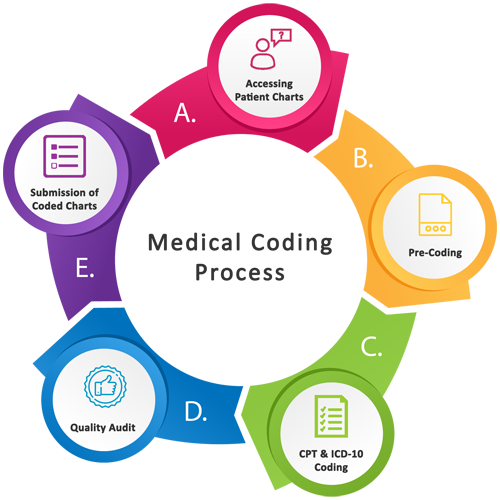
In the realm of healthcare, medical coding plays a crucial role in organizing and categorizing patient information for billing, research, and analysis purposes. However, have you ever wondered just how many types of medical coding exist? From the universally recognized International Classification of Diseases (ICD) codes to the intricate Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes, the world of medical coding is vast and multi-faceted. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of the different types of medical coding, shedding light on their distinctive characteristics and significance in the ever-evolving healthcare landscape. Whether you’re a medical professional or simply curious about the inner workings of healthcare administration, understanding the various types of medical coding is an essential aspect of navigating this intricate field.
This image is property of www.medicalcodingbuff.com.
Introduction
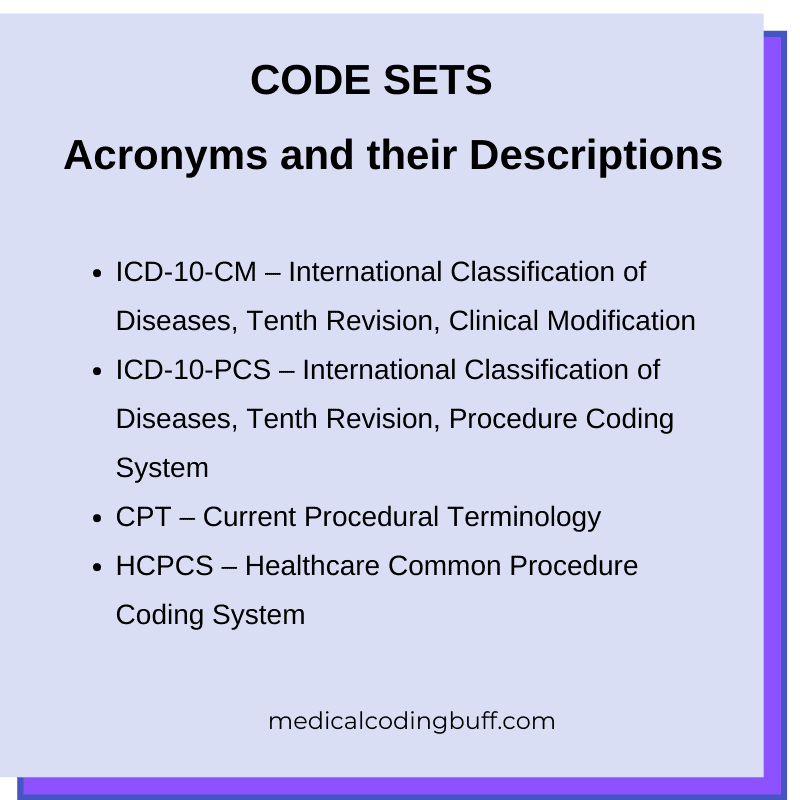
Medical coding is a crucial component of the healthcare industry, as it allows for the systematic recording and classification of medical procedures, diagnoses, treatments, and supplies. With accurate and detailed coding, healthcare organizations can properly bill and document patient care, ensuring efficient operations and accurate reimbursement. There are several different types of medical coding systems utilized in healthcare settings, each serving a specific purpose and covering various aspects of medical practice. In this article, we will explore the main types of medical coding, including CPT coding, ICD coding, HCPCS coding, DRG coding, SNOMED coding, NDC coding, LOINC coding, DSM coding, and ABC coding. Understanding these coding systems is essential for healthcare professionals and administrators to effectively navigate the complex landscape of medical billing and documentation.
