If you are considering a career in medical billing and coding, you may be wondering how long it will take to acquire the necessary skills and knowledge. The learning process for medical billing and coding can vary depending on several factors, such as prior experience, the learning method chosen, and individual dedication. In this article, we will explore the different avenues available for learning medical billing and coding and provide insights into the time it may take to become proficient in this field. By understanding the various aspects involved in the learning process, you can make an informed decision about embarking on your journey into the world of medical billing and coding.
Factors Affecting the Time Required
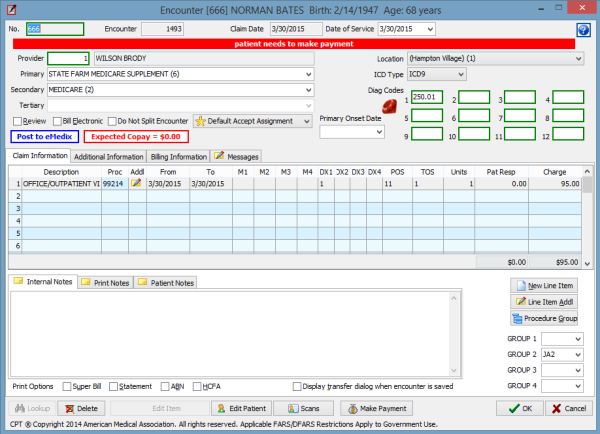
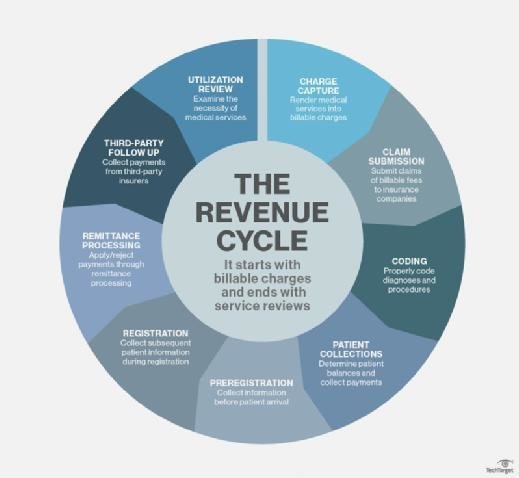
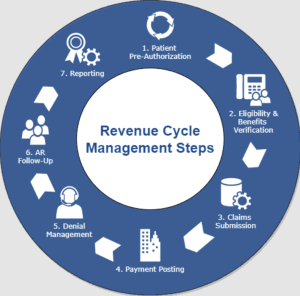
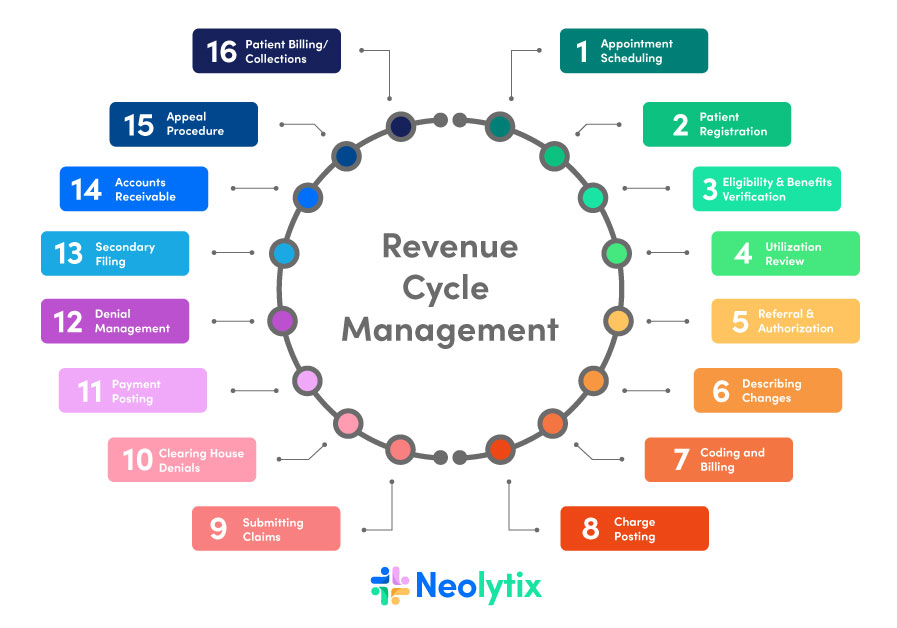
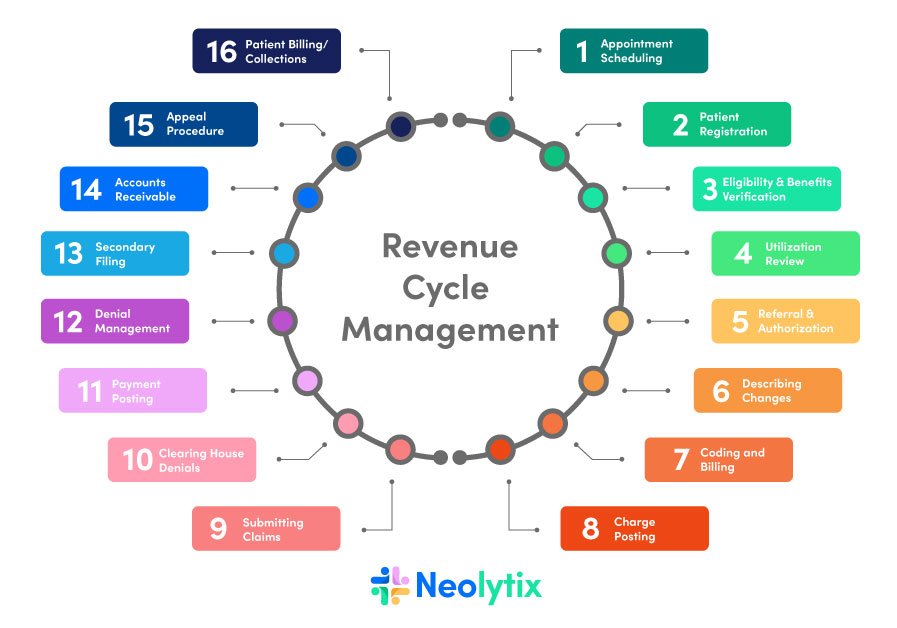
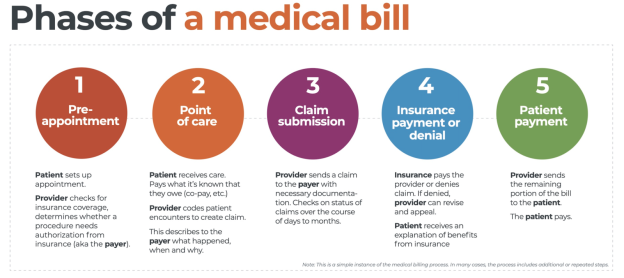
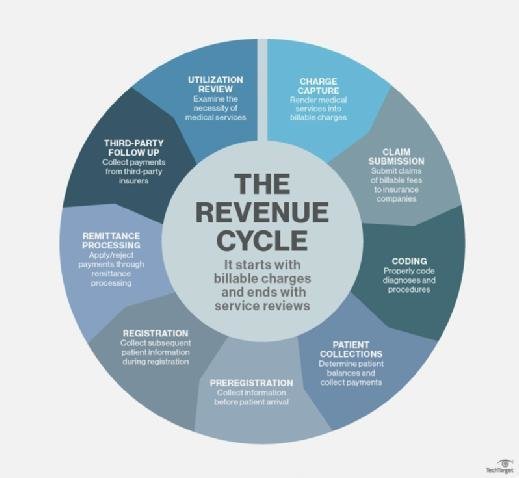
This image is property of medsitnexus.com.
