In this article, you will learn about the two most common types of medical billing. We will discuss the differences between these two types and how they are used in the healthcare industry. By understanding these types of medical billing, you will have a better understanding of how medical billing works and its importance in healthcare settings. Stay tuned to gain valuable insights into this topic!
Overview of medical billing
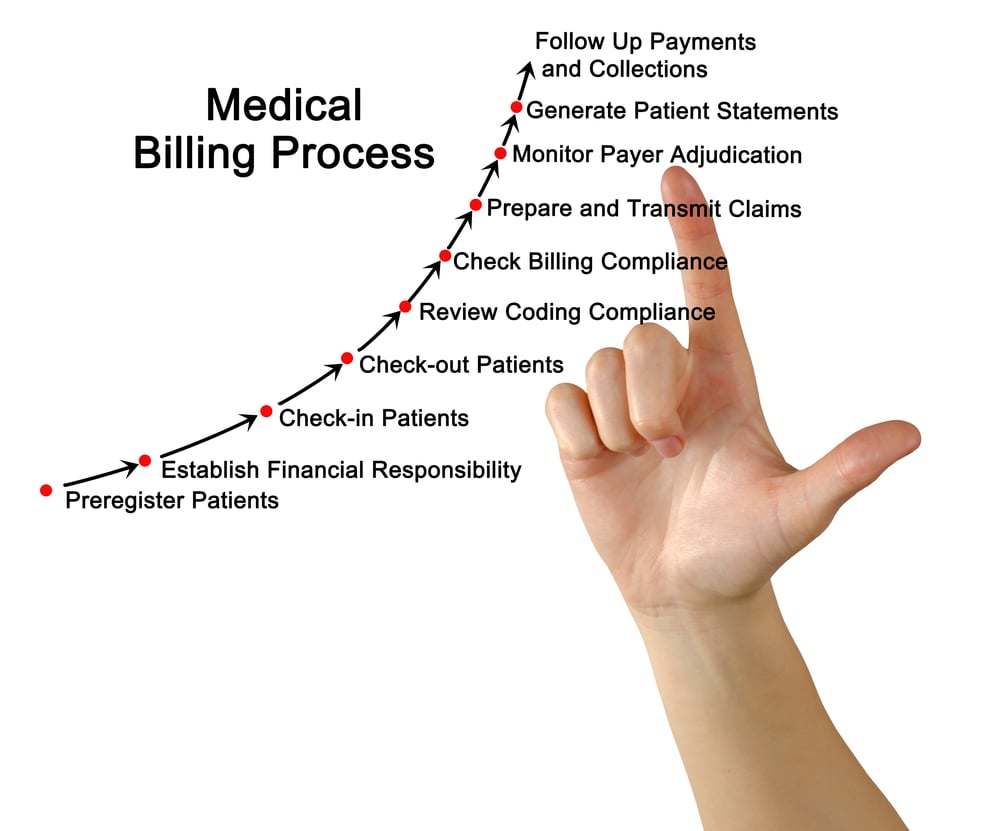
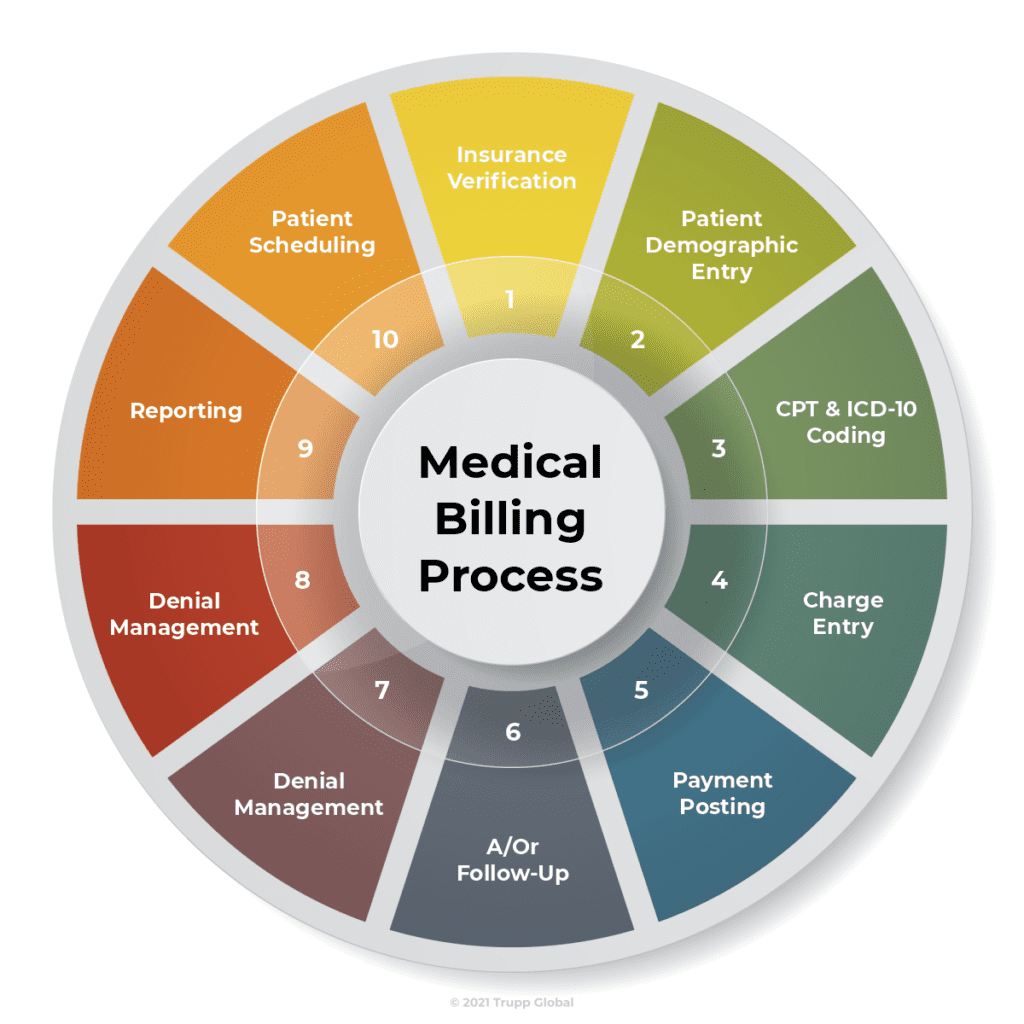
Medical billing is the process of submitting and following up on claims with health insurance companies in order to receive payment for medical services rendered. It involves the coding of diagnoses and procedures, as well as the completion of insurance forms and the coordination of benefits between multiple payers.
Importance of medical billing
Medical billing plays a crucial role in the healthcare industry. It ensures that healthcare providers receive payment for the services they provide, allowing them to continue offering quality care to patients. Additionally, accurate and efficient medical billing helps reduce billing errors and fraud, improves patient billing transparency, and promotes compliance with healthcare policies and regulations.
Role of medical billing in healthcare industry
Medical billing acts as a bridge between healthcare providers, patients, and insurance companies. It facilitates the reimbursement process and ensures that healthcare organizations maintain financial stability. Medical billing professionals work closely with insurance companies to navigate complex coding and reimbursement methods, while also providing patients with transparent billing information and resolving any issues that may arise during the claims process.
Type 1: Professional Medical Billing
Professional medical billing refers to the billing and collections process for services provided by individual healthcare providers, such as physicians, surgeons, and therapists. These services are typically performed in an outpatient setting, such as a private clinic or a physician’s office.
Process of professional medical billing
In professional medical billing, the process begins with patient registration and insurance verification. Once the medical services are provided, the healthcare provider identifies the appropriate codes for diagnoses and procedures based on the patient’s medical record. These codes are then entered into a billing software system, which generates a claim that is submitted electronically to the patient’s insurance company. The insurance company reviews the claim, determines the reimbursement amount, and sends the payment directly to the healthcare provider.
Key features of professional medical billing
Professional medical billing focuses on individual healthcare providers and their services. It requires a deep understanding of medical coding and documentation, as well as proficiency in using billing software systems. This type of billing involves one-on-one interactions with patients, insurance companies, and other healthcare professionals.
Benefits of professional medical billing
Professional medical billing offers several benefits to healthcare providers. It streamlines the billing process, reduces errors and rework, improves cash flow, and enhances reimbursement rates. By outsourcing professional medical billing to experienced billing professionals, healthcare providers can focus on patient care and leave the administrative tasks to the experts.

