In the complex landscape of medical billing, denials are an ever-present challenge for healthcare providers. Understanding the various types of denials is crucial for both medical billing professionals and healthcare organizations alike. From insurance policy exclusions to coding errors and eligibility issues, this article explores the common types of denials in medical billing, shedding light on how they impact revenue cycles and tips for preventing and resolving them efficiently.
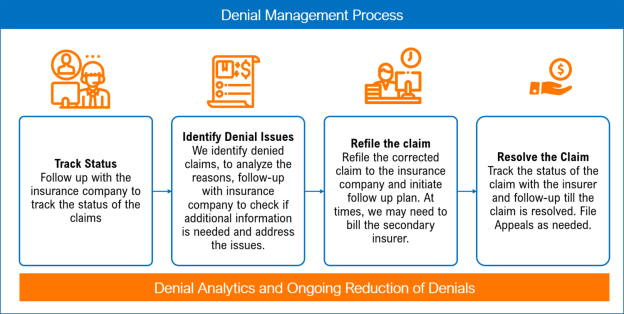
Claim Denials
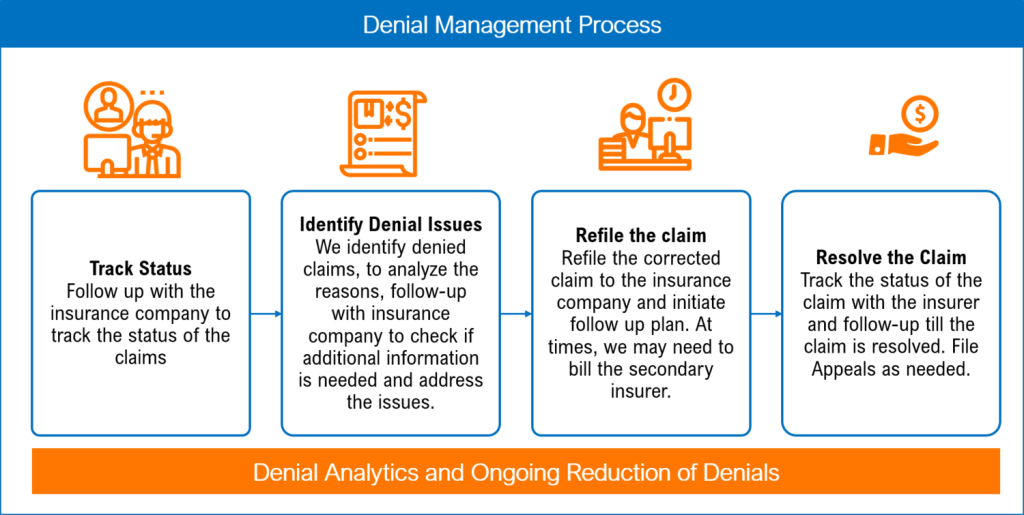
This image is property of nemadji.org.
Authorization Denials
Authorization denials occur when a healthcare provider fails to obtain proper authorization from the insurance company before providing services or procedures to a patient. Insurance companies require authorization to ensure that the treatment or service is medically necessary and meets their coverage criteria. Without proper authorization, the insurance company may deny the claim, leaving the provider to bear the financial burden.
To avoid authorization denials, providers should familiarize themselves with each insurance company’s specific requirements for authorization. They should also ensure that all necessary documentation, such as medical records or supporting documents, is submitted with the authorization request. Clear communication between the provider and the insurance company is crucial to avoid any misunderstandings or delays in obtaining authorization.
Eligibility Denials
Eligibility denials occur when a healthcare provider submits a claim for a patient who is not covered under the patient’s insurance policy or whose coverage has expired. Insurance companies maintain databases that contain information on each individual’s insurance coverage, including eligibility status. Providers should verify a patient’s eligibility and coverage before rendering any services to avoid eligibility denials.
To prevent eligibility denials, providers can implement a robust verification process. This process involves verifying a patient’s insurance coverage, confirming the effective dates of the policy, and checking for any exclusions or limitations that may affect coverage. Accurate and up-to-date patient information, such as insurance ID numbers and demographic details, is essential for a successful eligibility verification process.
Technical Denials
Technical denials occur due to errors or issues related to the technical aspects of claim submission. These denials are often the result of incomplete or incorrect information provided on the claim form, such as missing or invalid codes, incorrect patient information, or formatting errors. Insurance companies have specific guidelines and requirements for claim submission, and failing to adhere to these guidelines can result in a technical denial.
To avoid technical denials, providers should invest in robust claims management software or systems that can help validate claims before submission. These systems can check for errors and inconsistencies, ensuring that all required fields are completed accurately. Providers should also regularly train their billing staff to stay updated on the latest claim submission guidelines and requirements.
Medical Necessity Denials
Medical necessity denials occur when a service or procedure rendered to a patient is deemed not medically necessary by the insurance company. Insurance companies use medical guidelines and criteria to determine what they consider medically necessary. If a service or procedure does not meet these criteria, the insurance company may deny the claim, leaving the provider responsible for the charges.
To prevent medical necessity denials, providers should thoroughly document the patient’s medical condition and the need for the service or procedure. It is crucial to provide clear and concise documentation that supports the medical necessity of the claim. Providers should also familiarize themselves with the medical policies and guidelines of the insurance companies they work with to ensure that the services they provide align with the insurers’ criteria.
