spend significant time on manual data entry, claim submissions, and follow-ups. Automating these tasks through the use of technology and software can greatly improve efficiency, accuracy, and overall productivity. Automation can help streamline the billing process, reduce human error, and free up resources to focus on more complex tasks.
Data Security
Ensuring the security and privacy of patient data is a major concern in medical billing. Healthcare organizations are bound by strict regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) that mandate the protection of patient information. However, maintaining data security in an increasingly digital landscape poses challenges. Cybersecurity threats, data breaches, and unauthorized access to sensitive information are constant risks that medical billing professionals must address. Robust security measures, regular data backups, and staff training are essential to protect patient data and maintain compliance with regulations.
Regulatory Challenges
Frequent Changes in Regulations
The healthcare industry is subject to frequent changes in regulations, with new policies and guidelines being introduced regularly. Staying updated with these changes and ensuring compliance can be a significant challenge for medical billing professionals. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in penalties, claim denials, and legal consequences. To overcome this challenge, healthcare organizations must dedicate resources to continuous education, training, and keeping abreast of regulatory updates through industry associations, professional certifications, and regular communication with regulatory agencies.
Compliance Issues
Compliance with regulations is not only a challenge due to frequent changes but also because of the complex nature of rules and requirements. Medical billing professionals are responsible for accurately coding procedures, submitting claims within specified timeframes, and ensuring documentation meets the criteria for reimbursement. The complexity of compliance requirements can often lead to errors, resulting in claim denials and delayed reimbursements.
Complex Documentation Requirements
Proper documentation is crucial for medical billing and reimbursement. Each procedure and service must be supported by accurate and detailed documentation. However, deciphering and understanding the complex documentation requirements can be a challenge. Medical billing professionals need to work closely with healthcare providers to ensure complete and accurate documentation, including detailed descriptions of procedures performed, diagnosis codes, and patient information. Inadequate or incomplete documentation can lead to claim denials and subsequent financial loss.
Insurance Claims Denials
Insurance claims denials are a significant challenge in medical billing. Many claims are denied due to various reasons, such as missing information, coding errors, eligibility issues, or lack of documentation. Processing and resolving denied claims can be time-consuming, requiring careful review, correction, and resubmission. These denials can impact the financial health of healthcare organizations and delay reimbursements, making it essential to have robust denial management processes in place.
Financial Challenges
Delayed or Denied Reimbursements
One of the most pressing financial challenges in medical billing is delayed or denied reimbursements. Healthcare organizations heavily rely on timely reimbursements from insurance companies to cover operational expenses and provide quality patient care. Delays in reimbursements can disrupt cash flow and restrict the ability to invest in necessary resources. Moreover, denied claims further compound the financial challenges, as they require additional efforts to appeal or correct errors in order to secure reimbursement.
Coding Errors
Accurate medical coding is vital for successful reimbursement. However, coding errors can occur due to various reasons, such as misinterpretation of documentation, lack of coding knowledge, or rapidly changing coding guidelines. These errors can result in claim denials or incorrect payments, impacting the financial stability of healthcare organizations. Proper education and training of coding staff, implementation of coding software tools, and regular audits can help mitigate coding errors and improve overall reimbursement rates.
Insurance Coverage Confusion
Navigating the complex landscape of insurance coverage can be challenging for both healthcare providers and patients. Insurance policies often have intricate rules, limitations, and coverage exclusions that need to be understood and managed effectively. Determining patient eligibility, verifying coverage, and understanding the requirements for specific services can be time-consuming. Insurance coverage confusion can lead to billing errors, claim denials, and patient dissatisfaction, making it crucial for healthcare organizations to invest in resources and technology that facilitate accurate insurance coverage verification and billing processes.
High Administrative Costs
The administrative costs associated with medical billing can be a significant financial challenge. hiring and training skilled billing professionals, investing in technological solutions, and maintaining compliance with regulations all contribute to the overall administrative expenses. Additionally, the manual nature of many billing processes increases labor costs and the potential for errors. Streamlining workflows through automation, outsourcing certain functions, and optimizing staff and resource allocation can help mitigate high administrative costs and improve the financial efficiency of healthcare organizations.
Staffing Challenges
Shortage of Qualified Personnel
The healthcare industry faces a shortage of qualified personnel in various roles, including medical billers and coders. The demand for skilled billing professionals exceeds the available supply, making it challenging for healthcare organizations to recruit and retain qualified staff. The shortage of personnel can lead to increased workloads, decreased productivity, and potential errors in billing processes. To address this challenge, organizations can invest in training programs, offer competitive compensation packages, and create a supportive work environment to attract and retain talented billing professionals.
