In the rapidly evolving field of healthcare, the role of medical coders has become increasingly vital. These professionals are responsible for accurately translating the complex medical diagnoses, procedures, and treatments into a standardized code format, ensuring that healthcare providers, insurance companies, and government agencies can communicate and process medical information seamlessly. However, a burning question remains: Can you be a medical coder without a degree? In this article, we will explore the qualifications, skills, and potential pathways to becoming a medical coder, shedding light on an often debated topic in the healthcare industry.

This image is property of i.ytimg.com.
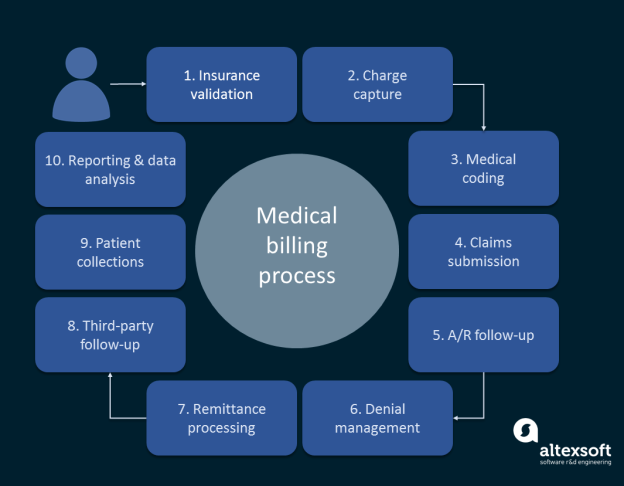
What is Medical Coding?
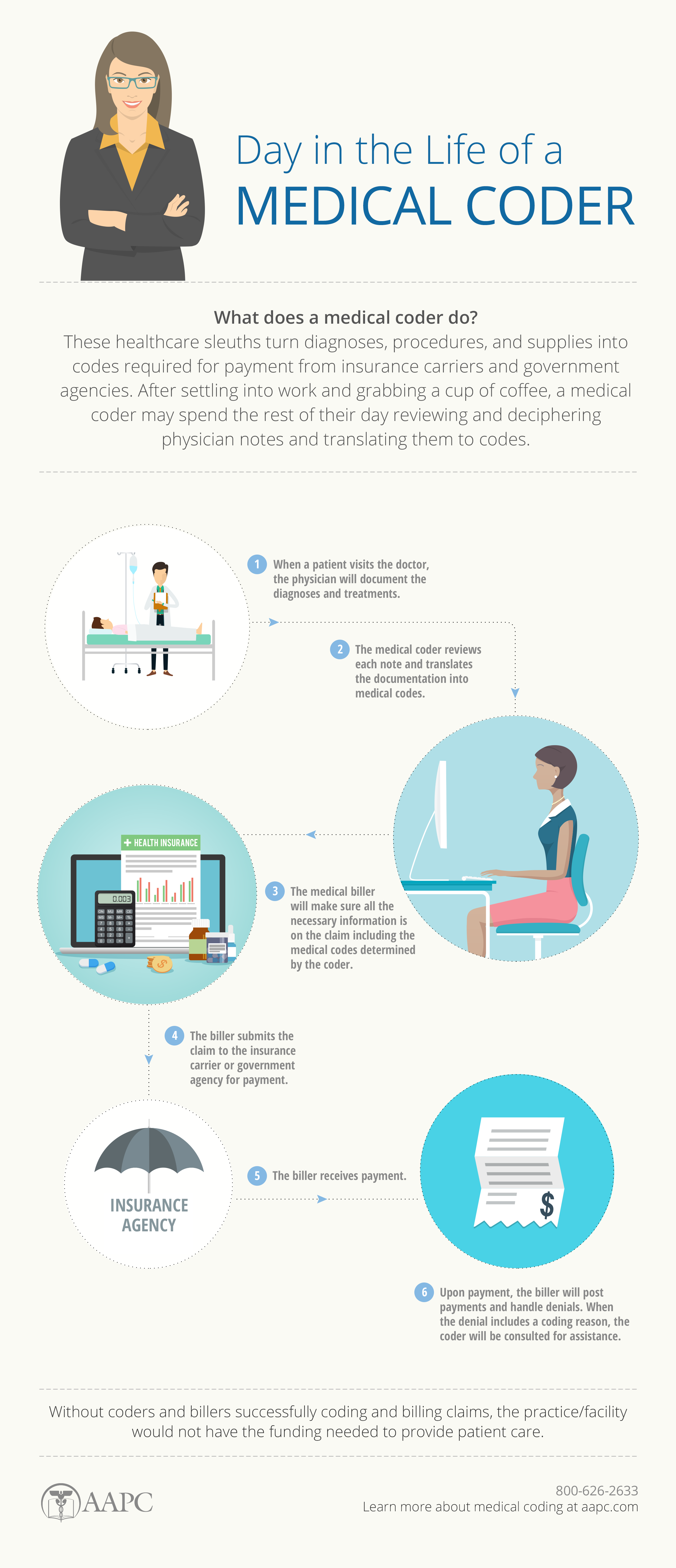
Medical coding is the process of assigning specific codes to medical diagnoses, procedures, and treatments. These codes are used to classify and organize medical information for efficient record-keeping, insurance billing, and statistical analysis. Medical coders play a crucial role in ensuring accurate and consistent documentation within the healthcare industry.
