In the field of healthcare, medical codes play a crucial role in accurately documenting and classifying various aspects of patient care. These codes not only assist in streamlining administrative processes but also ensure consistency in healthcare data management. With the aim of providing a comprehensive understanding of this important system, this article explores the different types of medical codes used in the medical industry. By delving into the world of medical coding, you will gain insights into the diverse classification systems employed to categorize diagnoses, procedures, medications, and more.
Introduction
Medical coding is an essential component of the healthcare industry. It involves the use of standardized codes to classify and categorize medical diagnoses, procedures, and services. These codes serve various purposes, including billing and reimbursement, medical research, and healthcare planning. In this article, we will delve into the different types of medical codes and explore their purpose, structure, and usage.
Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) Codes

Overview
CPT codes, developed and maintained by the American Medical Association (AMA), are used to describe medical procedures and services provided by healthcare professionals. These codes provide a uniform language that facilitates accurate reporting and billing for healthcare services.
Purpose
The primary purpose of CPT codes is to ensure proper documentation and accurate reimbursement for medical services. These codes are essential for billing purposes, as they allow healthcare providers to communicate the specific procedures performed during a patient’s visit to insurance companies and government agencies. CPT codes also aid in tracking and analyzing medical procedures for research and quality improvement purposes.
Structure
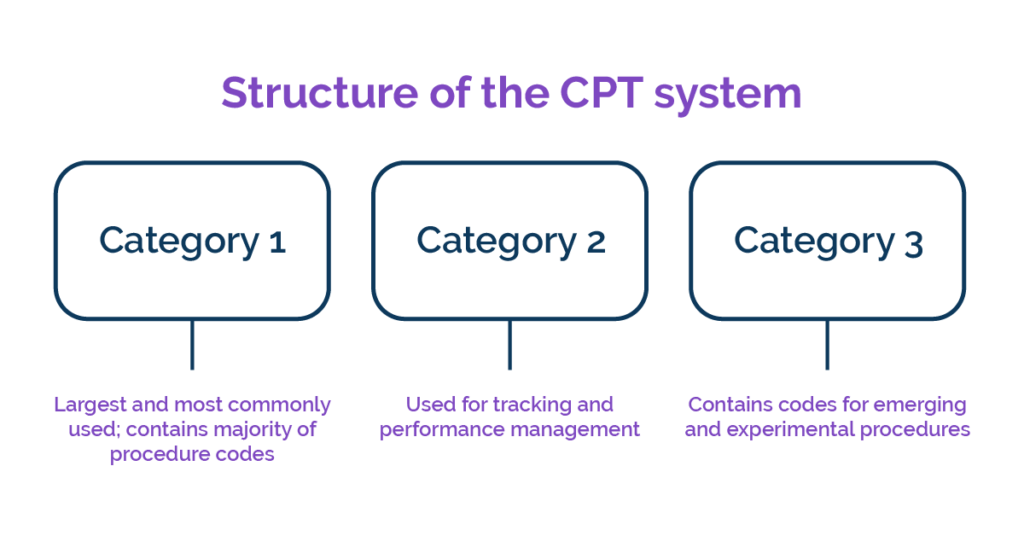
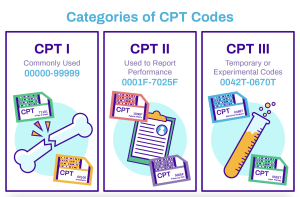
CPT codes are five-digit numeric codes that represent specific healthcare procedures or services. They are organized into three categories: Category I, Category II, and Category III. Category I codes cover common procedures and services, while Category II codes are used to track performance measures. Category III codes are temporary codes for emerging technologies, services, and procedures.
Usage
CPT codes are widely used by healthcare professionals, including physicians, surgeons, and other providers. These codes are essential for accurate billing and reimbursement, insurance claims processing, and tracking medical procedures for statistical and research purposes.
International Classification of Diseases (ICD) Codes
This image is property of www.medicalcodingbuff.com.
Overview
The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) is a system used for classifying diseases, injuries, and other health conditions. It provides a common language for health information and enables consistent reporting and analysis of health data.
Purpose
ICD codes are primarily used for clinical purposes, including diagnosis, treatment, and research. These codes allow healthcare professionals to accurately document and communicate the patient’s condition, facilitating proper treatment and care coordination. ICD codes also play a crucial role in healthcare management, epidemiology, and public health.
Structure
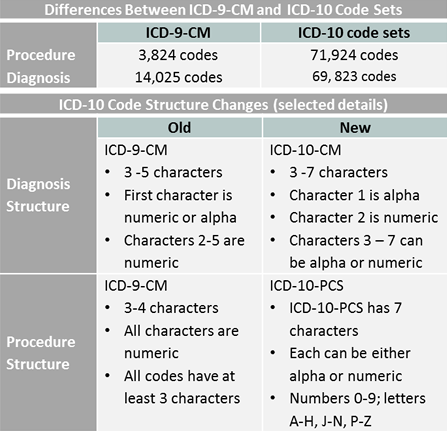
ICD codes follow a hierarchical structure and are organized into chapters, sections, and categories. The current version, ICD-10, has more than 70,000 diagnostic codes. Each code is alphanumeric and consists of three to seven characters, which represent different levels of specificity and detail about a particular condition or diagnosis.
Usage
ICD codes are used by healthcare providers, clinical coders, and other stakeholders in the healthcare system. These codes are essential for accurate diagnosis documentation, billing, and reimbursement purposes. They are also used for healthcare planning, public health monitoring, and epidemiological research.
Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) Codes