Training and Retention
Even when healthcare organizations manage to hire qualified personnel, training and retaining them can be challenging. Medical billing is a complex field that requires continuous education on changing regulations, coding guidelines, and software updates. Providing ongoing training opportunities and career development paths can help keep billing professionals engaged, up-to-date, and motivated. Proper mentorship, recognition programs, and a positive work culture are also key factors in retaining experienced billing staff and reducing turnover rates.
Workforce Burnout
The demanding nature of medical billing can contribute to workforce burnout. Billing professionals often face high workloads, tight deadlines, and the pressure to meet productivity targets. The repetitive and detail-oriented nature of their work can also lead to fatigue and reduced job satisfaction. To address this challenge, healthcare organizations can implement strategies to promote work-life balance, provide stress management tools and resources, and foster a supportive work environment. Empowering billing staff by involving them in process improvement initiatives and recognizing their contributions can also help alleviate burnout and boost morale.
Staff Productivity
Efficient staff productivity is crucial for effective medical billing. However, various factors can challenge productivity levels. Manual and fragmented processes, lack of proper training, and outdated systems can all contribute to decreased productivity. Implementing automation tools, streamlining workflows, and regularly evaluating and optimizing processes can enhance staff productivity. Additionally, providing ongoing feedback, setting achievable targets, and recognizing and rewarding high-performing individuals can motivate staff and improve overall productivity.
Communication Challenges
Information Exchange with Providers
Effective communication and information exchange between healthcare providers and billing professionals are vital for accurate and timely billing. However, communication challenges can arise due to factors such as busy schedules, limited availability, or misunderstandings. Incomplete or incorrect information received from providers can result in billing errors and claim denials. To improve communication, healthcare organizations can implement streamlined processes for information exchange, leverage technology solutions like secure messaging systems, and establish clear channels of communication between providers and billing staff.
Patient Communication
Communication with patients regarding their billing and insurance can also present challenges. Billing can be complex and overwhelming for patients, and misunderstandings can lead to confusion, frustration, and delayed payments. Clear and concise patient communication regarding insurance coverage, billing statements, payment options, and financial assistance programs is crucial. Healthcare organizations can provide educational materials, offer patient portals for accessing billing information, and establish dedicated support lines to address patient queries and concerns effectively.
Language Barriers
Language barriers can add another layer of complexity to medical billing communication. Healthcare organizations often serve diverse populations with varying language needs. Limited proficiency in the English language can hinder effective communication between billing professionals and patients. To overcome language barriers, organizations can invest in bilingual staff or interpreters to facilitate effective communication with non-English speaking patients. Utilizing multilingual patient education materials and implementing translation services can also improve patient understanding of billing-related information.
Lack of Standardization
The lack of standardization in medical billing practices poses communication challenges. Different healthcare organizations and insurance companies may have their own unique billing codes, documentation requirements, and reimbursement processes. This lack of standardization can result in confusion and errors during information exchange between parties involved in medical billing. Implementing industry-standard coding systems, promoting standardized documentation practices, and fostering collaboration among stakeholders can help address this challenge and improve overall communication efficiency.
Revenue Cycle Management Challenges
Inaccurate Patient Information
Accurate patient information is critical for successful revenue cycle management. However, gathering and maintaining accurate patient information can be challenging. Errors in patient demographics, insurance details, or eligibility data can lead to claim denials, payment delays, and lost revenue. Healthcare organizations can tackle this challenge by implementing robust patient registration processes, conducting data validation checks, and encouraging patients to provide updated information regularly. Utilizing technology solutions that automate data verification processes can also help improve the accuracy of patient information.
Inefficient Claims Processing
Inefficient claims processing can cause delays and impact revenue cycle management. Manual processing, lack of automated workflows, and inadequate claim tracking systems can hinder the timely processing of claims. This can result in delayed reimbursements, increased administrative costs, and ultimately affect the financial stability of healthcare organizations. Implementing electronic claim submission systems, utilizing claim scrubbing tools to identify errors, and regularly monitoring claim status can improve claims processing efficiency and accelerate revenue cycle management.
Unclaimed or Uncollected Payments
Unclaimed or uncollected payments pose a significant revenue cycle management challenge. Overlooking or failing to follow up on outstanding patient payments can lead to financial losses. Healthcare organizations must establish clear and efficient processes for identifying and pursuing unpaid balances. Utilizing technology solutions such as automated payment reminders, offering online payment options, and implementing robust accounts receivable management practices can help address this challenge and reduce unclaimed or uncollected payments.