Definition
Medical coding involves translating medical information into a standardized coding system, such as the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) or Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code sets. This allows healthcare providers, insurance companies, and government agencies to understand and analyze medical data consistently.
Importance
Accurate medical coding is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it ensures proper reimbursement for medical services rendered by healthcare providers. Insurance companies rely on medical codes to process claims and determine the appropriate payment. Secondly, medical coding enables efficient retrieval and analysis of medical records, which is crucial for research, epidemiological studies, and healthcare planning. Additionally, accurate coding contributes to patient safety by ensuring that healthcare professionals have access to comprehensive and reliable information when making treatment decisions.
Skills Required
Proficiency in medical coding requires a combination of technical knowledge and analytical skills. Medical coders must be familiar with anatomy, medical terminology, disease processes, and treatment protocols. They should also possess a strong attention to detail, as accurately recording and assigning codes is crucial for proper reimbursement and clinical decision-making. Furthermore, medical coders must stay up to date with evolving coding guidelines and regulations to maintain accuracy and compliance.
Requirements for Medical Coding
While a degree is not always a strict requirement for entering the field of medical coding, certain qualifications and certifications are typically expected.
Minimum Education
In terms of formal education, a high school diploma or GED is usually the minimum requirement for entry-level medical coding positions. However, employers often prefer candidates who have completed post-secondary education or professional training programs focused on medical coding.
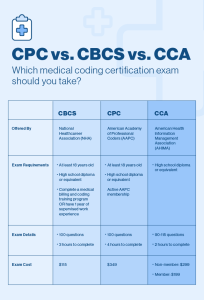
Certification
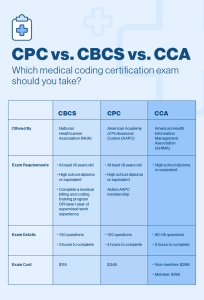
One of the most recognized certifications in medical coding is the Certified Professional Coder (CPC) credential, offered by the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC). To obtain this certification, individuals must pass an exam that tests their knowledge of medical coding principles and guidelines. Other reputable certifications include the Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) credential, offered by the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA).
Experience
While experience is not always mandatory, it can significantly enhance job prospects and earning potential in medical coding. Healthcare facilities and coding agencies may prefer candidates with practical experience in coding and a demonstrated understanding of coding guidelines, procedures, and medical terminology. Experience can be gained through internships, entry-level positions, or on-the-job training.
Pros of Pursuing a Degree in Medical Coding
Pursuing a degree in medical coding offers numerous benefits, both in terms of knowledge and career opportunities.
Enhanced Knowledge and Skills
A formal education in medical coding provides a comprehensive understanding of anatomy, medical terminology, and coding guidelines. It equips students with the knowledge and skills necessary for accurate coding and ensures a solid foundation in healthcare documentation. Additionally, degree programs often incorporate practical experience through internships or clinical rotations, further strengthening coding abilities.
Increased Job Opportunities
obtaining a degree in medical coding can open doors to a wider range of job opportunities. Many healthcare facilities and medical coding companies prefer candidates with formal education, as it demonstrates a higher level of commitment, professionalism, and proficiency in the field. With a degree, individuals may be eligible for supervisory or management positions, allowing for career advancement.