Overview
The Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) is a mechanism for coding healthcare services, procedures, and supplies. It is used primarily in the United States for Medicare, Medicaid, and other insurance programs.
Purpose
HCPCS codes serve a similar purpose to CPT codes, but they cover a broader range of services, including durable medical equipment, drugs, and supplies. These codes enable accurate billing and reimbursement for healthcare services provided to Medicare and Medicaid beneficiaries.
Structure
HCPCS codes are alphanumeric and consist of a single letter followed by four digits. They are organized into two levels: Level I and Level II. Level I codes are the same as CPT codes and represent procedures and services provided by physicians and other healthcare professionals. Level II codes, on the other hand, cover items and services not included in CPT.
Usage
HCPCS codes are primarily used by healthcare providers and suppliers who bill Medicare and Medicaid for their services. These codes are crucial for accurate billing, reimbursement, and claims processing. They also assist in monitoring and evaluating the utilization and cost of healthcare services.
Diagnosis-Related Group (DRG) Codes
Overview
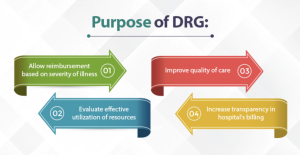
Diagnosis-Related Group (DRG) codes are a classification system used to categorize patients’ hospital stays into groups with similar clinical characteristics and resource requirements. This grouping enables efficient payment systems and provides a basis for comparing healthcare providers’ performance.
Purpose
DRG codes are primarily used for hospital reimbursement purposes. They help determine the appropriate payment for inpatient services based on the specific diagnosis, procedures performed, patient demographics, and other relevant factors. DRGs also serve as a tool for comparing the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare providers.
Structure
DRG codes are numeric and consist of a three-digit number. They are divided into several major diagnostic categories (MDCs) based on the organ system or medical condition. Each MDC is further divided into multiple DRGs, which are based on various factors such as the principal diagnosis, associated procedures, and patient demographic information.
Usage
DRG codes are primarily used by hospitals, health insurance companies, and government agencies responsible for healthcare reimbursement. These codes play a crucial role in determining the appropriate payment for inpatient services and comparing hospitals’ performance. DRGs also facilitate research and analysis of patient outcomes and resource utilization.
National Drug Codes (NDC)

Overview
National Drug Codes (NDCs) are unique identifiers for prescription and over-the-counter drugs. They provide a standardized system for tracking and cataloging medications, ensuring accurate identification, and supporting the safe and efficient distribution of pharmaceutical products.
Purpose
NDC codes are primarily used for drug identification, billing, and reimbursement purposes. They assist healthcare providers in accurately prescribing and dispensing medications and enable pharmacy claims processing by insurance companies. NDCs also facilitate medication monitoring, adverse event reporting, and drug utilization review.
Structure
NDC codes are alphanumeric and consist of three segments: the labeler code, the product code, and the package code. The labeler code identifies the manufacturer or distributor, the product code represents the specific drug formulation, and the package code indicates the package size and type.
Usage
NDC codes are used by healthcare professionals, pharmacies, health insurance companies, and government agencies involved in the regulation and oversight of pharmaceutical products. These codes ensure accurate identification and tracking of medications, facilitate reimbursement and claims processing, and support medication safety and monitoring efforts.
Revenue Codes

