Clinical coding plays a pivotal role in the healthcare industry, serving as the backbone of medical documentation and billing processes. By translating complex medical information into a standardized language, clinical coding ensures accurate and efficient communication among healthcare professionals, insurance providers, and regulatory agencies. This article explores the fundamental purpose of clinical coding, shedding light on its essential role in improving patient care, facilitating research, and facilitating reimbursement processes. Understanding the significance of clinical coding is crucial for healthcare professionals and stakeholders alike, as it directly impacts the quality, safety, and financial aspects of healthcare delivery.
Overview of Clinical Coding
Definition of clinical coding
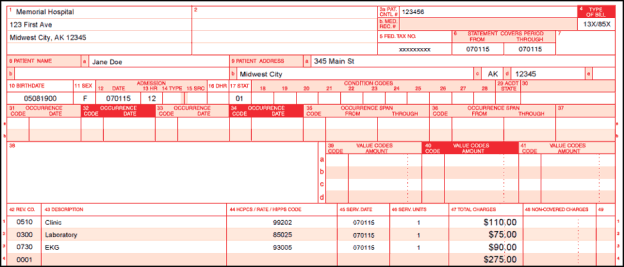
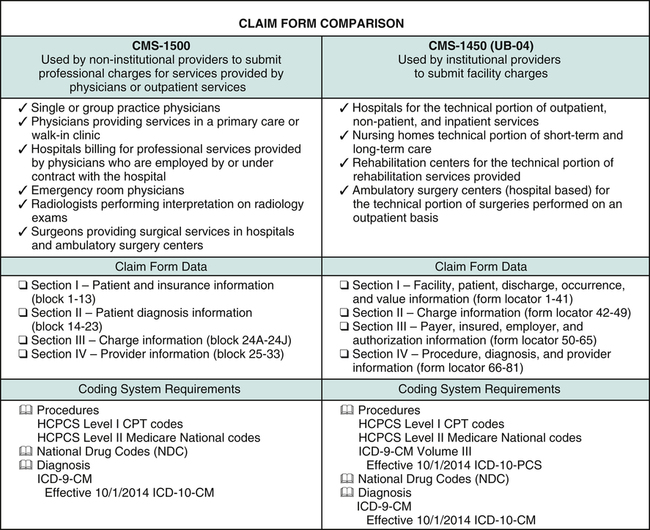
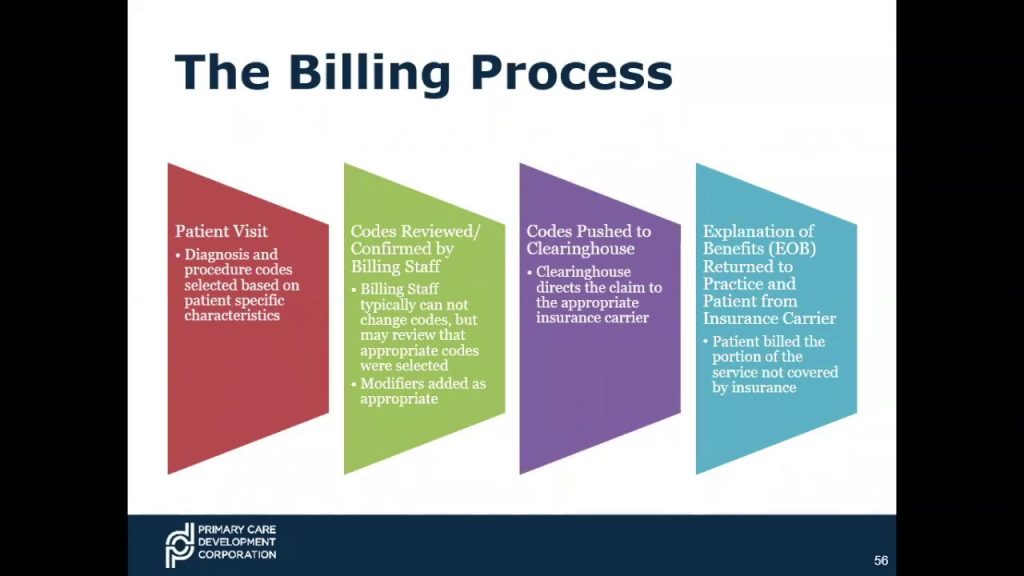
Clinical coding is the process of translating healthcare diagnoses, procedures, and other medical information into standardized codes. These codes are used for various purposes, including billing, reimbursement, healthcare research, and patient care. Clinical coding ensures that healthcare providers and payers have a common language to communicate and understand medical information accurately.
