Inhouse medical billing refers to the process of handling and managing the billing and coding for medical services within a healthcare facility, such as a hospital, clinic, or private practice. Instead of outsourcing this crucial task to external billing companies or third-party vendors, healthcare organizations choose to keep the billing process in-house, under their direct control and supervision. This article aims to explore the key aspects and benefits of inhouse medical billing, shedding light on the reasons why many healthcare providers opt for this approach to ensure efficient and accurate reimbursement for the services they deliver.
What Is Inhouse Medical Billing?
inhouse medical billing refers to the process of managing and submitting medical claims in-house within a healthcare organization. It involves the utilization of trained staff and advanced technological tools to ensure accurate and timely billing for provided services. This method allows healthcare facilities to have direct control over the entire billing process, from patient registration to claim submission and payment posting.
Definition and Overview

Medical cost concept with stethoscope and medical bill
The concept of inhouse medical billing
Inhouse medical billing is the practice of handling medical billing services within a healthcare organization rather than outsourcing them to a third-party billing service. This approach involves dedicated billing staff who are responsible for various billing functions, such as patient registration, insurance verification, charge entry and coding, claim submission, payment posting, denial management, and patient invoicing.
Role of inhouse medical billing in healthcare
The role of inhouse medical billing is crucial in the financial health of healthcare organizations. It ensures that medical services are appropriately coded, billed, and processed for reimbursement by insurance companies or patients. Effective inhouse billing allows healthcare facilities to maximize revenue, minimize billing errors, and maintain compliance with healthcare regulations.
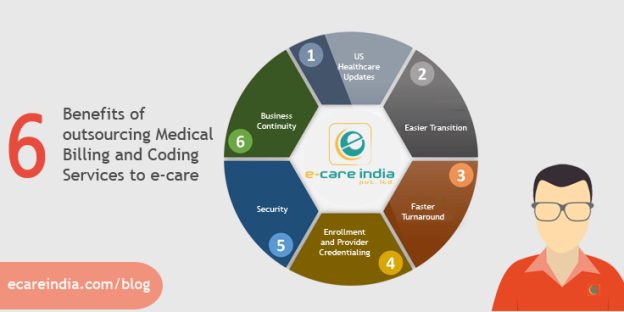
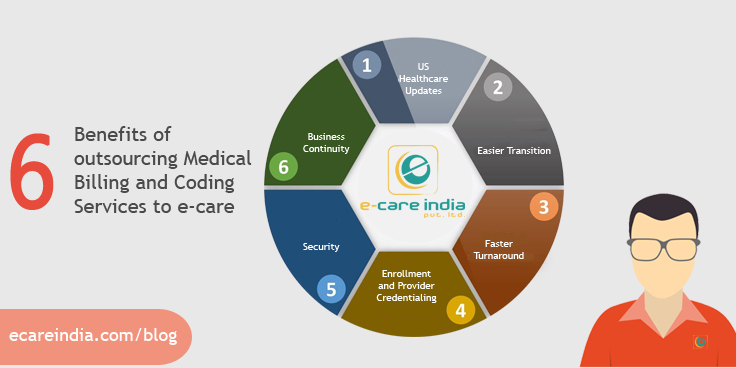
Benefits of inhouse medical billing
There are several benefits associated with implementing inhouse medical billing. Firstly, it provides enhanced control and transparency over the entire billing process. Healthcare organizations can closely monitor all aspects of the billing cycle and quickly address any issues or discrepancies. Secondly, inhouse medical billing often results in faster claim submission and reimbursement, improving cash flow for the organization. Additionally, organizations that handle their own billing have reduced dependency on third-party billing services, which can lead to cost savings. Moreover, inhouse billing allows for better patient communication and satisfaction, as patients can contact the organization directly with billing inquiries. Lastly, inhouse medical billing enables healthcare organizations to have better control over revenue cycle management and adapt to changing regulations more smoothly.
Key Functions of Inhouse Medical Billing