Prior Knowledge and Experience
The amount of time required to learn medical billing and coding can vary significantly based on prior knowledge and experience in the field. If you have a background in healthcare or have taken related courses, you may have a head start in understanding medical terminology and concepts, which can expedite the learning process. On the other hand, if you have no prior experience in the healthcare industry, it may take longer to grasp the fundamentals of medical billing and coding.
Educational Program Duration
The duration of the educational program you choose will also play a significant role in determining how long it takes to learn medical billing and coding. Certificate programs can typically be completed in a shorter duration compared to associate or bachelor’s degree programs. The length of the program can range from a few months to a year or more, depending on the intensity and structure of the curriculum.
Learning Style and Study Habits
Your preferred learning style and study habits can impact the time required to learn medical billing and coding. Some individuals may learn more efficiently in a traditional classroom setting, where they receive face-to-face instruction and have the opportunity to engage in discussions with instructors and peers. On the other hand, others may prefer online learning, which offers the flexibility to study at their own pace and convenience. Understanding your learning style and employing effective study habits can help you optimize your learning experience and potentially reduce the time needed to master the skills.
Classroom vs. Online Learning
The choice between classroom and online learning can also influence the time required to learn medical billing and coding. Classroom learning provides structured and guided instruction, allowing for immediate clarification of doubts and active participation in discussions. Online learning, on the other hand, offers flexibility, enabling individuals to balance their studies with other commitments. While both options have their advantages, it is essential to consider your personal preferences and learning style to choose the most suitable mode of learning.
Program Accreditation
The accreditation of the medical billing and coding program you choose can impact the time required to complete the program. Accredited programs adhere to certain standards of quality and comprehensiveness, ensuring that students receive a well-rounded education. Accreditation may also be a requirement for certain job opportunities or further certification. Opting for an accredited program can provide you with the necessary knowledge and skills to succeed in the field and potentially expedite the learning process.
Personal Commitment and Dedication
Perhaps the most crucial factor affecting the time required to learn medical billing and coding is personal commitment and dedication. Your level of motivation, perseverance, and willingness to put in the effort will significantly impact how quickly you can grasp the concepts and apply them effectively. Consistent practice, setting aside dedicated study time, and actively engaging in the learning process can significantly reduce the time needed to become proficient in medical billing and coding.
Types of Medical Billing and Coding Programs

Certificate Programs
Certificate programs in medical billing and coding provide a focused and accelerated path to gain the necessary skills for entry-level positions in the field. These programs typically have a shorter duration compared to degree programs and focus on specific competencies related to medical billing and coding. Certificate programs may be ideal for individuals who are looking to enter the workforce quickly or those who already have some experience or education in healthcare but want to specialize in medical billing and coding.
Associate Degree Programs
Associate degree programs in medical billing and coding offer a more comprehensive education, covering a broader range of topics related to healthcare administration and coding. These programs usually take two years to complete and include general education courses alongside specialized coursework in medical billing and coding. An associate degree can provide a more well-rounded education and may open up additional career opportunities beyond entry-level positions.
Bachelor’s Degree Programs
Bachelor’s degree programs in medical billing and coding provide a more in-depth and extensive education, encompassing a broader range of subjects related to healthcare administration, healthcare informatics, and medical coding. These programs typically take four years to complete and may include courses in leadership, research, and advanced coding practices. A bachelor’s degree can offer greater job prospects, potential for career advancement, and the opportunity to pursue leadership roles within the healthcare industry.
Certificate Programs
Certificate programs in medical billing and coding offer a streamlined path to entry-level positions in the healthcare industry. Here is an overview of the typical duration, curriculum, prerequisites, and career opportunities associated with these programs:
Duration and Curriculum
Certificate programs in medical billing and coding can typically be completed within nine months to one year. The duration may vary based on the institution and the intensity of the program. These programs focus on essential skills and knowledge required for medical billing and coding, such as medical terminology, ICD-10 coding, CPT coding, and healthcare reimbursement. The curriculum is often tailored to provide practical, hands-on experience to ensure graduates are job-ready.
