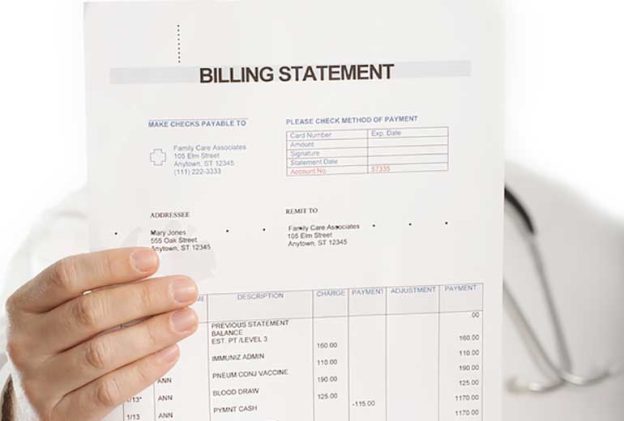
Medical coding is a fundamental process in the healthcare industry that involves the translation of medical diagnoses, procedures, and treatments into universally recognized codes. These codes serve as a unique language that helps healthcare professionals accurately document and communicate vital patient information. For example, when a patient visits a healthcare provider for a check-up, the physician will assign specific codes to document the visit, diagnostic tests performed, and any procedures or medications prescribed. These codes are crucial for accurate billing purposes, tracking patient outcomes, and conducting clinical research. In essence, medical coding plays a vital role in maintaining effective healthcare delivery and streamlining administrative processes.
This image is property of res.cloudinary.com.
Heading 1
Subheading 1.1
Medical Coding: An Essential Component of the Healthcare Industry
In the world of healthcare, medical coding plays a vital role in ensuring accurate and efficient communication between healthcare providers, insurance companies, and government agencies. Medical coding involves the transformation of medical diagnoses, procedures, and services into universally recognized alphanumeric codes. These codes provide a standardized way of documenting medical information, facilitating proper billing, reimbursement, and data analysis. Without medical coding, the healthcare industry would face significant challenges in managing patient records, conducting research, and ensuring appropriate financial transactions.
Subheading 1.2
Understanding the Purpose and Process of Medical Coding
Medical coding serves various purposes within the healthcare system. Firstly, it allows healthcare providers to record and communicate specific details about a patient’s medical condition and the services provided during a visit or treatment. This information is crucial for providing quality care, coordinating treatment plans, and preserving accurate medical histories. Secondly, coding facilitates accurate billing and reimbursement for healthcare services rendered. Insurance companies and government agencies rely on these codes to determine the appropriate amount to reimburse a healthcare provider. Finally, medical coding plays a key role in data analysis, research, and decision-making within the healthcare industry. It enables the identification of trends, patterns, and outcomes, contributing to advancements in medical science and healthcare delivery.
To ensure uniformity and consistency, medical coding follows specific guidelines and protocols. the coding process typically involves reviewing medical records, extracting relevant information, and assigning the appropriate codes based on the patient’s diagnosis, procedures performed, and any additional factors. This requires skilled medical coders who possess a thorough understanding of anatomy, medical terminology, and coding systems, such as the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) and the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT). With these codes in place, medical records become standardized, facilitating seamless communication and understanding among healthcare professionals.
