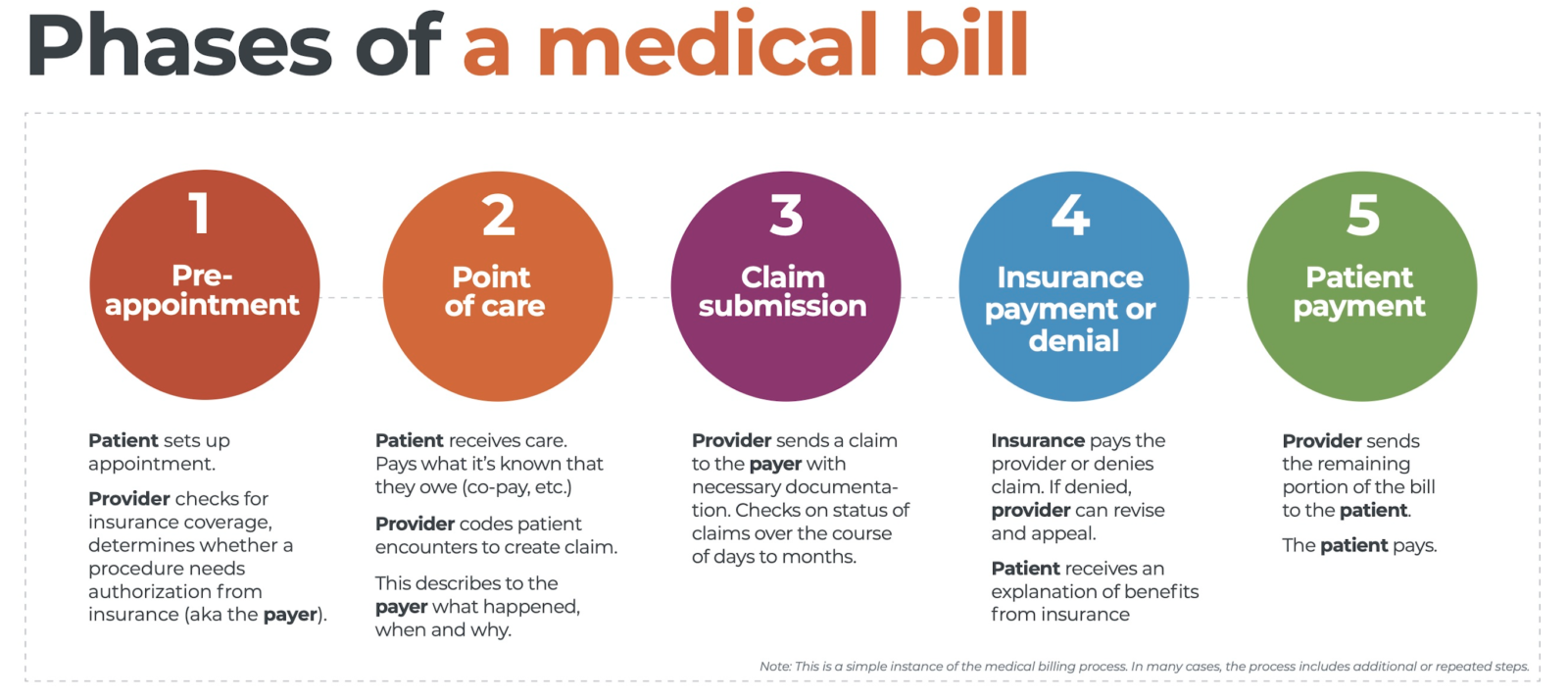
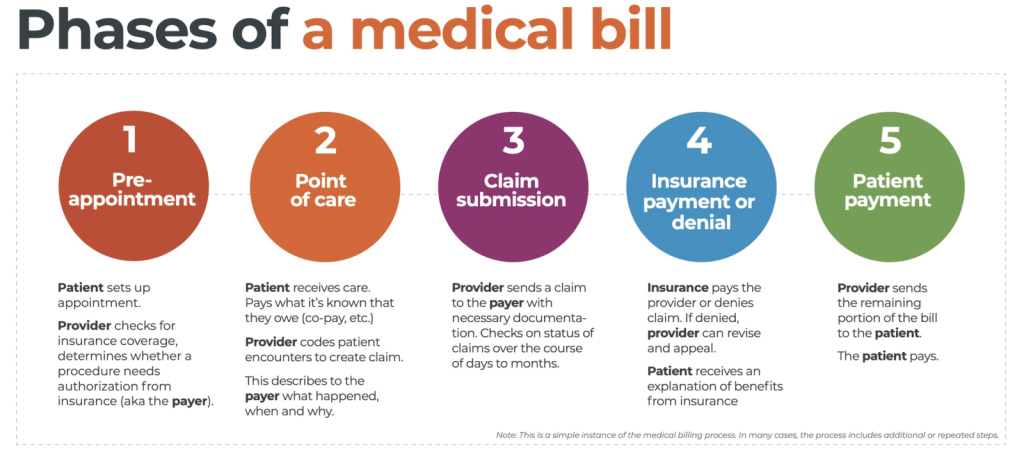
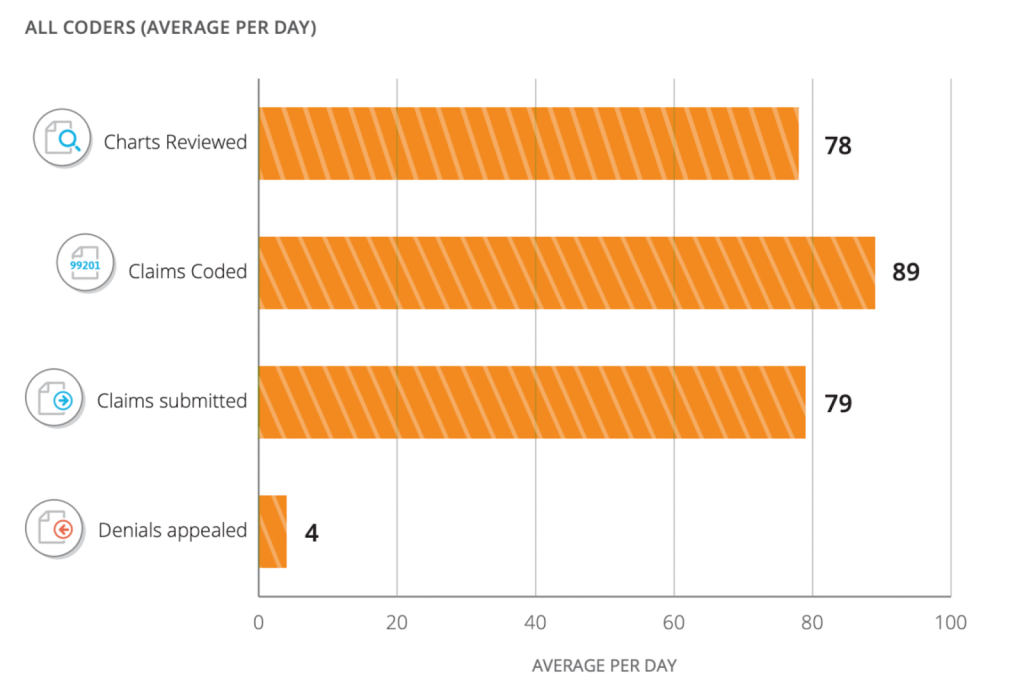
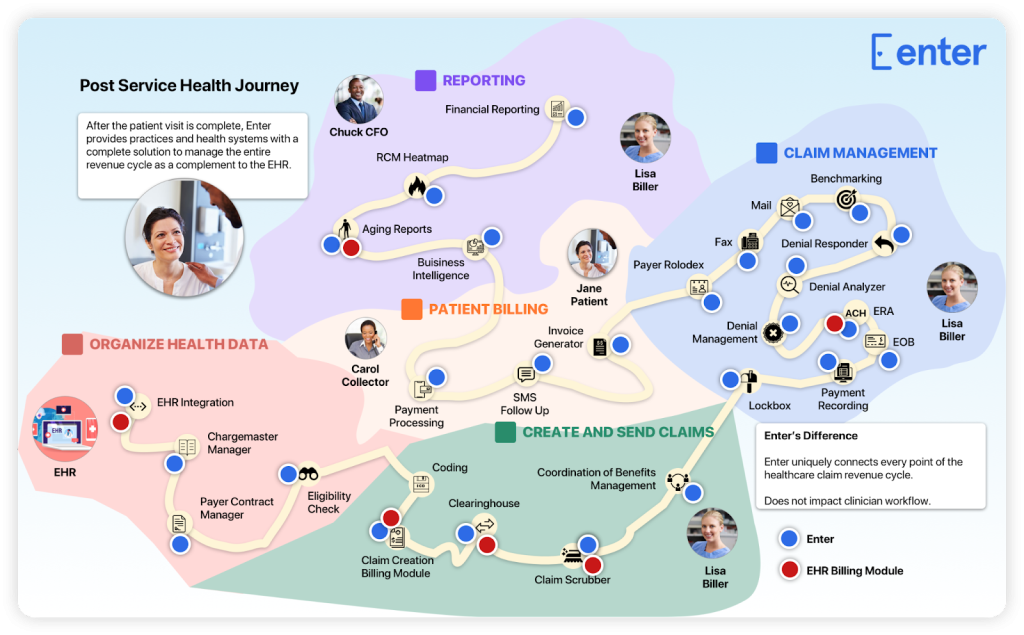
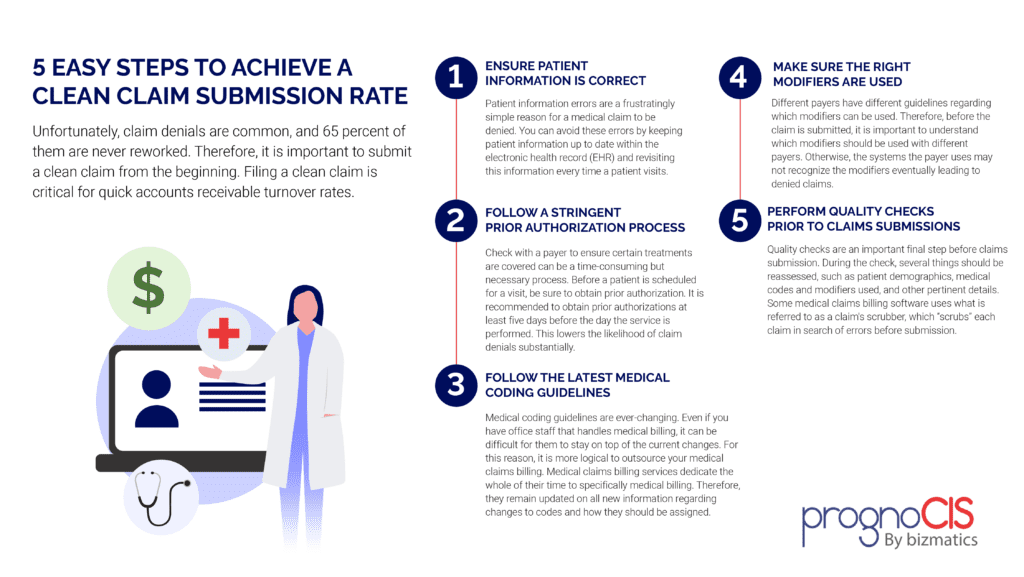
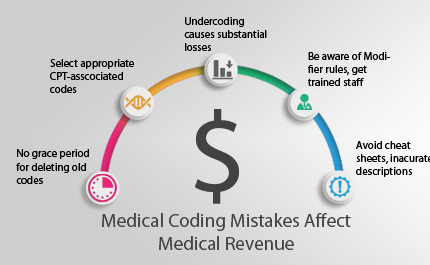
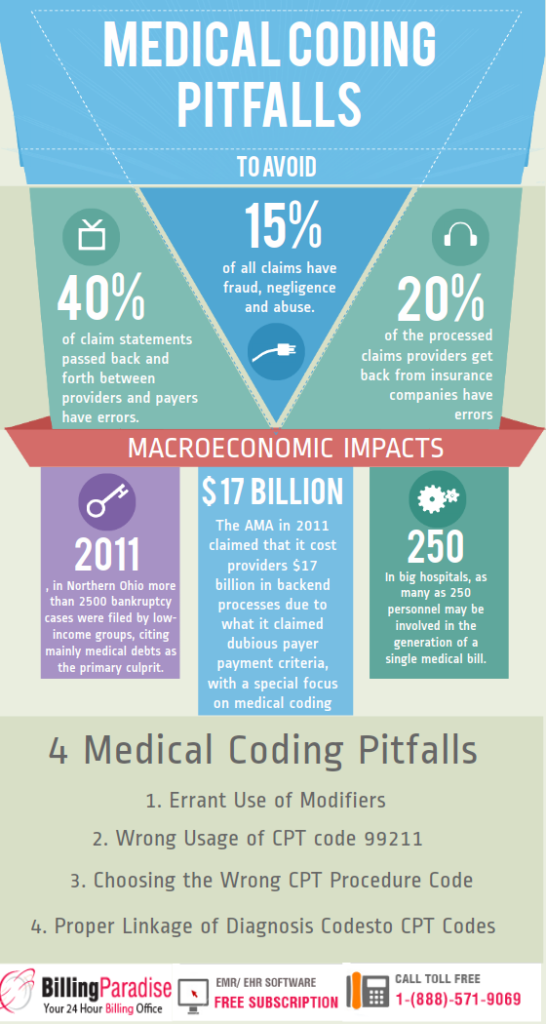
Medical coding is a crucial element in the healthcare industry that plays a pivotal role in the financial reimbursement process and information management. However, many aspiring professionals are often left wondering about the difficulty level of this field. “How Hard Is Medical Coding?” is a comprehensive analysis of the challenges and complexities faced by individuals venturing into this profession. From the intricacies of coding systems to the continuous advancements in medical practices, this article provides valuable insights into the demanding nature of medical coding and the skills required to succeed in this highly specialized field.