Potential for Higher Salary
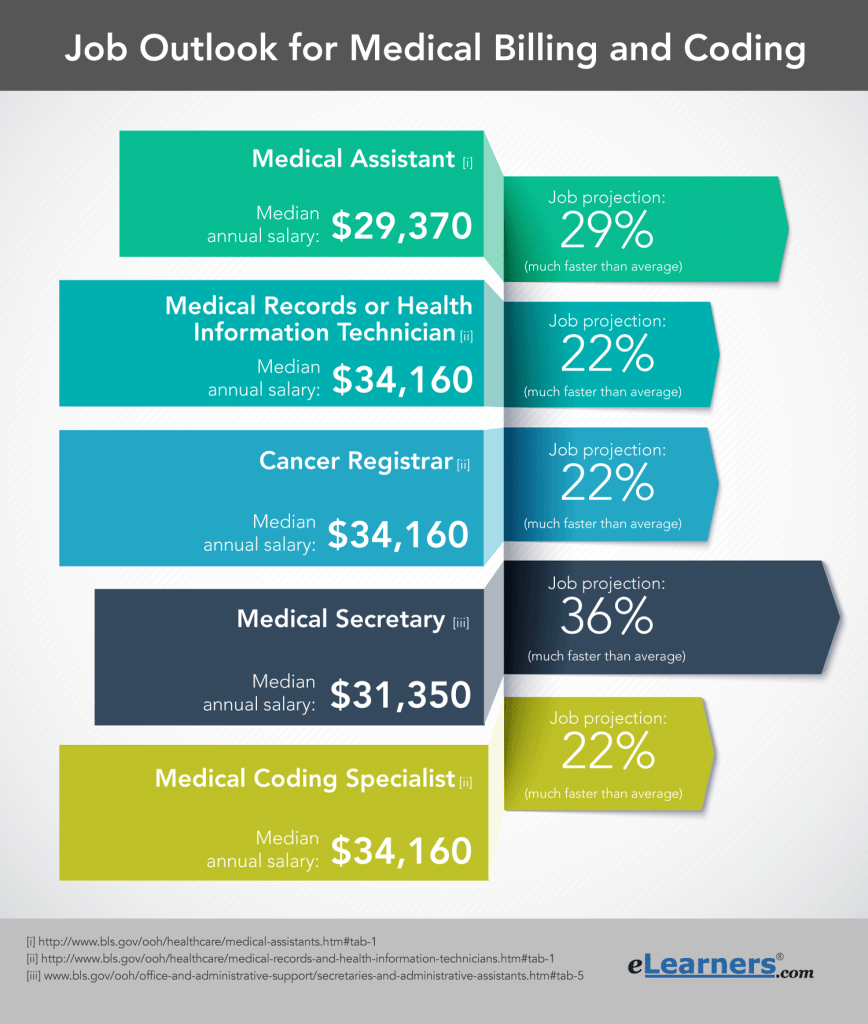
Having a degree in medical coding can lead to a higher earning potential. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, individuals with a degree or certification in medical coding typically earn higher salaries compared to those without formal education. Employers often compensate individuals with higher qualifications and specialized knowledge at a more competitive rate.
Options for Education in Medical Coding
Various educational pathways are available for individuals interested in pursuing a career in medical coding. These pathways range from associate degree programs to online courses and certifications.
Associate Degree Programs
Community colleges and vocational schools offer associate degree programs in medical coding, typically lasting two years. These programs provide in-depth instruction in medical coding practices, as well as foundational knowledge in healthcare management, anatomy, and medical terminology. Graduates of associate degree programs are well-prepared for entry-level coding positions and have a comprehensive understanding of the field.
Bachelor’s Degree Programs
For individuals seeking advanced knowledge and potential leadership opportunities in medical coding, bachelor’s degree programs are available at universities and colleges. These programs delve deeper into coding theory, healthcare ethics, and advanced coding techniques. A bachelor’s degree in medical coding may also prepare individuals for roles in healthcare administration, consultancy, or education.
Online Courses and Certifications
Online courses and certifications are versatile options for individuals looking to gain specific skills or enhance their existing knowledge in medical coding. Online courses offer flexibility in terms of scheduling and can be completed at an individual’s own pace. Certifications obtained through online training programs, such as the CPC certification offered by the AAPC, are highly regarded by employers and demonstrate proficiency in medical coding.

This image is property of storage.googleapis.com.
Alternative Routes to Become a Medical Coder
While a degree is beneficial, it is not the only path to becoming a medical coder. Several alternative routes can lead to a successful career in medical coding.
On-the-Job Training
Some healthcare facilities may offer on-the-job training programs for individuals interested in becoming medical coders. These programs typically provide hands-on experience in coding practices and may lead to certifications or advancement within the organization. On-the-job training allows individuals to acquire practical skills while earning a salary, making it an attractive option for those without a formal degree.
Specialized Coding Certifications
Obtaining specialized coding certifications can compensate for a lack of a formal degree in medical coding. These certifications focus on specific aspects of medical coding, such as anesthesia, surgical procedures, or medical auditing. While not mandatory, these certifications demonstrate expertise and can significantly enhance job prospects and earning potential.
Associate’s Degree in a Related Field
While not specifically in medical coding, obtaining an associate’s degree in a related field such as health information management or healthcare administration can be advantageous. These degrees provide a broader understanding of healthcare systems, information technology, and coding guidelines, complementing the skills required for medical coding. Graduates with related degrees may be eligible for coding positions or have the foundation to pursue further education in medical coding.
