In the field of healthcare, there exists a variety of billing systems that play a crucial role in managing financial transactions. Understanding these systems is vital for healthcare professionals and administrators alike. This article aims to introduce three distinct types of billing systems commonly used in healthcare settings. By exploring the unique features and functionalities of each system, you will gain valuable insights into how these systems optimize billing practices and enhance overall healthcare revenue management. So, let’s dive into the world of billing systems and explore the diverse ways in which healthcare organizations streamline their financial operations.
Traditional Billing System
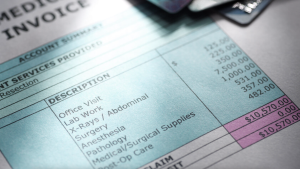
Definition of Traditional Billing System
The traditional billing system in healthcare refers to the conventional method of invoicing patients for the services rendered by healthcare providers. In this system, paper-based invoices are generated and sent to patients either by mail or in person.
Features of Traditional Billing System
The key features of the traditional billing system include manual data entry, paper-based invoices, and manual payment processing. Healthcare providers manually input patient information, services provided, and associated costs into the billing system. Invoices are then printed and mailed to patients or presented to them during their visit. Payments are received in person or through mail, and manual reconciliation is required.
Advantages of Traditional Billing System
One advantage of the traditional billing system is that it can be easily understood by both healthcare providers and patients due to its simplicity. Additionally, some patients may prefer receiving paper invoices and paying in person rather than through online methods. This system also allows for easy integration with existing manual workflows and infrastructure.
Disadvantages of Traditional Billing System
Despite its advantages, the traditional billing system has several disadvantages. Firstly, it is time-consuming and labor-intensive since it relies heavily on manual data entry and processing. Secondly, the paper-based approach is prone to errors, such as misplaced or lost invoices. Additionally, the delay in receiving payments can negatively impact cash flow for healthcare providers. Finally, the manual reconciliation process can be cumbersome and prone to human error.
Examples of Traditional Billing Systems in Healthcare
Examples of traditional billing systems in healthcare include hospitals that rely on paper invoices and manual payment processing. These facilities often have dedicated departments or staff members responsible for generating and managing the traditional billing system.
Electronic Health Record (EHR) Billing System

Definition of EHR Billing System
The Electronic Health Record (EHR) billing system is a technologically advanced approach to billing in healthcare that leverages electronic medical records to automate and streamline the billing process. This system integrates patient information, services provided, and associated costs directly from electronic health records.
Features of EHR Billing System
Key features of the EHR billing system include automated data entry, electronic invoices, and online payment processing. Healthcare providers enter patient information, services, and costs into the EHR, eliminating the need for manual data entry. Invoices are generated electronically and can be sent to patients via email or made available through patient portals. Online payment options allow for convenient and timely settlements.
Advantages of EHR Billing System
The EHR billing system offers numerous advantages over traditional billing methods. Firstly, it significantly reduces the workload of healthcare providers by automating data entry and invoice generation. Secondly, electronic invoices can be processed and delivered instantly, ensuring faster turnaround times for payments. Additionally, the integration of EHRs with the billing system improves accuracy and reduces errors. Online payment options also enhance convenience for patients.
Disadvantages of EHR Billing System
Despite its advantages, the EHR billing system has some disadvantages. Firstly, implementation or transitioning to an EHR system can be costly and may require staff training. Secondly, technical issues or system downtime can disrupt the billing process. Privacy and security concerns may also arise when transmitting sensitive patient information electronically. Finally, some patients may struggle with technology and prefer traditional methods of receiving and paying invoices.
Examples of EHR Billing Systems in Healthcare
Many healthcare organizations and practices have adopted EHR billing systems. Examples include electronic medical record software providers that offer integrated billing functionalities, as well as hospitals and clinics that have implemented custom EHR systems with integrated billing modules.
Consolidated Billing System
This image is property of cdn-aeclo.nitrocdn.com.
Definition of Consolidated Billing System
The consolidated billing system in healthcare refers to the integration of billing processes for multiple services or healthcare providers into a single, centralized system. This system combines different billing components, such as physician services, laboratory tests, and medications, into one invoice for patients.
Features of Consolidated Billing System
The key features of the consolidated billing system include centralized invoicing, integration of disparate billing components, and comprehensive billing statements. The system consolidates billing information from various sources, eliminating the need for separate invoices. It integrates billing data from different departments or healthcare providers, ensuring a unified invoice for patients. Comprehensive billing statements provide a clear breakdown of charges and services received.