Understanding Medical Coding
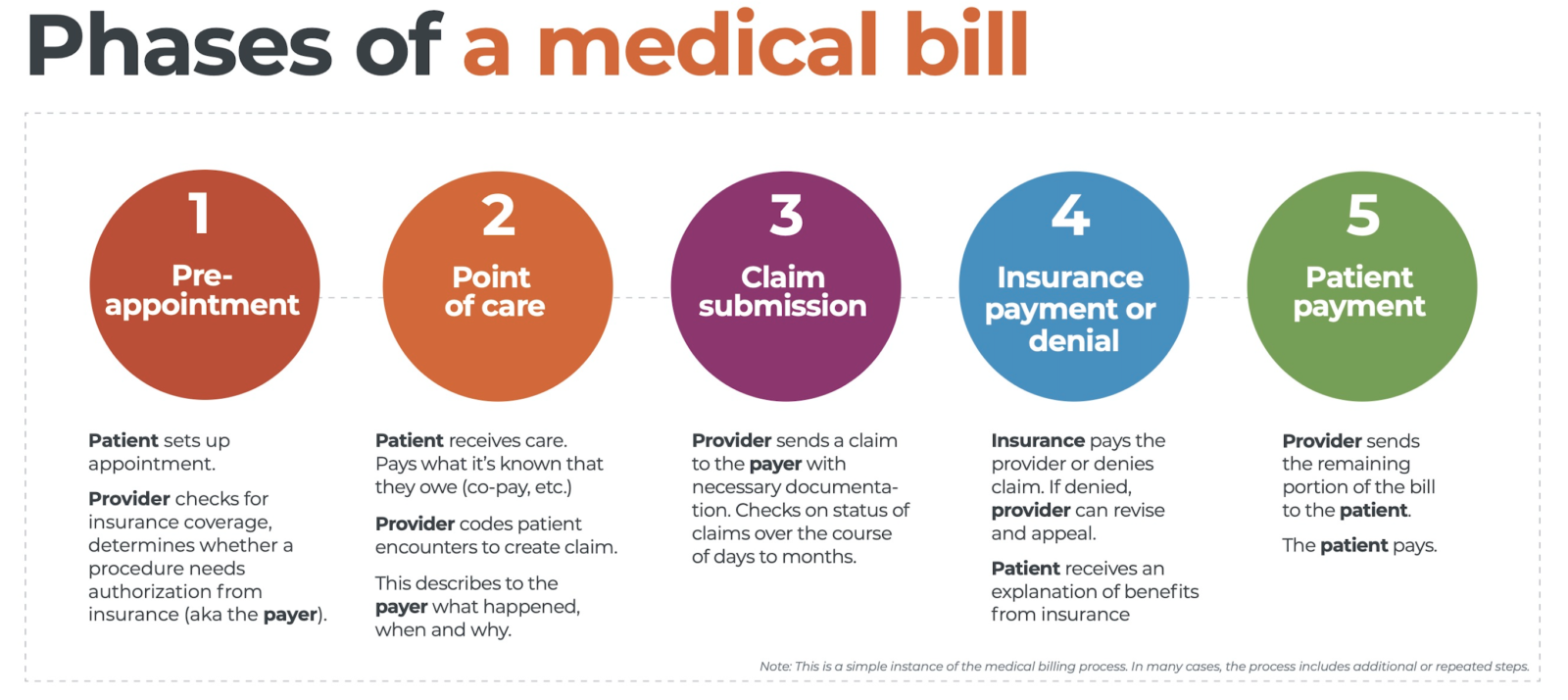
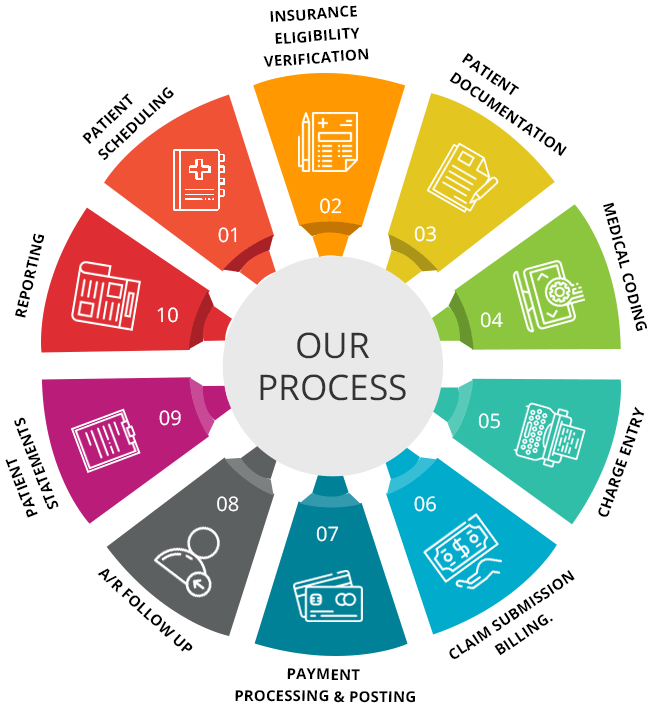
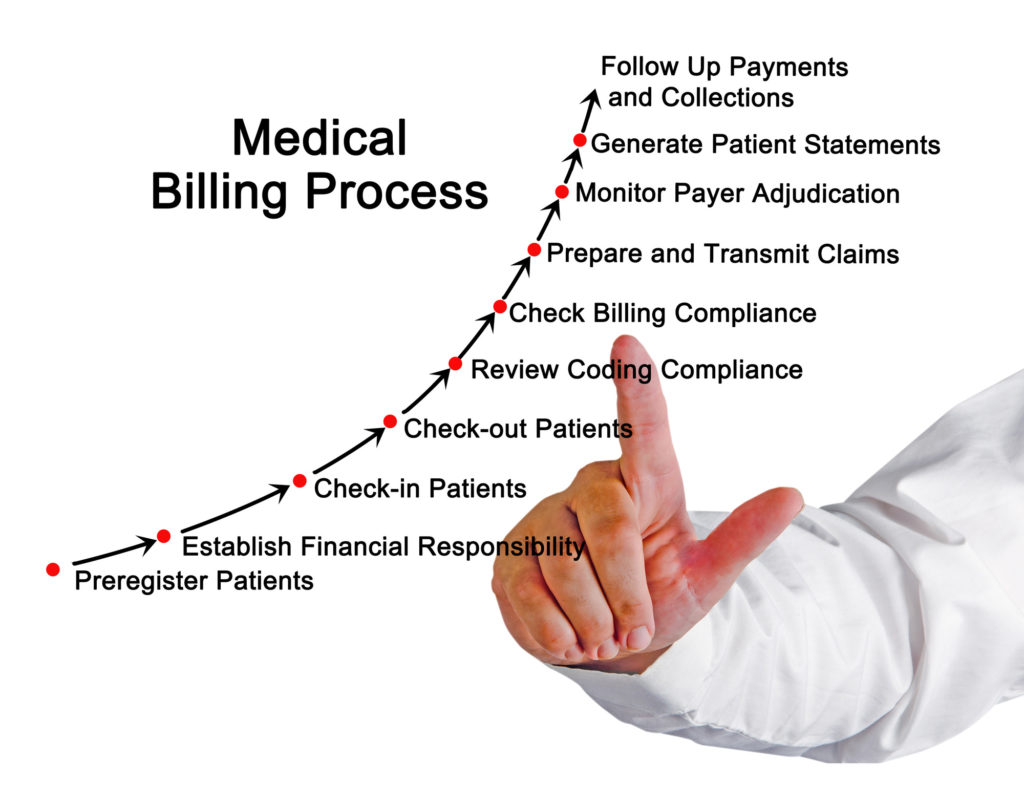
What is medical coding?
