Medical coding is an essential practice in the healthcare industry that involves assigning specific codes to medical procedures, diagnoses, and treatments. These codes serve as a universal language that facilitates efficient communication and accurate billing between healthcare providers and insurance companies. In this article, you will explore the fundamentals of medical coding, its significance in the healthcare system, and the vital role it plays in ensuring quality patient care. Gain a comprehensive understanding of the basics of medical coding, and discover how this meticulous process contributes to the smooth functioning of healthcare facilities.
Medical Coding Overview
Definition of medical coding
Medical coding is a crucial process in healthcare that involves assigning standardized codes to medical diagnoses, procedures, and services. This standardized coding system ensures accurate and consistent documentation, communication, and reimbursement within the healthcare industry. It allows healthcare professionals, insurance companies, and regulatory authorities to understand and track patient care, treatment outcomes, and financial transactions.
Importance of medical coding
Medical coding is essential for various reasons. Firstly, it enables healthcare providers to accurately document patient information, including diagnoses, treatments, and procedures performed. This documentation plays a vital role in patient care, as it provides a comprehensive history that can guide future treatments and facilitate effective communication between healthcare professionals.
Secondly, medical coding serves as the foundation for medical billing and insurance claims processes. Accurate and detailed coding ensures that healthcare providers are reimbursed appropriately for the services they provide, reducing billing errors and reimbursement delays. It also aids in preventing fraud and abuse by ensuring that services billed are supported by documented medical necessity.
Moreover, medical coding plays a crucial role in research and statistical analysis. The standardized codes enable the collection and aggregation of data on diseases, treatments, and outcomes for population health management and research purposes. This valuable information can guide healthcare policies, improve patient care, and drive medical advancements.
Medical Coding Systems

International Classification of Diseases (ICD)
The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) is the most widely used coding system for documenting and classifying diseases and health conditions. It provides a standard classification structure to facilitate data collection, analysis, and reimbursement. The current version, ICD-10, encompasses thousands of diagnosis codes that cover various medical conditions and related factors.
Current Procedural Terminology (CPT)
The Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) coding system is primarily used for coding medical procedures and services in the United States. Developed and maintained by the American Medical Association (AMA), CPT codes provide a standardized language for reporting medical services and are widely used in billing, insurance claims, and reimbursement processes.
Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS)
The Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) is another coding system used for reporting medical services and supplies. It consists of two levels: Level I codes, which are identical to CPT codes and used for physician services, and Level II codes, which cover non-physician services, durable medical equipment, and supplies. HCPCS codes are essential for Medicare and Medicaid reimbursements.
ICD Coding

ICD structure and format
ICD codes follow a specific structure and format, allowing for uniformity and ease of use. The codes are alphanumeric and typically contain three to seven characters, depending on the level of detail required. The first three characters represent the category of the disease or condition, followed by additional characters that provide more specificity, such as the site, severity, or etiology of the condition.
ICD code categories
ICD codes are organized into different categories, representing various diseases, conditions, and factors affecting health. These categories include infectious diseases, neoplasms, circulatory diseases, respiratory diseases, digestive system disorders, musculoskeletal conditions, and many more. Each category has specific subcategories and codes for capturing specific details about the condition being coded.
ICD code updates
The World Health Organization (WHO) periodically updates the ICD code set to reflect advancements in medical knowledge and changes in healthcare practices. These updates ensure that medical coding remains accurate and relevant. It is crucial for medical coders to stay updated with the latest coding guidelines and revisions to ensure compliance and accurate reporting of medical conditions.
CPT Coding

CPT structure and format
CPT codes consist of five-digit numeric codes that are organized into three main sections: Evaluation and Management (E/M) codes, which represent services related to patient encounters; Surgery codes, which cover operative procedures; and Ancillary codes, which include laboratory tests, radiology procedures, and other supplemental services.
CPT code categories
CPT codes are further divided into categories and subcategories based on the type and complexity of the services rendered. These categories include the following: Anesthesia, Surgery, Radiology, Pathology and Laboratory, Medicine, and Evaluation and Management. Each category has specific codes that capture the unique elements of the service provided.
CPT code updates
The American Medical Association (AMA) regularly updates the CPT code set to reflect changes in medical technology, procedures, and guidelines. These updates ensure that the coding system accurately represents the current medical landscape. Medical coders must stay abreast of these updates to ensure accurate coding, effective reimbursement, and compliance with billing regulations.
HCPCS Coding