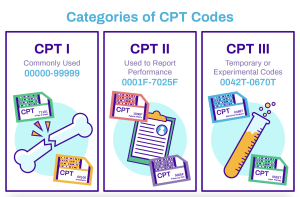
CPT coding (Current Procedural Terminology)
Overview
CPT coding, also known as Current Procedural Terminology, is a standardized coding system developed and maintained by the American Medical Association (AMA). It serves as a universal language for describing medical, surgical, and diagnostic procedures performed by healthcare professionals. CPT codes are alphanumeric characters that represent various services, such as surgeries, consultations, laboratory tests, and radiologic imaging. The codes provide a detailed description of the procedures performed and are widely used in medical billing, insurance claims, and reimbursement processes.
Purpose and Use
The primary purpose of CPT coding is to facilitate accurate and efficient communication between healthcare providers, payers, and regulatory bodies. By using standardized codes, healthcare professionals can effectively communicate the specific procedures performed, ensuring proper billing and reimbursement. CPT codes are also utilized for clinical research, healthcare policy development, and quality improvement initiatives. They play a vital role in understanding healthcare utilization patterns, identifying trends, and evaluating the effectiveness and efficiency of medical interventions.
Main Features
CPT coding consists of a five-digit numeric code that represents a specific procedure or service. The codes are organized into sections based on medical specialties, making it easier for healthcare professionals to locate the relevant codes. Each code is accompanied by a detailed description of the procedure, including the scope, techniques involved, and any specific requirements. CPT codes can also be modified with additional characters to further specify the procedure. The codes are regularly updated to reflect advancements in medical technology and the introduction of new procedures.
Common Procedures Covered
CPT coding covers a wide range of medical procedures across different specialties. Common procedures covered include office visits, surgical procedures, laboratory tests, radiologic imaging, vaccinations, physical therapy sessions, and more. Each procedure is assigned a specific CPT code based on its complexity, duration, and resources required. For example, a routine office visit may be assigned a lower-level code, while a complex surgical procedure would have a higher-level code.
Updates and Revisions
The CPT coding system is regularly updated by the American Medical Association to keep up with industry advancements and changes in medical practice. These updates ensure that the coding system remains accurate, relevant, and comprehensive. It is essential for healthcare professionals to stay updated with the latest revisions to ensure accurate coding and billing.
ICD coding (International Classification of Diseases)

Overview
ICD coding, also known as the International Classification of Diseases, provides a standardized system for classifying and coding diseases, conditions, injuries, and other health-related issues. It is maintained by the World Health Organization (WHO) and is used globally for statistical purposes, epidemiological studies, and healthcare resource allocation. ICD codes are alphanumeric characters that represent specific diagnoses, symptoms, and health-related issues.
Purpose and Use
The primary purpose of ICD coding is to provide a comprehensive and standardized way of classifying diseases and other health conditions. ICD codes facilitate accurate and consistent reporting of health data, enabling healthcare organizations, researchers, and policymakers to monitor disease prevalence, track trends, and develop effective public health strategies. ICD codes are also utilized for medical billing, insurance claims, and reimbursement processes, ensuring that healthcare providers are properly compensated for the services rendered.
Main Features
ICD coding consists of alphanumeric codes that provide a high level of specificity in describing diseases, conditions, and health-related issues. The codes are organized into chapters based on body systems, making it easier to locate the relevant codes. Each code is accompanied by a detailed description of the condition, including any associated symptoms, severity, and anatomical location. ICD codes can also be further specified with additional characters to provide more detailed information.
Common Conditions and Diseases Covered
ICD coding covers a wide range of conditions and diseases, including infectious diseases, chronic diseases, mental disorders, injuries, congenital anomalies, and more. Each condition or disease is assigned a specific ICD code based on its etiology, manifestations, and anatomical location. For example, a patient with a diagnosis of diabetes would be assigned a specific ICD code based on the type of diabetes and any associated complications.
