In a rapidly evolving healthcare industry, the role of medical coders has become increasingly vital. With advancing technology and the growing demand for accurate medical documentation, the future for medical coders appears to be promising. As the need for healthcare services continues to rise, medical coders serve as the backbone of the industry, ensuring that diagnoses, procedures, and treatments are properly translated into universally understood codes. This article explores the evolving landscape for medical coders, highlighting their indispensable role and discussing the potential career prospects in the field.
The Importance of Medical Coders

Ensuring Accurate Billing and Reimbursement
Medical coders play a critical role in the healthcare industry by ensuring accurate billing and reimbursement. These professionals are responsible for assigning specific codes to medical procedures, diagnoses, and services, which are then used for billing purposes. By accurately coding this information, medical coders help avoid errors that could result in under or overcharging patients, insurance companies, or the government.
Accurate billing and reimbursement are essential not only to maintain the financial health of healthcare organizations but also to ensure fair and appropriate compensation for the services provided. Medical coders are trained to meticulously review medical documentation, translate it into standardized codes, and apply the correct coding guidelines to reflect the complexity of the patient’s condition accurately. This accuracy is crucial in preventing billing disputes and maintaining the integrity of the healthcare system.
Supporting Healthcare Quality Measures
In addition to billing and reimbursement, medical coders also contribute to healthcare quality measures. By accurately coding medical data, these professionals provide vital information that is used to assess the quality of care provided by healthcare providers. Coded data helps track outcomes, monitor patient safety, measure the effectiveness of treatments, and identify potential areas for improvement.
The data generated by medical coders is used in a variety of ways to support healthcare quality measures. It plays a crucial role in identifying trends and patterns that can help healthcare organizations develop strategies to improve patient outcomes and enhance the overall quality of care. By ensuring accurate and consistent coding, medical coders contribute to the ongoing evaluation and improvement of healthcare services.
Facilitating Research and Data Analysis
Medical coders also play an essential role in facilitating research and data analysis. Coded medical data serves as the foundation for many healthcare studies, clinical trials, and population health research. By accurately coding patient information, medical coders provide researchers with reliable and standardized data that can be used to identify trends, analyze outcomes, and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions.
In an era of evidence-based medicine, research and data analysis are crucial for advancements in healthcare. Medical coders provide the necessary data to researchers, policymakers, and healthcare professionals, enabling them to make informed decisions and drive improvements in patient care. Their role in facilitating research and data analysis cannot be overstated, as it is an integral part of driving advancements and ensuring the delivery of high-quality healthcare services.
Technological Advances Impacting Medical Coders