Duplicate Claim Denials
Duplicate claim denials occur when a provider submits multiple claims for the same service or procedure, resulting in duplicate charges. Insurance companies have systems in place to detect and reject duplicate claims to prevent overbilling. Providers should ensure that they have proper checks and balances in place to prevent duplicate claim submissions. Regular audits of claim submissions can help identify any potential duplicates and rectify the issue before the claim is denied.
To prevent duplicate claim denials, providers should employ effective billing and claims management systems that can detect and prevent duplicate submissions. Clear communication within the billing department is essential to avoid inadvertent duplicate submissions. Well-documented procedures and protocols for claim submission can also help prevent errors that may lead to duplicate claims.
Timely Filing Denials
Timely filing denials occur when a provider fails to submit a claim within the designated timeframe specified by the insurance company. Insurance companies typically have strict guidelines regarding the submission of claims, and failure to comply with these guidelines can result in a denial. Each insurance company may have varying deadlines for claim submission, making it crucial for providers to stay informed about these deadlines.
To avoid timely filing denials, providers should establish efficient and well-organized billing processes that prioritize timely claim submission. Clear communication between the billing department and the healthcare providers is essential to ensure that all necessary documentation and codes are collected in a timely manner. Regular monitoring and tracking of claim submissions can help identify any potential delays and address them promptly.
Coordination of Benefits Denials
Coordination of benefits denials occur when a patient has multiple insurance coverages, and the primary and secondary insurance companies do not coordinate their coverage properly. This type of denial often arises due to errors in updating insurance information or lack of clear communication between the patient, provider, and insurance companies. Providers must ensure that accurate and up-to-date insurance information is obtained from the patient and that all relevant insurance companies are properly notified.
To prevent coordination of benefits denials, providers should have a clear understanding of the patient’s insurance coverage and coordination of benefits requirements. Verification of insurance information should be conducted at each visit to ensure accurate billing. Establishing effective communication channels with patients and insurance companies can help minimize errors and prevent coordination of benefits denials.
Non-Covered Service Denials
Non-covered service denials occur when a service or procedure rendered to a patient is not covered under the patient’s insurance policy. Insurance companies have specific coverage policies that outline what services, procedures, or treatments they consider covered. Providers should verify the patient’s coverage and eligibility for specific services before rendering them.
To prevent non-covered service denials, providers should have a clear understanding of the insurance policies they work with and their coverage criteria. Clear communication with the patient is essential to ensure that they understand what services are covered under their insurance policy and what may be considered non-covered. When there is uncertainty regarding coverage, obtaining a predetermination or prior authorization from the insurance company can help clarify any potential coverage issues.
Coding Denials
Coding denials occur when there are errors or inconsistencies in the codes used on the claim form. Common coding errors include using incorrect procedure codes, diagnosis codes, or modifiers. Insurance companies rely heavily on these codes to determine coverage and reimbursement, and discrepancies or errors can result in denials.
To prevent coding denials, providers should invest in regular training and education for their coding staff to ensure they are up to date with the latest coding guidelines and changes. The use of comprehensive coding manuals and coding software can also help minimize coding errors. Regular audits of coding practices can assist in identifying any areas of improvement and reducing coding-related denials.
Reimbursement Denials
Reimbursement denials occur when an insurance company denies payment for a service or procedure despite the claim meeting all necessary requirements. This type of denial can be frustrating for providers as they have provided the service or procedure but are not appropriately reimbursed. Reimbursement denials can occur due to various reasons, including errors in claim processing, fee schedule limitations, or lack of coverage for a specific service.
To address reimbursement denials, providers should conduct thorough reviews of the denial reasons and processes. Identifying patterns or common issues can help tailor solutions to reduce future denials. Effective communication with the insurance company, appeals processes, and detailed documentation of services rendered can potentially resolve reimbursement denials.
Payment Denials

Partial Payment Denials
Partial payment denials occur when an insurance company approves the claim but reimburses the provider with only a portion of the billed amount. This typically happens when the insurance company applies contractual adjustments, such as negotiated rates or fee schedules, which reduce the payment amount. Providers should familiarize themselves with the reimbursement rates for each insurance company to manage their revenue expectations accurately.
To mitigate partial payment denials, providers can consider negotiating favorable contracts with insurance companies. They can also implement sound financial policies that include clear communication to patients about their financial responsibilities, such as co-pays or deductibles. By managing patient expectations and setting up clear payment guidelines, providers can minimize potential partial payment denials.
Full Payment Denials
Full payment denials occur when an insurance company denies payment for the entire claim, leaving the provider with no reimbursement. This can happen due to various reasons, such as lack of coverage for the service, billing errors, or failure to meet specific claim submission requirements. Providers should thoroughly review the denial reasons and follow the necessary steps to address the issue promptly.
To address full payment denials, providers should review their claim submission processes and ensure compliance with insurance company requirements. Verifying patient coverage, accurate coding, and proper documentation are vital to preventing full payment denials. Prompt and thorough appeals, along with effective communication with the insurance company, can increase the chances of successful resolution.
Downcoding Denials
Downcoding denials occur when an insurance company reduces the level of service or downcodes the claim, resulting in lower reimbursement. This often happens when the documentation does not support the level of service billed by the provider. Providers must ensure that their documentation accurately reflects the complexity and severity of the patient’s condition to avoid downcoding denials.