Prerequisites
Certificate programs in medical billing and coding generally have minimal prerequisites. However, some institutions may require a high school diploma or equivalent. It is essential to review the specific requirements of the program you are interested in to ensure you meet the eligibility criteria.
Career Opportunities
Upon completion of a certificate program in medical billing and coding, graduates can pursue various entry-level positions in healthcare settings such as hospitals, physician offices, clinics, and insurance companies. Some common job titles include medical billing specialist, medical coder, coding specialist, reimbursement specialist, or healthcare administrative assistant. Graduates may also have the opportunity to work from home or seek employment in specialized coding departments.
Associate Degree Programs

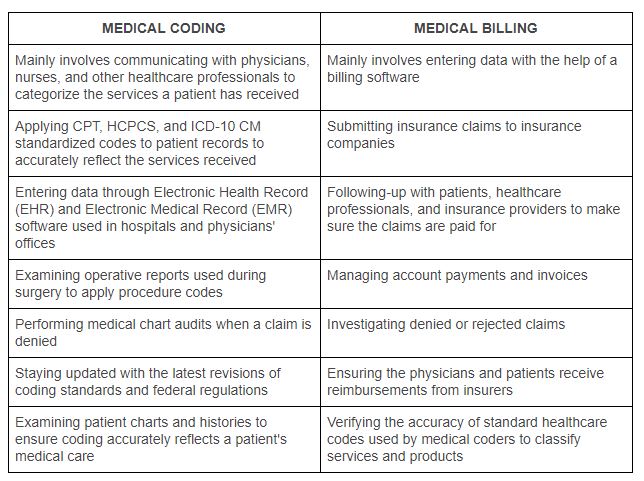
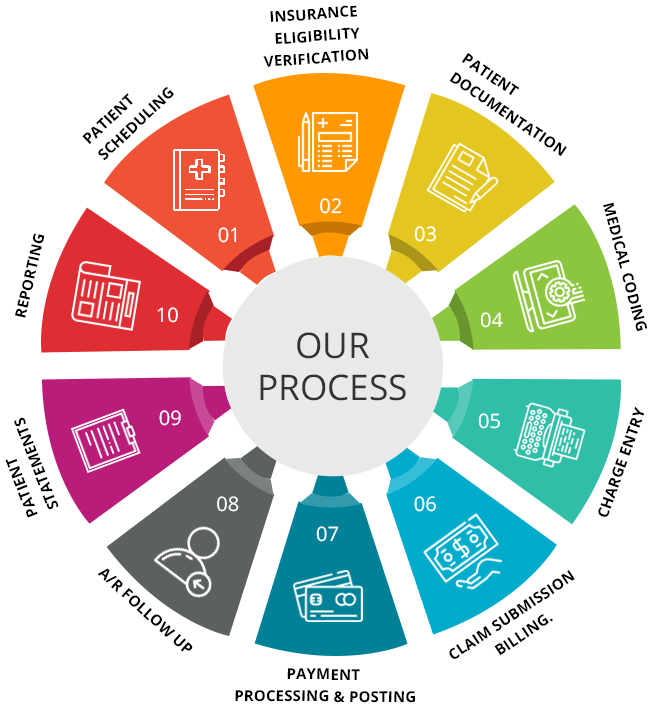
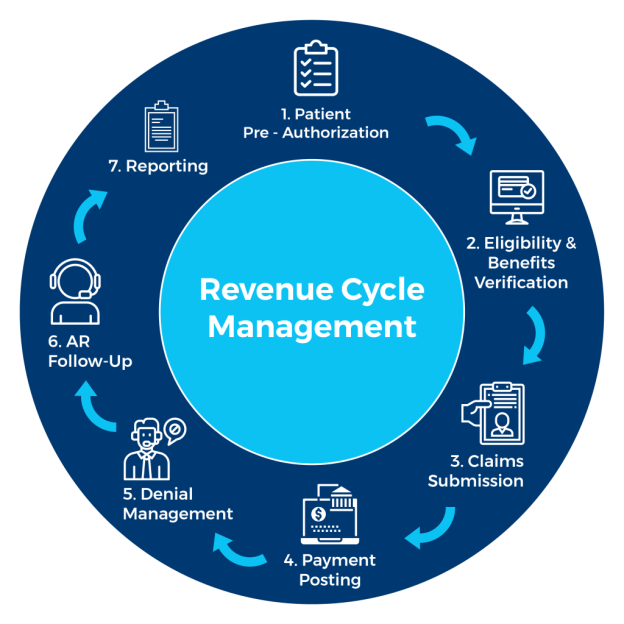
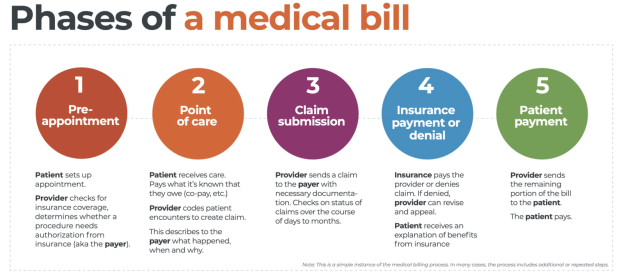
This image is property of greensensebilling.com.
Duration and Curriculum
Associate degree programs in medical billing and coding typically take two years to complete. These programs offer a comprehensive curriculum that includes general education courses alongside specialized coursework in medical billing and coding. In addition to medical terminology, coding practices, and reimbursement, students may study subjects such as anatomy and physiology, healthcare ethics, data management, and healthcare information systems.
Prerequisites
Associate degree programs in medical billing and coding generally require a high school diploma or equivalent. Some programs may also require students to complete prerequisite courses in subjects such as English, math, and medical terminology. It is essential to review the specific prerequisites of the program you are interested in and ensure you meet the requirements before applying.
Career Opportunities
