Medical billing is a critical process that ensures healthcare providers receive payment for the services they render. Understanding how medical billing works is essential for both healthcare professionals and patients. This article will provide an insightful overview of the intricacies involved in medical billing, covering the entire process from patient registration to reimbursement. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how this vital component of the healthcare industry operates.
Overview of Medical Billing

Medical cost concept with stethoscope and medical bill
Definition of Medical Billing
Medical billing is the process of submitting and following up on claims with health insurance companies in order to receive payment for medical services provided. It involves the translation of healthcare services into billing codes that are recognized and accepted by insurance companies. This ensures that healthcare providers are reimbursed for the services they have rendered to patients.
Importance of Medical Billing
Accurate and efficient medical billing is essential for the financial viability of healthcare providers. It ensures that they are properly reimbursed for the services they provide, allowing them to cover the costs of running their practices or facilities and providing quality patient care. Additionally, medical billing plays a crucial role in maintaining revenue cycle management, which is the process of managing the entire financial lifecycle of a patient encounter, from patient registration to final payment.
Role of Medical Billers
Medical billers play a crucial role in the healthcare industry as they are responsible for accurately translating healthcare services into billing codes, submitting claims to insurance companies, and following up on those claims to ensure timely payment. They must have a deep understanding of medical coding, insurance regulations, and billing processes. Medical billers also act as a liaison between healthcare providers and insurance companies, resolving any issues or discrepancies that may arise during the billing process.
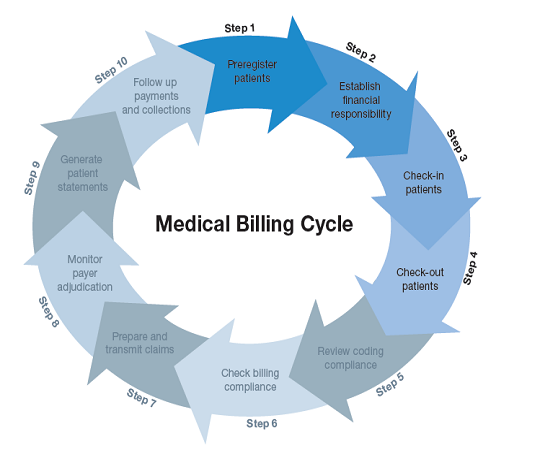
Medical Billing Process

Patient Registration
The medical billing process begins with patient registration. During this step, patient demographic information, insurance details, and medical history are collected. This information is essential for accurate billing and claim submission. Patient registration typically involves verifying insurance coverage and ensuring the healthcare provider is listed as a participating provider with the insurance company.
Insurance Verification
After patient registration, the medical biller verifies the patient’s insurance coverage to determine the services that are covered and any applicable copayments or deductibles. This step is crucial in ensuring the accuracy of claims and preventing claim denials or rejections. Insurance verification involves contacting the insurance company or using electronic systems to confirm the patient’s eligibility and coverage details.
Coding and Documentation
Coding and documentation are vital components of the medical billing process. Medical billers use standardized coding systems, such as Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) and International Classification of Diseases (ICD), to translate healthcare services and diagnoses into universal codes. Accurate coding enables clear communication between healthcare providers, insurance companies, and billing departments.
Claim Submission
Once the coding and documentation are complete, medical billers compile the necessary information and submit claims to the appropriate insurance companies. Claims can be submitted electronically or via paper forms, depending on the requirements of the insurance company. Electronic claim submission is generally faster and more efficient, reducing the risk of errors and expediting the payment process.
Claim Adjudication
After the claim submission, insurance companies review the claims through a process called claim adjudication. During this stage, the insurance company examines the claim for accuracy, verifies the patient’s eligibility and coverage, assesses the medical necessity of the services provided, and determines the allowable amount for reimbursement. The claim may be approved and paid in full, approved with modifications, or denied.
Payment Posting
Once the claim has been adjudicated and approved for payment, the insurance company will make a payment to the healthcare provider. This payment is often referred to as the remittance advice or explanation of benefits (EOB). Medical billers are responsible for reconciling the payment received with the expected reimbursement, ensuring accuracy, and posting the payment to the patient’s account. This step completes the medical billing process for that particular encounter.
Key Players in Medical Billing
Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers, including physicians, hospitals, clinics, and other medical facilities, are the primary entities involved in medical billing. They provide the medical services and treatments for patients, generate the necessary documentation and coding, and rely on accurate and timely reimbursement for their services to sustain their practice.
Medical Billers and Coders
Medical billers and coders are skilled professionals who specialize in translating healthcare services and diagnoses into billing codes. They are responsible for ensuring accurate and efficient claim submission, verifying insurance coverage, resolving any billing discrepancies, and following up on claims to ensure proper reimbursement. Medical billers and coders play a crucial role in the financial health of healthcare providers.
Insurance Companies
Insurance companies are key players in the medical billing process as they provide coverage for patients and reimburse healthcare providers for the services provided to their insured members. They review claims for accuracy, medical necessity, and coverage, and make payments accordingly. Insurance companies have their own set of rules, regulations, and coding guidelines that medical billers must adhere to when submitting claims.
Government Agencies
Government agencies, such as the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), play a significant role in medical billing, particularly in the United States. They administer public health insurance programs like Medicare and Medicaid, which provide coverage for specific populations, such as the elderly, low-income individuals, and those with disabilities. Medical billers must understand and comply with the regulations set forth by these government agencies when submitting claims for reimbursement.
Common Medical Billing Codes