Advantages of Consolidated Billing System
The consolidated billing system offers several advantages. Firstly, it simplifies the billing process for patients by providing a single invoice containing all the services received. This reduces confusion and ensures transparency regarding the overall costs. Secondly, consolidating billing components leads to more accurate and comprehensive statements, avoiding discrepancies or missing charges. Additionally, healthcare providers benefit from streamlined billing operations and reduced administrative burden.
Disadvantages of Consolidated Billing System
Despite its advantages, the consolidated billing system has some disadvantages. Firstly, the consolidation of billing components may result in complex and detailed invoices, which some patients may find overwhelming. Secondly, integrating billing systems from different departments or healthcare providers can be technically challenging and require significant coordination. Lastly, erroneous data entry or mismatched charges can occur during the consolidation process, leading to billing inaccuracies.
Examples of Consolidated Billing Systems in Healthcare
Examples of consolidated billing systems in healthcare include large hospitals or healthcare networks that offer multiple services under one roof. These organizations consolidate billing for services such as consultations, diagnostic tests, procedures, and medications into a single invoice for patients.
Episode-of-Care Billing System
Definition of Episode-of-Care Billing System
The episode-of-care billing system is a method of billing healthcare services based on a specific medical event or condition. Instead of charging per individual service, this approach groups related services into a single package, covering the entire episode of care from diagnosis to treatment.
Features of Episode-of-Care Billing System
Key features of the episode-of-care billing system include bundled billing, comprehensive care packages, and standardized pricing. Instead of separately billing for each service, healthcare providers combine relevant services, such as consultations, tests, procedures, and follow-up visits, into one package. These comprehensive care packages ensure that all necessary treatments are included and simplify the billing process. Standardized pricing helps establish consistent costs for each episode of care.
Advantages of Episode-of-Care Billing System
The episode-of-care billing system offers several advantages. Firstly, it promotes cost transparency by providing patients with a comprehensive package price upfront. This reduces confusion and allows patients to budget accordingly. Secondly, bundled billing incentivizes efficiency and encourages coordination among healthcare providers, resulting in improved care quality. Additionally, standardized pricing facilitates comparative analysis and benchmarking of treatment costs.
Disadvantages of Episode-of-Care Billing System
Despite its advantages, the episode-of-care billing system has some disadvantages. Firstly, determining the appropriate services to include and pricing for each episode can be complex and require extensive coordination among healthcare providers. Secondly, unforeseen complications or variations in patient conditions may necessitate additional services or treatments not initially bundled, potentially affecting costs. Lastly, some patients may prefer itemized billing to understand the breakdown of charges for each service.
Examples of Episode-of-Care Billing Systems in Healthcare
Examples of episode-of-care billing systems in healthcare include bundled payment models for specific procedures or conditions, such as joint replacements or maternity care. In these models, healthcare providers offer a bundled package covering all necessary services related to the episode of care, including pre-operative consultations, surgery, post-operative care, and rehabilitation.
Alternative Payment Models (APM) Billing System

This image is property of www.businessintegrityservices.com.
Definition of APM Billing System
The Alternative Payment Models (APM) billing system is a payment approach that deviates from the traditional fee-for-service model. APMs aim to incentivize value-based care and quality outcomes by linking reimbursement to patient outcomes or cost savings.
Features of APM Billing System
Key features of the APM billing system include value-based reimbursement, quality metrics, and risk-sharing arrangements. Instead of paying for individual services, healthcare providers receive payments based on the quality of care delivered and patient outcomes. APMs often include performance metrics tied to quality indicators or cost savings targets. Risk-sharing arrangements allocate financial responsibility among healthcare payers and providers, encouraging collaboration.
Advantages of APM Billing System
The APM billing system offers several advantages. Firstly, it incentivizes healthcare providers to focus on delivering high-quality care and achieving positive patient outcomes rather than simply providing more services. This shift towards value-based care can lead to improved patient satisfaction and better long-term health outcomes. Secondly, APMs encourage collaboration and coordination among healthcare providers by sharing financial risks, fostering a more integrated approach to care delivery.
Disadvantages of APM Billing System
Despite its advantages, the APM billing system has some disadvantages. Firstly, implementing and transitioning to APMs can be challenging and require significant changes to existing billing and care delivery models. Secondly, defining accurate quality metrics and determining fair reimbursement can be complex. Additionally, risk-sharing arrangements may lead to financial uncertainties for healthcare providers, especially in cases where target outcomes or cost savings are not attained.