Importance of clinical coding
Accurate clinical coding is vital for the functioning of the healthcare system. It plays a crucial role in facilitating communication, ensuring proper reimbursement, improving patient care, enabling research, and safeguarding patient safety. Clinical coding provides a standardized framework that enables healthcare organizations to efficiently manage their operations, collect data, and derive meaningful insights.
Types of Clinical Coding

International Classification of Diseases (ICD)
The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) is a widely recognized and used system in clinical coding. The ICD codes are used to classify and categorize diseases, injuries, and other health conditions. These codes help healthcare providers accurately describe a patient’s diagnoses and conditions, which are essential for appropriate treatment, billing, and reimbursement.
Procedure Coding System (PCS)
The Procedure Coding System (PCS) is another important coding system used in clinical coding. PCS codes are used to identify and classify medical procedures, interventions, surgeries, and other healthcare treatments. These codes provide detailed information about the specific procedures performed, enabling accurate billing and facilitating analysis of healthcare outcomes and trends.
Hierarchical Condition Categories (HCC)
Hierarchical Condition Categories (HCC) is a coding system that assigns certain health conditions and diagnoses into categories. These categories are used for risk adjustment and healthcare financial modeling purposes. HCC coding helps healthcare organizations predict an individual’s healthcare expenditures and adjust reimbursement accordingly, ensuring fair and accurate payment for services provided.
Benefits of Clinical Coding

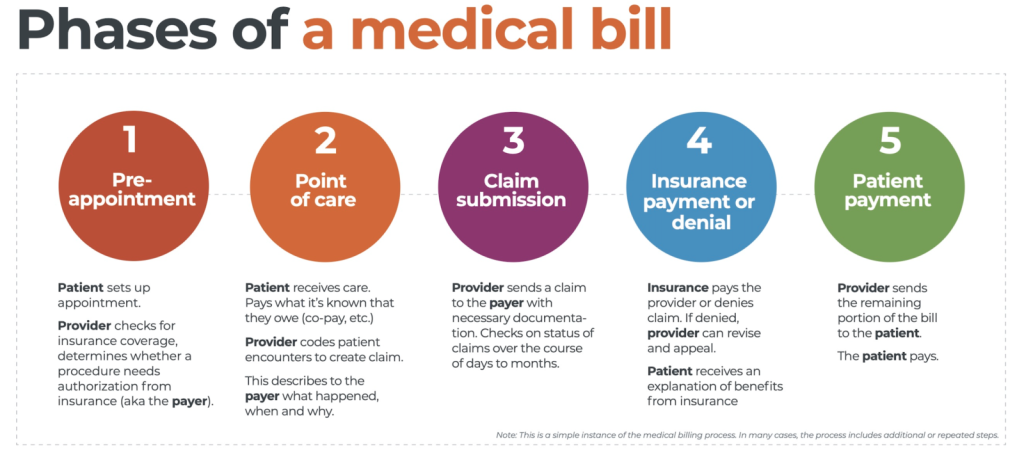
Accurate billing and reimbursement
One of the primary benefits of clinical coding is accurate billing and reimbursement. By assigning specific codes to diagnoses, procedures, and other healthcare services, clinical coders ensure that healthcare providers are appropriately compensated for the services they render. Accurate clinical coding also reduces the risk of underpayment or fraudulent billing, leading to fair reimbursement for both healthcare providers and payers.