Denials Management
Managing claim denials is a critical aspect of revenue cycle management. Denials can occur due to errors, lack of documentation, eligibility issues, or exceeding coverage limits. Tackling denials requires a proactive approach that involves identifying denial trends, initiating timely appeals, and implementing effective denial prevention strategies. Streamlining denials management through the use of denial tracking software, conducting regular audits, and providing staff training on denial resolution can help optimize revenue cycle management and minimize financial losses.
Compliance Challenges
Medical Necessity
Ensuring medical necessity in the billing process is essential to maintain compliance with regulations and receive reimbursement. Medical billing professionals must determine if a service or procedure meets the criteria for medical necessity as defined by insurance policies and regulations. Failure to accurately assess and document medical necessity can result in claim denials, investigations, and potential allegations of fraud. Healthcare organizations can address this challenge by implementing comprehensive medical necessity review processes, facilitating ongoing education for staff, and utilizing decision support tools that help determine the appropriateness of services.
Upcoding and Downcoding
Upcoding, the practice of assigning codes that reflect a higher level of service than provided, and downcoding, assigning codes that reflect a lower level of service, are compliance challenges in medical billing. Both practices are considered fraudulent and can lead to legal consequences, damage to a healthcare organization’s reputation, and significant financial losses. Implementing regular audits, internal control measures, and staff training on proper coding practices can help mitigate the risk of upcoding and downcoding and ensure compliance with regulations.
Billing Fraud
Billing fraud is a serious compliance challenge that can result in legal penalties, loss of provider licenses, and reputational damage. Healthcare organizations must be diligent in detecting and preventing fraudulent practices such as unbundling, billing for services not rendered, or submitting false claims. Implementing robust internal control measures, conducting thorough audits, and providing staff training on identifying and reporting fraudulent activities are essential in combating billing fraud. Collaboration with law enforcement agencies and regulatory bodies can also aid in identifying and prosecuting individuals involved in fraudulent billing practices.
Not Following Government Regulations
Compliance with government regulations is vital for healthcare organizations. Failure to adhere to regulations such as HIPAA, the False Claims Act, and the Anti-Kickback Statute can result in severe consequences. Non-compliance can lead to fines, lawsuits, loss of funding, and damage to an organization’s reputation. Medical billing professionals must stay informed about changes in regulations, establish internal policies that align with legal requirements, and conduct regular compliance audits to ensure adherence to government regulations.
Tackling Insurance Issues
Eligibility Verification
Verifying patient insurance eligibility is crucial to avoid claim denials and ensure timely reimbursement. However, insurance eligibility verification can be time-consuming and complex. Gathering accurate insurance information, confirming coverage details, and assessing any prior authorizations or referral requirements requires attention to detail and effective communication with insurance providers. Healthcare organizations can address this challenge by implementing automated insurance eligibility verification systems, utilizing electronic data interchange with insurance companies, and clearly communicating insurance coverage requirements to patients during the registration process.
Prior Authorization
Prior authorization is a process where healthcare providers must obtain approval from insurance companies before performing certain procedures or prescribing specific medications. The prior authorization process can be time-consuming, requiring extensive documentation and follow-up with insurance providers. Delays in obtaining prior authorization can impact the ability to provide timely care and delay reimbursement. Healthcare organizations can address this challenge by streamlining prior authorization processes, utilizing electronic prior authorization systems, and establishing effective communication channels with insurance companies to expedite the approval process.
Insurance Denials and Appeals
Insurance claim denials are common challenges faced by healthcare organizations. When claims are denied, it is crucial to initiate timely and effective appeals to secure reimbursement. Appeals require thorough review, gathering additional documentation, and presenting a strong case to the insurance company. To tackle insurance denials and appeals, healthcare organizations must have comprehensive denial management processes in place. This includes tracking denials, analyzing denial patterns, implementing timely appeals, and leveraging technology solutions that facilitate efficient denial management workflows.
Healthcare Provider Network Limitations
Healthcare provider networks play a crucial role in insurance coverage and billing. Insurance plans often have specific networks of preferred healthcare providers, and using out-of-network providers can result in higher costs or reduced coverage. Healthcare organizations may face challenges in managing relationships with insurance companies and ensuring that their providers are included in the networks. Regularly reviewing and updating provider network agreements, monitoring changes in insurance plans, and establishing open lines of communication with insurance companies are essential to overcoming healthcare provider network limitations.
Data Management Challenges
Incomplete or Inaccurate Patient Data
Incomplete or inaccurate patient data poses challenges in medical billing and revenue cycle management. Incorrect demographic information, outdated insurance details, or missing documentation can lead to errors, claim denials, and delayed reimbursements. Healthcare organizations must invest in robust data collection and validation processes, implement systems that identify and flag incomplete or inaccurate data, and educate staff on the importance of accurate and up-to-date patient information. Regular data audits and cleaning procedures can also help address data quality challenges.
