In the field of medical billing, understanding the intricacies of the claim cycle is paramount. Efficient and accurate claims submission is essential for healthcare providers and insurance companies alike. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of what the claim cycle entails and how it impacts the reimbursement process in medical billing. From the initial patient encounter to the final payment, every step in the claim cycle plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth operations and maximum financial reimbursement.
Overview of Medical Billing
Medical billing is the systematic process of submitting, processing, and tracking claims with health insurance companies to secure payment for healthcare services rendered by healthcare professionals or facilities. It involves a series of administrative and financial activities aimed at accurately documenting and invoicing for medical treatments, procedures, and consultations. The goal of medical billing is to ensure healthcare providers receive rightful compensation for the services they provide.
Definition of Medical Billing
medical billing is the process of submitting and following up on claims with health insurance companies in order to receive payment for services provided by healthcare professionals. It involves various steps and components that work together to ensure accurate and timely reimbursement.
Importance of Medical Billing
Medical billing is a critical aspect of the healthcare industry as it ensures that healthcare providers receive the financial compensation they are entitled to for the services they render. Without proper medical billing, healthcare providers would struggle to cover the costs of providing care, and patients may face difficulties in accessing necessary medical treatments.
Key Components of Medical Billing
Medical billing encompasses several key components that are essential for the successful management of the billing process. These components include patient registration, insurance verification, coding and documentation, claim submission, claim adjudication, payment processing, claim denial management, appeals and resubmission, follow-up and collection, and reporting and analysis. Each of these components plays a crucial role in the claim cycle and contributes to the overall efficiency of medical billing processes.
Understanding the Claim Cycle
It is a comprehensive process that begins when a patient receives medical services and extends through the submission, review, adjudication, and final resolution of a healthcare insurance claim. It encompasses all the stages and activities involved in the billing and reimbursement process, from initial service provision to the receipt of payment or claim denial by the insurance company.
Definition of Claim Cycle
The claim cycle refers to the entire process starting from the point a patient receives medical services to the final settlement of the claim by the insurance company. It is a systematic flow of steps that healthcare providers and medical billing professionals follow to ensure accurate and timely reimbursement for the services provided.
Role of Claim Cycle in Medical Billing
The claim cycle is of utmost importance in medical billing as it outlines the necessary steps and procedures that need to be followed to maximize reimbursements and minimize claim denials. It helps streamline the billing process, reduce billing errors, and ensure compliance with insurance industry guidelines.
Steps Involved in the Claim Cycle
The claim cycle consists of several sequential steps that healthcare providers and billing professionals must diligently follow. These steps include patient registration, insurance verification, coding and documentation, claim submission, claim adjudication, payment processing, claim denial management, appeals and resubmission, follow-up and collection, and reporting and analysis. Each step plays a critical role in the overall success of the claim cycle and requires careful attention and adherence to established protocols.
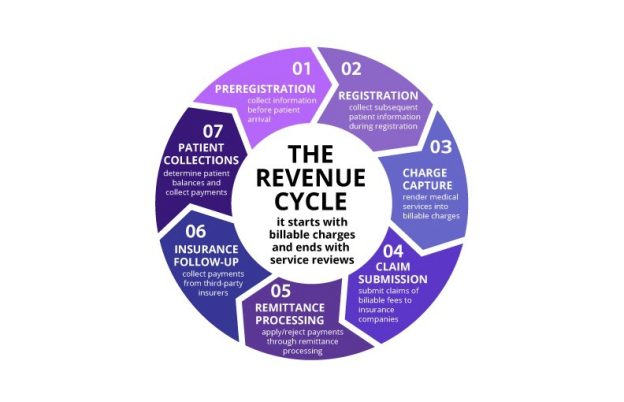
Components of the Claim Cycle