To prevent downcoding denials, providers should implement robust documentation practices that capture the level of service accurately. Clear and detailed documentation should include the patient’s medical history, examination findings, and the rationale for the services provided. Regular auditing of documentation and coding practices can help identify any potential downcoding issues and address them promptly.
Bundled Payment Denials
Bundled payment denials occur when an insurance company groups multiple services or procedures into a single reimbursement, resulting in a lower payment than expected. This typically happens when the insurance company has specific bundling rules in place, and the services provided by the provider are considered bundled under those rules. Providers should be aware of the bundling rules of each insurance company to accurately bill for their services.
To prevent bundled payment denials, providers should familiarize themselves with the bundling rules and guidelines of the insurance companies they work with. Ensuring that the services provided are appropriately billed and documented can minimize the risk of bundled payment denials. In cases where bundling is necessary, providers should clearly communicate with the patient and insurance company to manage expectations.
Rejection Denials
Rejection denials occur when the insurance company rejects a claim due to errors or inconsistencies in the claim submission process. Unlike denials, rejections refer to claims that are not even considered for payment due to issues that can be resolved by fixing the errors and resubmitting the claim. Providers should review rejection reasons and promptly address the issues to ensure timely payment.
To prevent rejection denials, providers should implement robust claim scrubbing processes that can identify and correct errors before submission. Verification of patient and insurance information, accurate coding, and thorough documentation are essential to prevent rejections. Regular monitoring and tracking of claim submissions can help identify any potential issues and rectify them promptly.
Appeal Denials
Administrative Denials
Administrative denials occur when a claim is denied due to administrative errors or omissions in the claim submission process. These errors can include missing or incomplete information, such as provider identification numbers, patient demographics, or authorization details. Providers should thoroughly review denial reasons and address any administrative issues promptly.
To address administrative denials, providers should establish clear protocols and procedures for claim submission that cover all necessary administrative requirements. Regular staff training and education on claim submission guidelines can help minimize administrative errors. Thorough reviews of claim documentation before submission can also help identify any missing or incomplete information and rectify it promptly.
Corrected Claim Denials
Corrected claim denials occur when a corrected or updated claim is denied after the initial claim was denied. This can happen if the corrections made to the claim do not address the reasons for denial or if the necessary documentation is not provided to support the corrections. Providers should carefully review denial reasons and ensure that all necessary information is included in the corrected claim.
To prevent corrected claim denials, providers should thoroughly review the original denial reasons and address them adequately. Clear documentation of the corrections made, along with any supporting documentation, should be included with the corrected claim. Regular communication with the insurance company and timely follow-up can help ensure that the corrected claim is processed without further denials.
Medical Record Denials
Medical record denials occur when the insurance company requests additional medical records or documentation to support a claim, and the provider either fails to provide the requested records or the records are incomplete or insufficient. Insurance companies rely on medical records to determine the validity and medical necessity of the services provided, and the lack of proper documentation can lead to claim denials.
To prevent medical record denials, providers should establish clear processes for medical record requests and ensure that all necessary documentation is provided promptly. Regular reviews of medical record documentation and audits can help identify any potential gaps or deficiencies in the documentation. Effective communication with the billing and medical staff is crucial to ensure that the requested records are provided promptly and accurately.
Medical Necessity Denials
Medical necessity denials in the appeal process occur when an insurance company continues to deny a claim based on their judgement that the service or procedure is not medically necessary, despite the provider’s appeal. This can happen when there is a difference of opinion between the provider and the insurance company regarding the need and appropriateness of the services provided. Providers should be prepared to provide clear and convincing documentation that supports the medical necessity of the services to overturn such denials.
To address medical necessity denials in the appeal process, providers should ensure that their appeal includes comprehensive and well-documented medical records that clearly articulate the patient’s condition and the need for the services provided. Engaging with the insurance company to understand their specific criteria and guidelines for medical necessity can help tailor the appeal and strengthen the documentation provided. Prompt follow-up and persistence in the appeal process can sometimes lead to a successful resolution.
Timely Filing Denials
Timely filing denials in the appeal process occur when the provider submits an appeal beyond the designated timeframe specified by the insurance company. Insurance companies often have strict deadlines for appeals, and failing to adhere to these deadlines can result in denials. Providers should familiarize themselves with the appeal deadlines of each insurance company to ensure timely submission.
To prevent timely filing denials in the appeal process, providers should establish efficient and well-organized appeal processes that prioritize timely submission. Clear communication between the billing department, the healthcare providers, and any necessary external resources, such as legal counsel or consultants, is essential to ensure that all necessary documentation and codes are collected in a timely manner. Regular monitoring and tracking of appeal submissions can help identify any potential delays and address them promptly.
