In the world of medical billing, understanding the various types of denials is crucial for efficient and accurate claim processing. Denials are a common occurrence in this field, often leading to delayed payments and increased administrative burden. By recognizing the different types of denials, healthcare providers can proactively address and prevent them, thereby streamlining the revenue cycle and ensuring smooth operations. This article will explore the various types of denials in medical billing, shedding light on their causes, implications, and strategies to overcome them effectively.
Overview
In the complex world of medical billing, denials can be a common occurrence. These denials can have a significant impact on the revenue cycle and can cause major headaches for healthcare providers. Understanding the different types of denials and the reasons behind them is crucial for success in the medical billing process.
This article will provide a comprehensive overview of the various types of denials in medical billing. We will delve into front-end denials, medical necessity denials, coding denials, claim submission denials, payment denials, coordination of benefits (COB) denials, as well as denials specific to Medicare, Medicaid, and the appeals process. Let’s explore each of these categories in detail.
Front-End Denials
Front-end denials refer to the denials that occur before the claim is even submitted to the insurance company. These denials often result from missing information, duplicate claims, eligibility issues, and coordination of benefits (COB) issues.
Missing Information
Missing information can result in denials, as insurance companies require complete and accurate documentation to process claims. Common missing information includes patient demographic data, provider credentials, treatment dates, and diagnosis codes. To prevent missing information denials, it is essential to double-check all documentation and ensure all required fields are properly filled out.
Duplicate Claims
Duplicate claims occur when the same service or procedure is billed multiple times for the same patient. Insurance companies have stringent guidelines on duplicate claims, and any attempt to bill for the same service twice is likely to result in a denial. It is crucial to implement effective systems and processes to avoid submitting duplicate claims.
Eligibility Issues
Eligibility denials happen when a patient’s insurance coverage has lapsed or does not cover a particular service. Verifying patients’ eligibility before providing services can help prevent these denials. Regularly updating and cross-checking insurance coverage can save time and resources by identifying potential eligibility issues upfront.
Coordination of Benefits (COB) Issues
COB denials occur when there are multiple insurance policies that cover the same patient, leading to confusion regarding primary and secondary coverage. Without proper coordination, insurance companies may deny claims, believing that another insurance provider should be responsible for the payment. Accurate documentation and coordination with patients to identify other insurance policies can help address COB issues and avoid potential denials.
Medical Necessity Denials
Medical necessity denials occur when the insurer determines that a service or procedure is not medically necessary, based on their coverage guidelines. These denials can result from a lack of documentation, experimental or investigational procedures, non-covered services, or inadequate justification or supporting information.
Lack of Documentation
Lack of documentation is a common reason for medical necessity denials. Insurers require detailed and comprehensive documentation to support the medical necessity of the provided services. Healthcare providers must ensure that all relevant medical records, test results, and clinical notes are accurately and thoroughly documented to prevent these denials.
Experimental or Investigational Procedures
Insurance providers may deny claims for procedures or treatments that they classify as experimental or investigational. These denials occur when the insurer determines that the procedure lacks sufficient evidence of its effectiveness or that other conventional treatments should be explored first. Staying up-to-date with insurance company policies and research on emerging treatments can help avoid these denials.
Non-Covered Services
Non-covered services are those that the insurance policy explicitly excludes from coverage. These denials occur when the services provided are not considered medically necessary or fall outside the scope of coverage. Reviewing and understanding each patient’s insurance plan is essential to avoid providing non-covered services and subsequent denials.
Inadequate Justification or Supporting Information
Insurers require comprehensive justification and supporting information to approve certain procedures or treatments. Inadequate documentation or lack of supporting evidence can result in medical necessity denials. Healthcare providers should ensure that they provide all necessary information, including lab results, test findings, and clinical notes, to support the medical necessity of the services rendered.
Coding Denials
Coding denials can occur due to errors or discrepancies in the coding of services provided. These denials often result from incorrect or inappropriate codes, unbundling of services, upcoding or downcoding, and lack of specificity in coding.