HCPCS structure and format
HCPCS codes are alphanumeric and consist of a letter (A through V) followed by four numeric digits. The first character of the code represents the level of the HCPCS code (Level I or Level II), followed by specific codes that provide details about the service, supply, or equipment being coded.
HCPCS code levels
HCPCS has two levels of codes. Level I codes are identical to CPT codes and are used for physician services, while Level II codes are used for non-physician services, supplies, and equipment. Level II codes are essential for Medicare and Medicaid claims and are more specific in capturing certain medical procedures and supplies not covered by Level I codes.
HCPCS code updates
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) updates the HCPCS code set annually to reflect changes in healthcare services, supplies, and equipment. These updates ensure accurate reporting and appropriate reimbursement for services rendered. Medical coders and billing specialists must stay informed about these updates to maintain compliance and optimize revenue capture.
Medical Coding Guidelines

Documentation requirements
Accurate and comprehensive documentation is vital for medical coding. Healthcare providers must maintain detailed records of patient encounters, including diagnoses, procedures, treatments, and relevant clinical information. Clear and thorough documentation supports accurate coding, effective communication, and appropriate reimbursement.
Coding conventions
Coding conventions provide guidelines for selecting the appropriate codes and ensure consistency in medical coding. These conventions include instructions on sequencing codes, determining principal diagnoses, using combination codes for related conditions, and applying coding rules for uncertain diagnoses. Following coding conventions enhances the accuracy and integrity of the coded medical data.
Coding guidelines by coding system
Each coding system, such as ICD, CPT, and HCPCS, has specific coding guidelines that must be adhered to. These guidelines provide detailed instructions on code selection, sequencing, and reporting requirements for various healthcare scenarios. Compliance with coding guidelines is crucial to ensure accurate coding and reimbursement and prevent errors or fraud.
Roles and Responsibilities

Medical coders
Medical coders are trained professionals responsible for translating healthcare diagnoses, procedures, and services into standardized codes. They review patient medical records, extract relevant information, and assign appropriate codes using the designated coding systems. The coders must possess a comprehensive understanding of medical terminology, disease processes, and coding guidelines to ensure accurate and compliant coding.
Medical auditors
Medical auditors play a critical role in ensuring accurate and compliant medical coding practices. They review coded medical records for accuracy, adherence to coding guidelines, and compliance with regulatory requirements. Auditors identify coding errors, inconsistencies, and potential areas for improvement. Their assessments promote coding integrity, compliance, and quality improvement within healthcare organizations.
Medical billing specialists
Medical billing specialists are responsible for translating coded medical data into accurate and timely insurance claims. They review coded medical records, verify insurance coverage, and generate and submit claims to payers for reimbursement. These specialists play a vital role in the revenue cycle management process, ensuring accurate coding, proper billing, and timely reimbursement for healthcare services.
Reimbursement and Revenue Cycle