Facilitating healthcare research
clinical coding plays a crucial role in healthcare research. By using standardized codes, researchers can analyze large datasets to identify patterns, trends, and associations related to diseases, treatments, and outcomes. Clinical coding allows for the comparison and integration of data from diverse sources, enabling researchers to gain valuable insights that can improve public health, drive evidence-based medicine, and advance medical knowledge.
Enhancing patient care and safety
Clinical coding contributes to enhancing patient care and safety by ensuring accurate documentation of diagnoses, treatments, and outcomes. When healthcare providers have access to comprehensive and consistent medical information, they can make well-informed decisions, create effective treatment plans, and significantly reduce the risk of medical errors. Furthermore, accurate coding supports the electronic exchange of patient information, improving care coordination and patient safety across healthcare settings.
Role of Clinical Coders

Responsibilities of clinical coders
Clinical coders have several responsibilities in the healthcare system. They review medical documentation to extract relevant clinical information and assign appropriate codes. Clinical coders must ensure accuracy, completeness, and consistency in their coding practices. They collaborate with healthcare providers, administrators, and other stakeholders to resolve coding discrepancies, answer coding-related queries, and support coding education and training programs.
Qualifications and training
Clinical coding requires specific qualifications and training to ensure proficiency in the coding process. Clinical coders typically possess a solid understanding of medical terminology, anatomy, physiology, and disease processes. They must complete specialized coding education programs and obtain professional certifications such as the Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) credential. Continuous learning and staying up-to-date with coding guidelines and regulations are essential for clinical coders to excel in their role.
Importance of ongoing education
Ongoing education is crucial for clinical coders to keep their skills sharp and stay updated with the latest coding guidelines, regulations, and technologies. Advancements in medical treatments and procedures, changes in coding systems, and updates to healthcare regulations necessitate continuous learning. Regular participation in coding workshops, webinars, conferences, and other educational opportunities ensures that clinical coders maintain their proficiency and deliver accurate, high-quality coding services.
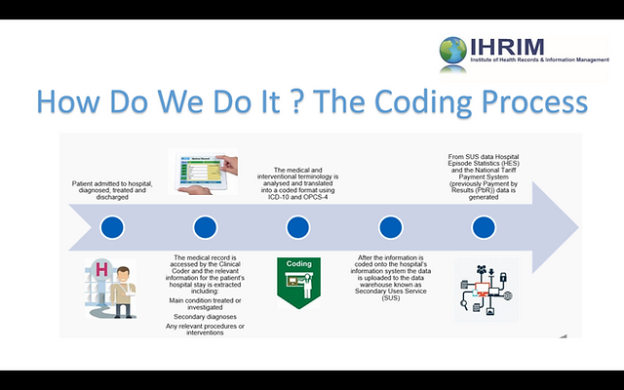
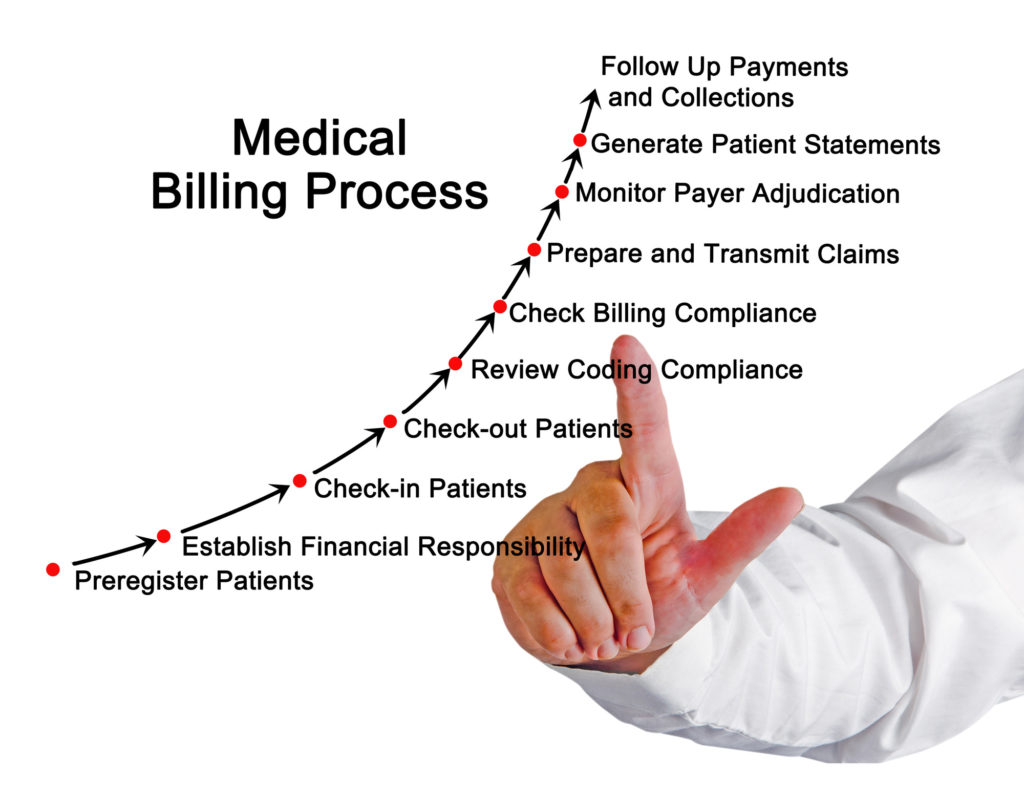
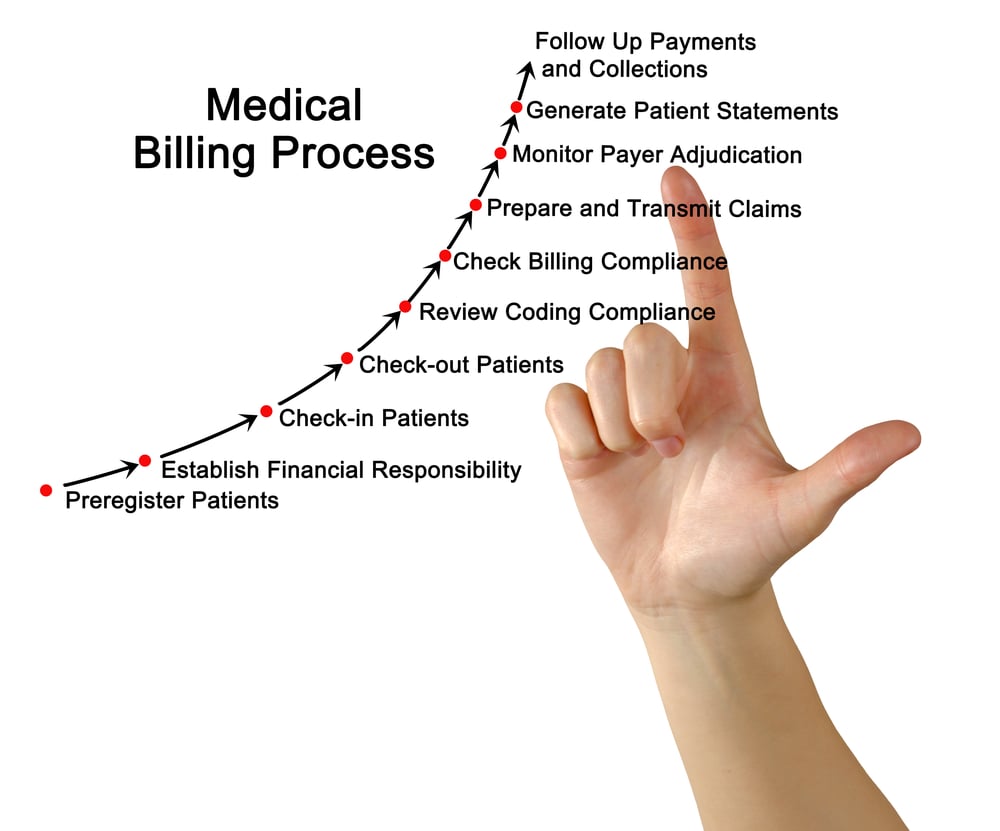
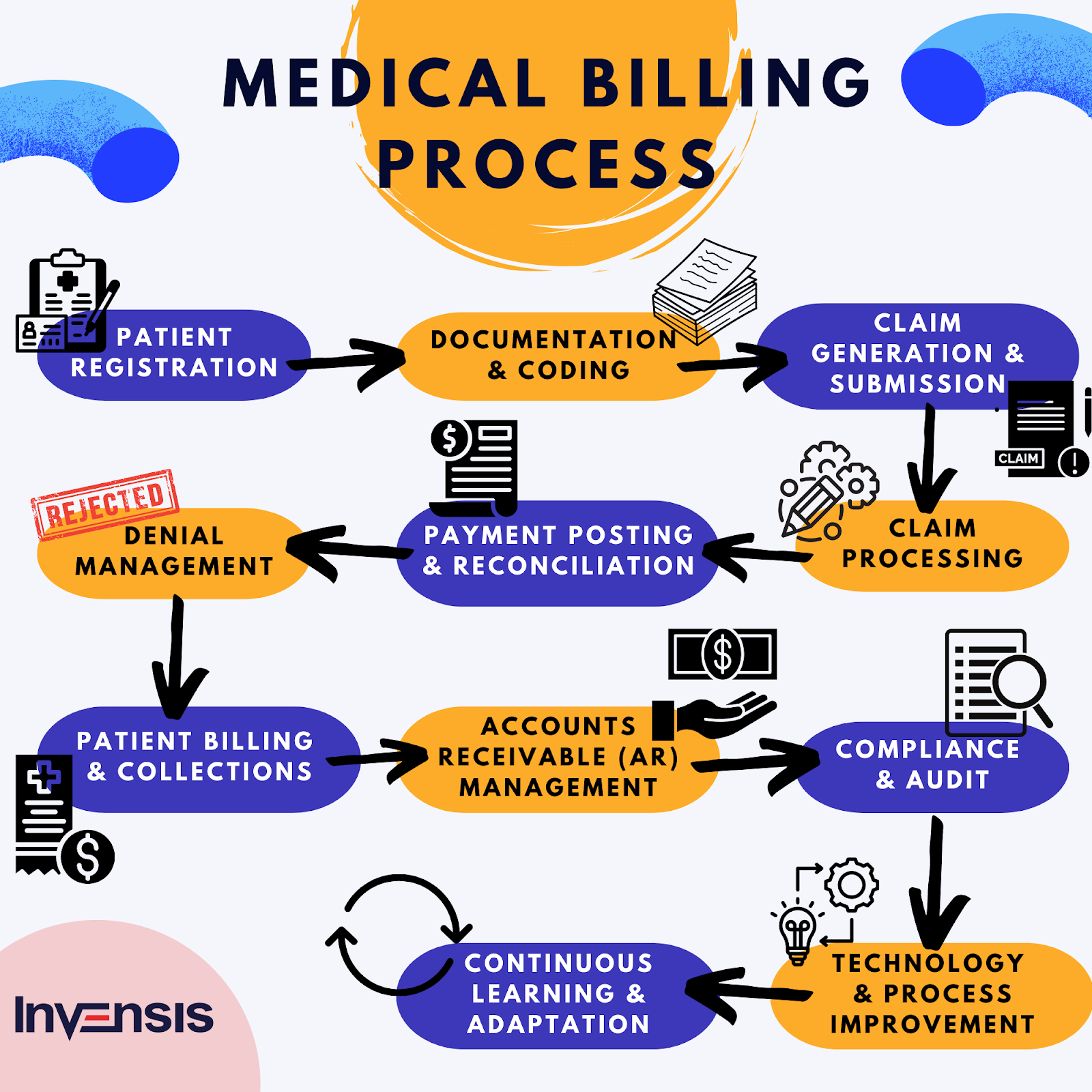
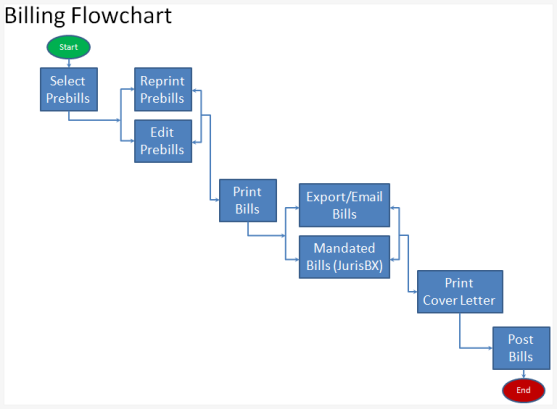
Clinical Coding Process