Overview
Revenue codes are used to classify and categorize various services and items provided by hospitals and other healthcare facilities. These codes play a crucial role in billing and reimbursement, as they indicate the specific department or service from which the revenue is derived.
Purpose
The primary purpose of revenue codes is to facilitate accurate billing and reimbursement for hospital services. These codes help healthcare providers and insurance companies identify the specific services or items for which reimbursement is sought. Revenue codes also provide a basis for financial analysis and cost accounting in healthcare organizations.
Structure
Revenue codes are three-digit numeric codes that represent specific departments or services within a healthcare facility. They are often used in conjunction with other billing codes, such as CPT or HCPCS codes, to provide a comprehensive description of the services rendered.
Usage
Revenue codes are primarily used by hospitals and other healthcare facilities for billing and reimbursement purposes. These codes are essential for accurate claims processing and payment, as they indicate the department or service from which the revenue is generated. Revenue codes also play a role in financial reporting, cost analysis, and budgeting within healthcare organizations.
Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System-Modifiers (HCPCS-M) Codes
HCPCS-M codes are essential modifiers in the realm of medical coding and billing. These alphanumeric codes play a crucial role in providing specific information about healthcare procedures or services. In
Overview
HCPCS-M codes are modifiers used in conjunction with CPT or HCPCS codes to provide additional information about a healthcare procedure or service. These codes help provide more specific details regarding the circumstances or conditions under which the procedure was performed.
Purpose
The purpose of HCPCS-M codes is to ensure accurate billing and reimbursement by conveying additional information about a healthcare procedure. These codes help identify specific circumstances, such as multiple procedures performed during a single visit, unusual anesthesia circumstances, or the use of specific equipment or devices.
Structure
HCPCS-M codes are alphanumeric and consist of two letters followed by two digits. They are used as modifiers to provide supplementary information about a CPT or HCPCS code. Each HCPCS-M code represents a specific circumstance or condition relevant to the procedure or service.
Usage
HCPCS-M codes are primarily used by healthcare providers, billing and coding professionals, and insurance companies. These codes assist in accurate claims processing and reimbursement by conveying additional details about a procedure or service. HCPCS-M codes ensure that the circumstances or conditions under which the procedure was performed are accurately documented and considered for appropriate payment.
Explanation of Benefits (EOB) Codes
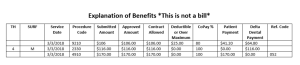
Overview
Explanation of Benefits (EOB) codes are used to provide a summary explanation of the services rendered, payments made, and any adjustments or denials related to a healthcare claim. These codes help healthcare providers and patients understand the details of the insurance claims processing and reimbursement.
Purpose
The primary purpose of EOB codes is to provide a clear and concise explanation of the reimbursement decisions and adjustments made by insurance companies. These codes help ensure transparency and understanding between the healthcare provider, the patient, and the insurance company regarding the claim outcome.
Structure
EOB codes are alphanumeric and can vary depending on the insurance company or healthcare payer. They are typically used in conjunction with other codes, such as CPT or HCPCS codes, to provide a comprehensive explanation of the reimbursement decision and any adjustments or denials.
Usage
EOB codes are used by insurance companies to communicate the outcome of a healthcare claim to the healthcare provider and the patient. These codes provide a summary explanation of the reimbursement decisions, payments, and any adjustments or denials made. EOB codes help ensure transparency and facilitate communication between all parties involved in the claims process.
Prescription Codes

Overview
Prescription codes, also known as Rx codes, are used to identify and classify prescription medications. These codes help ensure accurate and consistent prescribing, dispensing, and use of medications across healthcare settings.
Purpose
Prescription codes serve multiple purposes, including medication identification, prescription processing, and claims adjudication. These codes help healthcare providers accurately prescribe medications by ensuring the correct medication, dose, quantity, and instructions are communicated. Prescription codes also facilitate claims processing by insurance companies and support medication safety and monitoring efforts.
Structure
Prescription codes can vary depending on the country and healthcare system. They may include a combination of alphanumeric characters or may be based on standardized drug codes such as the National Drug Codes (NDC). These codes typically provide information about the medication name, strength, dosage form, and other relevant details.
Usage
Prescription codes are used by healthcare providers, pharmacies, insurance companies, and regulatory agencies involved in the prescribing, dispensing, and monitoring of medications. These codes ensure accurate identification and communication of medications, support claims processing, and aid in medication safety and monitoring efforts. Prescription codes are crucial for preserving patient safety and preventing medication errors.
In conclusion, medical coding plays a vital role in the healthcare industry by providing a standardized language for classifying and categorizing medical diagnoses, procedures, and services. The different types of medical codes discussed in this article, including CPT codes, ICD codes, HCPCS codes, DRG codes, NDCs, revenue codes, HCPCS-M codes, EOB codes, and prescription codes, serve various purposes in billing, reimbursement, clinical documentation, research, and healthcare management. Understanding these codes and their usage is essential for accurate documentation, effective communication, and efficient healthcare delivery.