Updates and Revisions
The ICD coding system undergoes periodic updates and revisions to accommodate new diseases, remove obsolete codes, and reflect advancements in medical knowledge. The most recent version of ICD coding is the ICD-10, which provides greater specificity and detailed information compared to its predecessor, ICD-9. It is important for healthcare professionals to stay updated with the latest revisions to ensure accurate coding and reporting of diseases and conditions.
HCPCS coding (Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System)
Overview
HCPCS coding, also known as the Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System, is a coding system utilized primarily for billing and reimbursement purposes in the United States. It consists of two levels of codes – Level I and Level II. Level I codes are identical to the CPT codes and represent medical procedures, while Level II codes represent non-physician services, supplies, and equipment.
Purpose and Use
The purpose of HCPCS coding is to provide a uniform system for reporting medical services, supplies, and equipment not covered by CPT codes. HCPCS codes are used by Medicare, Medicaid, and other third-party payers to determine reimbursement rates for healthcare services. Healthcare organizations and suppliers also use HCPCS codes for inventory management and reimbursement purposes.
Main Features
HCPCS coding consists of alphanumeric codes that provide a standardized and comprehensive system for reporting non-physician services, supplies, and equipment. Level I codes, which are identical to CPT codes, represent medical procedures performed by physicians. Level II codes represent non-physician services, supplies, and equipment such as ambulance services, medical supplies, prosthetics, and durable medical equipment. HCPCS codes are regularly updated to reflect changes in billing practices and the introduction of new services and supplies.
Common Services and Supplies Covered
HCPCS coding covers a wide range of non-physician services, supplies, and equipment. Common services and supplies covered include ambulance services, medical supplies, orthotics, prosthetics, durable medical equipment, wheelchairs, and more. Each service or supply is assigned a specific HCPCS code based on its nature, complexity, and resources required.
Updates and Revisions
The HCPCS coding system is regularly updated to accommodate changes in healthcare practices and reimbursement policies. Updates are implemented to reflect new services, supplies, and equipment, as well as revisions to existing codes. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) maintain the HCPCS coding system and release annual updates to ensure accurate billing and reimbursement.
DRG coding (Diagnosis-Related Group)
Overview
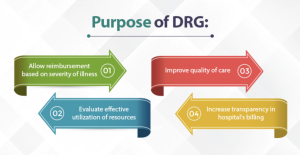
DRG coding, also known as Diagnosis-Related Group coding, is a classification system used in inpatient hospital settings for Medicare reimbursements in the United States. DRGs categorize patients into groups based on similar clinical characteristics and resource utilization patterns. Each group is assigned a payment weight that determines the reimbursement amount for the hospital.
Purpose and Use
The purpose of DRG coding is to provide a standardized and transparent system for reimbursing hospitals for inpatient care. DRGs take into account the complexity and severity of patient cases, as well as the resources required for treatment. They ensure that hospitals are reimbursed fairly and appropriately for the services rendered.
Main Features
DRG coding consists of numeric codes that represent specific groups of patients. The codes are based on criteria such as principal diagnosis, secondary diagnoses, surgical procedures performed, age, and sex. Each DRG is associated with a payment weight, which is used to calculate the reimbursement amount. DRGs are regularly updated to reflect changes in medical practice, cost of care, and advancements in technology.
Common Medical Conditions Covered
DRG coding covers a wide range of medical conditions and procedures that require inpatient hospital care. Common medical conditions covered include heart surgeries, joint replacements, pneumonia, kidney transplants, childbirth, and more. Each medical condition is assigned a specific DRG code based on the clinical characteristics and procedures involved. Hospitals can use DRG coding to assess resource utilization, compare performance, and identify areas for improvement.
Updates and Revisions
The DRG coding system is periodically updated and revised to reflect changes in medical practice and reimbursement policies. Updates are based on input from healthcare providers, coding experts, and industry stakeholders. It is important for hospitals and healthcare providers to stay updated with the latest revisions to ensure accurate coding and appropriate reimbursement.
SNOMED coding (Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine)

Overview
SNOMED coding, also known as the Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine, is a comprehensive clinical terminology and coding system used for recording and exchanging healthcare information. It is maintained by the International Health Terminology Standards Development Organization (IHTSDO) and is utilized globally for clinical documentation, electronic health records, and research.