Heading 2
Subheading 2.1
ICD Coding: Documenting Diagnoses
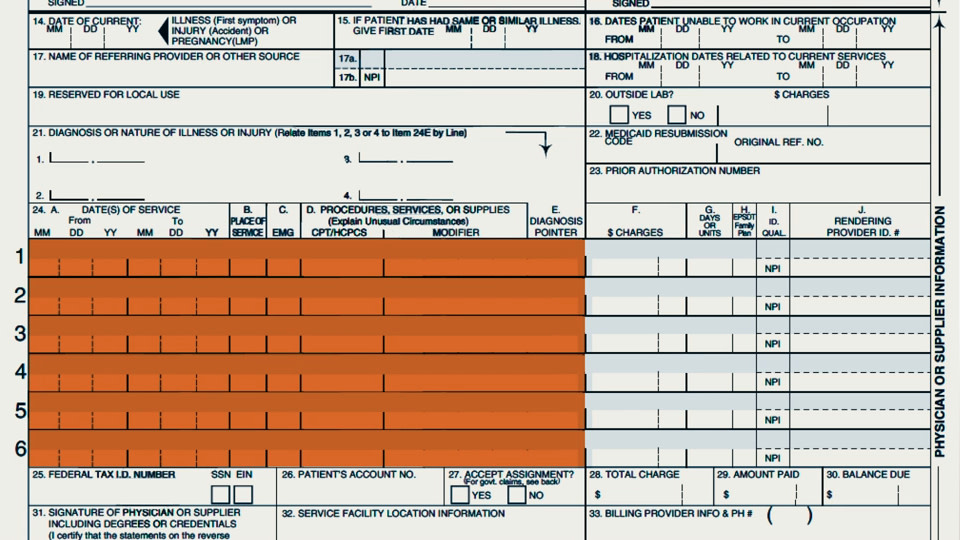
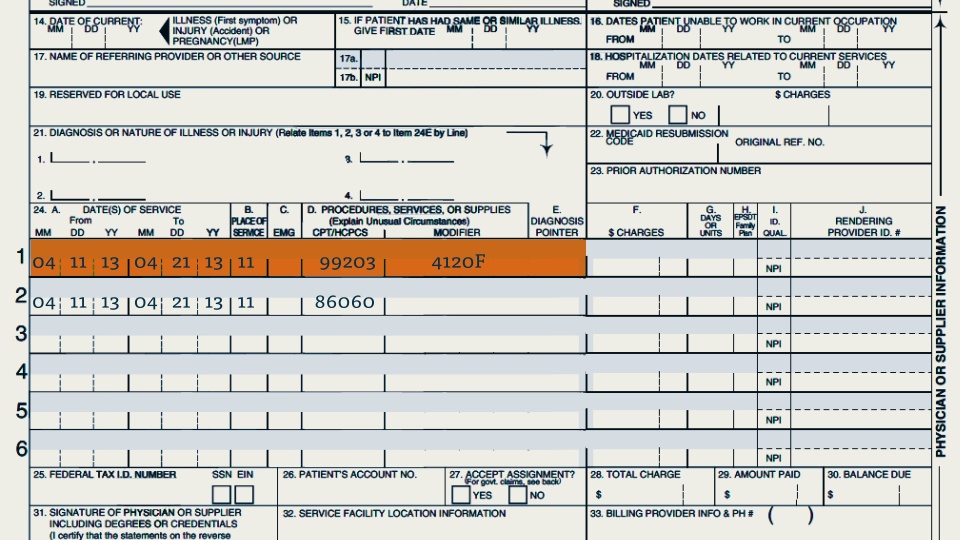
One example of medical coding is the use of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) codes to document and categorize diagnoses. The ICD is a globally recognized system that provides a comprehensive list of medical conditions and assigns them unique codes. By correctly applying ICD codes, healthcare professionals can accurately represent a patient’s medical condition, which enhances communication and contributes to improved patient care.
When a patient visits a healthcare provider, the healthcare professional will evaluate their symptoms, conduct tests, and ultimately arrive at a diagnosis. This diagnosis is then translated into an ICD code, which describes the condition using precise language that is universally understood. For instance, if a patient is diagnosed with pneumonia, a specific ICD code, such as J18.9, “Pneumonia, unspecified organism,” may be assigned to indicate the condition. This code captures essential information about the diagnosis, enabling accurate record-keeping and effective communication with other healthcare professionals involved in the patient’s care.
Subheading 2.2
CPT Coding: Documenting Medical Procedures
In addition to diagnosing medical conditions, healthcare providers also perform various procedures to treat their patients. To document these procedures adequately, healthcare professionals utilize Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes. CPT codes are numeric codes developed and maintained by the American Medical Association (AMA) and are used to communicate specific medical services performed during a patient encounter.