Current Procedural Terminology (CPT)
The Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) is a coding system developed by the American Medical Association to describe medical, surgical, and diagnostic services. CPT codes are used to document and report medical procedures and services performed by healthcare providers. These codes are essential for accurate claim submission and reimbursement.
International Classification of Diseases (ICD)
The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) is a coding system used to classify and code diagnoses, symptoms, and procedures related to patient care. It provides a standardized way of documenting and reporting medical conditions. Healthcare providers and medical billers use ICD codes to describe a patient’s condition or reason for seeking medical treatment.
Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS)
The Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) is a coding system used to describe specific medical supplies, equipment, and services that are not included in the CPT coding system. HCPCS codes are commonly used for durable medical equipment, prosthetics, orthotics, and other specialized services. These codes are important for accurate claim submission and reimbursement.
Electronic Medical Billing
Advantages of Electronic Medical Billing
Electronic medical billing offers several advantages over traditional paper-based billing methods. First and foremost, it allows for faster and more efficient claim submission, reducing turnaround times and accelerating the payment process. Electronic billing also reduces the risk of errors and omissions, as the software used for electronic billing often includes built-in coding and documentation checks. Additionally, electronic medical billing improves communication between healthcare providers and insurance companies, as claims can be submitted electronically and responses can be received in a timely manner.
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is a standard format for electronically exchanging healthcare information, including medical billing data, between different computer systems. It enables seamless and secure data transmission between healthcare providers and insurance companies, eliminating the need for manual data entry and reducing the risk of errors. EDI is widely used in electronic medical billing to streamline the claims submission and payment process.
HIPAA Compliance
HIPAA, or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, sets forth regulations and standards for the privacy, security, and electronic transmission of healthcare information. Electronic medical billing systems must comply with HIPAA requirements to protect patient confidentiality and ensure the secure exchange of sensitive medical data. Compliance with HIPAA regulations is essential in maintaining patient trust and avoiding penalties or legal consequences.
Compliance and Fraud Prevention

Importance of Compliance
Compliance with healthcare regulations and billing guidelines is of utmost importance in the medical billing field. Non-compliance can result in claim denials, rejections, penalties, fines, or even legal action. Medical billers must be knowledgeable about the specific regulations and guidelines set forth by government agencies and insurance companies to ensure accurate claim submission and proper reimbursement.
Anti-Fraud Measures
Fraud in medical billing can lead to significant financial losses for healthcare providers and insurance companies. Medical billers must be vigilant in identifying and preventing fraudulent activities, such as upcoding (billing for a higher-priced service than what was actually provided), unbundling (billing separately for services that should be billed together), or billing for services not rendered. Implementing internal controls, conducting regular audits, and staying updated on anti-fraud measures are essential in preventing fraudulent activities.
Auditing and Monitoring
Regular auditing and monitoring of the medical billing process are crucial in detecting and preventing errors, discrepancies, or fraudulent activities. Internal and external audits can identify potential issues and areas for improvement, ensuring compliance, accuracy, and the prevention of fraud. Healthcare providers should establish robust auditing and monitoring procedures to maintain the integrity of their medical billing processes.
Challenges in Medical Billing