Relationship between coding and reimbursement
Medical coding plays a significant role in the reimbursement process within the healthcare industry. Accurate and detailed coding ensures that healthcare providers are reimbursed appropriately for the services they provide. Insurance companies and payers rely on the coded information to determine reimbursement rates, coverage determinations, and claims adjudication. Effective coding practices ensure accurate and timely reimbursement, reducing financial risks for healthcare organizations.
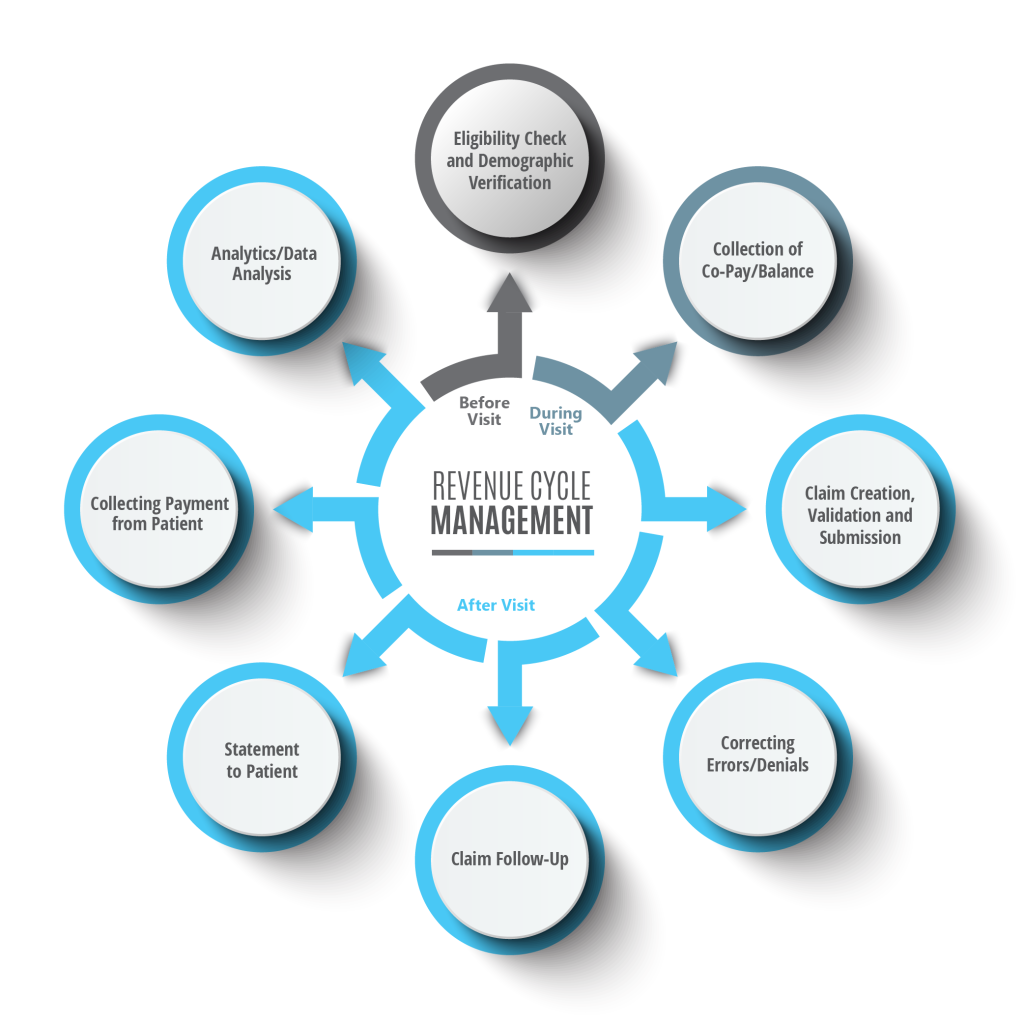
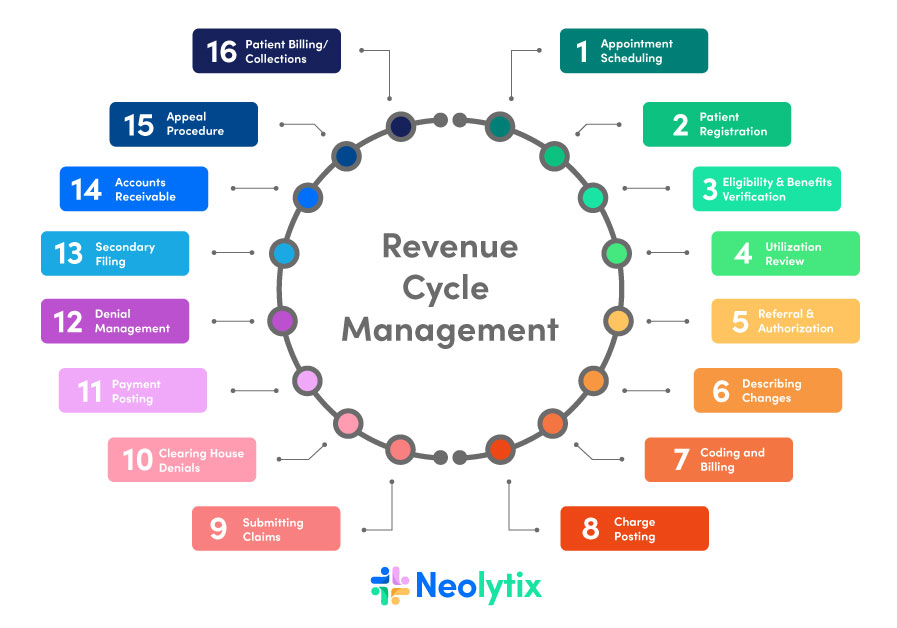
Revenue cycle management
Revenue cycle management encompasses the entire process of patient registration, scheduling, coding, billing, claims submission, payment processing, and financial reconciliation. Effective revenue cycle management ensures the timely and accurate collection of revenues for healthcare services provided. Medical coding is a critical component of this process, as accurate coding directly impacts the financial health and sustainability of healthcare organizations.
Importance of accurate coding for revenue optimization
Accurate coding is essential for revenue optimization in the healthcare industry. Properly coded medical services ensure appropriate reimbursement by payers, minimizing revenue loss and maximizing revenue capture. Accurate coding also aids in identifying any missed opportunities for enhanced reimbursement, such as capturing additional services provided or documenting comorbid conditions. By optimizing coding practices, healthcare organizations can maximize their revenue potential and improve overall financial performance.
Coding Compliance and Auditing