Incorrect or Inappropriate Codes
Using incorrect or inappropriate codes is a common reason for coding denials. Each medical procedure, diagnosis, or service has a specific code that accurately represents it. Applying incorrect codes can lead to denials as they may not align with the documented services. Ensuring proper training for coding personnel and regular audits can help identify and rectify any coding errors.
Unbundling of Services
Unbundling occurs when separate billing codes are used for services that should be billed together as a single procedure. Insurance providers often have guidelines that define which services should be bundled together. Failure to bundle services correctly can result in denials. Implementing automated coding systems and providing proper coding education can help prevent unbundling denials.
Upcoding or Downcoding
Upcoding involves billing for a higher-level service than was actually provided, while downcoding involves billing for a lower-level service. Both practices are fraudulent and can result in coding denials. Ensuring accurate and ethical coding practices, along with regular audits for coding accuracy, can help avoid upcoding or downcoding denials.
Lack of Specificity
Coding denials can occur when codes lack specificity, making it challenging for insurance companies to accurately determine the services provided. The use of generic or unspecified codes can lead to denials or payment delays. Ensuring that specific and detailed codes are used, based on the documented services, can help prevent these denials.

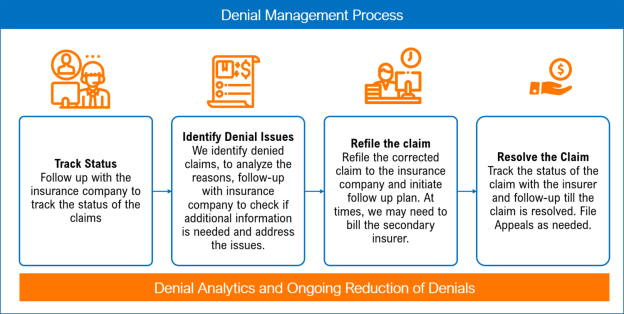
This image is property of www.selecthub.com.
Claim Submission Denials
Claim submission denials occur after the claim has been submitted to the insurance company. These denials typically result from timely filing issues, non-covered services, incorrect patient information, or incomplete or inaccurate claims.
Timely Filing
Each insurance provider has specific time limits within which claims must be submitted. Failure to submit claims within these timeframes can result in timely filing denials. Creating efficient systems and processes to submit claims promptly can help prevent these denials.
Non-Covered Services
Non-covered services can also result in claim submission denials. These denials occur when the services rendered fall outside the scope of coverage defined by the insurance policy. Thoroughly reviewing insurance policies and cross-referencing them with the services provided can help prevent these denials.
Incorrect Patient Information
Incorrect patient information, such as wrong name, policy number, or date of birth, can lead to denials. Insurance companies require accurate patient information to process claims effectively. Implementing verification processes to ensure correct patient information is recorded and cross-checked can help avoid these denials.
Incomplete or Inaccurate Claims
Incomplete or inaccurate claims often result in denials due to the lack of necessary information to process the claim. Missing required fields, incomplete documentation, or errors in the claim form can lead to denials. Implementing thorough quality checks and audits before submission can help prevent these denials.
Payment Denials
payment denials occur when insurance companies refuse to reimburse healthcare providers for services rendered. These denials can occur due to insufficient documentation, contractual obligations, service limitations, or non-par provider issues.
Insufficient Documentation
Insufficient documentation can result in payment denials as insurance companies require thorough records to support the services provided and billed. Incomplete medical records, test results, or missing clinical notes can lead to payment denials. Ensuring comprehensive and accurate documentation can help prevent these denials.
Contractual Obligations
Contractual obligations can cause denials if healthcare providers fail to adhere to the terms of their agreements with insurance companies. These obligations may include specific coding and billing practices, authorization requirements, or participation in preferred provider networks. Understanding and complying with contractual obligations can help prevent payment denials.