Examples of APM Billing Systems in Healthcare
Examples of APM billing systems in healthcare include accountable care organizations (ACOs) and bundled payment models. ACOs focus on coordinating care for a defined population, with payments tied to meeting quality and cost targets. Bundled payment models, as mentioned earlier, reimburse healthcare providers based on the entire episode of care, promoting value-based and coordinated care.
Subscription-Based Billing System

Definition of Subscription-Based Billing System
The subscription-based billing system in healthcare involves patients paying a fixed recurring fee to access a range of healthcare services over a specified period. This approach allows patients to receive comprehensive care without the need for individual service-based billing.
Features of Subscription-Based Billing System
Key features of the subscription-based billing system include recurring fees, access to bundled services, and membership benefits. Patients pay a predetermined amount on a regular basis, typically monthly or annually, to access a wide range of healthcare services. These services may include regular check-ups, preventive care, and selected treatments. Membership benefits might include priority access, discounted rates, or additional services beyond the subscription coverage.
Advantages of Subscription-Based Billing System
The subscription-based billing system offers several advantages. Firstly, it promotes preventive care and ongoing health management by providing patients with regular access to healthcare services. This model encourages patients to seek care proactively, leading to early detection and better disease management. Secondly, the fixed recurring fee helps patients budget for their healthcare expenses more precisely. Additionally, membership benefits can enhance patient experience and loyalty.
Disadvantages of Subscription-Based Billing System
Despite its advantages, the subscription-based billing system has some disadvantages. Firstly, patients who require infrequent medical care may find the recurring fee unnecessary or costly. Secondly, there may be limitations or additional charges for certain services not covered by the subscription. Lastly, patients may be required to commit to a subscription term, potentially limiting their freedom to choose alternative healthcare providers or treatments.
Examples of Subscription-Based Billing Systems in Healthcare
Examples of subscription-based billing systems in healthcare include concierge medicine practices and direct primary care models. These models typically offer patients access to a comprehensive range of primary care services for a fixed, recurring fee. Patients can benefit from increased access to personalized care, extended appointment times, and enhanced physician-patient relationships.
Outsourced Billing System
In the dynamic realm of healthcare administration, the use of outsourced billing systems has emerged as a strategic solution. These systems involve the delegation of billing processes to specialized third-party service providers, offering healthcare providers relief from administrative burdens. By exploring the features, advantages, and potential drawbacks of outsourced billing systems, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions regarding this transformative approach to billing.
Let’s delve into the key elements of outsourced billing systems in healthcare, shedding light on how they enhance efficiency, optimize revenue, and simplify the complexities of the billing landscape.
Definition of Outsourced Billing System
The outsourced billing system in healthcare involves utilizing third-party billing services to handle the billing processes on behalf of healthcare providers. This system allows healthcare providers to delegate billing tasks to specialized companies, relieving them of the administrative burden.
Features of Outsourced Billing System
Key features of the outsourced billing system include third-party providers, comprehensive billing services, and improved efficiency. Healthcare providers partner with specialized billing companies that offer end-to-end billing services. These services include patient data management, claims submission, payment processing, and follow-up on outstanding receivables. By outsourcing these tasks, healthcare providers can focus on patient care while benefiting from increased billing efficiency.
Advantages of Outsourced Billing System
The outsourced billing system offers several advantages. Firstly, it allows healthcare providers to offload the administrative burden of billing and focus on their core competency of providing patient care. Secondly, specialized billing companies often have extensive experience and expertise in navigating complex billing regulations, minimizing billing errors and maximizing reimbursement rates. Additionally, outsourcing can lead to improved billing efficiency, reducing claim denials and accelerating payment cycles.
Disadvantages of Outsourced Billing System
Despite its advantages, the outsourced billing system has some disadvantages. Firstly, entrusting billing tasks to an external party may create concerns related to privacy and security of patient data. Healthcare providers need to ensure proper contractual agreements and data protection measures are in place. Secondly, coordination and communication between the healthcare provider and the billing company are crucial to avoid miscommunications or delays in the billing process. Lastly, outsourcing can come with additional costs, which healthcare providers need to consider when deciding on the financial viability of the arrangement.
Examples of Outsourced Billing Systems in Healthcare
Examples of outsourced billing systems in healthcare include medical billing service providers, revenue cycle management companies, and healthcare consulting firms. These companies offer comprehensive billing solutions and expertise to healthcare providers, enabling them to streamline their billing processes and improve financial performance.
Self-Pay Billing System
n the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare finance, the self-pay billing system has emerged as a crucial avenue for patients and providers alike. This system places the responsibility of payment directly on patients, bypassing insurance providers or third-party payers. It offers a unique set of features and benefits that cater to individuals without insurance or those seeking more control over their healthcare expenses.
