In the field of medical billing, understanding the various types of codes is crucial for accurate and efficient billing processes. Medical codes play a vital role in identifying specific diagnoses, procedures, and medical services provided to patients. By assigning appropriate codes, healthcare providers can communicate with insurance companies, ensuring proper reimbursement for services rendered. This article explores the different types of codes commonly used in medical billing and their significance in the healthcare industry.
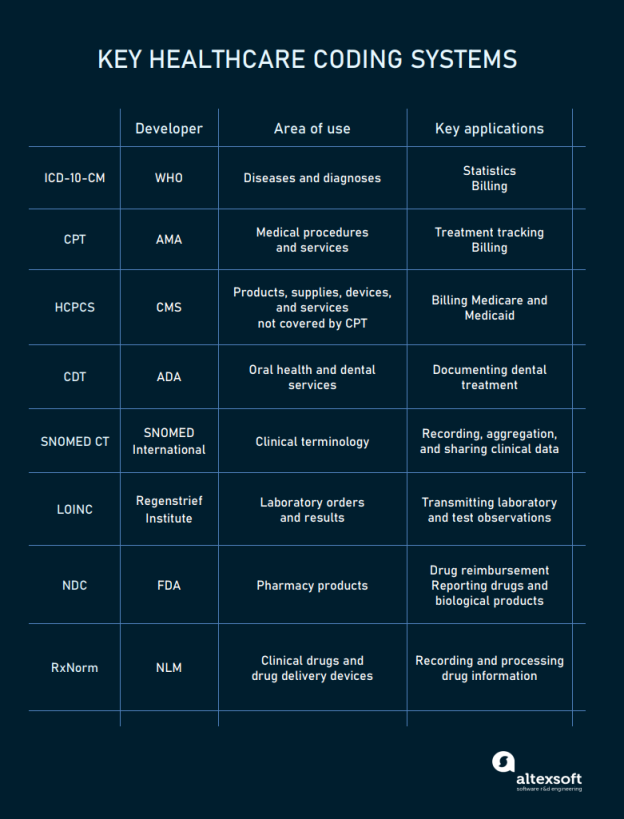
ICD-10-CM Codes

Basic Format
ICD-10-CM codes, which stands for International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification, are alphanumeric codes used in medical billing to classify diseases, symptoms, injuries, and other health conditions. The basic format of an ICD-10-CM code consists of three to seven characters, which are organized into chapters, sections, and categories.
Code Sections
ICD-10-CM codes are organized into sections, each representing a broad category of diseases or conditions. These sections include infectious and parasitic diseases, neoplasms, diseases of the circulatory system, diseases of the respiratory system, and many more. The sections provide a systematic approach to classifying and organizing the codes, making it easier for healthcare providers and coders to locate and assign the appropriate code.
Code Categories
Within each section, there are multiple code categories that further specify the disease or condition being classified. For example, within the neoplasms section, there are different categories for malignant neoplasms, benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain behavior. The code categories allow for more precise coding and ensure that the information captured in the medical record accurately reflects the patient’s condition.
Code Types
ICD-10-CM codes can be classified into different code types based on their characters and the information they convey. Some common code types include diagnosis codes, symptom codes, external cause codes, and procedure codes. Each code type serves a specific purpose in medical billing and coding, helping to document and communicate different aspects of a patient’s condition or treatment.
Code Updates
ICD-10-CM codes are periodically updated to reflect advances in medical knowledge and to accommodate changes in healthcare practices. These updates are essential to ensure accurate and up-to-date coding. The updates may include the addition of new codes, modification of existing codes, or deletion of codes that are no longer relevant. Healthcare professionals and coders need to stay informed about these updates to ensure proper coding and reimbursement.