CPT codes cover a wide range of medical procedures, including surgeries, office visits, laboratory tests, and therapeutic interventions. Each code corresponds to a particular procedure or service, ensuring accurate representation of the healthcare provided. For example, if a patient undergoes a knee arthroscopy, the corresponding CPT code, such as 29881, “Arthroscopy, knee, diagnostic, with or without synovial biopsy (separate procedure),” would be assigned to document the procedure accurately. These codes assist in standardized documentation, billing, and reimbursement processes, enabling efficient workflow and proper financial management within healthcare organizations.
This image is property of embed-ssl.wistia.com.
Heading 3
Subheading 3.1
The Benefits and Importance of Accurate Medical Coding
Accurate medical coding serves as the foundation for efficient healthcare operations and optimal patient care. Here are some key benefits and reasons why accurate medical coding is crucial:
- Improved Patient Care: Accurate medical coding ensures that relevant clinical information is properly recorded and easily accessible to healthcare professionals. This promotes better communication, care coordination, and treatment decision-making, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes.
- Proper Reimbursement: Insurance companies, government agencies, and other healthcare payers rely on accurate coding to determine reimbursement amounts for healthcare services. Incorrect coding can result in delayed or denied reimbursement, leading to financial strain for healthcare providers and potential challenges for patients in accessing necessary care.
- Billing and Revenue Cycle Management: Accurate coding directly impacts the billing and revenue cycle management process in healthcare organizations. Proper coding contributes to timely and accurate claim submissions, reduced billing errors, and improved cash flow for healthcare providers.
- Data Analysis and Research: Accurate coding produces reliable and consistent data, which is vital for healthcare research, tracking disease prevalence, analyzing treatment options, and identifying healthcare trends. Researchers and policymakers heavily rely on coded data to make informed decisions and advancements in healthcare.
- Compliance with Regulations: The healthcare industry is subject to various regulations and requirements, such as those set by insurance companies, government agencies, and professional organizations. Accurate coding ensures compliance with these regulations, reducing the risk of penalties, audits, and legal consequences for healthcare providers.
Efficient and precise medical coding is crucial to the success of any healthcare organization, benefiting patients, healthcare professionals, payers, and the overall healthcare system as a whole.
Subheading 3.2
Challenges and Future Trends in Medical Coding
While medical coding plays a pivotal role in the healthcare industry, it is not without its challenges. Some of these challenges include:
- Complexity and Updates: Medical coding systems, such as ICD and CPT, are intricate and constantly evolving. Keeping up with coding guidelines, updates, and new codes requires continuous education and training for medical coders.
- Coding Errors and Inaccuracies: Mistakes in medical coding can result in claim denials, billing discrepancies, and potentially compromise patient care. Precision and attention to detail are vital to avoid coding errors.
- Technology Integration: The implementation of electronic health records (EHRs) and computer-assisted coding (CAC) systems has revolutionized medical coding. However, successfully integrating these technologies and harnessing their full potential can be challenging for healthcare organizations.
As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, medical coding will also undergo changes and advancements. Some of the future trends in medical coding include:
- Automation and Artificial Intelligence: Automation and artificial intelligence (AI) have the potential to streamline the coding process, reducing the chances of errors and improving coding accuracy and efficiency.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): EHR systems are becoming increasingly commonplace, leading to improved documentation and coding capabilities. Integrating coding directly into EHRs can enhance workflow and reduce duplicative efforts.
- ICD-11: The transition to the latest edition of the ICD coding system, known as ICD-11, is underway. ICD-11 aims to improve coding accuracy, expand coding capabilities, and enable enhanced data analytics and research.
In conclusion, medical coding is a critical component of the healthcare industry, facilitating accurate communication, billing, reimbursement, and data management. Understanding the purpose, process, and examples of medical coding is essential for healthcare professionals, insurers, researchers, and policymakers alike. Accurate medical coding ensures optimal patient care, efficient operations, and the advancement of medical science. As the healthcare industry evolves, so will medical coding, embracing technological advancements and embracing new coding systems to meet the ever-changing needs of the industry.

This image is property of s3.resume.io.