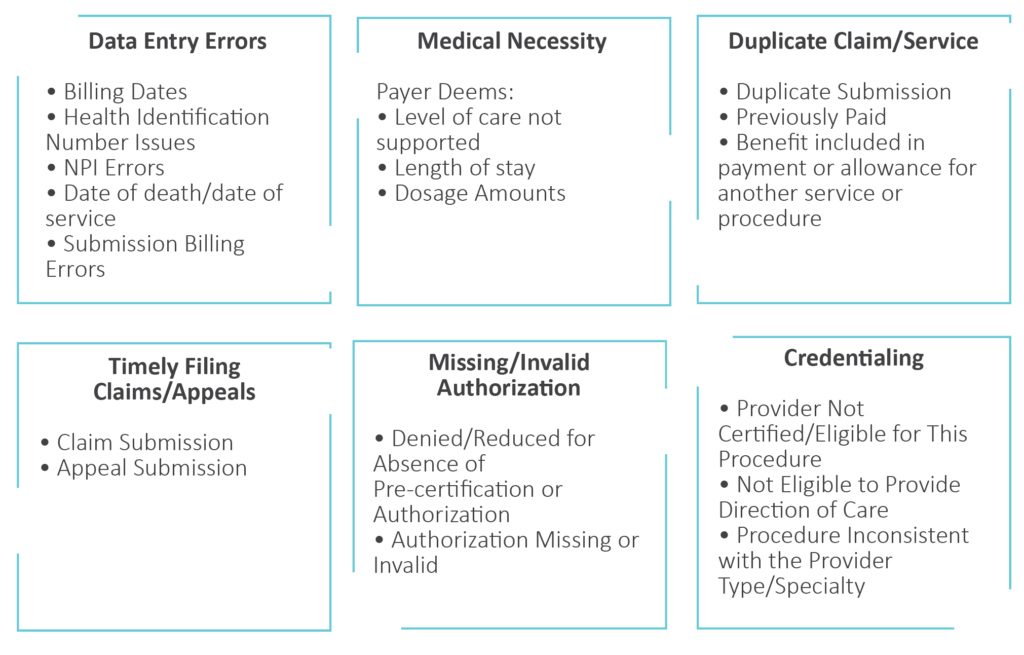
Billing Denials

Medical cost concept with stethoscope and medical bill
Incorrect Patient Information Denials
Incorrect patient information denials occur when patient information, such as name, date of birth, or insurance information, is entered inaccurately or incompletely on the claim form. Insurance companies rely on accurate patient information for claim processing, and discrepancies or errors can result in denials. Providers should ensure that they obtain and verify accurate patient information for each claim submission.
To prevent incorrect patient information denials, providers should implement robust patient registration and verification processes that capture accurate patient information. Regular staff training and education on the importance of accurate patient information can help minimize errors. Verification of patient demographics and insurance information at each visit can help ensure that accurate information is collected for claim submission.
Incorrect Provider Information Denials
Incorrect provider information denials occur when the provider’s information, such as identification numbers or credentials, is entered inaccurately or incompletely on the claim form. Insurance companies rely on accurate provider information for claim processing, and errors or discrepancies can result in denials. Providers should ensure that their information is accurately updated and communicated to the insurance company.
To prevent incorrect provider information denials, providers should regularly update and verify their provider information with the insurance companies they work with. Clear communication channels should be established to notify insurance companies of any changes or updates to the provider’s information. Regular reviews of claim submissions can help identify any potential errors or inconsistencies in the provider information and rectify them promptly.
Non-Compliance Denials
Non-compliance denials occur when a provider fails to comply with specific regulatory or contractual requirements set by the insurance company. These requirements can include timely submission of claims, adherence to coding and billing guidelines, or participation in specific programs or networks. Providers should thoroughly review their contracts and agreements with insurance companies to ensure compliance with all requirements.
To prevent non-compliance denials, providers should familiarize themselves with the specific requirements of each insurance company they work with. Establishing clear protocols and procedures that prioritize compliance with regulatory and contractual requirements can help minimize non-compliance denials. Regular reviews of billing and coding practices, as well as internal audits, can help identify any potential non-compliance issues and rectify them promptly.
Lack of Documentation Denials
Lack of documentation denials occur when there is insufficient or incomplete documentation to support the services or procedures billed on the claim form. Insurance companies rely on accurate and comprehensive medical records to determine the validity and medical necessity of the services provided. Insufficient documentation can result in denials, leaving the provider responsible for the charges.
To prevent lack of documentation denials, providers should implement robust documentation practices that capture all necessary information to support the services provided. Clear and detailed documentation should include the patient’s medical history, examination findings, treatment plans, and the rationale for the services provided. Regular training and education for medical and billing staff on documentation requirements can help minimize deficiencies in documentation.
Upcoding Denials
Upcoding denials occur when a provider submits a claim using codes that represent a higher level of service than what was actually provided. This can be an intentional or unintentional error and can result in increased reimbursement. Upcoding is considered fraudulent and can lead to severe consequences, including legal and financial penalties. Providers must ensure that their coding accurately reflects the services provided.
To prevent upcoding denials, providers should invest in regular training and education for their coding staff to ensure accurate coding practices. The use of comprehensive coding manuals and coding software can also help minimize upcoding errors. Regular audits of coding practices can assist in identifying any potential upcoding issues and address them promptly.
Unbundling Denials
Unbundling denials occur when a provider bills for separate services or procedures that should be billed together under a single code. Insurance companies have specific guidelines for bundling services, and failing to adhere to these guidelines can result in denials. Providers must ensure that their billing practices reflect accurate bundling of services.
To prevent unbundling denials, providers should familiarize themselves with the bundling rules and guidelines of the insurance companies they work with. It is essential to accurately code and bill for services based on the bundling rules, ensuring that services that should be bundled are not billed and charged separately. Regular reviews of billing practices and audits can help identify any potential unbundling issues and rectify them promptly.
Insurance Limit Denials
Insurance limit denials occur when a patient’s insurance coverage has reached its limit or maximum benefit for a specific service or procedure. Insurance policies often have limits on coverage amounts, such as annual maximums or visit limits for certain services. Providers should verify the patient’s coverage and ensure that the services provided are within the allowed limits to avoid insurance limit denials.