CPT Codes

Basic Format
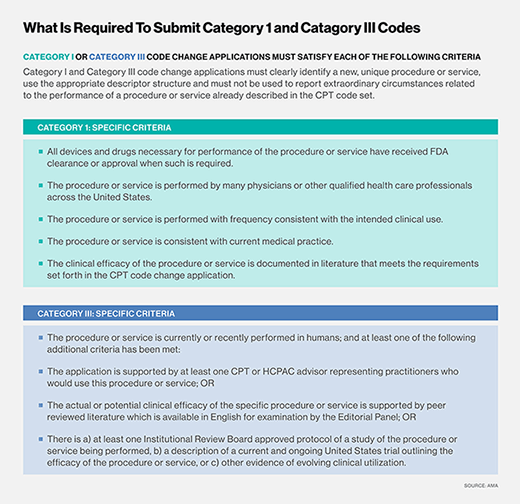
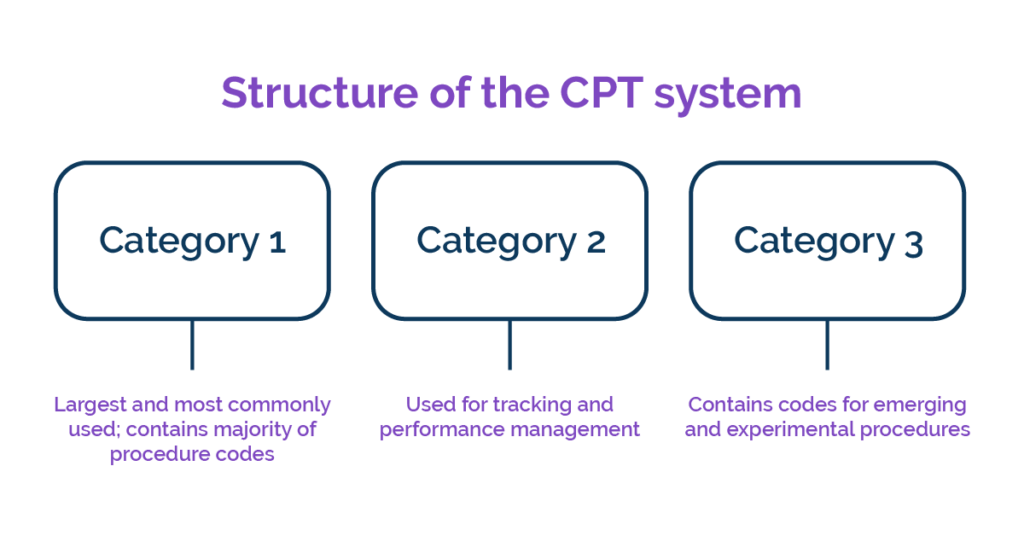
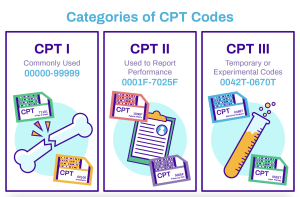
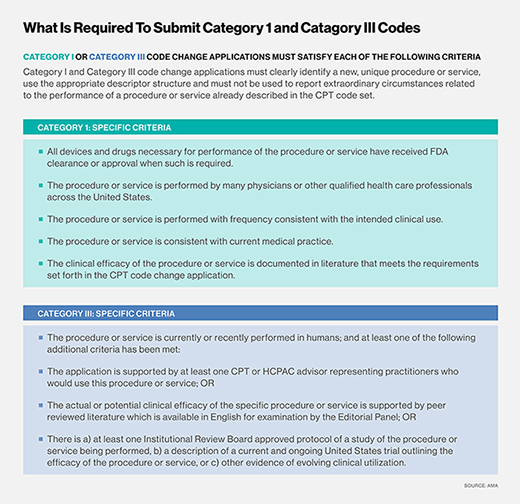
CPT codes, or Current Procedural Terminology codes, are used in medical billing to describe medical procedures and services. the basic format of a CPT code consists of five alphanumeric characters and is organized into three categories: Category I, Category II, and Category III codes.
Code Categories
Category I codes are the most commonly used CPT codes and describe procedures and services that are widely performed and recognized in medical practice. These codes cover a wide range of medical specialties and procedures, such as surgical procedures, radiology services, laboratory tests, and evaluation and management services.
Category II codes are optional supplemental codes used to track performance measures and patient outcomes. They provide additional information about the services provided and are used for quality improvement purposes.
Category III codes are temporary codes used for emerging procedures and technologies that don’t yet have an established Category I code. These codes allow for tracking and data collection for new procedures and technologies.
Modifiers
CPT codes can be further modified using two-digit alphanumeric modifiers. Modifiers provide additional information about the service or procedure being performed, such as whether it was bilateral, performed by multiple surgeons, or modified in some way. These modifiers help to provide more specific details about the service and ensure accurate billing and reimbursement.
Code Updates
CPT codes are regularly updated by the American Medical Association (AMA) to reflect changes in medical practice, new technologies, and evolving healthcare needs. These updates may include the addition of new codes, revisions to existing codes, or deletion of outdated codes. Accurate and up-to-date knowledge of these updates is crucial for healthcare providers and coders to ensure appropriate coding and reimbursement.
