In this article, you will learn all about medical coding and its importance in the healthcare field. We will explore what medical coding is, the different types of codes used, and how it impacts the billing and reimbursement process. By the end, you will have a better understanding of the fundamentals of medical coding and its role in accurately documenting patient care and ensuring accurate payments.
Overview of Medical Coding

Definition of Medical Coding
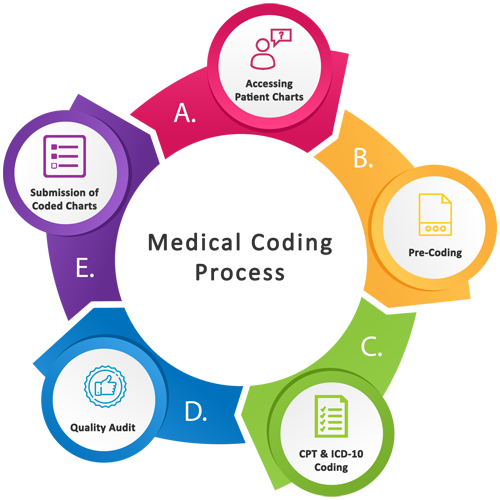
Medical coding is the process of translating medical diagnoses, procedures, and services into alphanumeric codes. These codes are used for documentation, insurance reimbursement, and statistical purposes. By assigning specific codes to various medical procedures and services, medical coders play a crucial role in ensuring accurate and efficient healthcare recordkeeping.
Importance of Medical Coding
Medical coding is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it helps healthcare professionals maintain accurate patient records, which are crucial for patient care coordination and information sharing among providers. Additionally, medical coding ensures proper reimbursement from insurance companies by accurately documenting the services provided. Moreover, coded data is utilized for healthcare analytics, research, and quality improvement initiatives.
Role of Medical Coders
Medical coders are responsible for reviewing medical documentation and assigning appropriate codes based on established guidelines and classification systems. Their role is pivotal in accurately documenting patient encounters, procedures, and diagnoses in a standardized format. Medical coders work closely with healthcare providers and insurance companies to ensure accurate coding and efficient reimbursement processes. They must stay updated with changes in coding guidelines and regulations to ensure compliance.
Education and Training for Medical Coders

Types of Education Programs for Medical Coders
There are several education paths to become a medical coder. Some individuals opt for certificate programs, which can typically be completed in less than a year. These programs focus on teaching the fundamentals of medical coding and provide a basic understanding of coding classifications and guidelines.
Another option is pursuing an associate’s degree in health information technology or a related field. This provides a more comprehensive education, covering not only medical coding but also other aspects of health information management.
Certification Requirements for Medical Coders
Certification is not mandatory for medical coders, but it is highly recommended as it demonstrates competency in the field. The most recognized certifications for medical coders are offered by the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC) and the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA).
To become certified, individuals must pass a certification exam that assesses their knowledge of coding guidelines and systems. These exams typically require a certain level of coding experience or completion of an approved coding education program.
Continuing Education for Medical Coders
Medical coding is a constantly evolving field, with frequent updates to coding guidelines and systems. Medical coders are expected to engage in continuing education to stay updated with these changes. This can be achieved through attending conferences, participating in webinars, or taking online courses specifically designed for medical coders. Continuing education is crucial to maintain coding accuracy and ensure compliance with ever-changing regulations.
Medical Coding Systems
ICD-10-CM Coding System
The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) coding system is used to classify and code diagnoses and symptoms. This system provides a standardized way of recording patient conditions and diseases, enabling accurate data analysis and research. ICD-10-CM codes consist of alphanumeric characters and allow for detailed description and specificity of medical conditions.
CPT Coding System
The Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) coding system is used to document medical procedures and services provided by healthcare professionals. This system ensures uniformity and consistency in coding both routine and specialized procedures. CPT codes are numeric and are widely used for billing purposes.
HCPCS Coding System
The Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) is used primarily for coding medical supplies, durable medical equipment, and outpatient services. It consists of two levels: Level I consists of CPT codes, while Level II codes are alphanumeric and provide further specificity for certain services and supplies.
Medical Coding Guidelines

Accuracy and Compliance in Medical Coding
Accuracy in medical coding is of utmost importance. Incorrect codes can lead to issues such as denied insurance claims, improper reimbursement, and potential audits. Coding must also be done in compliance with established guidelines and standards to ensure consistency and validity of medical records.
Documentation and Coding Guidelines
Medical coders must rely on accurate and detailed documentation from healthcare providers to assign appropriate codes. Proper documentation ensures that all relevant information is captured and coded accurately. Coding guidelines provide instructions on how to interpret and apply codes based on specific situations and conditions.
Modifiers in Medical Coding
Modifiers are used to provide additional information and clarification to the coded data. They can indicate changes in procedure circumstances, the use of multiple procedures, or exceptions to standard coding rules. Medical coders must understand the appropriate use of modifiers to accurately represent the services provided.
Common Medical Coding Errors

