Medical coding and clinical coding are often used interchangeably, but are they truly the same? In the healthcare industry, accurate documentation and coding are crucial for effective healthcare management, financial reimbursement, and accurate analysis of patient data. While medical coding and clinical coding share the objective of assigning standardized codes to medical procedures and diagnoses, they serve distinct purposes. This article aims to shed light on the similarities and differences between medical coding and clinical coding, providing valuable insights for healthcare professionals seeking to understand their unique roles within the industry.
Overview of Medical Coding and Clinical Coding
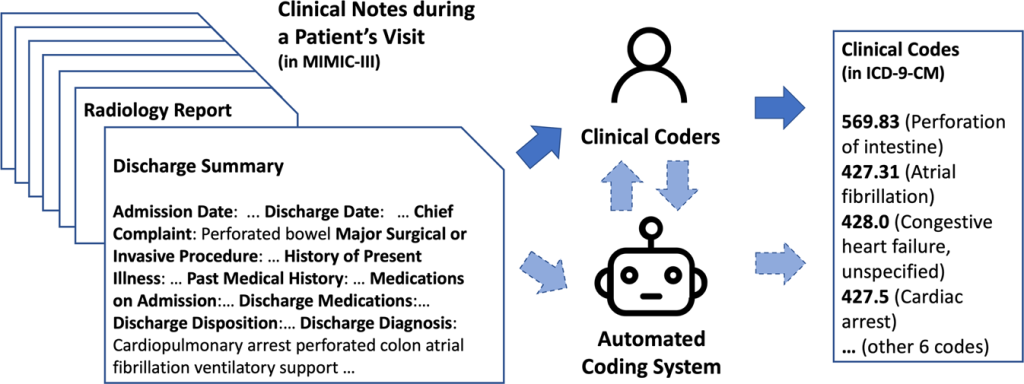
This image is property of media.springernature.com.
Definition of Medical Coding
Medical coding is the process of assigning standardized codes to medical procedures, diagnoses, and treatments. These codes are used for documentation, billing, and compliance purposes in the healthcare industry. Medical coding ensures that patient records are accurately coded to reflect the services provided, and it plays a vital role in the reimbursement and revenue cycle of healthcare organizations.
Definition of Clinical Coding
Clinical coding, on the other hand, focuses on coding clinical or healthcare data for research, analysis, and statistical purposes. It involves the transformation of medical diagnoses, symptoms, procedures, and other clinical information into alphanumeric codes that are used for clinical documentation, reporting, and data analysis. Clinical coding helps in tracking outcomes, epidemiological research, and designing appropriate healthcare interventions.
Importance of Coding in Healthcare
Coding in healthcare is crucial as it provides a standardized way to communicate medical information between healthcare professionals, insurance companies, and other stakeholders. Accurate and efficient coding ensures that medical records are complete, allowing for optimal patient care, proper billing, and compliance with regulations. It also plays a significant role in data analysis, research, and public health initiatives.
Differences Between Medical Coding and Clinical Coding

Scope and Purpose
Medical coding primarily focuses on coding procedures, diagnoses, treatments, and services to facilitate billing and reimbursement. The main goal is to accurately reflect the healthcare services provided and ensure appropriate reimbursement for healthcare providers. Clinical coding, on the other hand, involves coding clinical data for research, analysis, and statistical purposes to improve healthcare outcomes and support evidence-based decision-making.
Focus Areas
Medical coding is primarily concerned with coding for billing, insurance claims, and revenue cycle management. It involves assigning codes to document the services rendered, ensuring accurate reimbursement, and compliance with coding guidelines. Clinical coding focuses on coding clinical data for research, quality improvement, and population health management. It involves the translation of medical information into codes to support clinical decision-making, outcome tracking, and epidemiological research.
Education and Training
Medical coding typically requires specialized training and certification programs. These programs cover medical terminology, anatomy, coding guidelines, and coding systems such as ICD (International Classification of Diseases), CPT (Current Procedural Terminology), and HCPCS (Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System). Clinical coding may require additional education in fields such as epidemiology, biostatistics, and clinical data management to effectively code and analyze healthcare data for research purposes.
Job Roles and Responsibilities
In medical coding, professionals are responsible for accurately assigning codes to medical procedures, diagnoses, and treatments in compliance with coding guidelines. They may also be involved in claim review and auditing to ensure coding accuracy and prevent fraudulent activities. Clinical coders, on the other hand, are responsible for collecting and analyzing clinical data, translating medical records into codes, and ensuring the accuracy and completeness of coding to support research, data analysis, and clinical decision-making.
Coding Systems Used
Medical coding primarily uses coding systems such as ICD, CPT, and HCPCS. ICD codes are used to classify and code diagnoses and procedures, while CPT codes are used to code medical procedures and services. HCPCS codes are used to code supplies, equipment, and services not covered by CPT codes. Clinical coding utilizes coding systems such as SNOMED CT (Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine – Clinical Terms), LOINC (Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes), and RxNorm for coding clinical data for research and analysis.
Similarities Between Medical Coding and Clinical Coding
Coding as a Common Practice
Both medical coding and clinical coding share the common practice of assigning codes to healthcare data. Both types of coding involve the transformation of medical information into standardized codes for various purposes. While medical coding focuses on billing and reimbursement, clinical coding emphasizes research, analysis, and data management.
Usage of Medical Terminology
In both medical coding and clinical coding, a strong understanding of medical terminology is essential. Professionals in both fields need to be familiar with medical terms, procedures, and diagnoses to accurately assign codes. Both medical and clinical coders need to stay updated with changes in medical terminology to ensure the accuracy and consistency of coding practices.
Connection to Healthcare Revenue Cycle
Both medical coding and clinical coding play a significant role in the healthcare revenue cycle. Accurate coding in medical coding ensures appropriate reimbursement for healthcare services, which is essential for the financial stability of healthcare organizations. Clinical coding supports research and analysis that can lead to improved healthcare outcomes and cost-effective interventions, ultimately impacting the revenue cycle through evidence-based decision-making.
Understanding Medical Coding