HCPCS Codes

Basic Format
HCPCS codes, or Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System codes, are used in medical billing to identify and classify healthcare procedures, supplies, and equipment. The basic format of an HCPCS code consists of a single letter followed by four digits or a letter followed by four digits and then two letters.
Level II Codes
HCPCS codes are divided into two levels. Level I codes are the same as CPT codes and are used to report physician and outpatient services. Level II codes are used to report non-physician services, supplies, durable medical equipment, and other healthcare-related items. These Level II codes are often referred to as “DMEPOS” codes, which stands for Durable Medical Equipment, Prosthetics, Orthotics, and Supplies.
Modifiers
Similar to CPT codes, HCPCS codes can also be modified using two-digit alphanumeric modifiers. These modifiers provide additional information about the service or supply being billed, such as the appropriate use of a specific device or equipment. Modifiers help to ensure accurate billing and reimbursement for both providers and payers.
Code Updates
HCPCS codes are regularly updated by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) to accommodate changes in medical practices, technology advancements, and healthcare policies. These updates may involve the addition of new codes, modification of existing codes, or deletion of obsolete codes. Staying informed about these updates is essential for healthcare providers, suppliers, and coders to accurately code and bill for services and supplies.
DRG Codes
Definition
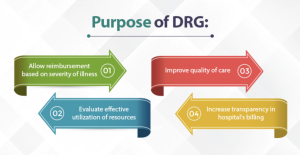
DRG codes, or Diagnosis-Related Group codes, are used in medical billing to classify patients into groups based on their diagnosis, procedures performed, age, and other relevant factors. DRG codes play a crucial role in the reimbursement process for inpatient hospital stays.
Grouping Methodology
DRG codes are assigned based on the patient’s principal diagnosis, secondary diagnoses, and procedures performed during their hospital stay. The codes are organized into different groups, each representing a specific medical condition or treatment category. These groups reflect the average treatment costs and resource utilization associated with a particular condition or procedure.
Code Updates
DRG codes are periodically updated by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) to ensure accurate reimbursement and reflect changes in medical practices and technology. These updates may include changes to the grouping methodology, the addition of new DRG codes, or revisions to existing codes. Healthcare providers and coders must stay abreast of these updates to ensure proper coding and billing for inpatient hospital stays.
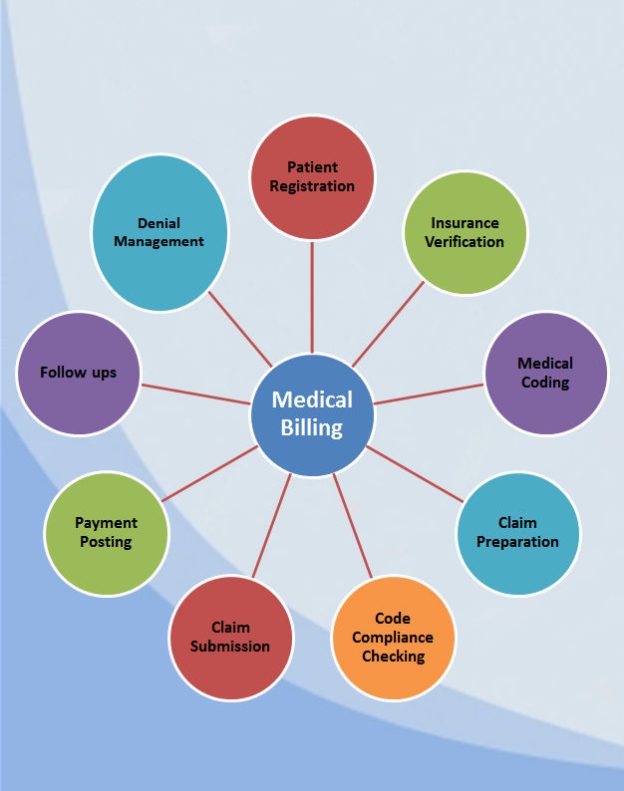
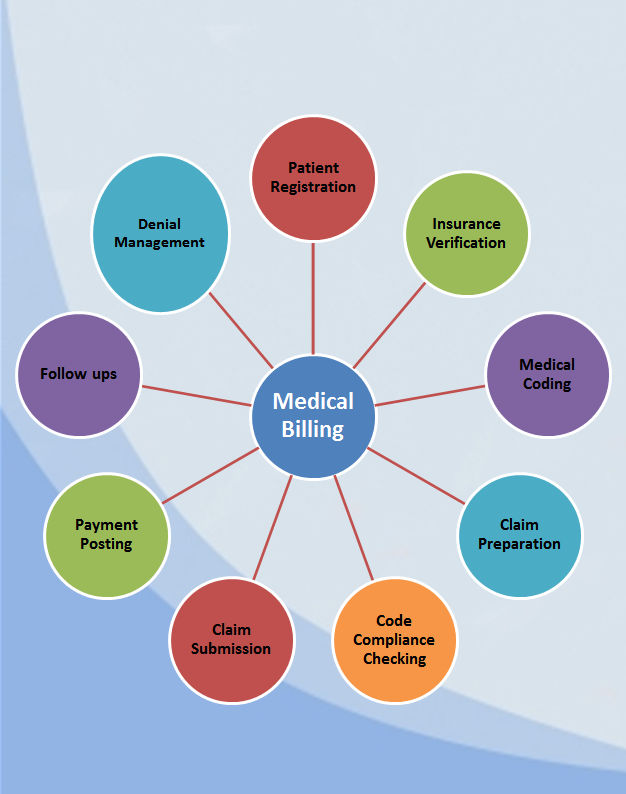
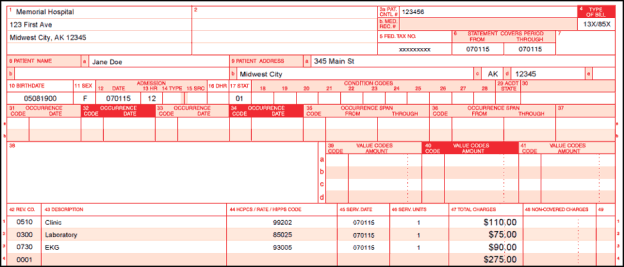