This image is property of qwayhealthcare.com.
Patient registration and demographics
One of the fundamental functions of inhouse medical billing is patient registration and demographics. This involves collecting essential patient information, such as name, contact details, insurance details, and demographic data. Accurate and up-to-date patient data is crucial for proper billing and reimbursement.
Insurance verification and eligibility checks
The inhouse medical billing team is responsible for verifying patients’ insurance coverage and conducting eligibility checks. This involves contacting insurance companies to ensure patients are eligible for specific services, as well as verifying their insurance benefits, deductibles, and copayments. Proper insurance verification helps avoid claim denials and ensures accurate billing.
Charge entry and coding
Charge entry and coding is a critical component of inhouse medical billing. It involves accurately coding medical services and procedures performed by healthcare providers, using standardized coding systems such as Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) and International Classification of Diseases (ICD). Accurate coding ensures proper reimbursement and compliance.
Claim submission and management
The inhouse billing team is responsible for submitting claims to insurance companies or government programs on behalf of the healthcare organization. This involves compiling all necessary documentation, including medical records and supporting documents, and submitting them electronically or via paper claims. Efficient claim management, including tracking and follow-up on claim status, is crucial for timely reimbursement.
Payment posting and reconciliation
Once medical claims are processed and reimbursed, the inhouse billing team is responsible for posting payments received from insurance companies or patients. This involves reconciling payments with the billed amounts and ensuring accuracy. Payment posting helps track outstanding balances and maintain accurate financial records.
Denial management and appeals
Inhouse medical billing also encompasses denial management and appeals. This involves analyzing and addressing claim denials promptly, identifying the reasons for denials, and taking necessary actions to rectify errors or resubmit claims. The billing team may also handle the appeal process for denied claims, ensuring appropriate documentation and justification for services provided.
Patient invoicing and statements
Inhouse medical billing includes generating and sending patient invoices and statements for services rendered. This involves accurately calculating the patient’s responsibility, such as deductibles, copayments, and non-covered services. Providing clear and comprehensive invoices helps patients understand their financial obligations and facilitates prompt payment.
Accounts receivable follow-up
Inhouse medical billing teams are responsible for following up on outstanding accounts receivable. This includes identifying unpaid or underpaid claims, contacting insurance companies or patients to resolve payment issues, and taking necessary actions to collect outstanding balances. Effective accounts receivable follow-up is essential for maximizing revenue and reducing billing errors.
Reporting and analytics
Inhouse medical billing also involves generating various reports and performing analytics to assess the financial performance of the healthcare organization. These reports provide insights into key billing metrics, such as revenue cycle efficiency, denial rates, payment trends, and reimbursement patterns. Analyzing this data helps identify areas for improvement and optimize the billing process.
Advantages of Inhouse Medical Billing

Enhanced control and transparency
One of the primary advantages of inhouse medical billing is the enhanced control and transparency it offers. Healthcare organizations have direct oversight of the entire billing process, allowing them to closely monitor each step, identify bottlenecks or issues, and swiftly address them. This level of control enhances accuracy, improves compliance, and reduces the risk of potential revenue loss or fraud.
Faster claim submission and reimbursement
Inhouse medical billing often results in faster claim submission and reimbursement. Since the billing team is dedicated to processing claims promptly, there is a reduced turnaround time for claim submission. This translates to quicker reimbursement, improving the cash flow for the healthcare organization. Speedy reimbursement allows organizations to meet financial obligations and invest in further improving patient care.
Reduced dependency on third-party billing services
By managing their own billing inhouse, healthcare organizations can reduce their dependency on third-party billing services. This reduces costs associated with outsourcing billing functions and allows organizations to allocate resources more efficiently. Independence from external service providers also provides flexibility in adapting to changing billing requirements and regulations.
Better patient communication and satisfaction
Inhouse medical billing enables direct communication between the healthcare organization and patients regarding billing inquiries or concerns. Patients can contact the billing team directly, allowing for efficient communication and quick resolution of any billing-related issues. This direct interaction enhances patient satisfaction and fosters a positive patient experience.
Improved revenue cycle management
Inhouse medical billing empowers healthcare organizations to have better control over their revenue cycle management. With direct oversight of billing functions, organizations can implement effective strategies for optimizing the billing process, reducing claim denials, and improving overall revenue generation. Enhanced revenue cycle management facilitates financial stability and supports the organization’s growth and expansion.
Flexibility to adapt to changing regulations
Managing the billing process inhouse provides healthcare organizations with the flexibility to adapt to changing regulations and industry standards. Billing staff can stay up-to-date with regulatory changes and implement necessary adjustments or updates promptly. This adaptability ensures compliance with evolving healthcare requirements and mitigates the risk of regulatory non-compliance.
Considerations for Implementing Inhouse Medical Billing