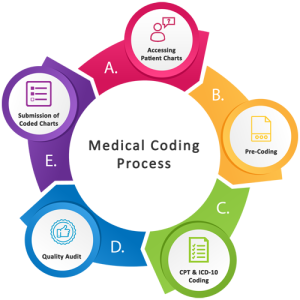
Medical documentation
The clinical coding process starts with medical documentation, including healthcare records, physician notes, lab results, and other relevant information. Clinical coders carefully review these documents to extract diagnoses, procedures, and other essential details. They must analyze complex information, interpret medical terminology accurately, and identify the appropriate codes to represent the medical information correctly.
Assigning codes
Once the relevant information is extracted from the medical documentation, clinical coders assign appropriate codes using the designated coding systems such as ICD, PCS, or HCC. They apply coding guidelines, conventions, and rules to accurately translate medical diagnoses, procedures, and treatments into standardized codes. The coding process requires attention to detail, analytical skills, and the ability to navigate complex coding systems effectively.
Review and validation
After the codes are assigned, the work of clinical coders undergoes a review and validation process. Quality assurance measures, such as internal audits and external reviews, ensure that the coding is accurate, complete, and compliant with coding guidelines and regulations. This review process is essential to maintain coding integrity, reduce errors, and uphold coding standards.
Challenges and Limitations of Clinical Coding

Incomplete or inconsistent documentation
Clinical coding heavily relies on the accuracy and completeness of medical documentation. Inadequate or incomplete documentation can hamper the coding process, leading to inaccuracies and incomplete coding results. Healthcare providers and coders must maintain clear, comprehensive, and consistent documentation practices, ensuring that all pertinent information is captured correctly to support accurate clinical coding.
Complex coding systems
Coding systems such as ICD, PCS, and HCC can be complex and challenging to navigate. These systems have numerous codes, guidelines, and updates, requiring clinical coders to stay updated with the latest changes. Inaccurate code assignment due to incomplete understanding or misinterpretation of coding guidelines can lead to coding errors and adverse financial and clinical outcomes. Thorough training and ongoing education are essential to mitigate these challenges.
Human error and subjectivity
Clinical coding is inherently prone to human error and subjectivity. Coders may have different interpretations of medical documentation, leading to inconsistencies in code assignment. Furthermore, the complexity of certain medical conditions and procedures may introduce subjectivity in the coding process. To mitigate these challenges, coding audits, ongoing education, and the use of coding decision-support tools can enhance accuracy and reduce the impact of human error.
Evolution of Clinical Coding

This image is property of slideplayer.com.