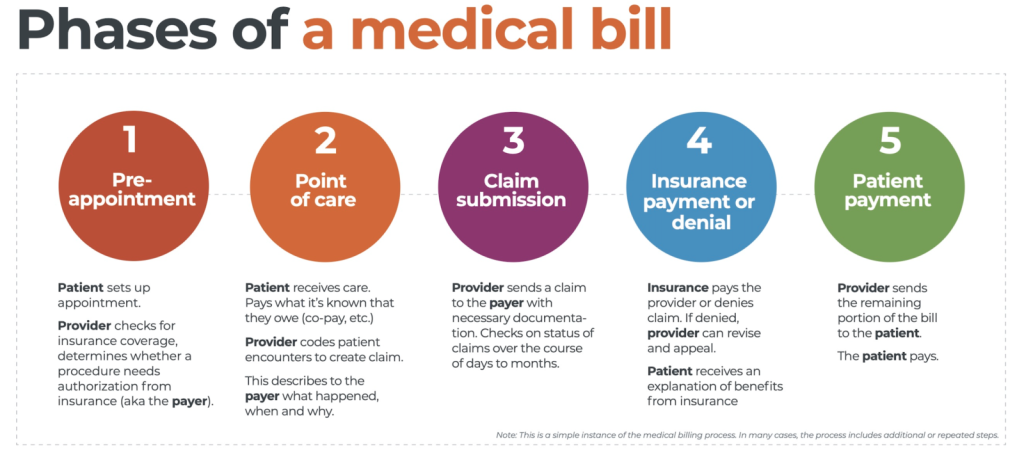
This image is property of www.waystar.com.
Patient Registration
Patient registration is the first component of the claim cycle. It involves gathering necessary information from the patient, such as demographic details, insurance information, and contact information. Accurate and complete patient registration is crucial to ensure proper identification and billing of the patient.
Insurance Verification
Insurance verification is a crucial step in the claim cycle as it determines the patient’s coverage and benefits. This step involves contacting the insurance provider to verify the patient’s insurance details, including policy number, coverage limits, deductibles, and co-pays. Verifying insurance information helps in determining the patient’s eligibility and ensures appropriate pre-authorization, if required.
Coding and Documentation
Coding and documentation play a vital role in medical billing as they involve assigning diagnosis and procedure codes to the services provided. These codes are used to communicate the specific details of the medical services to the insurance company. Accurate coding and proper documentation are essential to ensure proper reimbursement and compliance with coding guidelines and regulations.
Claim Submission
Claim submission involves preparing and formatting the claim for submission to the insurance company. The claim may be submitted electronically or through traditional paper forms, depending on the insurance provider’s requirements. Proper submission of the claim, including all necessary supporting documentation, is crucial to ensure it is processed accurately and in a timely manner.
Claim Adjudication
Claim adjudication is the process of reviewing and processing the submitted claim by the insurance company. During this step, the insurance company verifies the coverage, evaluates medical necessity, and determines the reimbursement amount. This step ensures that the claim is processed correctly and reimbursed according to the terms of the patient’s insurance policy.
Payment Processing
Payment processing involves reviewing the processed claim for accuracy and issuing reimbursement or payment to the healthcare provider. The insurance company provides an Explanation of Benefits (EOB) to explain the payment details. Payment processing ensures that healthcare providers receive the appropriate financial compensation for the services rendered.
Claim Denial Management
claim denial management involves handling and resolving claim denials or rejections. If a claim is denied, it needs to be carefully reviewed to identify the reasons for denial and take necessary action to resubmit the claim or file an appeal. Effective claim denial management helps in maximizing revenue and minimizing claim rejections.
Appeals and Resubmission
Appeals and resubmission are necessary when a claim has been denied or rejected by the insurance company. Healthcare providers can appeal the decision by submitting additional supporting documentation or clarifying any discrepancies. Resubmission ensures that the claim is reconsidered based on the updated information and increases the chances of successful reimbursement.
Follow-up and Collection
Follow-up and collection involve tracking the progress of unpaid claims and taking appropriate actions to ensure timely reimbursement. This step includes regular follow-up with insurance companies and patients to resolve any outstanding payment issues. Prompt and persistent follow-up helps in minimizing delays in payment and optimizing revenue collection.
Reporting and Analysis
Reporting and analysis play a crucial role in the claim cycle as they provide valuable insights into the financial performance and efficiency of the medical billing processes. Generating financial reports and analyzing claim metrics help identify trends, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement. This information can be used to optimize billing processes, enhance revenue generation, and improve overall financial management.
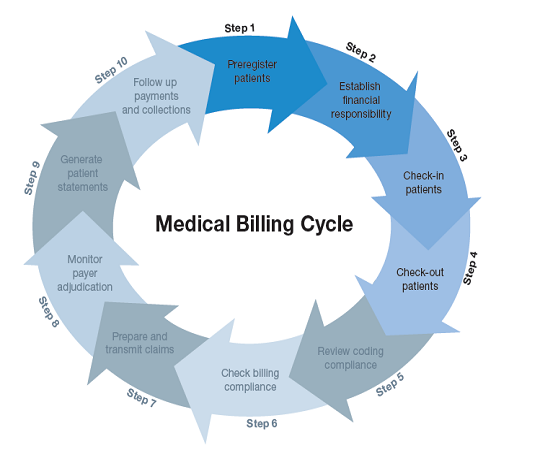
Step 1: Patient Registration