To prevent insurance limit denials, providers should verify the patient’s insurance coverage and limits before rendering services. This includes understanding any restrictions, maximums, or limitations set by the insurance company. Clear communication with the patient about their coverage and financial responsibilities is essential to manage expectations and minimize insurance limit denials.
Duplicate Billing Denials
Duplicate billing denials occur when a provider submits multiple claims for the same service or procedure, resulting in duplicate charges. Insurance companies have systems in place to detect and reject duplicate claims to prevent overbilling. Providers should ensure that they have proper checks and balances in place to prevent duplicate billing. Regular audits of billing practices can help identify any potential duplicates and rectify the issue before the claim is denied.
To prevent duplicate billing denials, providers should implement effective billing and claims management systems that can detect and prevent duplicate submissions. Clear communication within the billing department is essential to avoid inadvertent duplicate submissions. Well-documented procedures and protocols for billing can also help prevent errors that may lead to duplicate billing denials.
Service Not Authorized Denials
Service not authorized denials occur when a claim is denied because the insurance company did not authorize or approve the service or procedure. Providers must obtain proper authorization or pre-authorization from the insurance company before rendering the service to avoid service not authorized denials. Failure to obtain authorization can leave the provider responsible for the charges.
To prevent service not authorized denials, providers should familiarize themselves with each insurance company’s specific authorization requirements. They should also ensure that all necessary documentation, such as medical records or supporting documents, is submitted with the authorization request. Clear communication between the provider and the insurance company is crucial to avoid any misunderstandings or delays in obtaining authorization.
Expired Time Limit Denials
Expired time limit denials occur when a claim is denied due to submission beyond the designated timeframe specified by the insurance company. Insurance companies typically have strict guidelines regarding the submission of claims, and failure to comply with these guidelines can result in denials. Providers should familiarize themselves with the claim submission deadlines of each insurance company to ensure timely submission.
To prevent expired time limit denials, providers should establish efficient and well-organized billing processes that prioritize timely claim submission. Clear communication between the billing department and the healthcare providers is essential to ensure that all necessary documentation and codes are collected in a timely manner. Regular monitoring and tracking of claim submissions can help identify any potential delays and address them promptly.
Internal Denials

Coding Errors Denials
Coding errors denials occur when there are errors or inconsistencies in the codes used on the claim form within the provider’s own coding processes. These errors can result from incorrect coding practices, lack of training, or underutilization of coding resources. Providers must ensure that their coding practices follow the industry-standard guidelines and accurately reflect the services provided.
To prevent coding errors denials, providers should invest in regular training and education for their coding staff to ensure accurate coding practices. The use of comprehensive coding manuals and coding software can also help minimize coding errors. Regular audits of coding practices can assist in identifying any potential errors and provide opportunities for education and improvement.
Lack of Documentation Denials
Lack of documentation denials within the provider’s organization occur when there is insufficient or incomplete documentation to support the services or procedures billed on the claim form. Providers rely on accurate and comprehensive medical records to determine the validity and medical necessity of the services provided. Insufficient documentation can result in internal denials, creating financial losses for the organization.
To prevent lack of documentation denials within the provider’s organization, providers should implement robust documentation practices that ensure all necessary information to support the services provided is recorded accurately. Clear and detailed documentation should include the patient’s medical history, examination findings, treatment plans, and the rationale for the services provided. Regular training and education for medical and billing staff on documentation requirements can help minimize deficiencies in documentation.
Miscommunication Denials
Miscommunication denials occur when there is a breakdown in communication between different departments or individuals within the provider’s organization, leading to errors or inconsistencies in claim submission or billing processes. Clear and effective communication is vital to ensure accurate and timely claim processing. Regular staff meetings and collaboration can help minimize miscommunication denials.
To prevent miscommunication denials, providers should establish clear lines of communication and protocols for interdepartmental collaboration and information sharing. Regular staff meetings, training sessions, and updates on billing and claims processes can help ensure that everyone involved in the claims management process is on the same page. Clear escalation protocols and designated points of contact can help address and resolve any miscommunication issues promptly.
Incomplete Claim Denials
Incomplete claim denials occur when a claim is denied due to missing or incomplete information on the claim form within the provider’s organization. Insurance companies have specific guidelines and requirements for claim submission, and failure to adhere to these guidelines can result in denials. Providers should thoroughly review claim submission processes and ensure compliance with the insurance company’s requirements.
To prevent incomplete claim denials within the provider’s organization, providers should establish clear protocols and procedures for claim submission that cover all necessary requirements. Regular staff training and education on claim submission guidelines can help minimize errors. Thorough reviews of claim documentation before submission can also help identify any missing or incomplete information and rectify it promptly.
Coordination of Benefits Denials
Coordination of benefits denials within the provider’s organization occur when there is a failure to properly coordinate benefits for patients with multiple insurance coverages. This can be a result of errors in updating patient insurance information or a lack of clear communication between the patient, provider, and insurance companies. Providers must ensure that accurate and up-to-date insurance information is obtained from the patient and that all relevant insurance companies are properly notified.
To prevent coordination of benefits denials within the provider’s organization, providers should have a clear understanding of the patient’s insurance coverage and coordination of benefits requirements. Verification of insurance information should be conducted at each visit to ensure accurate billing. Establishing effective communication channels with patients and insurance companies can help minimize errors and prevent coordination of benefits denials.
