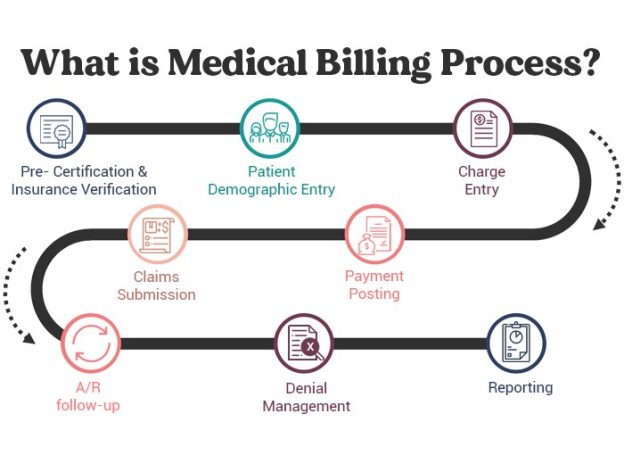
The Rcm Billing Process is a comprehensive system designed to streamline and optimize the billing operations of medical organizations. Tailored to the unique needs of the healthcare industry, this process utilizes cutting-edge technology and industry best practices to ensure accurate, efficient, and timely billing. With a focus on eliminating manual errors and reducing administrative burden, the Rcm Billing Process aims to maximize revenue and enhance overall financial performance.
What is RCM Billing Process
Definition
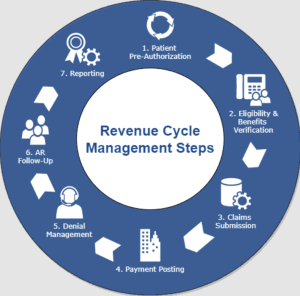
The RCM billing process, also known as Revenue Cycle Management, refers to the comprehensive end-to-end approach of managing the financial aspects of medical services provided by healthcare providers. It encompasses various activities, ranging from patient registration and scheduling to claim submission, payment posting, denial management, and accounts receivable follow-up.
Importance of RCM Billing Process
The RCM billing process plays a crucial role in ensuring the financial viability and success of healthcare organizations. By efficiently managing the billing and reimbursement cycle, healthcare providers can optimize revenue collection, minimize claim denials, improve cash flow, and enhance overall operational efficiency. Effective revenue cycle management is essential for the financial stability of healthcare organizations, enabling them to deliver high-quality patient care and invest in technology, resources, and staff development.
Key Components of RCM Billing Process
The RCM billing process comprises several key components that work together to facilitate efficient and accurate financial management within healthcare organizations. These components include patient registration and scheduling, insurance eligibility and pre-authorization, patient encounter and documentation, coding and charge capture, claim submission, payment posting and reconciliation, denial management and appeals, accounts receivable follow-up, compliance and auditing. Let’s explore each of these components in more detail.
Patient Registration and Scheduling

Gathering Patient Information
The process of patient registration involves collecting and verifying crucial demographic and insurance information. It is essential to ensure that accurate patient details are obtained, including name, contact information, date of birth, social security number, and insurance coverage details. Gathering comprehensive patient information at the initial stage helps in minimizing errors, ensuring proper insurance reimbursement, and promoting a smooth billing process.
Insurance Verification
Verification of patient insurance coverage is a critical step in the RCM billing process. It involves confirming the patient’s insurance details, policy type, coverage limitations, and eligibility for specific medical services. Verifying insurance eligibility helps healthcare providers understand the patient’s financial responsibility, determine the need for pre-authorization, and ensure that services rendered will be reimbursed appropriately. This step is crucial for avoiding claim denials and reducing revenue loss.
Appointment Scheduling
Efficient appointment scheduling is another vital aspect of the RCM billing process. Proper scheduling ensures that medical services are provided in a timely manner, optimizing the utilization of healthcare resources and minimizing patient wait times. Coordinating appointments with the availability of healthcare providers and ensuring that the necessary resources are in place streamlines the billing process by preventing delays and maximizing revenue generation.
Insurance Eligibility and Pre-Authorization