This image is property of lirp.cdn-website.com.
Staffing and training requirements
Implementing inhouse medical billing necessitates proper staffing with trained professionals to handle various billing functions. Organizations must ensure they have an adequate number of billing staff with the appropriate skill set and knowledge of billing regulations and coding systems. Additionally, regular training and continuing education programs should be provided to keep the billing team updated on industry changes.
Technology infrastructure and software selection
Effective inhouse medical billing requires a robust technology infrastructure and appropriate software solutions. Healthcare organizations need to invest in billing software that offers comprehensive functionality and integration capabilities with other systems, such as electronic health records (EHR). A reliable IT infrastructure is essential for secure data management, efficient claims processing, and accurate reporting.
Compliance with regulatory requirements
Inhouse medical billing entails strict adherence to various regulatory requirements, including but not limited to HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) regulations. Organizations must ensure that their billing processes comply with relevant laws and guidelines to protect patient privacy and avoid potential legal issues. Regular compliance audits and benchmarking can help identify areas of improvement and ensure ongoing adherence to regulations.
Cost and financial considerations
Implementing inhouse medical billing involves upfront investment in staffing, technology, and training. Healthcare organizations should carefully evaluate the overall cost-effectiveness of inhouse billing compared to outsourcing options. Factors such as potential cost savings, revenue generation capabilities, and long-term financial sustainability should be taken into account.
Integration with existing systems and workflows
Smooth integration of inhouse billing with existing systems and workflows is crucial for minimizing disruptions and maximizing efficiency. Healthcare organizations should assess the compatibility of their billing software with other systems, such as EHR or practice management systems. Considering the potential impact on existing workflows and implementing necessary changes or modifications is essential for a successful transition to inhouse billing.
Quality assurance and auditing processes
To ensure accuracy and compliance, healthcare organizations should establish robust quality assurance and auditing processes for inhouse medical billing. This includes regular internal audits of billing activities, claims reviews, and performance evaluations. Consistent monitoring and auditing help identify errors, inefficiencies, or potential fraudulent activities, allowing for timely corrective actions and process improvements.
Challenges and Potential Drawbacks

Upfront investment and ongoing costs
Implementing inhouse medical billing requires significant upfront investment in staffing, training, and technology infrastructure. Organizations need to carefully assess the financial implications and accurately estimate the ongoing costs associated with maintaining an inhouse billing team, software licenses, hardware maintenance, and software updates. It is important to weigh the costs against the potential benefits and long-term financial sustainability.
Potential for increased billing errors
While inhouse medical billing allows for enhanced control, there is an increased risk of billing errors due to the complexity of billing processes. Human errors in coding, data entry, or documentation can lead to claim denials, delayed reimbursements, or potential non-compliance. Robust training programs, quality assurance processes, and ongoing monitoring are essential for preventing and identifying errors.
Need for continuous updates on regulatory changes
The healthcare industry is constantly evolving, with frequent changes in regulations, coding systems, and reimbursement guidelines. Inhouse medical billing teams must stay updated on these changes and ensure compliance to avoid potential penalties or revenue loss. Continuous education, participation in industry events, and regular communication with regulatory authorities are critical to staying abreast of changes.
Resource intensiveness and time commitment
Managing inhouse medical billing can be resource-intensive and time-consuming for healthcare organizations. Hiring and training billing staff, investing in technology infrastructure, and overseeing day-to-day billing activities require significant commitment and allocation of resources. Organizations must carefully assess their capacity and ability to dedicate the necessary time, personnel, and financial resources to handle inhouse billing effectively.
Limited scalability for larger healthcare organizations
While inhouse medical billing may work well for smaller or mid-sized healthcare organizations, larger organizations may face scalability challenges. As the volume of medical services and claims increases, managing inhouse billing for a large number of patients becomes more complex. In such cases, larger organizations may need to explore hybrid solutions that involve a combination of inhouse and outsourced billing or consider outsourcing entirely.
Comparison with Outsourced Medical Billing