Transition from paper-based to electronic coding
The evolution of clinical coding has seen a significant shift from manual, paper-based coding to electronic coding systems. Electronic health records (EHRs) and computer-assisted coding (CAC) tools have revolutionized the coding process, improving efficiency, accuracy, and communication between healthcare providers and coders. Electronic coding allows for faster retrieval of medical information, real-time documentation, and streamlined coding workflows, ultimately enhancing the quality and timeliness of clinical coding.
Advancements in artificial intelligence
Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have the potential to revolutionize clinical coding further. AI technologies, such as natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms, can automate certain aspects of the coding process by extracting relevant information from medical documentation and suggesting appropriate codes. AI-assisted coding not only improves coding accuracy and efficiency but also reduces the burden on clinical coders, allowing them to focus on more complex coding tasks.
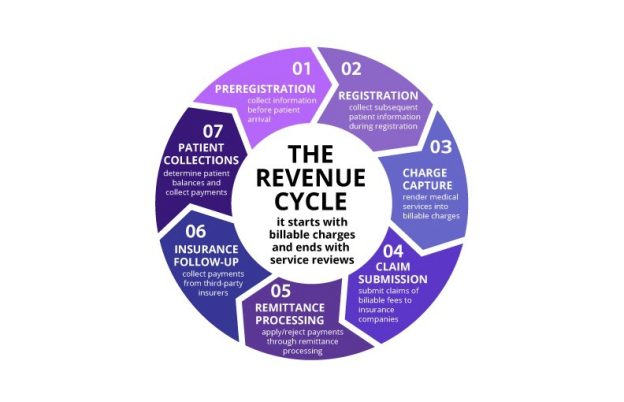
Integration of clinical coding with other systems
Clinical coding is increasingly being integrated with other healthcare systems and processes, such as revenue cycle management, electronic health records, and population health management. Integration enables seamless data exchange, reduces redundancies, and improves data accuracy and consistency. It also supports the interoperability of healthcare information, enhancing care coordination and patient outcomes across different healthcare settings.
Regulations and Standards in Clinical Coding
Regulations and standards in clinical coding are essential to maintain accuracy, consistency, and compliance in healthcare documentation and billing. Here are some key elements related to regulations and standards in clinical coding:
HIPAA regulations
Clinical coders must adhere to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) regulations, which protect the privacy and security of patients’ health information. HIPAA establishes guidelines for the appropriate use and disclosure of protected health information (PHI), including the coding and billing process. Compliance with HIPAA regulations is crucial to maintaining patient confidentiality, preventing data breaches, and ensuring ethical coding practices.
Coding compliance programs
Healthcare organizations implement coding compliance programs to maintain coding integrity, prevent fraud and abuse, and comply with legal and regulatory requirements. These programs include internal audits, coding training, and regular monitoring of coding practices to identify areas of improvement and address any coding deficiencies. Coding compliance programs ensure that clinical coding practices align with coding guidelines, regulations, and ethical standards.
Standardization organizations
Several standardization organizations play a crucial role in clinical coding. The World Health Organization (WHO) oversees the development and maintenance of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) coding system. In the United States, the American Medical Association (AMA) provides guidance and updates through the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) coding system. These organizations ensure that coding standards are continuously updated, standardized, and relevant to the evolving healthcare landscape.