Insurance Denials and Rejections
Insurance denials and rejections are common challenges in medical billing. Denials occur when an insurance company refuses to pay for a claim, while rejections happen when claims are returned to the healthcare provider due to errors or missing information. Medical billers must address denials and rejections promptly, identify the reasons for the denials or rejections, rectify any errors, and resubmit or appeal the claims if necessary.
Complex Billing Regulations
The healthcare industry is highly regulated, and medical billers must stay updated on the complex billing regulations set forth by government agencies and insurance companies. These regulations can vary based on location, type of insurance, and patient population. Keeping abreast of changes and understanding the intricacies of billing regulations can be challenging but critical to ensuring compliance and accurate claim submission.
Keeping Up with Coding Changes
Medical coding is continuously evolving due to updates, additions, and revisions to coding systems like CPT and ICD. Staying up to date with these coding changes is essential to accurately translate healthcare services and diagnoses and prevent claim denials or underpayments. Medical billers must actively participate in continuing education and professional development to stay current with coding changes and guidelines.
Outsourcing Medical Billing

Pros of Outsourcing
Outsourcing medical billing can provide several benefits to healthcare providers. Firstly, it allows healthcare providers to focus on patient care and other core aspects of their practice, leaving the complex and time-consuming billing tasks to specialized professionals. Outsourcing can also result in increased efficiency, as dedicated medical billing companies often have advanced billing software, experienced staff, and streamlined processes. Additionally, outsourcing can lead to cost savings, as healthcare providers can avoid hiring and training in-house billing staff.
Cons of Outsourcing
Despite the advantages, outsourcing medical billing also comes with potential drawbacks. One primary concern is the loss of control or lack of transparency in the billing process. Healthcare providers may feel disconnected from the billing process and face challenges in communicating or resolving any issues that may arise. Confidentiality and data security can also be a concern when outsourcing, as sensitive patient information is shared with external entities.
Choosing the Right Medical Billing Company
When considering outsourcing medical billing, healthcare providers must carefully choose a reputable and reliable medical billing company. Factors to consider include the company’s years of experience, track record, certifications, staff qualifications, references, and testimonials. It is also important to ensure that the medical billing company understands the specific needs, specialties, and billing nuances of the healthcare provider.
Medical Billing and Revenue Cycle Management

Revenue Cycle Overview
Revenue cycle management (RCM) encompasses the financial processes involved in managing the revenue generated from patient care. It involves various stages, starting from patient registration to the final payment received by the healthcare provider. Medical billing is a critical component of RCM, as it ensures accurate and timely reimbursement for the services provided.
Integration of Billing and Revenue Cycle Management
Effective medical billing requires the seamless integration of billing processes with the broader revenue cycle management of a healthcare provider. This integration includes coordinating patient registration, insurance verification, coding and documentation, claim submission, claim adjudication, payment posting, and revenue analysis. The integration of billing and revenue cycle management streamlines financial operations, improves cash flow, and enhances overall revenue performance.
Future Trends in Medical Billing

Automation and Artificial Intelligence
The future of medical billing is likely to be heavily influenced by automation and artificial intelligence (AI). Automation can streamline repetitive and time-consuming tasks, such as claim submission and payment posting, reducing errors and increasing efficiency. AI technologies, including machine learning and natural language processing, can improve coding accuracy, identify billing patterns, and detect potential fraud or errors.
Value-Based Reimbursement
In healthcare, there is a growing shift from fee-for-service reimbursement to value-based reimbursement. Value-based reimbursement focuses on rewarding healthcare providers based on the quality and outcomes of patient care rather than the quantity of services rendered. This transition will require changes in medical billing processes to accurately capture and report the value and quality of care provided.
Telehealth and Remote Billing
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of telehealth, which allows for remote delivery of healthcare services. As telehealth continues to expand, medical billing processes will need to adapt to accommodate billing for virtual visits and remote services. Medical billers will play a crucial role in ensuring accurate and compliant billing for telehealth encounters.
In conclusion, medical billing is a complex and vital aspect of the healthcare industry. It involves translating healthcare services into billing codes, submitting claims to insurance companies, and ensuring accurate and timely reimbursement. Medical billers play a crucial role in this process, acting as a liaison between healthcare providers and insurance companies. They must navigate complex coding systems, billing regulations, and compliance requirements. The future of medical billing is expected to be influenced by automation, AI, value-based reimbursement, and the continued growth of telehealth. It is essential for healthcare providers to understand the intricacies of medical billing, staying up to date with changes and trends, and considering the potential benefits and challenges of outsourcing.