Gathering Patient Information
During the patient registration process, healthcare providers or their front desk staff gather relevant information from the patient. This includes personal details such as name, address, date of birth, contact information, and insurance information. Gathering complete and accurate patient information is essential for proper identification, billing, and communication throughout the billing process.
Creating a Patient Account
Once the patient information is collected, a patient account is created in the healthcare provider’s system. This account serves as a central repository for all the patient’s medical and billing records. The patient account includes demographic details, insurance information, medical history, and any relevant notes or remarks to ensure proper management and organization of the patient’s records.
Verifying Insurance Details
As part of the patient registration process, healthcare providers need to verify the patient’s insurance details. This involves contacting the insurance provider to confirm the patient’s coverage, benefits, and eligibility. Verifying insurance details helps determine the extent of coverage for the services provided and ensures appropriate pre-authorization, if required. Accurate insurance verification is crucial to avoid claim denials and delays in reimbursement.
Step 2: Insurance Verification

Contacting the Insurance Provider
Insurance verification involves directly contacting the patient’s insurance provider to gather all necessary information. Healthcare providers or their billing staff initiate this process by calling the insurance company’s designated department for verification purposes. This may involve providing the patient’s personal information, policy number, and any other relevant details requested by the insurance provider.
Verifying Coverage and Benefits
During the insurance verification process, healthcare providers verify the patient’s coverage and benefits. This includes determining the scope of coverage, such as inpatient or outpatient services, primary care or specialist visits, and any specific limitations or exclusions outlined in the insurance policy. Verifying coverage and benefits ensures that the provided services are eligible for reimbursement and helps in accurate claim submission.
Determining Eligibility and Pre-authorization
Insurance verification also involves determining the patient’s eligibility for medical services and any necessary pre-authorization requirements. Healthcare providers check if the patient’s insurance policy covers the specific services being provided and if any pre-authorization is required before the services can be performed. Determining eligibility and pre-authorization helps avoid claim denials due to lack of coverage or non-compliance with insurance company policies.
Step 3: Coding and Documentation

Assigning Diagnosis and Procedure Codes
Coding and documentation involve assigning specific diagnosis and procedure codes to the healthcare services provided to the patient. Diagnosis codes describe the patient’s medical condition, while procedure codes indicate the specific medical procedures performed. These codes adhere to standardized coding systems such as the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) and the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes. Accurate coding is crucial as it impacts claim reimbursement and ensures effective communication between healthcare providers and insurance companies.
Ensuring Proper Documentation
Proper documentation is a vital aspect of medical billing and coding. Healthcare providers must ensure that all necessary medical records, such as progress notes, test results, imaging reports, and treatment plans, are accurately documented and maintained. Complete and precise documentation helps support the assigned diagnosis and procedure codes, provides a clear understanding of the services rendered, and enhances the accuracy and success of the claim submission process.
Medical Necessity Verification
Medical necessity verification is an essential aspect of coding and documentation. Healthcare providers must ensure that the services provided to the patient are medically necessary, as determined by the insurance company’s guidelines. This verification involves validating that the services align with the patient’s diagnosis, symptoms, and treatment plan. Accurate medical necessity verification helps minimize claim denials and ensures compliance with insurance industry regulations.
Step 4: Claim Submission

Preparing and Formatting the Claim
Claim submission involves preparing the claim for submission to the insurance company. This includes ensuring that all necessary information, such as patient details, healthcare provider information, diagnosis and procedure codes, and supporting documentation, is accurately included in the claim. The claim is carefully reviewed to ensure its completeness and compliance with insurance industry standards.
Electronic vs. Paper Claim Submission
Healthcare providers have the option to submit claims electronically or through traditional paper forms. Electronic claim submission involves using specialized medical billing software to electronically transmit the claim to the insurance company. Paper claim submission involves printing the claim form, manually completing it, and sending it via mail to the insurance company. Electronic claim submission offers numerous advantages, including faster processing, reduced errors, and improved efficiency.
Submitting the Claim to Insurance
Once the claim is prepared and formatted according to the insurance company’s requirements, it is submitted for processing. Electronic claims are typically directly transmitted to the insurance company’s claims processing system. In the case of paper claims, they are mailed to the designated address of the insurance company. Proper submission ensures that the claim is received by the insurance company and begins the process of claim adjudication.
Step 5: Claim Adjudication