Importance of coding compliance
Coding compliance is of paramount importance in healthcare to ensure accurate reporting, prevent fraud and abuse, and maintain legal and regulatory compliance. Proper coding practices, adherence to coding guidelines, and accurate documentation support coding compliance. Compliance with coding standards protects healthcare organizations from financial penalties, audits, and legal consequences.
Auditing processes and procedures
Auditing plays a vital role in assessing coding accuracy and compliance. Regular internal and external coding audits evaluate the quality and compliance of coding practices. Auditors review coded medical records, documentation, and supporting documents to verify accuracy, adherence to coding guidelines, and compliance with regulatory requirements. Auditing identifies areas for improvement, training needs, and potential risks, ultimately enhancing coding accuracy and compliance.
Coding compliance program components
A robust coding compliance program consists of various components aimed at maintaining coding integrity and compliance. These components include coding policies and procedures, ongoing education and training for coders and providers, regular coding audits, documentation improvement initiatives, internal and external reporting mechanisms, and a culture of accountability and ethics. A comprehensive coding compliance program ensures accurate coding, supports regulatory compliance, and mitigates financial and legal risks for healthcare organizations.
Industry Standards and Regulations
HIPAA regulations
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) establishes privacy and security standards for protecting patients’ health information. HIPAA regulations require healthcare organizations to adhere to specific coding and documentation practices to maintain patient privacy and confidentiality. Medical coders must comply with HIPAA regulations when extracting, coding, storing, and transmitting patient information.
Coding ethics
Coding ethics encompass professional standards and principles that guide medical coders’ behavior and decision-making. Coders must adhere to strict ethical guidelines, ensuring honesty, integrity, confidentiality, and accuracy in all coding practices. Adhering to coding ethics promotes trust, credibility, and professionalism within the healthcare industry.
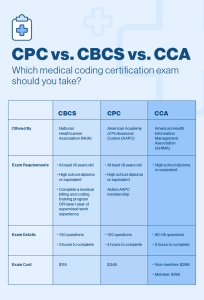
Industry certifications
Professional certifications in medical coding validate a coder’s knowledge, skills, and expertise in the field. Certifications such as Certified Professional Coder (CPC), Certified Coding Specialist (CCS), or Registered Health Information Technician (RHIT) signify a coder’s proficiency and dedication to coding excellence. Holding industry certifications enhances professional credibility and career opportunities in the healthcare sector.