Revenue Codes
This image is property of medicalbillingservicereview.com.
Definition
Revenue codes are used in medical billing to identify specific hospital services and procedures for billing purposes. These codes help healthcare facilities track and differentiate the revenue generated by various departments and services, such as room and board charges, pharmaceuticals, laboratory tests, and radiology services.
Code Categories
Revenue codes are organized into different categories based on the type of service or department being billed. Common categories include room and board, emergency room services, laboratory services, radiology services, and operating room services. The use of revenue codes ensures that the charges are appropriately classified and billed in a consistent manner.
Billing Purposes
Revenue codes serve various purposes in medical billing. They help healthcare facilities generate accurate invoices and statements for patients, enabling proper reimbursement. Additionally, revenue codes play a vital role in financial reporting, cost analysis, and strategic planning for healthcare organizations. By tracking revenue by department or service, healthcare facilities can identify areas of profitability and potential areas for improvement.
Place of Service Codes
Definition
Place of service codes are used in medical billing to identify the location where a healthcare service was provided. These codes help distinguish between different types of healthcare settings, such as hospitals, clinics, nursing homes, and patient homes.
Code Categories
Place of service codes are organized into different categories based on the type of healthcare setting. Some common categories include inpatient hospital, outpatient hospital, office, emergency room, ambulatory surgical center, skilled nursing facility, and home. Each category represents a different physical location where healthcare services may be rendered.
Billing Purposes
Place of service codes are essential for accurate billing and reimbursement. They help payers determine the appropriate payment rates based on the type of healthcare setting and the associated costs. Additionally, place of service codes provide valuable information for healthcare providers and researchers to analyze healthcare utilization patterns and trends.
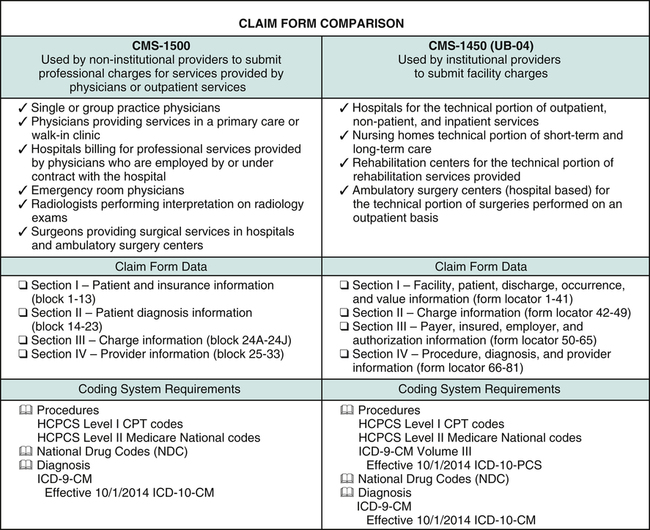
Diagnosis Codes vs Procedure Codes
Diagnosis codes focus on describing the patient’s medical condition, while procedure codes detail the specific medical services or interventions provided to diagnose or treat that condition. Both types of codes are essential for accurate medical record keeping, billing, and communication among healthcare professionals and payers. Proper coding ensures that patients receive the appropriate care, providers are reimbursed correctly, and accurate data is available for research and healthcare management.