External Denials

Inadequate Insurance Coverage Denials
Inadequate insurance coverage denials occur when a patient’s insurance policy does not provide sufficient coverage for the services rendered by the provider. This can include limitations on specific services or procedures, low coverage limits, or exclusions for certain types of treatments or conditions. Providers should verify the patient’s insurance coverage and ensure that the services provided are within the covered benefits.
To prevent inadequate insurance coverage denials, providers should thoroughly review the patient’s insurance policy and coverage before rendering services. Clear communication with the patient about their insurance coverage and financial responsibilities is essential to manage expectations and minimize inadequate coverage denials. In cases where there is uncertainty regarding coverage, obtaining a pre-authorization or predetermination from the insurance company can help clarify any potential coverage issues.
Authorization Denials
Authorization denials occur when a provider submits a claim for services or procedures that require prior authorization, but the insurance company denies the authorization request. Verification of authorization requirements and obtaining proper authorization from the insurance company before rendering services is crucial to avoid authorization denials. Failure to obtain authorization can leave the provider responsible for the charges.
To prevent authorization denials, providers should familiarize themselves with each insurance company’s specific requirements for authorization. They should also ensure that all necessary documentation, such as medical records or supporting documents, is submitted with the authorization request. Clear communication between the provider and the insurance company is crucial to avoid any misunderstandings or delays in obtaining authorization.
Medical Necessity Denials
Medical necessity denials occur when a service or procedure rendered to a patient is deemed not medically necessary by the insurance company. Insurance companies use medical guidelines and criteria to determine what they consider medically necessary. If a service or procedure does not meet these criteria, the insurance company may deny the claim, leaving the provider responsible for the charges.
To prevent medical necessity denials, providers should thoroughly document the patient’s medical condition and the need for the service or procedure. It is crucial to provide clear and concise documentation that supports the medical necessity of the claim. Providers should also familiarize themselves with the medical policies and guidelines of the insurance companies they work with to ensure that the services they provide align with the insurers’ criteria.
Incorrect Patient Information Denials
Incorrect patient information denials occur when patient information, such as name, date of birth, or insurance information, is entered inaccurately or incompletely on the claim form. Insurance companies rely on accurate patient information for claim processing, and discrepancies or errors can result in denials. Providers should ensure that they obtain and verify accurate patient information for each claim submission.
To prevent incorrect patient information denials, providers should implement robust patient registration and verification processes that capture accurate patient information. Regular staff training and education on the importance of accurate patient information can help minimize errors. Verification of patient demographics and insurance information at each visit can help ensure that accurate information is collected for claim submission.
Non-Covered Service Denials
Non-covered service denials occur when a service or procedure rendered to a patient is not covered under the patient’s insurance policy. Insurance companies have specific coverage policies that outline what services, procedures, or treatments they consider covered. Providers should verify the patient’s coverage and eligibility for specific services before rendering them.
To prevent non-covered service denials, providers should have a clear understanding of the insurance policies they work with and their coverage criteria. Clear communication with the patient is essential to ensure that they understand what services are covered under their insurance policy and what may be considered non-covered. When there is uncertainty regarding coverage, obtaining a predetermination or prior authorization from the insurance company can help clarify any potential coverage issues.
Reason Denials

Pre-Authorization Denials
Pre-authorization denials occur when a provider submits a claim for services or procedures that require pre-authorization, but the insurance company denies the authorization request. Verification of pre-authorization requirements and obtaining proper pre-authorization from the insurance company before rendering services is crucial to avoid pre-authorization denials. Failure to obtain pre-authorization can leave the provider responsible for the charges.
To prevent pre-authorization denials, providers should familiarize themselves with each insurance company’s specific requirements for pre-authorization. They should also ensure that all necessary documentation, such as medical records or supporting documents, is submitted with the pre-authorization request. Clear communication between the provider and the insurance company is crucial to avoid any misunderstandings or delays in obtaining pre-authorization.
Invalid Diagnosis Denials
Invalid diagnosis denials occur when the diagnosis reported on the claim form is deemed incorrect or invalid by the insurance company. Insurance companies have specific guidelines and criteria for valid diagnoses, and discrepancies or errors can result in denials. Providers should ensure that their coding accurately reflects the patient’s diagnosis and matches the required criteria of the insurance company.
To prevent invalid diagnosis denials, providers should invest in regular training and education for their coding staff to ensure accurate coding practices. The use of comprehensive coding manuals and software that includes coding tips and guidelines can also help minimize errors. Regular audits of coding practices can assist in identifying any potential invalid diagnosis issues and rectify them promptly.
Procedure Not Covered Denials
Procedure not covered denials occur when a procedure or service rendered to a patient is not covered under the patient’s insurance policy. Insurance companies have specific coverage policies that outline what services, procedures, or treatments they consider covered, and discrepancies or errors can result in denials. Providers should verify the patient’s coverage and eligibility for specific procedures before rendering them.
To prevent procedure not covered denials, providers should familiarize themselves with the insurance policies they work with and their coverage criteria. Clear communication with the patient is essential to ensure that they understand what procedures are covered under their insurance policy. When there is uncertainty regarding coverage, obtaining a predetermination or prior authorization from the insurance company can help clarify any potential coverage issues.