Job Outlook for Medical Coders without a Degree
While a degree can provide valuable advantages, individuals without a formal degree still have opportunities in the field of medical coding.
Employment Opportunities
The demand for skilled medical coders continues to grow in various healthcare settings, such as hospitals, clinics, insurance companies, and coding agencies. With the increasing adoption of electronic health records, the need for accurate and efficient coding is vital. While employers may prioritize candidates with degrees or certifications, there are still entry-level positions available for individuals without formal education.
Salary Potential
Although individuals without a degree may face more competition for positions, their salary potential can still be promising. Entry-level medical coding positions often provide opportunities for growth and advancement, with salaries increasing as experience and expertise in coding develop. Employers recognize the value of practical experience and a strong work ethic, which can compensate for the lack of a formal degree.
Advancement Opportunities
While a degree can offer a higher likelihood of advancement in the field of medical coding, individuals without a degree can still pursue growth in their careers. By gaining experience, pursuing certifications, and showcasing strong coding skills, individuals can demonstrate their competence and dedication to potential employers. Advancement opportunities may include management roles, consultancy, or specialization in certain coding areas.
Challenges of Being a Medical Coder without a Degree
Although it is possible to pursue a career in medical coding without a degree, there are some challenges to consider.
Limited Job Options
Not having a degree can limit the range of job options available for individuals interested in medical coding. Some employers may specifically require a degree or certification as a minimum qualification, excluding candidates without formal education from certain positions. However, focusing on gaining practical experience, certifications, and specialized knowledge can help mitigate this limitation.
Competitive Job Market
The field of medical coding is highly competitive due to the increasing demand for accurate coding and the limited number of entry-level positions available. Individuals without a degree may face stronger competition from candidates who possess formal education or relevant certifications. To stand out in a competitive job market, it is crucial to highlight one’s skills, practical experience, and commitment to professional development.
Lack of Formal Education
Not having a formal degree in medical coding may result in a knowledge gap, as degree programs provide a comprehensive understanding of coding principles and practices. Candidates without formal education might need to invest additional time and effort in self-study and continuous learning to stay updated with changing coding guidelines and best practices. However, with dedication and a commitment to ongoing education, this knowledge gap can be overcome.
Key Skills and Competencies
To excel as a medical coder, certain key skills and competencies are essential.
Medical Terminology
Proficiency in medical terminology is crucial for accurate coding. Medical coders must have a deep understanding of medical terms, abbreviations, and anatomical references to interpret medical records correctly and assign appropriate codes. This knowledge ensures proper communication with healthcare providers and ensures the accuracy of coded information.
Understanding Coding Systems
medical coders must be familiar with coding systems, most notably the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) and Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code sets. They must understand the structure and hierarchy of these code sets and stay updated with evolving guidelines and revisions. An in-depth understanding of coding systems ensures accurate code assignment and compliance with coding regulations.
Attention to Detail
Precision and attention to detail are vital skills for medical coders. They must meticulously review medical records, ensuring that all relevant diagnoses, procedures, and treatments are accurately captured and coded. A single error in coding can have significant consequences, including inaccurate reimbursement, compromised patient care, or legal and regulatory issues. Medical coders must maintain a high level of accuracy and attention to detail.

This image is property of askdegrees.com.
Building a Career Path as a Medical Coder
To build a successful career as a medical coder, certain strategies can be implemented to maximize growth and advancement opportunities.
Gaining Experience
Practical experience is invaluable for medical coders. Entry-level coding positions or internships provide opportunities to apply coding knowledge, learn from experienced professionals, and gain exposure to various healthcare settings. By continuously strengthening coding skills and seeking diverse coding experiences, individuals can enhance their competence and increase their chances of career progression.
Continuing Education
Medical coding is a dynamic field, with coding guidelines and regulations frequently evolving. To stay updated and maintain proficiency, medical coders should engage in continuous education. This can involve attending coding seminars, workshops, or webinars, as well as participating in online courses or certification programs. By staying abreast of industry developments, coders can adapt to changing coding practices and seize new opportunities.
Professional Networking
Building a professional network can foster growth and open doors to new opportunities. Joining professional organizations, such as the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC) or American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA), allows coders to connect with peers, access resources, and stay informed about industry trends. Networking can lead to mentorship opportunities, job referrals, and career advancement through a broader professional network.
Conclusion
While a degree can provide numerous advantages in a career as a medical coder, it is not the sole determinant of success. The field of medical coding offers a range of opportunities for both degree-holders and those without formal education. By acquiring practical experience, pursuing certifications, and continuously improving skills, individuals can thrive as medical coders, enjoying a rewarding and fulfilling career in the healthcare industry.

This image is property of i.ytimg.com.