In the realm of healthcare, clinical coders play a vital role in decoding the language of medicine and ensuring accurate and consistent documentation. With meticulous attention to detail, they meticulously analyze medical records, decipher complex diagnoses and procedures, and assign standardized codes to each entry. This process not only facilitates efficient data management but also enables healthcare providers and organizations to deliver optimal patient care, streamline billing processes, and contribute to important health research. So, what exactly does a clinical coder do? Let’s explore their responsibilities and the impact they have in the healthcare industry.
This image is property of static.wixstatic.com.
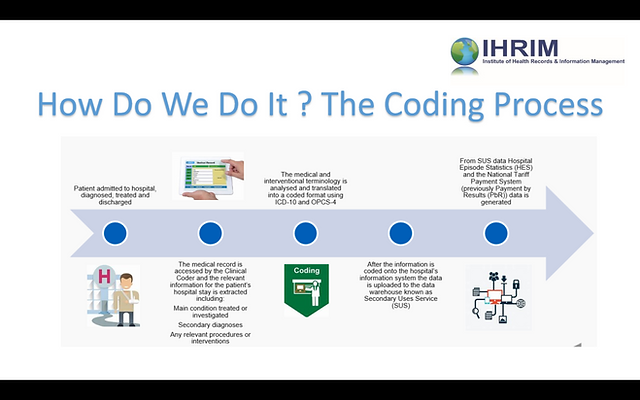
Overview of Clinical Coders
Clinical coders play an integral role in the healthcare industry. They are responsible for translating medical information into standardized codes, ensuring accurate documentation and data collection. This article will provide an in-depth look at the role and responsibilities of clinical coders, the importance of accurate coding, the qualifications and skills required for this profession, certifications and education options, work environment, advancement opportunities, challenges faced, and the future outlook for clinical coders.
Role of Clinical Coders in Healthcare

Data Collection
One of the primary roles of clinical coders is data collection. They are responsible for accurately documenting and coding various medical procedures, diagnoses, and treatments. These codes are used for statistical analysis, research, and reimbursement purposes. By ensuring the accuracy and consistency of coded data, clinical coders contribute to the overall quality of healthcare delivery.
Responsibilities of Clinical Coders
Clinical coders play a crucial role in the healthcare industry, ensuring that medical records are accurately translated into standardized codes.
Assigning Medical Codes
The core responsibility of clinical coders is assigning appropriate medical codes to the provided documentation. These codes, such as the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) or Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes, are standardized and universally recognized. The coding process involves carefully reviewing medical records, identifying relevant information, and selecting the appropriate codes that accurately represent the diagnoses, procedures, and treatments provided to the patients.
Reviewing Medical Documentation
Clinical coders work closely with healthcare professionals to review and interpret medical documents. They analyze physicians’ notes, laboratory reports, diagnostic imaging results, and other relevant information to ensure accurate coding. This collaboration with healthcare providers helps ensure that the coding reflects the medical services accurately, leading to correct billing, reimbursement, and quality assurance.
Collaborating with Healthcare Professionals
Clinical coders often collaborate with physicians, nurses, laboratory technicians, and other healthcare professionals to obtain clarification on medical documentation and codes. This collaboration helps address any discrepancies, improve coding accuracy, and ensures that the coded data aligns with the actual medical services provided. Effective communication and a strong understanding of medical terminologies are crucial for productive collaboration in this role.
Importance of Accurate Coding

Quality Assurance
Accurate coding is of paramount importance for maintaining high-quality healthcare standards. Properly coded data allows for accurate tracking of medical conditions, procedures, and treatments. This information is vital for measuring healthcare outcomes, identifying trends, monitoring public health concerns, and facilitating evidence-based decision making. Clinical coders play a vital role in ensuring the accuracy and integrity of coded data, thus contributing to the overall quality assurance in healthcare.
Billing and Reimbursement
Accurate coding also has significant financial implications for healthcare institutions. Proper coding ensures appropriate billing and reimbursement from insurance companies and government healthcare programs. Inaccurate coding can lead to claim denials or underpayment, negatively impacting the financial stability of healthcare providers. Clinical coders play a crucial role in accurately translating medical services into standardized codes to facilitate correct billing and reimbursement processes.
Qualifications and Skills for Clinical Coders
This image is property of static.wixstatic.com.
Medical Knowledge
Clinical coders must possess a strong foundation in medical knowledge. They need to have a comprehensive understanding of anatomy, physiology, and disease processes. This knowledge allows them to accurately interpret medical documentation and assign appropriate codes. Clinical coders must stay updated with the evolving medical field, including changes in coding guidelines, regulations, and advancements to ensure accurate coding practices.
Analytical Skills
Analytical skills are essential for clinical coders to effectively analyze medical documentation and identify the relevant information required for coding. They must possess the ability to critically evaluate complex medical documents, extract essential details, and link them to appropriate codes. Strong analytical skills help clinical coders navigate through vast amounts of information and make accurate coding decisions.
Attention to Detail
Attention to detail is a crucial skill for clinical coders as they deal with intricate medical documentation. They must possess a keen eye for detail to ensure accurate coding, as even a minor error in coding could have significant implications. Clinical coders must consistently maintain a high level of accuracy and precision to prevent coding errors that could potentially compromise patient care and financial outcomes.
Certifications and Education