Comparison
Diagnosis codes and procedure codes are both essential components of medical billing, but they serve different purposes. Diagnosis codes, such as ICD-10-CM codes, are used to classify and document a patient’s medical condition or disease. These codes help describe what is wrong with the patient and why they are seeking medical care. On the other hand, procedure codes, such as CPT codes and HCPCS codes, describe the specific medical procedures, treatments, or services performed on the patient. These codes provide information about the actions taken to address the patient’s condition.
Purpose
Diagnosis codes are primarily used for medical decision-making, documenting the patient’s condition, and tracking epidemiological data. They help healthcare providers understand the patient’s medical history and determine appropriate treatment plans. Procedure codes, on the other hand, are vital for billing and reimbursement purposes. They provide the necessary information to calculate the appropriate payment for the services rendered, ensuring that healthcare providers are reimbursed accurately and in a timely manner.
Evaluation and Management (E/M) Codes

Definition
Evaluation and Management (E/M) codes are used in medical billing to classify and bill for healthcare services related to patient evaluation and management. These codes encompass a wide range of services, including office visits, hospital visits, consultations, and nursing facility visits.
Code Levels
E/M codes are divided into different levels based on the complexity of the patient’s condition and the intensity of the physician’s effort. The code levels range from straightforward and minimal services to complex and comprehensive services. The level of service is determined by considering factors such as history taking, examination, medical decision-making, and counseling.
Documentation Guidelines
E/M codes have specific documentation guidelines that healthcare providers must follow to support the level of service billed. These guidelines outline the necessary elements to include in the medical record, such as the patient’s history, physical examination findings, assessment and plan, and the complexity of medical decision-making. Accurate and detailed documentation is crucial to ensure appropriate billing and reimbursement for E/M services.
Anesthesia Codes

Definition
Anesthesia codes are used in medical billing to describe the administration of anesthesia during surgical or medical procedures. These codes provide information about the type of anesthesia used, the duration of administration, and the complexity of the procedure.
Code Formats
Anesthesia codes follow a specific format and include both a base code and additional time units, if applicable. The base code represents the anesthesia service provided, while the time units indicate the total duration of anesthesia administration. Proper coding of anesthesia services is essential for accurate billing and reimbursement.
Modifiers
Modifiers can also be applied to anesthesia codes to provide additional information about the anesthesia service. These modifiers indicate special circumstances or the provision of additional anesthesia services beyond the scope of the base code. The use of modifiers ensures that anesthesia services are accurately coded and billed.
Code Updates
Anesthesia codes are periodically updated to reflect changes in medical practice, advancements in anesthesia technology, and updates to reimbursement policies. These updates may involve the addition of new codes, revisions to existing codes, or the deletion of obsolete codes. Healthcare providers and coders must stay informed about these updates to ensure accurate coding and billing for anesthesia services.
Radiology Codes
Definition
Radiology codes are used in medical billing to describe diagnostic imaging procedures, such as X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and ultrasound. These codes provide information about the type of imaging procedure performed, the body part imaged, and any special circumstances or contrast used.
Code Formats
Radiology codes follow a specific format, typically consisting of a three- to five-digit numeric code. The codes are organized into different categories based on the imaging modality or technology used. The correct coding of radiology services is crucial for accurate billing and reimbursement.
Code Categories
Radiology codes are grouped into various categories based on the type of imaging procedure being performed. These categories may include diagnostic radiology, nuclear medicine, radiation oncology, and interventional radiology. Proper assignment of the correct code category ensures accurate billing and appropriate reimbursement for radiology services.
In conclusion, medical billing relies on various types of codes to accurately document and communicate healthcare services, procedures, and conditions. ICD-10-CM codes provide detailed information about a patient’s diagnosis and condition. CPT codes describe the medical procedures and services performed, while HCPCS codes identify supplies, equipment, and non-physician services. DRG codes group patients based on their diagnosis and procedures for inpatient reimbursement. Revenue codes help healthcare facilities track revenue by department and service. Place of service codes identify the location where services were provided. Anesthesia codes describe anesthesia administration, and radiology codes specify diagnostic imaging procedures. Understanding and correctly applying these codes is essential for accurate medical billing and reimbursement.