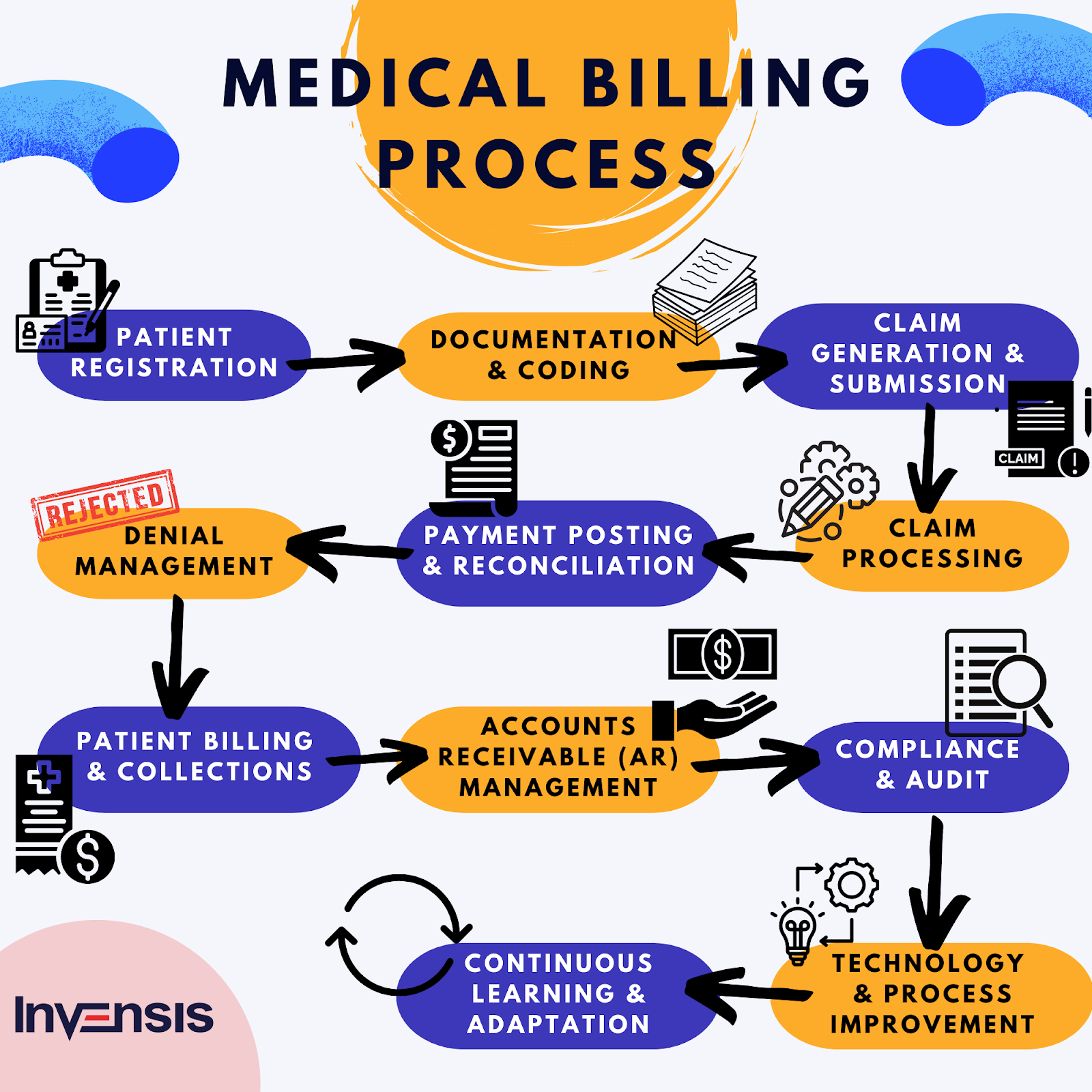
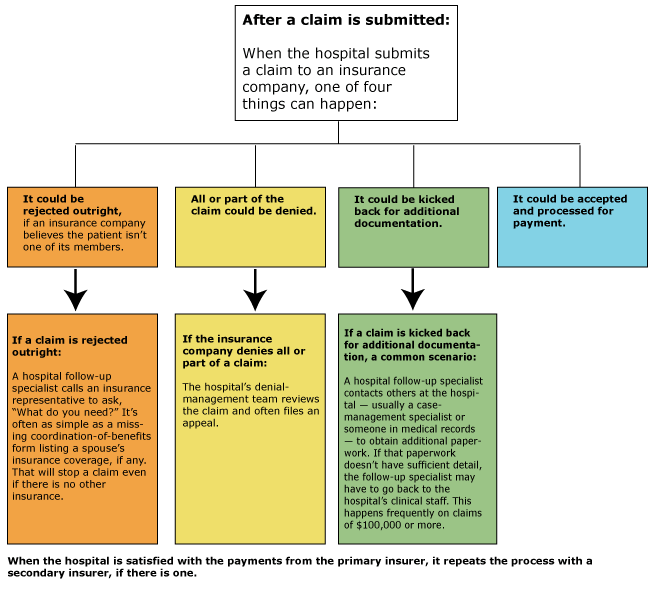
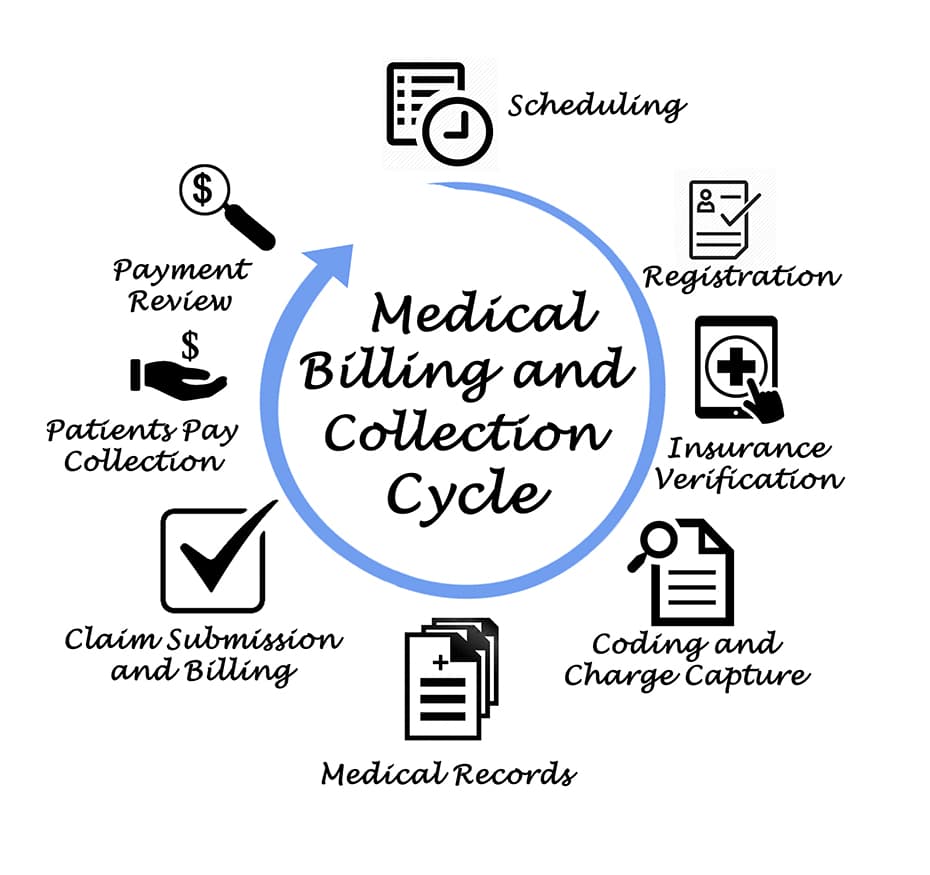
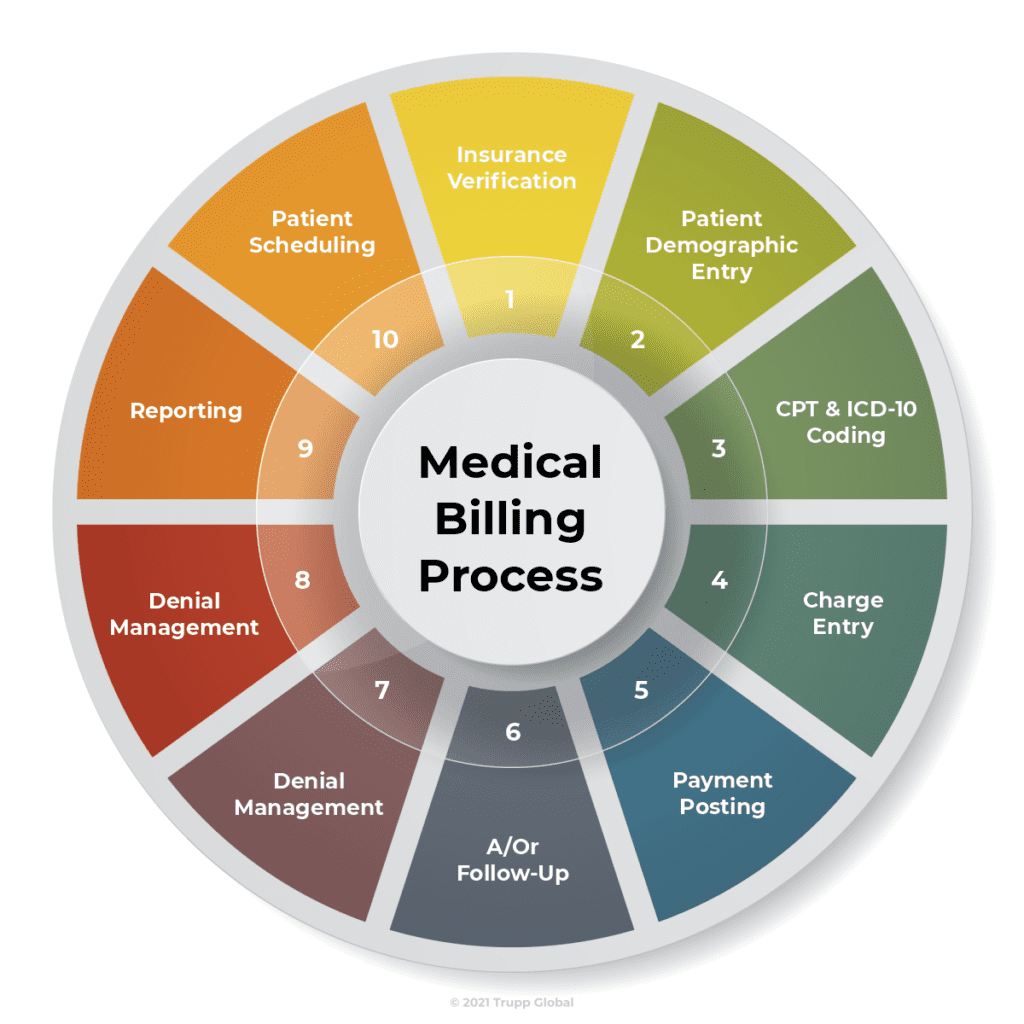
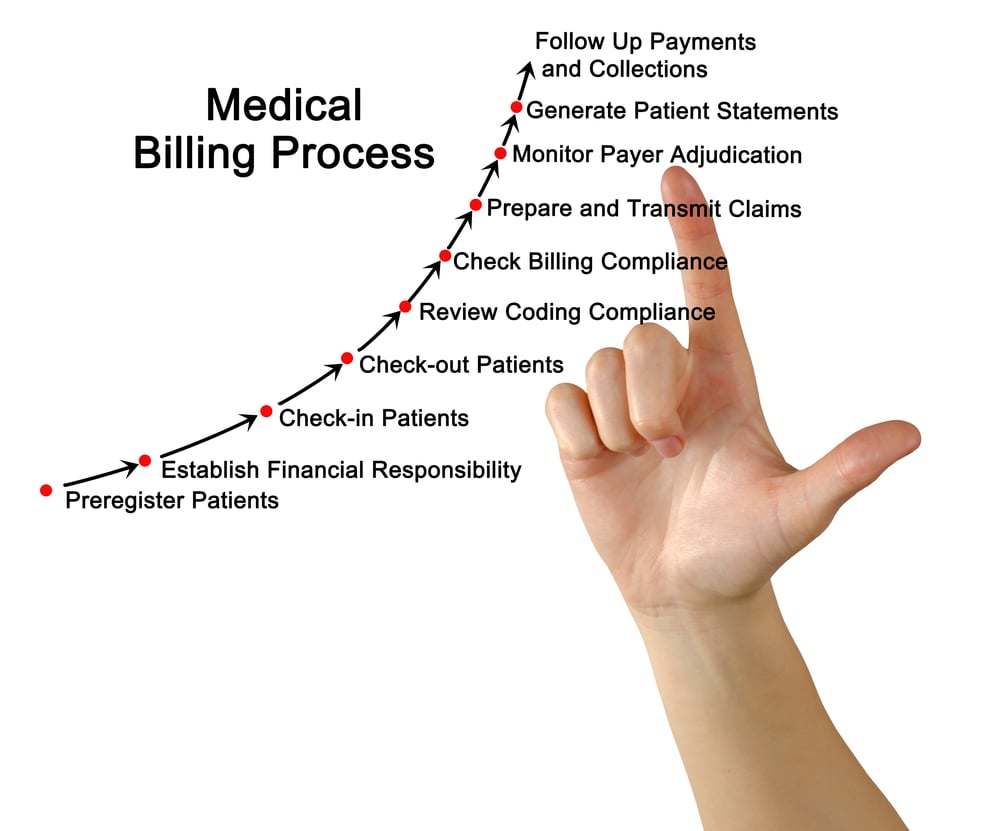
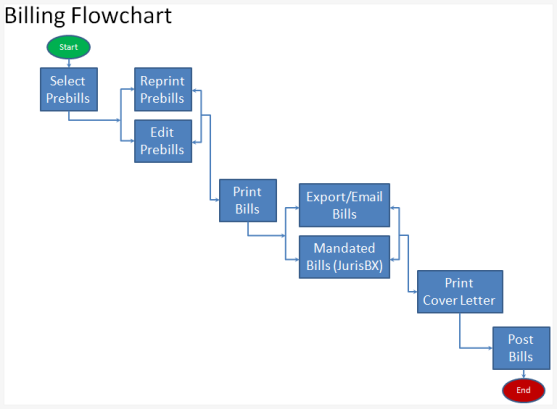
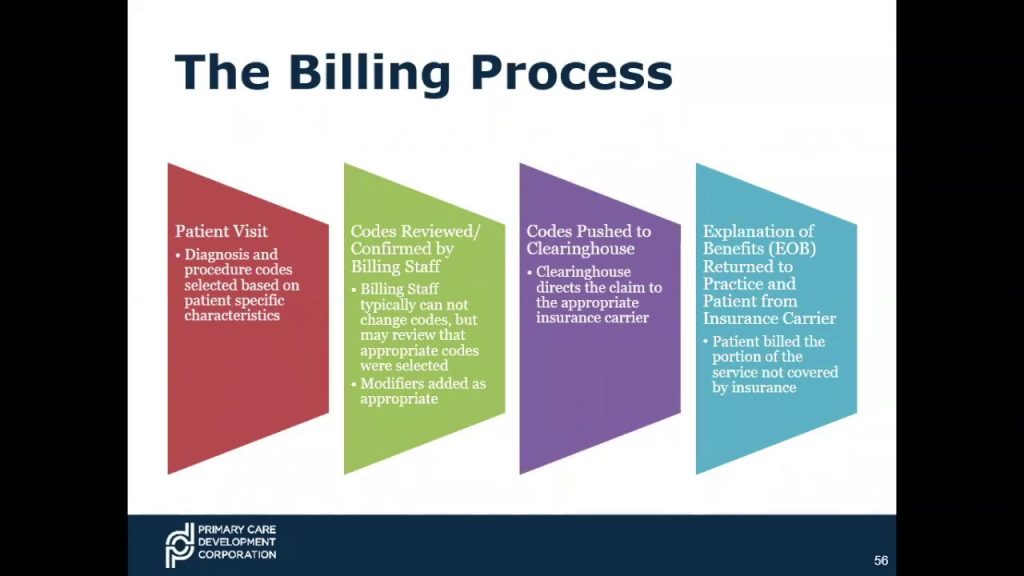
Medical coding is the process of translating medical diagnoses, procedures, and treatments into alphanumeric codes. These codes are essential for capturing and organizing patient data, as well as ensuring accurate billing and reimbursement for healthcare services. Medical coders play a critical role in the healthcare industry by assigning these codes to various medical records, such as doctor’s notes, laboratory results, and operative reports.
Importance of medical coding
Accurate medical coding is crucial for several reasons. First and foremost, it ensures that healthcare providers receive proper reimbursement for the services they provide. Medical codes also contribute to medical research, population health management, and public health reporting. Additionally, coding plays a significant role in fraud prevention and compliance with government regulations and insurance requirements.