Reviewing and Processing the Claim
Claim adjudication involves the review and processing of the submitted claim by the insurance company. During this step, the insurance company examines the claim for accuracy and completeness. They verify the patient’s coverage, evaluate the medical necessity of the services provided, and determine the appropriate reimbursement amount. The claim is reviewed in line with the insurance company’s policies, procedures, and industry guidelines.
Verification of Coverage
During the claim adjudication process, the insurance company verifies the patient’s coverage to determine if the services provided are within the scope of the insurance policy. This involves confirming the eligibility and terms of coverage as outlined in the insurance agreement. Verification of coverage ensures that the services rendered are eligible for reimbursement and helps avoid claim denials due to lack of coverage.
Evaluation of Medical Necessity
Medical necessity evaluation is a crucial aspect of claim adjudication. The insurance company carefully examines the medical records, diagnosis codes, and supporting documentation to determine whether the services provided were medically necessary. They assess if the services align with the patient’s diagnosis, symptoms, and treatment plan. Evaluation of medical necessity helps ensure appropriate reimbursement and conformity with insurance industry regulations.
Determining Reimbursement Amount
The final step in claim adjudication is determining the reimbursement amount. The insurance company calculates the reimbursement based on the agreed-upon terms of the insurance policy, fee schedules, and industry standards. The reimbursement amount may be influenced by factors such as deductibles, co-pays, and maximum allowable amounts. Once the reimbursement amount is determined, it is processed for payment to the healthcare provider.
Step 6: Payment Processing

Reviewing Claim for Accuracy
Upon receipt of the adjudicated claim, the healthcare provider reviews it for accuracy. They confirm that the reimbursement amount aligns with the charges for the services provided and the terms of the insurance policy. Reviewing the claim ensures that any potential discrepancies or errors are identified and addressed before processing the reimbursement.
Issuing Reimbursement or Payment
Once the claim has been reviewed and deemed accurate, the insurance company issues the reimbursement or payment to the healthcare provider. This may involve electronic fund transfer (EFT) or issuing a paper check. The reimbursement amount depends on the adjudicated claim and the specific terms of the insurance policy. Issuing reimbursement ensures that healthcare providers receive the financial compensation for the services rendered.
Explanation of Benefits (EOB)
Along with the reimbursement or payment, the insurance company provides an Explanation of Benefits (EOB) to the healthcare provider. The EOB details the specifics of the claim adjudication, including the reimbursement amount, any adjustments made, and any patient responsibility. The EOB serves as a communication tool that explains the payment details to both the healthcare provider and the patient.
Step 7: Reporting and Analysis

Generating Financial Reports
Reporting and analysis are crucial steps in the claim cycle as they provide valuable insights into the financial performance of the healthcare provider’s billing processes. Healthcare providers generate financial reports that summarize the financial status, revenues, and expenses associated with the medical billing operations. These reports help in monitoring financial metrics, identifying trends, and assessing the overall profitability and efficiency of the billing process.
Analyzing Claim Metrics
Claim metrics analysis involves evaluating various key performance indicators (KPIs) related to the claim cycle. This includes metrics such as claim submission accuracy, claim acceptance rates, claim denial rates, reimbursement rates, and average payment turnaround time. Analyzing claim metrics helps identify areas of improvement, potential bottlenecks, and opportunities for optimizing revenue generation.
Identifying Areas for Improvement
Based on the reporting and analysis, healthcare providers can identify areas for improvement within their medical billing processes. This may involve addressing issues related to claim denials, streamlining claim submission procedures, improving coding accuracy, enhancing documentation practices, or optimizing reimbursement rates. Identifying areas for improvement allows healthcare providers to implement strategies that enhance overall efficiency, reduce costs, and maximize revenue.
In conclusion, medical billing is a complex process that involves numerous components and steps. The claim cycle provides a systematic framework for managing the billing process and ensuring accurate and timely reimbursement. Proper patient registration, insurance verification, coding and documentation, claim submission, claim adjudication, payment processing, claim denial management, appeals and resubmission, follow-up and collection, and reporting and analysis are all essential to optimize the medical billing process. Adherence to established protocols and continuous evaluation of claim metrics helps healthcare providers maximize revenue, minimize claim denials, and ensure effective financial management.