Definition of Self-Pay Billing System
The self-pay billing system in healthcare involves patients directly paying for their services without involving insurance providers or third-party payers. This system applies to patients who do not have insurance coverage or choose to pay out-of-pocket for healthcare services.
Features of Self-Pay Billing System
Key features of the self-pay billing system include direct patient payments, customization of service costs, and flexible payment options. In this system, patients are responsible for paying the full cost of their healthcare services at the time of service. Service costs can be customized based on individual patients’ needs and financial capabilities. Flexible payment options, such as installment plans or discounts for upfront payments, may be offered to facilitate affordability.
Advantages of Self-Pay Billing System
The self-pay billing system offers several advantages. Firstly, it eliminates the complexity associated with insurance claims and third-party reimbursement, streamlining the billing process for healthcare providers. Secondly, patients without insurance coverage can receive healthcare services without the need to navigate insurance requirements or worry about claim denials. Additionally, offering flexible payment options improves accessibility to care for individuals who may not have insurance or face financial limitations.
Disadvantages of Self-Pay Billing System
Despite its advantages, the self-pay billing system has some disadvantages. Firstly, patients may find it challenging to afford the full cost of healthcare services without the support of insurance coverage. This could deter individuals from seeking necessary care or lead to financial hardships. Secondly, healthcare providers may face challenges in determining service costs and pricing structures, as they need to strike a balance between affordability and maintaining sustainable financial operations.
Examples of Self-Pay Billing Systems in Healthcare
Examples of self-pay billing systems in healthcare include cash-only clinics, cosmetic or elective procedure centers, and certain specialty practices. These providers cater to patients who are not covered by insurance or who prefer to pay out-of-pocket for specific services, such as aesthetic treatments or alternative therapies.
Third-Party Billing System

This image is property of www.outsourceaccelerator.com.
Definition of Third-Party Billing System
The third-party billing system in healthcare involves billing services being facilitated by an intermediary, such as insurance companies or government payers. This system is commonly used to process healthcare claims and manage reimbursements.
Features of Third-Party Billing System
Key features of the third-party billing system include submission of claims, adjudication of claims, and reimbursement processes. Healthcare providers submit claims to the third-party payer, providing details of the services rendered and associated costs. The payer then reviews the claims, verifying eligibility, adherence to coverage guidelines, and accurate coding. Upon approval, the payer reimburses the healthcare provider based on predetermined rates or negotiated agreements.
Advantages of Third-Party Billing System
The third-party billing system offers several advantages. Firstly, it provides a standardized and efficient approach to claim processing for healthcare providers. By outsourcing the billing process, healthcare providers can focus on patient care while relying on the expertise of the third-party payer. Secondly, patients benefit from the convenience of not having to pay the full cost upfront and can access covered services without the financial burden.
Disadvantages of Third-Party Billing System
Despite its advantages, the third-party billing system has some disadvantages. Firstly, healthcare providers may face challenges related to claim denials, delayed reimbursements, or disputes over coding and reimbursement rates. Secondly, coordinating billing processes with multiple third-party payers can be administratively demanding and require specialized expertise. Additionally, limited control over reimbursement rates may impact the financial viability of certain services or procedures.
Examples of Third-Party Billing Systems in Healthcare
Examples of third-party billing systems in healthcare include insurance companies, managed care organizations, and government payers, such as Medicare or Medicaid. These entities act as intermediaries between healthcare providers and patients, managing the billing and reimbursement processes for covered services.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the healthcare industry offers a range of billing systems to accommodate various operational needs and the evolving landscape of healthcare delivery. The traditional billing system, despite its simplicity, can be time-consuming and prone to errors. On the other hand, electronic health record (EHR) billing systems leverage technology to streamline the billing process and improve accuracy. The consolidated billing system integrates various services into a single invoice, simplifying the billing experience for patients. The episode-of-care billing system bundles related services for specific medical events, promoting cost transparency and quality outcomes. Alternative payment models (APM) incentivize value-based care and quality outcomes, shifting the focus from fee-for-service. Subscription-based billing systems offer comprehensive care packages for a recurring fee, while outsourced billing systems relieve healthcare providers of administrative burdens. Self-pay billing systems cater to patients paying directly for services, while third-party billing systems involve intermediaries like insurance companies or government payers. Each system has its advantages and disadvantages, highlighting the complexity and diversity of billing in healthcare. Healthcare providers must carefully evaluate their needs and consider the best fit to ensure optimal financial performance and patient satisfaction.