Purpose and Use
The purpose of SNOMED coding is to provide a standardized and precise system for describing clinical concepts and healthcare-related information. SNOMED codes cover a vast array of clinical terms, including diseases, procedures, medications, clinical findings, and more. The use of SNOMED coding ensures consistency and interoperability of healthcare information across different healthcare systems and settings.
Main Features
SNOMED coding consists of alphanumeric codes that uniquely represent clinical concepts and terms. The codes are organized into hierarchies and relationships based on clinical context, allowing for detailed and precise documentation of healthcare information. SNOMED codes are designed to enable comprehensive and accurate recording of patient data, making it easier for healthcare professionals to retrieve and exchange information.
Common Medical Concepts Covered
SNOMED coding covers a wide range of medical concepts and terms across different medical specialties. It includes diagnoses, symptoms, procedures, medications, laboratory findings, social determinants of health, and more. Each concept is assigned a specific SNOMED code, allowing for standardized and interoperable documentation of clinical data.
Updates and Revisions
The SNOMED coding system undergoes regular updates and revisions to accommodate changes in medical terminology, advances in medical knowledge, and evolving clinical practices. Updates are based on input from healthcare professionals, researchers, and coding experts. Staying updated with the latest revisions is crucial for healthcare organizations to ensure accurate and interoperable documentation of patient data.
NDC coding (National Drug Code)

Overview
NDC coding, also known as the National Drug Code, is a unique identification system used for identifying and tracking medications in the United States. It is maintained by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and is utilized in various aspects of the medication management process, including prescribing, dispensing, and billing.
Purpose and Use
The purpose of NDC coding is to provide a standardized and universally recognized system for identifying and tracking medications. NDC codes facilitate accurate medication prescribing, dispensing, and billing, ensuring patient safety and proper reimbursement. NDC codes are also used for medication inventory management, adverse event reporting, and monitoring medication utilization.
Main Features
NDC coding consists of numeric codes that include three segments – the labeler code, product code, and package code. The labeler code represents the manufacturer or distributor of the medication, the product code represents the specific medication formulation or strength, and the package code represents the packaging size or type. NDC codes provide a unique identifier for each medication, allowing for accurate identification and tracking.
Common Medications Covered
NDC coding covers a wide range of medications across different therapeutic classes and dosage forms. It includes both prescription and over-the-counter medications. Each medication is assigned a specific NDC code, ensuring accurate identification and tracking throughout the medication management process.
Updates and Revisions
The NDC coding system is regularly updated to accommodate changes in medication formulations, packaging, and manufacturing practices. Updates are based on input from medication manufacturers, regulatory agencies, and industry stakeholders. It is important for healthcare professionals and organizations to stay updated with the latest revisions to ensure accurate medication identification and tracking.
LOINC coding (Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes)

Overview
LOINC coding, also known as Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes, is a standardized system for identifying and exchanging laboratory test results and clinical observations. It is maintained by the Regenstrief Institute and is widely utilized in healthcare settings for electronic health records, laboratory test ordering, and data exchange.
Purpose and Use
The purpose of LOINC coding is to provide a standardized and interoperable system for identifying and exchanging laboratory test results and other clinical observations. LOINC codes facilitate accurate and efficient electronic reporting and interpretation of laboratory data, ensuring seamless communication between healthcare providers, laboratories, and patients.
Main Features
LOINC coding consists of alphanumeric codes that represent laboratory tests and clinical observations. The codes are organized into hierarchies and relationships based on clinical context and properties of the observations. LOINC codes provide a standardized and precise way of describing laboratory tests, including the analyte, method, scale, and other relevant attributes.
Common Laboratory Tests Covered
LOINC coding covers a wide range of laboratory tests and clinical observations, including blood tests, urine tests, microbiology tests, pathology tests, and more. Each test is assigned a specific LOINC code, allowing for consistent and interoperable reporting and interpretation of laboratory data. LOINC codes are widely used in electronic health records, laboratory information systems, and data exchange platforms.