Types of medical coding systems
There are different coding systems used in medical coding, each serving a specific purpose. The two primary coding systems are:
- International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM): This system is used to code medical diagnoses and is crucial for accurately representing a patient’s condition or disease.
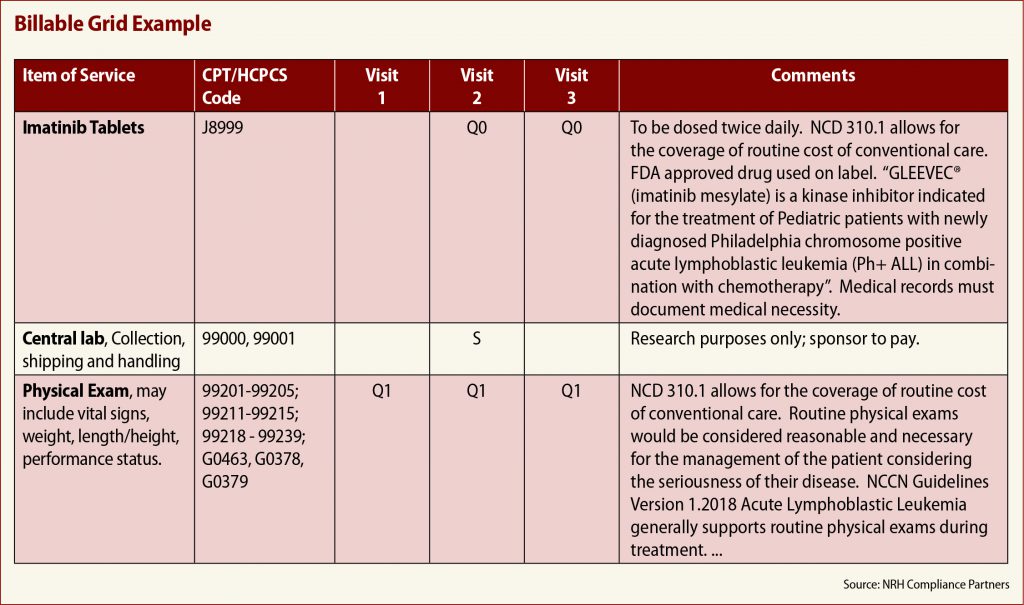
- Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes: CPT codes are used to describe medical procedures, surgeries, and other services provided by healthcare professionals.
In addition to these two coding systems, there are also other specialized coding systems, such as Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) codes, used for Medicare and Medicaid billing.
Challenges in Medical Coding

Complexity of medical terminology
One of the most significant challenges in medical coding is the complexity of medical terminology and jargon. Medical coders must have a strong understanding of anatomy, physiology, and various medical conditions to accurately assign the appropriate codes. They need to decipher and interpret medical documentation correctly, ensuring that every detail is accounted for and coded accurately.
Continuous updates and changes
The medical field is constantly evolving, with new procedures, treatments, and diseases emerging regularly. Medical coders face the challenge of staying updated with these changes and learning new codes as they are introduced. Continuous education and keeping abreast of the latest coding guidelines and updates are crucial to maintaining accuracy and compliance.
Understanding multiple coding systems
As mentioned earlier, there are multiple coding systems used in medical coding. Medical coders need to be proficient in all relevant coding systems and understand how they interact with each other. This can be challenging, as each system has its own set of rules, guidelines, and conventions.
Accuracy and attention to detail
Medical coding is a meticulous process that requires a high level of accuracy and attention to detail. A single mistake in code assignment could have severe consequences for patient care, reimbursement, and compliance. Coders must have a keen eye for detail and be able to analyze complex medical documentation to ensure accurate coding.