Certified Coding Specialist (CCS)
One of the recognized certifications for clinical coders is the Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) credential offered by the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA). This certification demonstrates proficiency in medical coding and validates the coder’s knowledge and skills. Obtaining the CCS credential requires passing a rigorous examination and meeting specific education and work experience requirements, ensuring that certified coders possess the necessary expertise to perform their role effectively.
Associate’s or Bachelor’s Degree in Health Information Management
Completing an associate’s or bachelor’s degree program in Health Information Management (HIM) can provide a solid educational foundation for clinical coders. These programs cover a wide range of subjects, including medical terminology, anatomy, physiology, coding systems, and healthcare regulations. Gaining formal education in HIM equips coders with the necessary knowledge and skills to excel in their coding responsibilities. Additionally, a degree in HIM may open doors to career advancement opportunities in healthcare administration and management.
Work Environment

Hospital Settings
Clinical coders are commonly employed in hospital settings. They work within the health information management departments, collaborating with medical and administrative staff to ensure accurate coding and documentation. Hospital-based coders code a wide range of medical services, including inpatient procedures, surgical interventions, emergency room visits, and outpatient consultations.
Outpatient Clinics
Clinical coders also play a vital role in outpatient clinics. They code ambulatory care services, such as clinic visits, diagnostic testing, and minor procedures. The accurate coding of these services is essential for proper reimbursement and maintaining accurate medical records for patients. Outpatient clinical coders often work closely with physicians, nurses, and other healthcare professionals to ensure accurate coding and billing.
Health Information Management Companies
Some clinical coders find employment in health information management companies, where they work as coding specialists. These companies often provide coding services to multiple healthcare facilities, requiring a comprehensive understanding of various coding systems and guidelines. Clinical coders working in these environments must possess strong coding skills and demonstrate efficiency in coding across different healthcare settings.
Advancement Opportunities

Supervisory Roles
Clinical coders who excel in their coding responsibilities and demonstrate leadership qualities may be promoted to supervisory roles. In these positions, coders oversee a team of coders, ensuring coding accuracy, providing guidance and training, and supervising workflow. Supervisory roles bring opportunities for professional growth and advancement within the health information management field.
Health Information Management Leadership
Clinical coders also have the potential to advance into positions of leadership within the health information management field. With additional education and experience, clinical coders can pursue careers as HIM directors or managers, overseeing all aspects of health information management within healthcare organizations. These leadership roles involve strategic planning, managing information systems, ensuring compliance with regulations, and overseeing coding and documentation processes.
Consulting and Teaching
Experienced clinical coders may choose to explore consulting opportunities or transition into teaching roles. Consulting allows coders to utilize their expertise to assist healthcare organizations in improving their coding processes, ensuring compliance, and optimizing reimbursement. By sharing their knowledge and experience, clinical coders can also contribute to the education and development of future coders by teaching medical coding courses or working as instructors in educational institutions.
Challenges Faced by Clinical Coders

Evolving Medical Coding Systems
Clinical coders constantly face the challenge of keeping up with evolving medical coding systems. These systems undergo regular updates and revisions to accommodate changes in medical practices and advances in healthcare. Staying updated with these changes and maintaining coding accuracy requires continuous education and professional development to ensure compliance with coding guidelines and regulations.
Complex Medical Terminology
The use of complex medical terminology poses a significant challenge for clinical coders. Medical documentation often contains specialized language and abbreviations that can be confusing and difficult to interpret. Clinical coders must possess a strong understanding of medical terminology and the ability to decipher complex documentation to assign accurate codes. Continuous learning and familiarization with various medical specialties are vital in overcoming this challenge.
Future Outlook for Clinical Coders
Technology Advancements
The future of clinical coding is intertwined with technological advancements. Electronic health record systems, artificial intelligence, and natural language processing are transforming the way clinical coders gather and process data. As technology continues to evolve, clinical coders will need to adapt and embrace new tools and software to enhance their coding efficiency and accuracy.
Increased Demand
The demand for clinical coders is expected to grow in the coming years as the healthcare industry expands and regulations become more stringent. The accurate coding of medical services is vital for healthcare organizations to comply with regulations, monitor patient outcomes, improve quality assurance, and ensure proper reimbursement. As a result, skilled clinical coders will continue to be in high demand within hospitals, outpatient clinics, and health information management companies.
In conclusion, clinical coders play a vital role in accurately translating medical documentation into standardized codes. Their responsibilities include assigning appropriate codes, reviewing medical documentation, and collaborating with healthcare professionals. Accurate coding is essential for quality assurance and proper billing and reimbursement. Clinical coders need to possess medical knowledge, analytical skills, and attention to detail. Certification options and academic programs in health information management provide the necessary qualifications. Clinical coders work in hospital settings, outpatient clinics, and health information management companies. Advancement opportunities include supervisory roles, leadership positions, consulting, and teaching. Challenges include evolving coding systems and complex medical terminology. The future outlook for clinical coders includes technology advancements and increased demand. With their expertise and dedication, clinical coders contribute significantly to the efficient and accurate functioning of the healthcare industry.