This image is property of velaninfo.com.
Pros and cons of outsourcing medical billing
Outsourced medical billing involves contracting a third-party billing service to handle billing functions on behalf of the healthcare organization. This option offers several advantages, such as reduced administrative burden, access to specialized billing expertise, and potential cost savings. However, outsourcing can also have drawbacks, including potential loss of control over the billing process, reliance on external service providers, and reduced visibility into billing operations.
Factors influencing decision-making between inhouse and outsourced billing
The decision between inhouse and outsourced medical billing depends on several factors. These include the size and complexity of the healthcare organization, the volume of medical services provided, available resources, financial considerations, desired control and transparency, and the organization’s capability to manage billing inhouse. A careful assessment of these factors helps organizations determine the most suitable billing approach for their specific needs.
Case studies and industry experiences
Examining case studies and leveraging industry experiences can provide valuable insights into the benefits and challenges associated with both inhouse and outsourced medical billing. Organizations can learn from the experiences of similar healthcare facilities, understand the impact of various billing approaches on financial performance, and make informed decisions based on real-world scenarios.
Compliance and Legal Considerations

HIPAA and patient data confidentiality
Inhouse medical billing must comply with HIPAA regulations to ensure the confidentiality and security of patient data. Healthcare organizations must implement robust data security measures, maintain privacy safeguards, and provide training for staff handling patient information. Failure to comply with HIPAA regulations can result in severe penalties and damage to the organization’s reputation.
Fraud and abuse prevention
Inhouse medical billing must also prioritize fraud and abuse prevention. Organizations should establish internal controls, such as regular audits and segregation of duties, to detect and prevent fraudulent activities. By implementing effective fraud prevention measures, healthcare organizations can protect their financial integrity and ensure ethical billing practices.
Benchmarking and compliance audits
Regular benchmarking and compliance audits are essential for evaluating the effectiveness and efficiency of inhouse medical billing processes. Organizations should compare their performance metrics with industry benchmarks and participate in external audits to identify areas for improvement and ensure ongoing compliance with regulations. Benchmarking and audits provide valuable insights into the organization’s billing performance and facilitate continuous quality improvement.
Future Trends and Innovations

Advancements in billing software and automation
The future of inhouse medical billing lies in advancements in billing software and automation. With the development of intelligent billing systems, healthcare organizations can benefit from increased accuracy, decreased manual labor, and improved operational efficiency. Automated processes, such as claims submission and payment posting, minimize errors and reduce administrative burden, allowing staff to focus on higher-value tasks.
Integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML)
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies holds great promise for inhouse medical billing. AI-powered solutions can analyze vast amounts of data, detect patterns, and identify errors or anomalies in billing processes. Machine learning algorithms can continuously learn from data and improve accuracy in coding, claim submission, and denial management. These technologies have the potential to enhance efficiency, reduce billing errors, and optimize revenue cycle management.
Telehealth and remote billing capabilities
The increasing prevalence of telehealth services brings new opportunities and challenges for inhouse medical billing. Healthcare organizations need to adapt their billing processes to accommodate remote services and billing for telehealth visits. This may involve integrating telehealth platforms with billing software, ensuring proper coding and documentation for telehealth services, and navigating reimbursement policies specific to virtual care.
Blockchain technology for secure data exchange
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize medical billing by ensuring secure and transparent data exchange. Blockchain’s decentralized and tamper-proof nature can enhance data security and privacy, prevent fraudulent activities, and streamline claims processing. Implementing blockchain-based solutions for inhouse medical billing can lead to increased trust, reduced administrative costs, and improved interoperability among healthcare stakeholders.
Conclusion
Inhouse medical billing plays a vital role in the financial health and operational efficiency of healthcare organizations. It involves various key functions, including patient registration, insurance verification, charge entry and coding, claim submission and management, payment posting, denial management, patient invoicing, accounts receivable follow-up, and reporting. While implementing inhouse medical billing requires careful consideration of staffing, technology, compliance, and financial aspects, it offers numerous advantages such as enhanced control, faster reimbursement, reduced dependency on third-party providers, better patient communication, improved revenue cycle management, and flexibility to adapt to regulatory changes. However, organizations must be mindful of potential challenges, such as upfront investment, increased billing errors, the need for continuous regulatory updates, resource intensiveness, and limited scalability. Comparing inhouse and outsourced billing, addressing compliance and legal considerations, and staying abreast of future trends and innovations are crucial for successful inhouse medical billing implementation. Ultimately, a well-executed inhouse medical billing strategy can optimize revenue, improve patient satisfaction, and contribute to the overall success of healthcare organizations.