Automation and Artificial Intelligence
Technological advances, such as automation and artificial intelligence (AI), have had a significant impact on the field of medical coding. Automation tools are increasingly being used to assist medical coders in their work, reducing the time and effort required to assign codes accurately. AI-powered coding systems can analyze medical documentation and suggest appropriate codes based on predefined algorithms, improving accuracy and efficiency.
Automation and AI have the potential to streamline the coding process, making it faster and more accurate. This allows medical coders to focus on complex cases that require their expertise, while routine coding tasks can be handled by automated systems. However, it is important to note that automation and AI should be seen as tools to augment the work of medical coders rather than replace them entirely. Human expertise and judgment are still critical in ensuring accurate coding and interpreting complex medical information.
Emerging Trends in Electronic Health Records
The widespread adoption of electronic health records (EHRs) has revolutionized the way medical coders access and process patient information. EHRs provide a comprehensive digital record of a patient’s medical history, including diagnoses, procedures, and medications. This wealth of information can be leveraged by medical coders to assign accurate codes and generate detailed reports for billing and reimbursement.
With the increasing use of EHRs, medical coders need to develop proficiency in navigating these systems and effectively extracting the necessary information for coding purposes. Additionally, advancements in EHR technologies, such as natural language processing and voice recognition, can further streamline the coding process by automatically capturing relevant data from clinical documentation.
Challenges and Opportunities for Medical Coders
Changes in Coding Systems and Guidelines
One of the major challenges facing medical coders is the constant evolution of coding systems and guidelines. The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) system, currently in its 10th revision (ICD-10), is regularly updated with new codes and guidelines to reflect advancements in medical knowledge and technology. Medical coders need to stay updated with these changes and ensure their coding practices align with the latest standards.
Keeping up with coding system changes requires ongoing education and training. Medical coders must invest time and effort in learning about new codes, guidelines, and documentation requirements to maintain accurate and compliant coding practices. Failure to adapt to these changes could result in incorrect coding, leading to claim denials, billing discrepancies, and potential legal implications.
Increasing Demand for Specialized Coding Skills
As the healthcare industry becomes more complex, there is an increasing demand for medical coders with specialized coding skills. Certain medical specialties, such as cardiology, oncology, and orthopedics, have specific coding rules and guidelines that require in-depth knowledge and expertise. Medical coders proficient in these specialty areas are highly sought after and can command higher salaries.
To meet this demand, medical coders should consider pursuing specialized training and education in specific areas of coding. This specialized knowledge not only enhances career prospects but also ensures accurate and efficient coding in specialties where precision is critical. Additionally, specialized coding skills can lead to opportunities for advancement and career growth within healthcare organizations.
Remote Work Opportunities
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of remote work arrangements across various industries, including healthcare. Medical coders are no exception and have witnessed an increase in remote work opportunities. Advancements in technology and the availability of secure remote access to medical records have made it possible for medical coders to work from anywhere, providing flexibility and work-life balance.
Remote work offers several benefits for medical coders, such as reduced commute time and expenses, increased productivity and focus, and the ability to create a personalized work environment. However, it also requires self-discipline, strong communication skills, and the ability to adapt to virtual collaboration tools. Medical coders considering remote work should ensure they have a reliable internet connection, up-to-date technology, and a dedicated workspace to maintain productivity and professionalism.
The Role of Education and Certification
Importance of Formal Training and Education
Formal training and education play a vital role in preparing medical coders for the demands of their profession. While some medical coders may enter the field with on-the-job training or a coding certificate, obtaining a formal education can provide a comprehensive understanding of medical coding principles, coding systems, and guidelines.
A formal education program in medical coding typically covers topics such as anatomy and physiology, medical terminology, ICD and Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) coding systems, healthcare laws and regulations, and medical billing processes. These programs provide a solid foundation of knowledge and skills necessary for accurate and compliant coding.
In addition to the technical aspects of medical coding, formal education programs often emphasize critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills. These skills are essential in interpreting complex medical documentation, resolving coding ambiguities, and effectively communicating with healthcare providers, insurers, and other stakeholders.
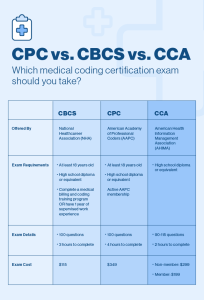
Certifications for Medical Coders
Obtaining a professional certification is an essential step in demonstrating proficiency and credibility in the field of medical coding. The most widely recognized certifications for medical coders are offered by the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC) and the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA).
Certifications from these organizations validate an individual’s knowledge of coding systems, guidelines, and ethical coding practices. They require candidates to pass rigorous exams, which assess their coding skills and understanding of medical coding principles. These certifications are highly regarded by employers and can enhance job prospects, earning potential, and professional credibility.
Medical coders should carefully consider the certification pathway that aligns with their career goals and desired areas of specialization. Continuous education and adherence to professional ethical standards are essential for maintaining certification and staying current in an ever-changing field.
The Impact of Healthcare Policies