Type 2: Institutional Medical Billing
Institutional medical billing involves billing and collections for services provided by healthcare organizations, such as hospitals, nursing homes, and rehabilitation centers. These services are typically performed in an inpatient setting, where patients receive more complex and extended care.
Differences between professional and institutional medical billing
While professional and institutional medical billing share some similarities, there are also significant differences between the two. First, institutional medical billing typically involves a higher volume of claims due to the nature of inpatient care. Additionally, the billing process in institutional settings is more complex and involves coordination with various departments and systems within the healthcare organization.
Process of institutional medical billing
Institutional medical billing starts with the patient’s admission to the healthcare facility. During the patient’s stay, healthcare providers document the services provided, including diagnoses, treatments, and medications. Once the patient is discharged, the billing department reviews the medical records and assigns appropriate codes based on the documentation. These codes are then used to generate a claim, which is submitted to the insurance company for reimbursement.
Key features of institutional medical billing
Institutional medical billing requires a comprehensive understanding of healthcare systems, as well as expertise in coding and billing for various inpatient services. It involves collaboration with multiple departments within the healthcare organization, including nursing, pharmacy, and finance. Accuracy and attention to detail are crucial in institutional medical billing to ensure proper reimbursement and compliance with healthcare regulations.
Benefits of institutional medical billing
Institutional medical billing offers several advantages for healthcare organizations. It enables efficient revenue cycle management, improves financial stability, and ensures accurate reimbursement for complex inpatient services. Additionally, institutional medical billing helps healthcare organizations comply with regulatory requirements and optimize their revenue through proper coding and documentation practices.
Comparison of Type 1 and Type 2 Medical Billing

Medical cost concept with stethoscope and medical bill
Differences in focus
Professional medical billing focuses on the services provided by individual healthcare providers, while institutional medical billing involves the comprehensive billing and reimbursement process for healthcare organizations.
Patient care settings
Professional medical billing predominantly occurs in outpatient settings, while institutional medical billing is associated with inpatient care in healthcare facilities.
Coding and reimbursement methods
Professional medical billing often requires simpler coding and reimbursement methods, while institutional medical billing involves more complex coding and reimbursement processes due to the nature of inpatient care.
Complexity and regulation
Institutional medical billing is generally more complex and highly regulated compared to professional medical billing, which is influenced by the type and volume of services provided.
Qualifications and training required
Professional medical billing typically requires basic certifications in medical billing and coding, along with proficiency in using billing software systems. Institutional medical billing often demands more advanced certifications and a deeper understanding of healthcare systems and compliance requirements.
Key Components of Medical Billing
Patient registration and insurance verification
The first step in medical billing is patient registration, which involves collecting demographic information, insurance details, and consent forms. Insurance verification ensures that the patient’s coverage is active and confirms the benefits and limitations of their insurance plan.
Coding and documentation
Accurate coding and documentation are crucial in medical billing. Healthcare providers assign appropriate codes to diagnoses, procedures, and services performed during patient encounters. These codes are used for billing purposes and must align with the patient’s medical record documentation.
Claim submission
After coding and documentation, the billing department generates a claim, typically through a billing software system. The claim contains patient and provider information, as well as the codes and charges associated with the services rendered. It is then submitted electronically to the patient’s insurance company.
Insurance reimbursement
Once the claim is submitted, the insurance company reviews it and determines the reimbursement amount based on the patient’s coverage and the provider’s contracts with the insurer. The reimbursement is then sent to the healthcare provider, either through direct deposit or by mail.
Patient billing and collections
After insurance reimbursement, the healthcare provider may bill the patient for any remaining deductible, co-insurance, or non-covered services. Patient billing and collections involve generating statements, sending them to patients, and following up on any outstanding balances.
Challenges in Medical Billing

Coding errors
Coding errors can lead to claim denials or underpayments, affecting the financial stability of healthcare providers. Accurate and up-to-date knowledge of medical coding guidelines is essential to minimize coding errors.
Denied and rejected claims
Denied and rejected claims can result from various reasons, such as incomplete or incorrect information, missing documentation, or lack of medical necessity. Timely follow-up and appeals are necessary to resolve these issues and ensure proper reimbursement.
Changes in healthcare regulations
The ever-changing landscape of healthcare regulations poses challenges for medical billing. Healthcare organizations need to stay informed and adapt to new regulations to ensure compliance and avoid penalties.