Service Limitations
Insurance policies often have limitations on the coverage for certain services or procedures. Exceeding these limitations can result in payment denials. Familiarizing oneself with the coverage limitations within each insurance policy can help avoid billing for services that are not reimbursable.
Non-Par Provider
Being a non-par provider (non-participating provider) may lead to payment denials. Non-par providers have not entered into a contract with the insurance company and may have different reimbursement rates or additional administrative burdens. Verifying participation status and understanding the implications of being a non-par provider can help prevent payment denials.
Coordination of Benefits (COB) Denials
COB denials occur when a patient has multiple insurance policies that cover the same services. These denials often result from duplicate payments, other insurance coverage, incorrect primary payer information, or other COB issues.
Duplicate Payments
Duplicate payments occur when multiple insurance providers both reimburse for the same services, resulting in overpayment. Insurance companies typically coordinate benefits to prevent duplicate payments. However, failure to communicate and coordinate effectively can lead to COB denials. Accurate documentation and close communication with patients can help avoid duplicate payment denials.
Other Insurance Coverage
COB denials can occur when other insurance coverage is present but not disclosed or not known. Failing to identify additional insurance policies can result in incorrect billing and subsequent denials. Ensuring patients provide accurate and updated insurance information can help prevent these denials.
Incorrect Primary Payer Information
Incorrectly identifying the primary payer can lead to COB denials. Each insurance policy has guidelines on which insurance is primary and which is secondary. Failure to identify the correct primary payer can result in claims being denied by the primary insurance provider. Verifying primary payer information and communicating with patients about their insurance coverage can help avoid these denials.
Other COB Issues
Other COB issues that can lead to denials include failure to follow COB rules, lack of coordination between insurance providers, or confusion regarding primary and secondary coverage. Inaccurate coordination between insurance providers can result in denials due to incorrect billing or overlapping coverage. Understanding COB guidelines and establishing effective communication with insurance providers can help address these issues and avoid denials.
Medicare Denials
Medicare denials occur specifically in relation to claims submitted to Medicare, the federal health insurance program for individuals 65 and older. These denials can result from documentation errors, medical necessity issues, insufficient documentation, or inadequate clinical information.
Documentation Errors
Documentation errors are a common reason for Medicare denials. Medicare has specific documentation requirements, and failure to meet these requirements can lead to denials. These errors can include missing or incomplete information, illegible handwriting, or errors in diagnosis coding. Ensuring comprehensive and accurate documentation can help prevent these denials.
Medical Necessity Issues
Medical necessity issues can also result in Medicare denials. Medicare follows strict guidelines to determine the medical necessity of provided services, and failure to meet these guidelines can lead to denials. Similar to other payers, healthcare providers must ensure that they have sufficient documentation to justify the medical necessity of the services rendered.
Insufficient Documentation
Medicare denials can occur if there is insufficient documentation to support the services billed. Healthcare providers must ensure that records are complete, accurate, and thorough. Insufficient documentation can lead to denials due to the inability to determine the medical necessity or appropriateness of the services provided.
Inadequate Clinical Information
Inadequate clinical information can result in Medicare denials. Medicare requires comprehensive clinical information to determine the appropriateness and medical necessity of the services rendered. Failing to provide sufficient clinical information can lead to denials. Healthcare providers should ensure they provide detailed clinical notes, lab results, test findings, and other supporting information required by Medicare.