Implementation of ICD-10 Coding System
The implementation of the ICD-10 coding system in 2015 was a significant milestone in the field of medical coding in the United States. This transition from the previous ICD-9 system expanded the number of available codes, allowing for more detailed documentation of diagnoses, procedures, and medical conditions.
The ICD-10 coding system has enabled improved accuracy and specificity in coding, providing a more comprehensive picture of patients’ health conditions. This enhanced level of detail has facilitated better tracking of healthcare outcomes, epidemiological studies, and population health monitoring.
Medical coders need to be proficient in ICD-10 coding to ensure accurate and compliant coding practices. The shift to ICD-10 has required extensive training and education for medical coders, as the system is more complex and includes a broader range of codes. However, this shift has ultimately resulted in more precise and detailed coding, supporting improved patient care and the generation of valuable data for research and analysis.
Potential Changes in Healthcare Policies
The healthcare industry is subject to constant changes in policies and regulations. Changes in healthcare policies can have a significant impact on medical coders, as they directly affect coding guidelines, reimbursement rates, and documentation requirements.
As healthcare policies continue to evolve, medical coders must stay informed and adapt their coding practices accordingly. This requires a proactive approach to continuing education and staying updated with regulatory changes, such as updates to the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule or changes in coding guidelines issued by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS).
Medical coders should actively engage with professional organizations, attend industry conferences, and participate in ongoing training programs to ensure they remain well-informed and compliant with evolving healthcare policies. Adapting to these changes is crucial to maintain accurate and efficient coding practices and to provide optimal support to healthcare organizations, providers, and patients.
Growing Demand for Medical Coders

Expanding Healthcare Industry
The demand for medical coders is expected to grow significantly in the coming years due to the expanding healthcare industry. As the population continues to grow and age, there is an increased need for healthcare services and a corresponding increase in the volume of medical records and documentation.
The expanding healthcare industry creates a higher demand for medical coders to ensure accurate and efficient coding of medical data. This demand is fueled not only by hospitals and medical clinics but also by outpatient facilities, physician practices, and other healthcare providers. The growing complexity of healthcare services and the associated coding requirements make the role of medical coders increasingly crucial.
Aging Population and Increased Medical Needs
The aging population is another factor contributing to the growing demand for medical coders. As individuals age, they often require more medical care and services, resulting in an increased need for accurate coding and billing. Conditions associated with aging, such as chronic diseases and complex medical conditions, require detailed and accurate coding to appropriately capture the complexity of care provided.
Medical coders specializing in geriatric care and chronic disease management are particularly in demand as they possess the necessary expertise to accurately code and document the unique needs of the aging population. The ability to navigate complex coding systems and accurately reflect the medical services provided to the elderly is essential in ensuring adequate reimbursement and appropriate healthcare resource allocation.
Future Job Prospects for Medical Coders

Job Growth and Stability
The future job prospects for medical coders remain promising due to the continued growth and evolution of the healthcare industry. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects a 8% job growth rate for medical records and health information technicians, which includes medical coders, from 2019 to 2029, faster than the average for all occupations.
The demand for medical coders is driven by factors such as the increasing use of electronic health records, the need for accurate coding to support billing and reimbursement, and the ongoing focus on healthcare quality measures. As healthcare organizations continue to rely on accurate and efficient coding, medical coders will remain an integral part of the healthcare delivery system.
Furthermore, the stability of the medical coding profession provides job security for individuals entering the field. The demand for healthcare services is not diminishing, and medical coders are essential to ensure that healthcare organizations can effectively manage their billing, reimbursement, and data analysis needs.
Evolution of Coding Roles
While the core responsibilities of medical coders remain consistent, the profession is evolving to meet the changing needs of the healthcare industry. Medical coders are increasingly being involved in activities such as clinical documentation improvement (CDI), coding audits, and compliance monitoring.
CDI involves working closely with healthcare providers to ensure accurate and complete clinical documentation. Medical coders with CDI expertise offer valuable insights to healthcare providers, assisting them in capturing all necessary information for coding and billing. This collaboration between coders and providers not only improves coding accuracy but also enhances the quality of clinical documentation for better patient care and compliance.
With healthcare organizations placing greater emphasis on compliance and risk management, medical coders with auditing and compliance skills are in high demand. These professionals review coding practices, identify areas for improvement, and ensure adherence to coding guidelines and regulatory requirements. The evolving role of medical coders allows for career advancement and the opportunity to specialize in areas beyond traditional coding responsibilities.
Emerging Specializations in Medical Coding