Inadequate EHR Systems
The use of electronic health record (EHR) systems is widespread in healthcare organizations, but inadequate systems can hinder efficient data management in medical billing. EHR systems that lack interoperability, poor user interfaces, or limited functionalities can negatively impact billing operations. Healthcare organizations must invest in EHR systems that have robust billing and coding modules, seamless integration capabilities with billing software, and are intuitive and user-friendly. Regular assessments of EHR system performance and user feedback can help identify limitations and guide system improvements.
Data Entry Errors
Data entry errors can occur at various stages of the medical billing process and lead to claim rejections or inaccuracies in reimbursement. Manual data entry is particularly prone to typographical errors, transposed numbers, or incorrect coding assignments. Implementing automation tools, such as optical character recognition (OCR) technology or intelligent data capture systems, can significantly reduce data entry errors. Regular training, data validation checks, and systems that flag potential errors can also improve data accuracy and minimize the risk of errors in medical billing.
Data Privacy and Security
Ensuring data privacy and security is a significant challenge in medical billing. Healthcare organizations handle vast amounts of sensitive patient information, including personal, financial, and medical data. Protecting this data from unauthorized access, data breaches, and cybersecurity threats is vital to maintaining patient trust and compliance with regulations. Implementing robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and regular vulnerability assessments, can help safeguard patient data. Staff training on data privacy best practices and adherence to industry standards, such as HIPAA, are also essential to address data management challenges.
Resource Allocation Challenges
Budget Constraints
Budget constraints are common challenges faced by healthcare organizations in medical billing. Adequate resources, including staff, technology, training, and infrastructure, are essential for efficient billing operations. However, limited budgets can hinder the organization’s ability to invest in necessary resources. To address budget constraints, healthcare organizations must conduct thorough financial analyses, identify opportunities for cost savings, and prioritize resource allocation based on critical needs. Exploring alternative funding sources, such as grants or partnerships, can also help mitigate budget limitations.
Strategic Planning and Decision-making
Strategic planning and decision-making play a vital role in effectively managing medical billing challenges. Healthcare organizations must develop a clear vision and roadmap for optimizing billing processes, improving revenue cycle management, and addressing compliance requirements. Strategic planning involves setting goals, establishing priorities, and allocating resources accordingly. Effective decision-making requires data-driven analysis, collaboration among stakeholders, and consideration of industry trends and best practices. Engaging key decision-makers, investing in strategic planning resources, and regularly evaluating progress are essential to overcoming resource allocation challenges.
Team Collaboration and Coordination
Effective collaboration and coordination between different teams involved in medical billing are crucial for smooth operations and optimal revenue cycle management. Billing staff, coding professionals, healthcare providers, and administrative personnel must work together seamlessly to ensure accurate documentation, proper coding, and timely claim submission. Inefficiencies in team collaboration and coordination can lead to errors, delays, and financial losses. Healthcare organizations can foster collaboration through regular meetings, cross-training opportunities, clear communication channels, and shared access to information and systems.
Adapting to Industry Changes
The healthcare industry is continuously evolving, with new regulations, technologies, and best practices emerging regularly. Adapting to these changes can be a challenge for healthcare organizations engaged in medical billing. Staying updated requires continuous education and training, monitoring industry trends and benchmarks, and fostering a culture of innovation and adaptability. Healthcare organizations must allocate resources for staff development and invest in technologies that support industry advancements. Regular reassessment of processes, systems, and strategic plans can help healthcare organizations adapt and remain competitive in the evolving healthcare landscape.
In conclusion, medical billing faces a multitude of challenges across various domains. Technological challenges, such as outdated systems and lack of automation, hinder efficiency and accuracy. Regulatory challenges, including frequent changes in regulations and compliance issues, require continuous education and accurate documentation. Financial challenges, such as delayed reimbursements and high administrative costs, impact the financial stability of healthcare organizations. Staffing challenges, including shortages of qualified personnel and workforce burnout, affect productivity and performance. Communication challenges, like information exchange and language barriers, can lead to billing errors and patient dissatisfaction. Revenue cycle management challenges, compliance challenges, insurance issues, data management challenges, and resource allocation challenges also contribute to the complexities of medical billing. Overcoming these challenges requires a combination of technological solutions, process improvements, ongoing training, effective communication strategies, and a focus on compliance and accuracy. By addressing these challenges head-on, healthcare organizations can optimize their medical billing operations, improve financial outcomes, and provide better, more efficient care to patients.