Exceeded Benefit Limit Denials
Exceeded benefit limit denials occur when a patient’s insurance coverage has reached its limit or maximum benefit for a specific service or procedure. Insurance policies often have limits on coverage amounts, such as annual maximums or visit limits for certain services. Providers should verify the patient’s coverage and ensure that the services provided are within the allowed limits to avoid exceeded benefit limit denials.
To prevent exceeded benefit limit denials, providers should thoroughly review the patient’s insurance policy and coverage before rendering services. Clear communication with the patient about their coverage and financial responsibilities is essential to manage expectations and minimize exceeded benefit limit denials. In cases where there is uncertainty regarding coverage, obtaining a pre-authorization or predetermination from the insurance company can help clarify any potential coverage issues.
Lack of Medical Necessity Denials
Lack of medical necessity denials occur when there is insufficient documentation or evidence to support the medical necessity of the services provided. Insurance companies rely on accurate and comprehensive medical records to determine the validity and medical necessity of the services provided, and deficiencies in documentation can lead to denials.
To prevent lack of medical necessity denials, providers should implement robust documentation practices that capture all necessary information to support the services provided. Clear and detailed documentation should include the patient’s medical history, examination findings, treatment plans, and the rationale for the services provided. Thorough training and education for medical and billing staff on documentation requirements can help minimize deficiencies in documentation.
Documentation Denials

Incomplete Documentation Denials
Incomplete documentation denials occur when there is insufficient or incomplete documentation to support the services or procedures billed on the claim form. Insurance companies rely on accurate and comprehensive medical records to determine the validity and medical necessity of the services provided. Insufficient documentation can result in denials, leaving the provider responsible for the charges.
To prevent incomplete documentation denials, providers should implement robust documentation practices that capture all necessary information to support the services provided. Clear and detailed documentation should include the patient’s medical history, examination findings, treatment plans, and the rationale for the services provided. Regular training and education for medical and billing staff on documentation requirements can help minimize deficiencies in documentation.
Lack of Medical Necessity Documentation Denials
Lack of medical necessity documentation denials occur when there is insufficient documentation or evidence to support the medical necessity of the services provided. Insurance companies rely on accurate and comprehensive medical records to determine the validity and medical necessity of the services provided, and deficiencies in documentation can lead to denials.
To prevent lack of medical necessity documentation denials, providers should implement robust documentation practices that capture all necessary information to support the services provided. Clear and detailed documentation should include the patient’s medical history, examination findings, treatment plans, and the rationale for the services provided. Thorough training and education for medical and billing staff on documentation requirements can help minimize deficiencies in documentation.
Missing Prior Authorization Denials
Missing prior authorization denials occur when a claim is denied because the insurance company did not receive the necessary prior authorization for the services or procedures rendered. Verification of prior authorization requirements and obtaining proper authorization from the insurance company before rendering services is crucial to avoid missing prior authorization denials. Failure to obtain prior authorization can leave the provider responsible for the charges.
To prevent missing prior authorization denials, providers should familiarize themselves with each insurance company’s specific requirements for prior authorization. They should also ensure that all necessary documentation, such as medical records or supporting documents, is submitted with the prior authorization request. Clear communication between the provider and the insurance company is crucial to avoid any misunderstandings or delays in obtaining prior authorization.
Insufficient Documentation Denials
Insufficient documentation denials occur when there is a lack of adequate supporting documentation to substantiate the services or procedures billed on the claim form. Insurance companies rely on accurate and comprehensive medical records to determine the validity and medical necessity of the services provided, and deficiencies in documentation can lead to denials.
To prevent insufficient documentation denials, providers should implement robust documentation practices that capture all necessary information to support the services provided. Clear and detailed documentation should include the patient’s medical history, examination findings, treatment plans, and the rationale for the services provided. Regular training and education for medical and billing staff on documentation requirements can help minimize deficiencies in documentation.
Unreadable Documentation Denials
Unreadable documentation denials occur when the documentation submitted with the claim is illegible or cannot be easily read or understood by the insurance company. Clear and legible documentation is essential for accurate claims processing and to avoid denials. Providers should ensure that all documentation submitted is easily readable and understandable.
To prevent unreadable documentation denials, providers should establish clear documentation guidelines and standards for the organization. Training and education for medical and billing staff on the importance of legible and clear documentation can help minimize errors. Regular audits of documentation practices can assist in identifying any potential issues with the readability of documentation and rectify them promptly.
Coding Denials

Incorrect CPT Code Denials
Incorrect CPT code denials occur when there are errors or inconsistencies in the current procedural terminology (CPT) codes used on the claim form. Incorrect coding can result from errors in selecting the appropriate code, using outdated codes, or misinterpretation of the documentation. Insurance companies rely on accurate coding to determine reimbursement and discrepancies or errors can result in denials.
To prevent incorrect CPT code denials, providers should invest in regular training and education for their coding staff to ensure accurate coding practices. The use of comprehensive coding manuals and coding software can also help minimize coding errors. Regular audits of coding practices can assist in identifying any potential incorrect CPT code issues and rectify them promptly.
Incorrect ICD-10 Code Denials
Incorrect ICD-10 code denials occur when there are errors or inconsistencies in the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) codes used on the claim form. Incorrect coding can result from errors in selecting the appropriate code, using outdated codes, or misinterpretation of the documentation. Insurance companies rely on accurate coding to determine reimbursement and discrepancies or errors can result in denials.