Medical Coding for Telemedicine Services
The increased utilization of telemedicine services has created a need for medical coders with specialized knowledge in this area. Telemedicine involves the remote provision of healthcare services through the use of technology, such as video conferencing and secure messaging. Medical coders specializing in telemedicine coding understand the unique coding requirements and documentation guidelines associated with these services.
Telemedicine coding requires an understanding of the different types of telehealth encounters, the appropriate use of telehealth modifiers, and the coding for remote monitoring and virtual visits. As telemedicine continues to gain prominence, medical coders with expertise in this area will play a vital role in ensuring accurate coding and proper reimbursement for telemedicine services.
Genomic Coding and Precision Medicine
Advancements in genomics and precision medicine have opened up new opportunities for medical coders specializing in genomic coding. Genomic coding involves the interpretation and coding of genetic information to support personalized medicine, targeted therapies, and genetic testing.
Proper coding for genomic services is essential to accurately represent the complexity of genetic testing, molecular pathology, and targeted therapies. Medical coders with expertise in genomic coding can ensure the appropriate capture and reporting of genetic information, enabling healthcare providers to deliver personalized care and advance genetic research.
As precision medicine becomes more integrated into healthcare practice, the demand for medical coders with genomic coding skills is likely to increase. Medical coders interested in this emerging specialization should seek additional education and training to develop a deep understanding of genomic coding principles and guidelines.
Adapting to Industry Changes

Continuing Education and Skill Enhancement
Medical coding is a profession that requires ongoing learning and skill enhancement to keep pace with industry changes. Changes in coding systems, guidelines, and healthcare policies necessitate continuous education to maintain accurate and compliant coding practices.
Medical coders should actively engage in continuing education through workshops, seminars, webinars, and professional conferences. These opportunities provide valuable updates on coding best practices, industry trends, and regulatory changes. Professional organizations, such as the AAPC and AHIMA, offer a wide range of educational resources and networking opportunities to support the professional development of medical coders.
Additionally, medical coders can pursue advanced credentials or certifications in specialized coding areas to enhance their career prospects and marketability. Specialized certifications, such as Certified Professional Coder (CPC) and Certified Coding Specialist (CCS), validate a coder’s expertise in specific coding domains and can open doors to new career opportunities.
Embracing Technological Advancements
To thrive in the changing landscape of healthcare, medical coders must embrace and adapt to technological advancements. Automation tools, AI-powered coding systems, and electronic health records are transforming the coding process and streamlining workflows. Medical coders should familiarize themselves with these technologies to effectively leverage their benefits.
Medical coders can also explore opportunities to specialize in health information technology roles, such as coding system implementation and maintenance, health data analytics, or revenue cycle management. By expanding their skill set to include a deep understanding of coding technologies and systems, medical coders can position themselves for career growth and opportunities within healthcare organizations.
Embracing technological advancements not only enhances efficiency and accuracy in coding but also demonstrates adaptability and a willingness to evolve with the industry. This proactive approach will allow medical coders to remain relevant and valuable in an increasingly digital healthcare landscape.
Conclusion
Medical coders play a critical role in ensuring accurate billing and reimbursement, supporting healthcare quality measures, and facilitating research and data analysis in the healthcare industry. Technological advances, such as automation and AI, are impacting the field of medical coding, improving efficiency and accuracy. However, medical coders must also adapt to changes in coding systems, guidelines, and healthcare policies. The demand for medical coders is growing due to the expanding healthcare industry, the aging population, and increased medical needs. Future job prospects for medical coders are promising, with job growth and stability expected. The profession is evolving, offering opportunities for specialization and advancement. Adapting to industry changes through continuing education and embracing technological advancements are essential for medical coders to thrive in the dynamic healthcare field.