Definition and Scope
Medical coding involves the translation of medical information, such as procedures, diagnoses, and treatments, into alphanumeric codes. These codes provide a standardized way of documenting, billing, and communicating medical services. The scope of medical coding includes various coding systems, including ICD, CPT, and HCPCS, and it plays a crucial role in healthcare reimbursement, compliance, and revenue cycle management.
Types of Medical Codes
There are different types of codes used in medical coding. ICD codes are provided by the World Health Organization (WHO) and are used to classify and code diagnoses and procedures. CPT codes, developed by the American Medical Association (AMA), are used to code medical procedures and services. HCPCS codes, administered by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), are used to code supplies, equipment, and services not covered by CPT codes.
ICD Coding
ICD coding is a critical aspect of medical coding as it involves coding diagnoses and procedures recorded in patient medical records. ICD codes are continuously updated with new codes and revisions to reflect changes in medical practices and emerging diseases. Medical coders need to be well-versed in ICD coding guidelines and updates to accurately assign the appropriate codes.
CPT Coding
CPT coding is essential for coding medical procedures and services. CPT codes provide a standardized way to communicate the services provided by healthcare professionals across different specialties. They are regularly updated to accommodate new procedures and technologies, ensuring accurate coding and reimbursement for the services rendered.
HCPCS Coding
HCPCS coding is used to code supplies, durable medical equipment, drugs, and other services not covered by CPT codes. These codes are used primarily for billing purposes and are necessary for ensuring accurate reimbursement from insurance providers and government healthcare programs.
Understanding Clinical Coding

This image is property of blissacademy.in.
Definition and Scope
Clinical coding involves assigning codes to clinical or healthcare data for research, analysis, and statistical purposes. It supports the use of coded data for clinical documentation, reporting, and data analysis to improve patient care and healthcare outcomes. The scope of clinical coding includes coding systems such as SNOMED CT, LOINC, and RxNorm, which are used to code and classify clinical data for research and analysis.
Types of Clinical Codes
There are various types of codes used in clinical coding. SNOMED CT is a widely used clinical coding system that provides a comprehensive language for coding clinical information. It covers medical conditions, procedures, medications, and other clinical concepts and enables interoperability and data exchange across different healthcare systems. LOINC is a coding system used to standardize laboratory test names and results, facilitating consistency in documentation and data sharing. RxNorm is a coding system that provides standardized names for medications, ensuring accurate communication and data integration.
SNOMED CT Coding
SNOMED CT is a coding system specifically designed for clinical coding. It is a comprehensive language that covers a broad range of clinical concepts, allowing for accurate and detailed coding of clinical data. SNOMED CT supports interoperability and semantic interoperability, enabling the exchange of coded data between healthcare systems.
LOINC Coding
LOINC coding is primarily focused on laboratory testing and results. It provides standardized names and codes for laboratory tests, ensuring consistency in documentation and enabling efficient data exchange between healthcare organizations. LOINC codes help in improving the quality and efficiency of laboratory testing and result reporting.
RxNorm Coding
RxNorm coding is used for coding medications and supporting accurate communication and data integration. It provides standardized names for medications, including generic names, brand names, and various other drug attributes. RxNorm enables seamless exchange of medication information between healthcare systems, improving medication safety and efficiency.
Educational Requirements for Medical Coders

Qualifications and Certifications
To become a medical coder, a high school diploma or equivalent is generally required. However, many employers prefer candidates with a formal education in medical coding, such as a certificate or associate’s degree in medical coding or health information management. certification from recognized organizations, such as the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC) or the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA), is highly valued and can enhance job prospects.
Training Programs
Training programs for medical coding are available through community colleges, vocational schools, and online platforms. These programs provide in-depth knowledge of medical terminology, anatomy, coding systems, and coding guidelines. Practical training may be included to develop hands-on coding skills. Ongoing education and professional development are essential for medical coders to stay updated with changes in coding guidelines and systems.
Educational Requirements for Clinical Coders