Updates and Revisions
The LOINC coding system is regularly updated to accommodate changes in laboratory testing practices, advances in technology, and new clinical observations. Updates are based on feedback from healthcare professionals, laboratory experts, and stakeholders. Staying updated with the latest revisions is crucial for healthcare organizations to ensure accurate and interoperable reporting and interpretation of laboratory data.
DSM coding (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders)

Overview
DSM coding, also known as the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders coding, is a classification system used for diagnosing and categorizing mental health disorders. It is maintained by the American Psychiatric Association (APA) and is widely utilized by mental health professionals for clinical assessment, treatment planning, and research purposes.
Purpose and Use
The purpose of DSM coding is to provide a standardized and universally recognized system for diagnosing and categorizing mental health disorders. DSM codes facilitate accurate and consistent communication between mental health professionals, ensuring proper treatment planning and access to appropriate care. DSM codes are also used for research, epidemiological studies, and healthcare policy development.
Main Features
DSM coding consists of numeric codes that represent specific mental health disorders and conditions. The codes are organized into chapters and sections based on diagnostic categories, making it easier for mental health professionals to locate the relevant codes. Each disorder is assigned a specific DSM code, allowing for consistent and standardized diagnosis and treatment.
Common Mental Health Disorders Covered
DSM coding covers a wide range of mental health disorders and conditions, including mood disorders, anxiety disorders, psychotic disorders, personality disorders, substance use disorders, and more. Each disorder is assigned a specific DSM code, ensuring consistent and standardized diagnosis across different mental health settings. DSM codes are regularly updated to reflect advancements in the understanding and classification of mental health disorders.
Updates and Revisions
The DSM coding system undergoes periodic updates and revisions to reflect changes in the understanding and classification of mental health disorders. Updates are based on new research, clinical experience, and feedback from mental health professionals. Staying updated with the latest revisions is essential for mental health professionals to ensure accurate and standardized diagnosis and treatment.
ABC coding (Alternative Primary Care Code Set)

Overview
ABC coding, also known as Alternative Primary Care Code Set, is a coding system used for documenting and billing alternative healthcare services. It is maintained by the Alternative Link and is primarily focused on complementary and alternative medicine practices.
Purpose and Use
The purpose of ABC coding is to provide a standardized coding system specifically for alternative healthcare services. ABC codes facilitate accurate documentation, billing, and reimbursement for alternative healthcare practitioners. The use of ABC codes ensures that these practitioners receive appropriate recognition and reimbursement for the services they provide.
Main Features
ABC coding consists of alphanumeric codes that represent alternative healthcare services, such as acupuncture, chiropractic care, homeopathy, naturopathy, and more. The codes are organized into categories and subcategories, making it easier for healthcare practitioners to locate the relevant codes. Each code is accompanied by a description of the service, ensuring accurate documentation and billing.
Common Alternative Healthcare Services Covered
ABC coding covers a wide range of alternative healthcare services across different modalities and practices. Common alternative healthcare services covered include acupuncture treatments, chiropractic adjustments, herbal medicine consultations, energy healing sessions, and more. Each service is assigned a specific ABC code, allowing for accurate documentation, billing, and reimbursement.
Updates and Revisions
The ABC coding system is periodically updated and revised to accommodate changes in alternative healthcare practices and to incorporate new services and modalities. Updates are based on input from alternative healthcare practitioners, coding experts, and industry stakeholders. Staying updated with the latest revisions ensures accurate coding, documentation, and reimbursement for alternative healthcare services.
In conclusion, medical coding plays a critical role in accurately documenting, billing, and reimbursing healthcare services and procedures. Different types of coding systems, such as CPT coding, ICD coding, HCPCS coding, DRG coding, SNOMED coding, NDC coding, LOINC coding, DSM coding, and ABC coding, serve specific purposes and cover various aspects of medical practice. Understanding these coding systems is essential for healthcare professionals and administrators to effectively navigate the complexities of medical billing and documentation. Staying up to date with the latest revisions and updates in these coding systems is crucial to ensuring accurate coding, proper reimbursement, and high-quality patient care.