Maintaining coding compliance
Medical coders must adhere to coding compliance guidelines, which are established to ensure ethical and accurate coding practices. Maintaining compliance with these guidelines can be challenging, as the rules and regulations frequently change. Coders must stay updated and implement best practices to ensure proper documentation, coding, and billing practices.
Education and Training

Educational requirements
To become a medical coder, a minimum of a high school diploma or equivalent is typically required. However, many employers prefer candidates with post-secondary education, such as an associate’s degree in health information management, health services administration, or a related field. Some employers may also require professional coding certifications along with formal education.
Certification options
There are several recognized certifications for medical coders, including the Certified Professional Coder (CPC) credential offered by the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC) and the Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) credential offered by the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA). These certifications demonstrate a coder’s proficiency in coding systems and knowledge of coding guidelines.
Specialized training programs
In addition to formal education and certifications, there are specialized training programs available for medical coders. These programs provide in-depth training on coding systems, medical terminology, anatomy, and physiology. They help coders develop a solid foundation and prepare them for the complexities of the job.
Hands-on practical experience
While education and certifications are essential, hands-on practical experience is equally valuable in the field of medical coding. Many employers require candidates to have practical coding experience before hiring them. Internships, apprenticeships, or working in entry-level coding positions provide opportunities to gain practical experience and enhance coding skills.
Continuing education
Continuing education is vital in the field of medical coding due to constant updates and changes. Medical coders must stay updated with the latest coding guidelines, industry trends, and regulations. Continuing education courses, workshops, conferences, and webinars help coders enhance their skills and stay current with industry changes.
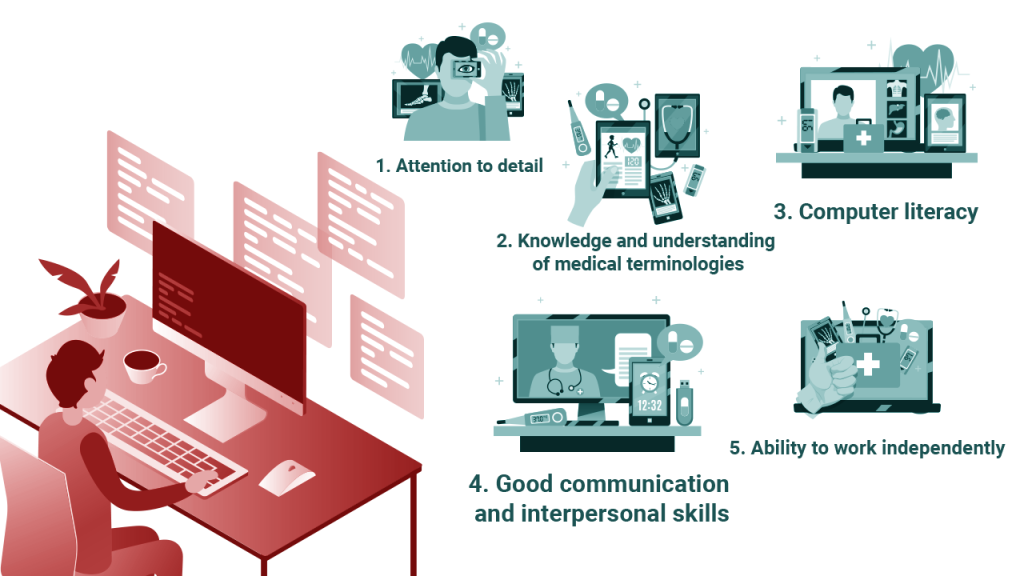
Skills Required for Medical Coding

Medical knowledge
Medical coders need a solid foundation of medical knowledge to understand the terminology, diagnoses, procedures, and treatments they encounter in medical records. They must have a working knowledge of anatomy, physiology, medical conditions, and disease processes to assign accurate codes.
Understanding anatomy and physiology
An in-depth understanding of anatomy and physiology is crucial for medical coders. They need to know how the body’s different systems work, how they interact, and the specific terms used to describe various body parts and processes. This knowledge helps coders accurately assign codes based on the documentation provided.
Proficiency in coding systems
Medical coders must have proficiency in various coding systems, such as ICD-10-CM and CPT codes. They need to understand the structure and organization of these coding systems and know how to navigate their respective guidelines. Proficiency in coding systems allows coders to accurately assign codes based on the documentation provided.
Analytical and critical thinking
Medical coders often encounter complex medical records that require analysis and critical thinking skills. They must be able to interpret and assess the documentation, identify relevant information, and assign appropriate codes. Analytical and critical thinking skills are essential for accurate code assignment and documentation review.
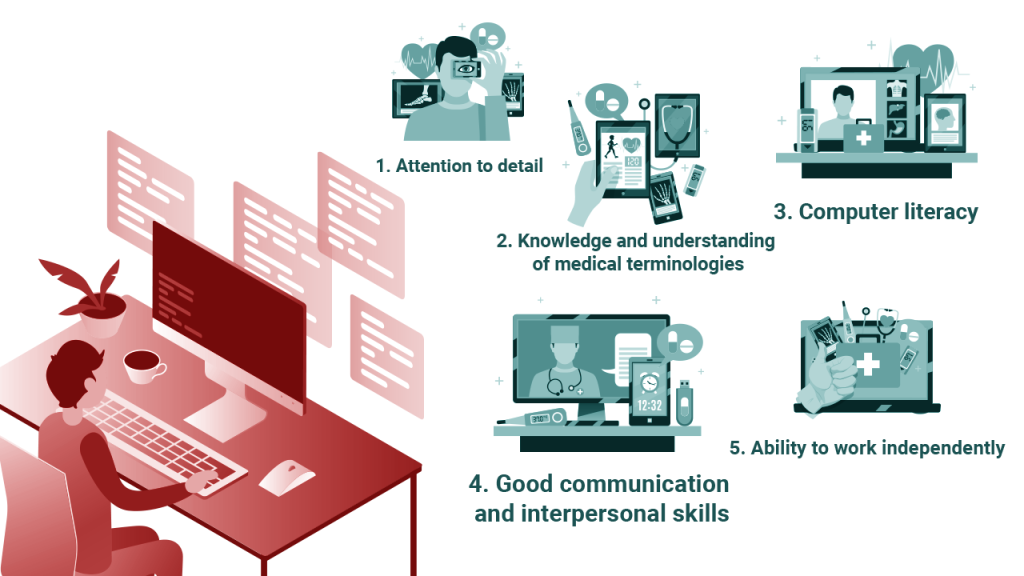
Attention to detail and accuracy
Medical coding is a detail-oriented process that requires a high level of accuracy. Coders must pay close attention to every detail, ensuring that all relevant information is coded and documented correctly. Even a minor error or omission can have significant consequences, so attention to detail is crucial in preventing coding errors.
Ability to work independently
Medical coders often work independently and must be self-motivated and disciplined. They need to manage their workload, prioritize tasks, and meet coding deadlines. The ability to work independently allows coders to efficiently code medical records and ensure timely and accurate coding.