Determining Patient’s Insurance Coverage
Once patient insurance details are gathered and verified, the next step is to determine the patient’s insurance coverage for specific services. This involves understanding the insurance provider’s policies, covered services, copayment requirements, deductibles, and any limitations or exclusions. By assessing insurance coverage accurately, healthcare providers can estimate the patient’s financial responsibility and communicate this information to the patient beforehand, ensuring transparency and avoiding any surprises related to out-of-pocket costs.
Obtaining Prior Authorization for Services
Certain medical services require prior authorization from insurance providers to ensure reimbursement. Obtaining pre-authorization involves submitting relevant medical documentation and obtaining approval from the insurance company before providing the services. This step is critical to prevent claim denials and delays in payment. By proactively securing authorization, healthcare providers can avoid the financial burden of services that may be deemed medically unnecessary or not covered under the patient’s insurance plan.
Patient Encounter and Documentation
Providing Medical Services
The patient encounter is the central focus of the RCM billing process as it involves the actual provision of medical services. During this phase, healthcare providers deliver the necessary care, treatments, and procedures to address the patient’s healthcare needs. It is crucial for healthcare providers to accurately document the details of services rendered, including diagnosis, treatments provided, medications prescribed, and any other pertinent information. Timely and accurate documentation ensures proper coding and billing, leading to accurate reimbursement and minimizing the risk of claim denials.
Accurate Documentation of Services Rendered
Accurate documentation is a vital aspect of the RCM billing process, as it forms the basis for coding, claim submission, and reimbursement. It is essential for healthcare providers to maintain detailed records of the services performed, recording all relevant information accurately and comprehensively. Proper documentation allows for correct coding, facilitates proper claim submission, and provides a clear audit trail for compliance purposes. Detailed documentation also helps in justifying services provided, supporting medical necessity, and avoiding potential coding or billing discrepancies.
Coding and Charge Capture

Assigning Appropriate Medical Codes
Medical coding is a critical step in the RCM billing process, as it involves translating the medical services provided into specific alphanumeric codes. Healthcare providers use standard coding systems such as ICD-10-CM for diagnoses and CPT/HCPCS codes for procedures and services. accurate coding is crucial for proper reimbursement, as insurance companies rely on these codes to determine the amount payable for each service rendered. Coding errors can result in claim denials, payment delays, or incorrect reimbursement, impacting the financial health of healthcare organizations.
Capturing Charges for Services Rendered
In addition to coding, accurately capturing charges for services rendered is essential for the RCM billing process. This involves documenting the fees associated with each service, medication, or procedure provided. Proper charge capture ensures that healthcare providers bill for all services rendered, helping maximize revenue generation. Timely and accurate charge capture also facilitates the claim submission process, ensuring that all relevant charges are included, and reducing the risk of missed reimbursement opportunities.
Claim Submission

Preparing and Submitting Claims to Payers
Claim submission is a crucial step in the RCM billing process, involving the preparation and submission of claims to insurance payers for reimbursement. Properly prepared claims include accurate patient and provider information, detailed service descriptions, appropriate coding, and supporting documentation. Healthcare organizations must follow the specific submission requirements and timelines of each insurance payer to ensure timely and accurate claim processing. Efficient claim submission optimizes the reimbursement process, reduces claim denials, and accelerates revenue collection.
Ensuring Correct Coding and Documentation
Ensuring correct coding and documentation is of paramount importance in the claim submission process. Healthcare providers must review claims rigorously to verify that the assigned codes accurately reflect the services provided and comply with coding guidelines. Claims should also include sufficient supporting documentation, such as medical records, to substantiate the services billed. By ensuring accurate coding and documentation, healthcare organizations can increase the likelihood of successful claim adjudication, minimize claim denials, and expedite reimbursement.
Payment Posting and Reconciliation