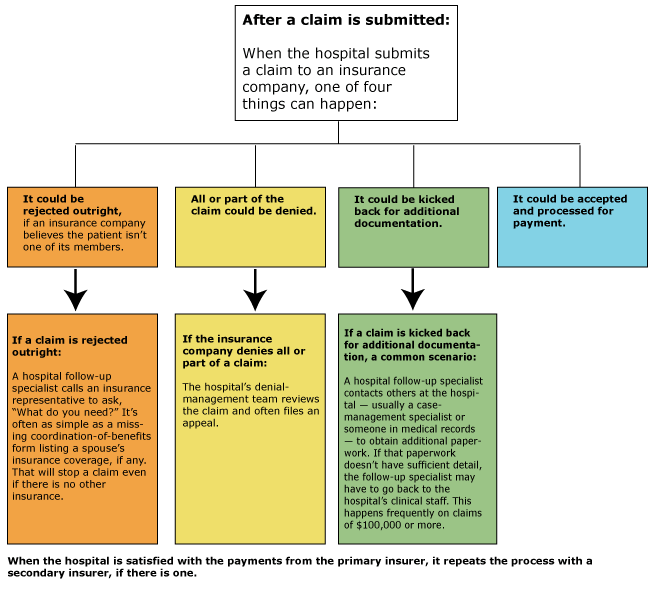
Importance of Coding Accuracy

This image is property of fabnhsstuff.net.
Impact on healthcare outcomes
Coding accuracy has a significant impact on healthcare outcomes. Accurate and specific clinical coding allows for accurate identification of diseases, conditions, and procedures, enabling evidence-based decision-making and appropriate treatment planning. Inaccurate coding can lead to misdiagnoses, inadequate treatment, and adverse patient outcomes. Therefore, ensuring coding accuracy is crucial for delivering high-quality healthcare and improving patient outcomes.
Identification of healthcare trends and patterns
Accurate clinical coding enables the identification of healthcare trends and patterns. By analyzing coded data, researchers and healthcare organizations can identify prevalent diseases, treatment effectiveness, and emerging health concerns. This information helps inform public health policies, resource allocation, and preventive healthcare initiatives. Coding accuracy is vital for capturing and analyzing data accurately, leading to insights that can drive positive changes in healthcare delivery.
Avoidance of fraud and abuse
Coding accuracy plays a critical role in preventing fraud and abuse in healthcare. Accurate coding ensures appropriate reimbursement for services rendered and prevents incorrect billing practices. It also helps identify potential fraudulent activities, such as upcoding or unbundling of services, that can result in financial losses for payers and compromise the integrity of the healthcare system. Maintaining coding accuracy is essential in safeguarding healthcare resources and promoting transparency in healthcare billing practices.
Future of Clinical Coding

Increasing use of automation and machine learning
The future of clinical coding is expected to see an increasing use of automation and machine learning technologies. AI-assisted coding tools, powered by machine learning algorithms and NLP, will continue to streamline and automate the coding process. These technologies will improve coding accuracy, enhance productivity, and reduce the burden on clinical coders. Automation will also enable real-time analysis of clinical data, leading to faster insights and evidence-based decision-making.
Integration with telemedicine and remote healthcare
As telemedicine and remote healthcare continue to expand, clinical coding will need to adapt to these evolving modes of healthcare delivery. Clinical coders will play a critical role in accurately coding virtual visits, remote monitoring, and other telehealth services. The integration of clinical coding with telemedicine platforms and EHR systems will ensure accurate documentation, appropriate coding, and seamless reimbursement for telemedicine services.
Improving interoperability between systems
In the future, there will be a greater focus on improving interoperability between different healthcare systems and coding platforms. Standardizing data exchange protocols, coding terminologies, and documentation formats will enhance the seamless flow of information across healthcare settings. Improved interoperability will enable more comprehensive and accurate clinical coding, leading to better care coordination, enhanced patient safety, and improved healthcare outcomes.
In conclusion, clinical coding plays a critical role in the healthcare system by accurately translating medical information into standardized codes. From facilitating accurate billing and reimbursement to supporting healthcare research and improving patient care and safety, clinical coding is vital for efficient and effective healthcare delivery. Clinical coders have significant responsibilities, requiring specific qualifications, ongoing education, and attention to detail. The evolution of clinical coding, advancements in technology, and adherence to regulations and standards will shape the future of this essential healthcare function. By ensuring coding accuracy and embracing automation, integration, and interoperability, the future of clinical coding holds great potential to drive positive changes in healthcare delivery and patient outcomes.