Qualifications and Certifications
Educational requirements for clinical coders may vary depending on the specific job role and organization. A bachelor’s degree in health information management, health informatics, epidemiology, or a related field is often preferred. Clinical coders may also have additional certifications related to clinical coding systems, research methodologies, or data management.
Training Programs
Training programs for clinical coders may focus on advanced coding systems, research methodologies, biostatistics, and data management techniques. These training programs can be obtained through universities, professional organizations, and online platforms. Practical experience in coding clinical data and research projects may also be included in these programs.
Job Roles and Responsibilities of Medical Coders

Medical Records Abstraction
Medical coders are responsible for reviewing and abstracting relevant information from patient medical records. This includes identifying and extracting diagnoses, procedures, treatments, and other relevant data required for coding. accurate and complete abstraction is crucial for ensuring the integrity and accuracy of coded data.
Code Assignment
Medical coders are responsible for assigning appropriate codes to the extracted medical information according to coding guidelines and systems. This involves selecting the correct codes based on the patient’s diagnoses, procedures, treatments, and other relevant information. Coding accuracy plays a vital role in appropriate billing, reimbursement, and compliance.
Claim Review and Auditing
Medical coders may be involved in claim review and auditing processes to ensure coding accuracy, identify potential errors or fraudulent activities, and ensure compliance with coding guidelines and regulations. They may analyze claims and medical records, review coding practices, and provide feedback or recommendations for improvement.
Job Roles and Responsibilities of Clinical Coders

This image is property of images.ctfassets.net.
Collecting and Analyzing Clinical Data
Clinical coders are responsible for collecting and analyzing clinical data from various sources such as medical records, research databases, and healthcare systems. They identify and extract relevant clinical information for coding, ensuring accuracy and completeness.
Translating Medical Records to Codes
Clinical coders translate medical records into codes using appropriate coding systems and guidelines. They assign codes to clinical diagnoses, procedures, treatments, and other relevant information. Accurate and detailed coding is essential for supporting research, analysis, and clinical decision-making.
Ensuring Coding Accuracy and Completeness
Clinical coders are responsible for ensuring the accuracy and completeness of coded clinical data. They review coding practices, perform quality checks, and collaborate with healthcare professionals to resolve coding issues or discrepancies. Clinical coders play a vital role in maintaining the integrity and reliability of clinical data for research, analysis, and quality improvement initiatives.
Challenges and Future Trends in Medical and Clinical Coding

Complexity of Coding Systems
One of the challenges in medical and clinical coding is the complexity and constant evolution of coding systems. New codes are regularly added, and coding guidelines are updated to reflect changes in medical practices and advancements in healthcare. Medical and clinical coders need to stay updated with these changes to ensure accurate and compliant coding.
Transition to New Code Sets
The transition to new code sets, such as ICD-10, has been a significant challenge for medical and clinical coders. It requires additional training and education to understand the new coding systems and guidelines. This transition has improved coding accuracy and specificity but has also added complexity to the coding process.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements, such as electronic health records (EHR) and coding software, have transformed the field of medical and clinical coding. These advancements have increased efficiency, accuracy, and interoperability in coding practices. However, healthcare organizations and coding professionals need to adapt to these technological changes and stay updated with emerging coding technologies.
Increasing Demand for Coding Professionals
The demand for coding professionals is continually increasing due to the growing complexity of coding systems, expanding healthcare data, and the emphasis on accurate coding for reimbursement, compliance, and research purposes. The need for coding professionals extends beyond traditional healthcare settings, with opportunities in consulting firms, government agencies, research institutions, and insurance companies.
In conclusion, while medical coding and clinical coding share similarities and involve the transformation of medical information into codes, they differ in their focus areas, education requirements, coding systems used, and job responsibilities. Both medical and clinical coding play critical roles in healthcare by ensuring accurate documentation, appropriate reimbursement, and facilitating research and analysis. The field of coding is constantly evolving, and coding professionals need to stay updated with changes in coding guidelines and technological advancements to maintain accuracy and compliance. With increasing demand for coding professionals, the future of medical and clinical coding offers promising career opportunities in the healthcare industry.
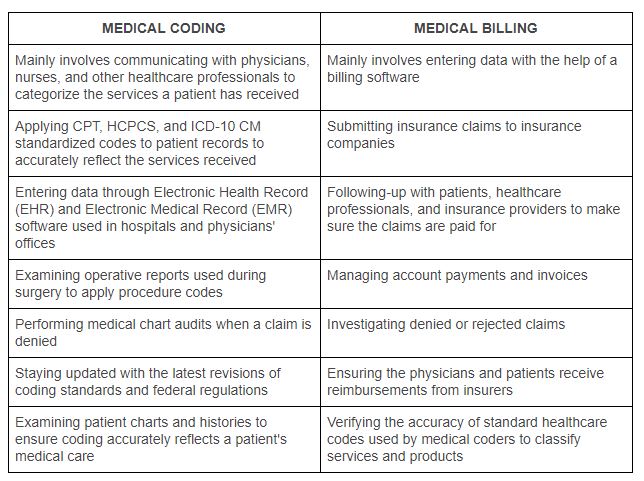
This image is property of www.parkmedicalbilling.com.