To prevent incorrect ICD-10 code denials, providers should invest in regular training and education for their coding staff to ensure accurate coding practices. The use of comprehensive coding manuals and coding software can also help minimize coding errors. Regular audits of coding practices can assist in identifying any potential incorrect ICD-10 code issues and rectify them promptly.
Upcoding Denials
Upcoding denials occur when a provider submits a claim using codes that represent a higher level of service than what was actually provided. This can be an intentional or unintentional error and can result in increased reimbursement. Upcoding is considered fraudulent and can lead to severe consequences, including legal and financial penalties. Providers must ensure that their coding accurately reflects the services provided.
To prevent upcoding denials, providers should invest in regular training and education for their coding staff to ensure accurate coding practices. The use of comprehensive coding manuals and coding software can also help minimize upcoding errors. Regular audits of coding practices can assist in identifying any potential upcoding issues and rectify them promptly.
Unbundling Denials
Unbundling denials occur when a provider bills for separate services or procedures that should be billed together under a single code. Insurance companies have specific guidelines for bundling services, and failing to adhere to these guidelines can result in denials. Providers must ensure that their billing practices reflect accurate bundling of services.
To prevent unbundling denials, providers should familiarize themselves with the bundling rules and guidelines of the insurance companies they work with. It is essential to accurately code and bill for services based on the bundling rules, ensuring that services that should be bundled are not billed and charged separately. Regular reviews of billing practices and audits can help identify any potential unbundling issues and rectify them promptly.
Modifier Errors Denials
Modifier errors denials occur when there are errors or inconsistencies in the modifiers used on the claim form. Modifiers provide additional information about the services provided and can affect reimbursement. Incorrect or missing modifiers can result in denials or reduced reimbursement. Providers must ensure that modifiers are used accurately and appropriately.
To prevent modifier errors denials, providers should invest in regular training and education for their coding staff to ensure accurate use of modifiers. The use of comprehensive coding manuals and coding software can also help minimize modifier errors. Regular audits of coding practices can assist in identifying any potential modifier issues and rectify them promptly.
Reimbursement Denials

Fee Schedule Denials
Fee schedule denials occur when a provider’s billed amount exceeds the maximum allowable amount set by the insurance company’s fee schedule. Insurance companies negotiate fee schedules with providers, determining the maximum reimbursement amount for each service or procedure. Providers should be aware of the fee schedule rates for each insurance company to manage their revenue expectations accurately.
To mitigate fee schedule denials, providers can consider negotiating favorable contracts with insurance companies or participating in preferred provider networks. They can also implement sound financial policies that include clear communication to patients about their financial responsibilities, such as co-pays or deductibles. Understanding the fee schedules and reimbursement rates of each insurance company is crucial for accurate billing and reimbursement.
Out of Network Denials
Out of network denials occur when a provider does not have a contractual agreement with an insurance company, resulting in reduced reimbursement or denial of the claim altogether. Providers who are out of network for a particular insurance company may face challenges in obtaining full reimbursement and may need to negotiate separate agreements or contracts to ensure fair reimbursement.
To address out of network denials, providers can consider negotiating contracts with insurance companies to be included in their network. This can help ensure fair reimbursement for services provided. Effective communication with patients about their insurance coverage and financial responsibilities is crucial to manage expectations and minimize out of network denials.
Maximum Benefit Reached Denials
Maximum benefit reached denials occur when a patient’s insurance coverage has reached its maximum benefit or limit for a specific service or procedure. Insurance policies often have limits on coverage amounts, such as annual maximums or visit limits for certain services. Providers should verify the patient’s coverage and ensure that the services provided are within the allowed limits to avoid maximum benefit reached denials.
To prevent maximum benefit reached denials, providers should thoroughly review the patient’s insurance policy and coverage before rendering services. Clear communication with the patient about their coverage and financial responsibilities is essential to manage expectations and minimize maximum benefit reached denials. In cases where there is uncertainty regarding coverage, obtaining a pre-authorization or predetermination from the insurance company can help clarify any potential coverage issues.
Managed Care Denials
Managed care denials occur when a provider submits a claim to a managed care organization (MCO) that does not have a contract or agreement with the provider. Managed care organizations typically require providers to have a contract and participate in their network to ensure proper reimbursement. Providers should verify their participation status with the MCO and establish contractual agreements if necessary.
To prevent managed care denials, providers should verify their participation status with each managed care organization they work with. Clear communication with the patient about their insurance coverage and financial responsibilities is essential to manage expectations and minimize managed care denials. Negotiating contracts or agreements with managed care organizations can ensure proper reimbursement and reduced denials.
Billing Errors Denials
Billing errors denials occur when there are errors or inconsistencies in the billing processes, such as inaccurate coding, incorrect patient information, or lack of proper documentation. These errors can result in denials or delays in reimbursement. Providers should establish robust billing processes that prioritize accuracy and adherence to billing guidelines.
To prevent billing errors denials, providers should invest in regular training and education for their billing staff to ensure accurate billing practices. The use of comprehensive billing software or systems that can validate claims before submission can help identify and correct errors. Regular audits of billing processes can assist in identifying any potential billing errors and rectify them promptly.
In conclusion, there are various types of denials in medical billing, each with its unique reasons and challenges. Providers must understand the different denial types, establish robust processes and protocols, and invest in staff training and education to reduce denials and improve revenue cycle management. By addressing each denial type and implementing proactive strategies, providers can strive for optimal reimbursement and minimize financial losses.