Managing multiple payers
Healthcare providers often deal with multiple insurance companies, each with their own billing requirements and payment processes. Managing these complexities requires expertise and efficient coordination with various payers.
Keeping up with medical coding updates
Medical coding systems and guidelines are regularly updated to reflect changes in medical practices. Medical billers must stay updated with these changes to ensure accurate and compliant coding and documentation.
Latest Developments in Medical Billing

Automation and artificial intelligence
Automation and artificial intelligence are revolutionizing medical billing processes. Intelligent software systems can analyze medical records, code diagnoses and procedures, and generate claims with minimal human intervention, improving efficiency and reducing errors.
Electronic health records integration
Integrating electronic health records (EHRs) with billing systems allows for seamless flow of patient information, reducing duplication, and improving accuracy. EHR integration also enables real-time access to patient data, which enhances claim submission and reimbursement processes.
Real-time claim tracking
Real-time claim tracking enables healthcare providers to monitor the status of their claims, from submission to payment. This transparency helps identify and resolve any issues in a timely manner, minimizing delays in reimbursement.
Predictive analytics in reimbursement
Predictive analytics uses historical data to forecast reimbursement patterns, identify payment trends, and optimize revenue cycle management. By leveraging data analytics, healthcare providers can proactively address potential issues and improve financial performance.
Patient portals and online payment
Patient portals provide patients with access to their billing information, including statements, payment history, and online payment options. This enhances patient satisfaction and promotes a streamlined billing experience.
Impact of Medical Billing on Healthcare

Financial stability of healthcare organizations
Accurate and efficient medical billing is essential for the financial stability of healthcare organizations. Proper reimbursement ensures that healthcare providers can continue to offer quality care to patients and invest in necessary resources and infrastructure.
Patient satisfaction and access to care
Transparent and patient-friendly billing processes contribute to higher patient satisfaction. When patients understand their bills and have convenient payment options, it improves their overall healthcare experience.
Efficiency in reimbursement process
Efficient medical billing processes reduce administrative burden for healthcare providers. Streamlining the reimbursement process allows healthcare organizations to focus on providing patient care instead of dealing with complex billing tasks.
Reducing billing errors and fraud
Accurate coding, documentation, and proper checks and balances in medical billing help reduce billing errors and prevent fraudulent activities. This safeguards the financial integrity of healthcare organizations and maintains trust among all stakeholders.
Compliance with healthcare policies
Medical billing ensures compliance with healthcare policies and regulations. By adhering to guidelines set by insurance companies and government agencies, healthcare organizations can avoid penalties and maintain their reputation.
Future Trends in Medical Billing

Transition to value-based billing
As healthcare evolves, there is a growing emphasis on value-based care, which focuses on quality outcomes rather than quantity of services rendered. Medical billing will shift towards incentivizing and rewarding healthcare providers based on patient outcomes and overall value.
Interoperability and standardized coding
Interoperability between different healthcare software systems and the adoption of standardized coding sets, such as the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) and Current Procedural Terminology (CPT), will streamline the billing process and improve data exchange across healthcare entities.
Telemedicine and remote billing
With the rising popularity of telemedicine, medical billing will need to adapt to remote service delivery models. Billing processes for virtual consultations and remote monitoring will become more prevalent and require specialized coding and documentation practices.
Data analytics for revenue optimization
Medical billing will increasingly leverage data analytics to optimize revenue cycle management. Advanced analytics tools will identify patterns, trends, and opportunities for improving billing processes, minimizing denials, and maximizing reimbursement.
Improved patient billing transparency
Enhanced patient billing transparency through clear and understandable statements, real-time access to billing information, and transparent pricing models will continue to improve the patient billing experience and empower patients to make informed decisions about their healthcare.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the two most common types of medical billing are professional medical billing and institutional medical billing. Professional medical billing focuses on individual healthcare providers and their services, while institutional medical billing involves billing and collections for healthcare organizations. Both types of billing play crucial roles in the healthcare industry, ensuring financial stability, promoting compliance with healthcare policies, and improving patient satisfaction. As advancements in technology and healthcare policies continue to shape the field, accurate and efficient medical billing will remain essential for healthcare organizations and the overall delivery of quality care to patients.