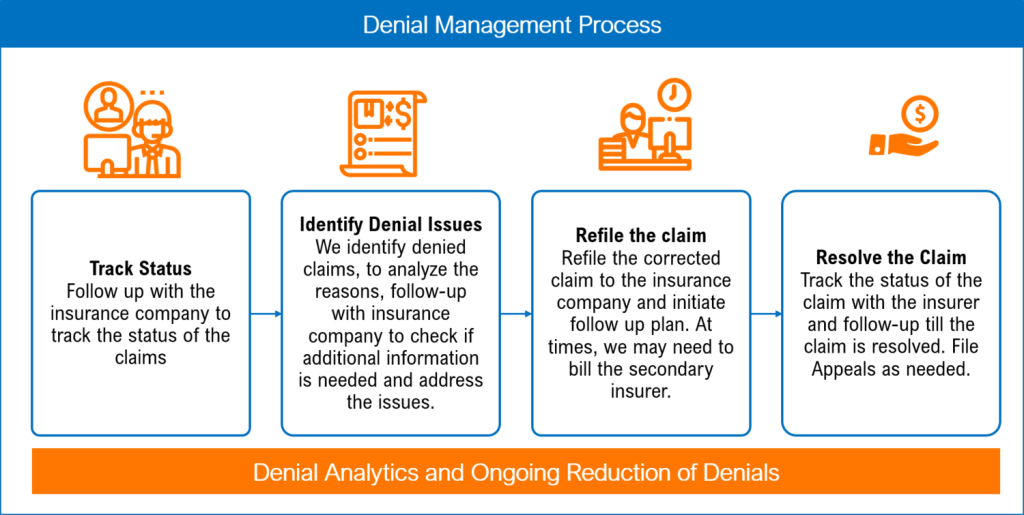
This image is property of images.squarespace-cdn.com.
Medicaid Denials
Medicaid denials occur specifically in relation to claims submitted to Medicaid, the joint federal and state program that provides healthcare coverage for low-income individuals and families. These denials can result from billing errors, lack of medical necessity, eligibility issues, or prior authorization requirements.
Billing Errors
Billing errors can cause Medicaid denials. These errors can include inaccurate coding, incomplete or inaccurate claims, or missing information. Inaccurate billing can lead to denials and delay reimbursement from Medicaid. Implementing thorough quality checks and audits can help prevent billing errors and subsequent denials.
Lack of Medical Necessity
Medicaid follows stringent guidelines to determine medical necessity. Failing to meet these guidelines can result in denials. It is essential to carefully review and understand Medicaid’s medical necessity criteria to ensure that the services billed meet the required standards.
Eligibility Issues
Eligibility issues can also lead to Medicaid denials. Verification of Medicaid eligibility before providing services is crucial to prevent potential denials. Cross-checking Medicaid eligibility records and addressing any issues upfront can save time and resources.
Prior Authorization Requirement
Medicaid may require prior authorization for certain services or procedures. Failure to obtain the necessary prior authorization can result in denials. Understanding which services require prior authorization and following the proper authorization process can help prevent denials and ensure timely reimbursement.
Appeal Denials
Appeal denials occur when a denied claim is challenged through the appeals process. These denials can result from insufficient documentation, missed deadlines, lack of communication, or inadequate justification.
Insufficient Documentation
Insufficient documentation is a common reason for appeal denials. When challenging a denial, it is essential to provide additional documentation that supports the original claim. Submitting comprehensive and relevant documentation can help strengthen the appeal and increase the likelihood of a successful outcome.
Missed Deadlines
Each insurance company has specific deadlines for filing appeals. Failing to meet these deadlines can result in appeal denials. Creating robust systems and processes to track and meet appeal deadlines is essential to maximize the chances of a successful appeal.
Lack of Communication
Lack of communication can lead to appeal denials. It is crucial to engage in open and effective communication with insurance companies throughout the appeals process. Clear and timely communication can help address any concerns, clarify requirements, and avoid denials.
Inadequate Justification
Inadequate justification is another reason for appeal denials. When challenging a denial, it is crucial to provide a strong justification for the claim. Clearly outlining the medical necessity, providing additional evidence, and addressing any concerns raised by the insurance company can strengthen the appeal and increase the chances of a successful outcome.
In conclusion, understanding the different types of denials in medical billing is vital for healthcare providers seeking to optimize their revenue cycle. From front-end denials to appeal denials, each category presents unique challenges and requires specific strategies to mitigate denials. By employing rigorous documentation practices, staying up-to-date with insurance policies, providing accurate coding, verifying patient information, and effectively communicating with insurance providers, healthcare providers can minimize denials and improve their overall financial performance.