Recording Payments and Adjustments
Payment posting involves recording the payments received from insurance payers and patients into the healthcare organization’s financial systems. Each payment must be accurately posted to the appropriate patient’s account, allocating the funds to the relevant service codes and outstanding balances. In addition to payments, adjustments such as contractual write-offs, discounts, or refunds need to be recorded. Proper payment posting ensures financial accuracy, facilitates revenue reconciliation, and provides an up-to-date snapshot of the healthcare organization’s financial position.
Reconciling Payments with Outstanding Balances
Revenue reconciliation is a critical activity within the RCM billing process, as it involves comparing the payments received with the outstanding balances owed by insurance payers and patients. Reconciliation ensures that the full amount of revenue due to the healthcare provider is collected and accounted for. Discrepancies or discrepancies in payment amounts can be investigated and resolved promptly, preventing potential revenue leakage. Accurate and timely revenue reconciliation supports financial reporting, budgeting, and enables proactive management of the healthcare organization’s financial health.
Denial Management and Appeals

Identifying and Resolving Claim Denials
Claim denials are a common challenge faced by healthcare organizations, impacting their revenue and cash flow. denial management involves identifying the reasons for claim denials and taking appropriate steps to resolve them promptly. This includes investigating denial reasons, correcting errors, gathering additional documentation, or appealing the denials when necessary. Effective denial management helps optimize revenue by maximizing the number of claims paid while minimizing the financial impact of denials on the healthcare organization.
Appealing Denied Claims When Necessary
In cases where a claim denial is deemed unfair or unjustified, healthcare organizations have the option to appeal the decision. Appeals involve submitting additional documentation, conducting a thorough investigation, and providing a strong argument to support the claim’s validity. Skilled appeals management can result in successful claim reversals, ensuring that healthcare providers are rightfully reimbursed for services provided. Timely and strategic appeals can significantly improve revenue recovery, mitigate financial losses, and support the overall financial stability of healthcare organizations.
Accounts Receivable Follow-Up

Tracking Unpaid Claims
The accounts receivable (AR) follow-up process is an essential component of the RCM billing process, focusing on tracking unpaid claims and outstanding balances. Healthcare organizations must proactively monitor and follow up on unpaid claims, identifying reasons for non-payment, such as claim denials, payer delays, or outstanding patient balances. By tracking unpaid claims, healthcare providers can take prompt action to resolve issues, resubmit claims when necessary, and minimize the risk of extended payment delays or write-offs.
Contacting Payers and Patients for Payment
The AR follow-up process involves ongoing communication with insurance payers and patients to secure timely payment of outstanding balances. This includes contacting insurance payers to address claim payment delays, resolve denials, or obtain clarification on reimbursement issues. Additionally, healthcare organizations must engage with patients to communicate outstanding balances, facilitate prompt payment, and arrange payment plans if necessary. Effective communication and follow-up with payers and patients promote timely revenue collection, reduce bad debt, and maintain a healthy financial position.
Compliance and Auditing

Ensuring Compliance with Regulations
Compliance with healthcare regulations is a critical aspect of the RCM billing process. Healthcare organizations must adhere to a multitude of federal, state, and industry-specific regulations to ensure ethical and legal billing practices. Compliance includes maintaining patient privacy and confidentiality according to HIPAA regulations, following coding and documentation guidelines, and resolving billing discrepancies ethically. By ensuring compliance, healthcare organizations protect their reputation, avoid legal penalties, and maintain high standards of ethical billing practices.
Conducting Regular Audits for Quality Assurance
Regular auditing is an integral part of the RCM billing process, providing quality assurance and identifying any deficiencies, discrepancies, or areas for improvement. Internal and external audits assess the accuracy and integrity of the billing process, coding practices, documentation standards, and overall compliance with regulations. Through audits, healthcare organizations can identify areas of risk, implement corrective actions, and enhance their revenue cycle management processes. Conducting regular audits promotes accountability, improves financial performance, and safeguards against potential billing errors or fraudulent activities.
In conclusion, the RCM billing process is a comprehensive approach to managing the financial aspects of medical services provided by healthcare organizations. Each component within the RCM billing process plays a critical role in ensuring accurate, timely, and optimized reimbursement. By implementing effective revenue cycle management practices, healthcare organizations can maximize revenue generation, minimize claim denials, and maintain financial stability in an evolving healthcare landscape.