Effective communication skills
Medical coders frequently interact with healthcare professionals, such as physicians, nurses, and administrators. Effective communication skills are essential for clarifying documentation queries, seeking additional information, and resolving coding-related issues. Clear and concise communication helps ensure accurate code assignment and documentation.
Computer literacy
Medical coding is heavily reliant on technology and computer systems. Coders must be proficient in using coding software, electronic health record systems, and other relevant tools. Computer literacy allows coders to efficiently navigate coding systems, electronic records, and coding databases.
Industry Standards and Regulations

HIPAA and patient privacy
Medical coders must comply with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), which protects patient privacy and confidentiality. Coders must handle medical records and patient information with the utmost discretion and ensure that all coding processes maintain patient privacy and security.
Coding compliance guidelines
Coding compliance guidelines are a set of rules and regulations that govern the coding process. Coders must adhere to these guidelines to ensure accurate and ethical coding practices. Compliance guidelines help maintain uniformity and consistency in coding across healthcare organizations.
Code of Ethics for medical coders
Professional organizations such as the AAPC and AHIMA have established a Code of Ethics for medical coders. This code outlines the professional standards and conduct expected from coders. Coders must adhere to this code, which includes maintaining confidentiality, practicing accurate coding, and promoting ethical behavior.
Reimbursement and billing regulations
Medical coding directly impacts reimbursement and billing processes. Coders must be aware of reimbursement and billing regulations to ensure accurate code assignment and documentation. Knowledge of these regulations helps coders prevent coding errors, improve reimbursement accuracy, and avoid compliance issues.
Job Opportunities

Wide range of healthcare settings
Medical coders can find employment opportunities in various healthcare settings, including hospitals, physician offices, clinics, long-term care facilities, and insurance companies. The versatility of medical coding allows professionals to choose a work environment that aligns with their preferences and career goals.
Variety of coding specialties
Medical coding offers a wide range of coding specialties based on different areas of medicine, such as cardiology, orthopedics, radiology, and dermatology. Coders can choose to specialize in a specific field based on their interests and career aspirations. Specialization allows coders to develop expertise in a particular area of coding and potentially earn higher salaries.
Potential for career growth
Medical coding provides opportunities for career growth and advancement. With experience, additional certifications, and ongoing professional development, coders can take on leadership roles, become coding educators or auditors, or transition into management positions. The field offers avenues for continuous learning and upward mobility.
Remote and freelance opportunities
In recent years, there has been a rise in remote and freelance opportunities for medical coders. Advances in technology and the adoption of electronic health records have made it possible for coders to work from the comfort of their homes. Remote and freelance work offers flexibility and autonomy, allowing coders to achieve a healthy work-life balance.
Salary and Job Outlook

Average salary for medical coders
The average salary for medical coders can vary depending on factors such as experience, education, certification, geographic location, and work setting. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for medical records and health information technicians (which includes medical coders) was $44,090 as of May 2020.
Factors influencing salary
Several factors can influence a medical coder’s salary. These include additional certifications, level of education, years of experience, specialized coding knowledge, and geographic location. Coders with advanced certifications and extensive experience in specialized coding areas may command higher salaries.
Job growth and demand
The demand for medical coders is expected to grow in the coming years. The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 8% employment growth for medical records and health information technicians from 2019 to 2029, which is much faster than the average for all occupations. The increasing aging population and the expansion of healthcare services contribute to the growing demand for medical coders.
Advancement opportunities
Medical coding offers opportunities for advancement and professional growth. Coders can advance their careers by pursuing additional certifications, gaining experience in leadership roles, or transitioning into coding auditing or management positions. Continuous professional development and staying updated with industry trends and regulations are essential to capitalize on advancement opportunities.
Tips for Success in Medical Coding

Develop a strong knowledge base
Building a strong foundation of medical knowledge is crucial for success in medical coding. Continuous learning about anatomy, physiology, medical terminology, and coding guidelines helps coders accurately assign codes and stay updated with industry changes.
Stay updated with industry changes
Medical coding is a rapidly evolving field, and staying updated with industry changes is crucial. Coders must keep abreast of the latest coding guidelines, coding updates, regulatory changes, and industry trends. Continuous education, attending workshops and conferences, and subscribing to coding publications help coders stay informed.
Join professional organizations
Joining professional organizations such as the AAPC or AHIMA is beneficial for medical coders. These organizations provide resources, educational opportunities, networking events, and forums for knowledge exchange. Being part of a professional network enhances professional growth and allows coders to stay connected with industry experts.
Network with others in the field
Networking is valuable for professional growth in medical coding. Connecting with other coders, attending industry events, and participating in coding forums or online communities foster collaboration, knowledge sharing, and career opportunities. Networking helps coders expand their professional circle and stay connected with peers.
Continuously improve coding skills
Continuous improvement of coding skills is essential for success in medical coding. Coders should regularly review coding guidelines, practice coding exercises, and seek feedback to enhance their coding accuracy and efficiency. Continuous learning and practice contribute to expertise development and career advancement.
Enhance communication abilities
Effective communication skills are vital for medical coders. Clear and concise communication with healthcare professionals and colleagues fosters collaboration, ensures accurate code assignment, and prevents coding errors. Coders should continuously work on enhancing their communication abilities to excel in their roles.
Seek mentorship and guidance
Seeking mentorship and guidance from experienced coders can accelerate professional growth in medical coding. Mentors can provide insights, share best practices, offer feedback on coding skills, and provide guidance on career advancement. Having a mentor helps coders navigate challenges and gain valuable knowledge from experienced professionals.
Maintain accuracy and attention to detail
Accuracy and attention to detail are paramount in medical coding. Coders should make it a habit to double-check their work, review documentation thoroughly, and ensure coding compliance. Consistently maintaining accuracy and attention to detail builds trust and credibility in the coding work performed.
Work-Life Balance

Flexible work schedules
Medical coding offers flexibility in work schedules, depending on the employer and job setting. Some employers offer flexible work hours, allowing coders to create a schedule that suits their personal needs. Flexibility in work schedules contributes to a better work-life balance.
Opportunity for remote work
The advent of technology has opened up remote work opportunities for medical coders. Remote coding jobs allow coders to work from home or any location with internet access. Remote work removes commuting time and provides flexibility in managing personal and professional commitments.
Balancing productivity and quality
Balancing productivity and quality is essential in medical coding. Coders need to find a balance between efficiently coding medical records without compromising accuracy and attention to detail. Striking the right balance ensures high-quality coding while meeting productivity goals.
Handling work-related stress
Medical coding can be demanding and stressful at times. Coders may experience pressure to meet deadlines and maintain accuracy in coding. It is essential to have effective stress management strategies in place, such as practicing self-care, setting realistic expectations, and seeking support when needed.
Conclusion
Medical coding is a challenging but rewarding profession that requires a strong foundation in medical knowledge, proficiency in coding systems, and attention to detail. Despite the complexity and continuous updates in the field, medical coding offers a variety of job opportunities, potential for career growth, and options for work-life balance. Continuous learning, professional development, and maintaining accuracy are key to success in this ever-evolving field. As medical coding continues to play a vital role in the healthcare industry, skilled and knowledgeable medical coders will be in high demand.