Incorrect Code Selection
One common error in medical coding is the selection of incorrect codes. This can occur due to lack of understanding of coding guidelines, inadequate documentation, or simply human error. Incorrect code selection can result in underpayment or overpayment, impacting both healthcare providers and patients.
Upcoding and Downcoding
Upcoding refers to the practice of assigning a higher-level code than justified by the services provided. This can be done intentionally to increase reimbursement or unintentionally due to coding errors. Downcoding, on the other hand, involves assigning a lower-level code than appropriate. Both upcoding and downcoding can have financial and legal implications.
Incomplete Documentation
Incomplete documentation can lead to inaccurate coding and billing. Missing details or insufficient information can result in codes that do not accurately reflect the services provided. It is crucial for healthcare providers to ensure thorough and complete documentation to support accurate coding.
Medical Coding in Healthcare Settings

Hospital Coding
In hospital settings, medical coding plays a critical role in billing, reimbursement, and statistical reporting. Hospital coders review medical records to assign appropriate codes for diagnoses, procedures, and services provided. Hospital coding may involve more complex cases compared to other healthcare settings, and coders must have a deep understanding of coding systems and guidelines.
Physician Office Coding
Physician office coding primarily focuses on coding outpatient services and plays a crucial role in ensuring accurate reimbursement. Coders in physician offices review documentation from office visits, procedures, and diagnostic tests to assign appropriate codes. They must be knowledgeable about coding guidelines specific to office services and have a good understanding of medical terminology.
Outpatient Facility Coding
Outpatient facilities, such as ambulatory surgery centers or diagnostic imaging centers, also require medical coding. Coders in these settings assign codes for procedures and services performed in the outpatient setting. Outpatient facility coding may have specific coding guidelines and requirements that differ from hospital or physician office coding.
Career Opportunities in Medical Coding

Medical Coding Specialist
Medical coding specialists work directly with healthcare providers and insurance companies to ensure accurate documentation and coding. They review medical records, assign codes, and respond to coding-related inquiries. Medical coding specialists may also analyze coded data for reimbursement and quality improvement purposes.
Medical Coding Auditor
Medical coding auditors play a crucial role in maintaining coding accuracy and compliance. They review coded data to identify errors, inconsistencies, and areas for improvement. Medical coding auditors ensure that coding guidelines and regulations are followed and provide feedback and training to coders to enhance their skills.
Medical Coding Trainer
Medical coding trainers are responsible for educating and training individuals aspiring to become medical coders. They develop and deliver coding courses and materials, stay updated with coding changes, and provide guidance and support to students. Medical coding trainers play a vital role in preparing future coders for the challenges of the profession.
Challenges in Medical Coding

Complexity of Coding Rules
Coding rules can be complex and require a deep understanding of medical terminology, anatomy, and coding guidelines. Keeping up with changes in coding rules and systems can pose a challenge, especially for those new to the field. Continuous education and staying updated with coding resources are essential to overcome these challenges.
Integration of New Coding Systems
As healthcare evolves, new coding systems are introduced to accommodate technological advancements and changes in healthcare practices. Integrating new coding systems and guidelines can be challenging for healthcare organizations, requiring training and adaptation from coders and providers alike.
Data Privacy and Security
Medical coders have access to sensitive patient information, making data privacy and security a significant concern. It is crucial for coders to adhere to HIPAA regulations and maintain strict confidentiality to protect patient data. Healthcare organizations must implement robust security measures to safeguard patient information from unauthorized access.
Advancements in Medical Coding Technology

Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
Electronic health records (EHRs) have revolutionized medical coding by providing a centralized digital platform for documentation, coding, and information sharing. EHRs streamline the coding process, improve accuracy, and facilitate collaboration among healthcare providers. They also enable seamless integration with coding systems and automated coding tools.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Coding
Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to transform medical coding by automating certain coding tasks and enhancing accuracy. Machine learning algorithms can analyze medical documentation and suggest appropriate codes based on patterns and past records. AI coding systems can help reduce coding errors, increase efficiency, and free up valuable time for medical coders.
Automated Coding Tools
Automated coding tools leverage AI and natural language processing to assist coders in assigning codes accurately and efficiently. These tools analyze medical records, extract relevant information, and suggest appropriate codes. Automated coding tools can significantly reduce the time and effort required for manual coding, allowing coders to focus on complex or nuanced cases.
Conclusion
Medical coding is a critical component of healthcare recordkeeping, reimbursement, and analytics. It involves assigning codes to diagnoses, procedures, and services to ensure accurate documentation, billing, and data analysis. Medical coders play a vital role in maintaining coding accuracy and compliance, and their expertise is valued in various healthcare settings.
To become a medical coder, individuals can pursue education programs, obtain certifications, and engage in continuing education. Familiarity with coding systems such as ICD-10-CM, CPT, and HCPCS is essential, as is adherence to coding guidelines and regulations.
While medical coding can be challenging, advancements in technology, such as EHRs, AI, and automated coding tools, are revolutionizing the field and making coding processes more efficient and accurate. As healthcare continues to evolve, the role of medical coders will remain crucial in ensuring accurate documentation, efficient reimbursement, and meaningful data analysis for effective patient care.