An associate degree in medical billing and coding can open up a range of career opportunities. Graduates may work in various healthcare settings, including hospitals, physician offices, nursing homes, outpatient clinics, insurance companies, and coding consulting firms. Job titles may include medical coding specialist, billing coordinator, compliance auditor, coding supervisor, or medical records manager. With additional experience, graduates may also have the opportunity to advance into healthcare management or consulting roles.
Bachelor’s Degree Programs
Bachelor’s degree programs in medical billing and coding offer a more comprehensive and advanced education in the field, preparing students for a wide range of healthcare administration and coding roles. Here’s an overview of the typical duration, curriculum, prerequisites, and career opportunities associated with these programs:
Duration and Curriculum
Bachelor’s degree programs in medical billing and coding typically take four years to complete. These programs offer a comprehensive curriculum that combines healthcare administration, medical coding, healthcare informatics, and advanced coding practices. In addition to topics covered in associate degree programs, students may study subjects such as healthcare leadership, research methods, healthcare policy, and advanced healthcare information systems.
Prerequisites
Bachelor’s degree programs in medical billing and coding generally require a high school diploma or equivalent. Some programs may have additional prerequisites, such as completion of prerequisite courses in medical terminology, anatomy and physiology, or statistics. Reviewing the specific prerequisites of the program you are interested in and ensuring you meet the requirements is essential before applying.
Career Opportunities
A bachelor’s degree in medical billing and coding can provide graduates with a competitive edge in the job market and open up diverse career opportunities. Graduates may pursue roles in healthcare administration, coding management, healthcare consulting, healthcare policy, or healthcare informatics. Job titles may include coding manager, compliance officer, healthcare consultant, health information manager, or healthcare administrator.
Additional Considerations in Learning Medical Billing and Coding
Indeed, understanding medical terminology, gaining practical experience, and considering certification and continuing education are crucial aspects of excelling in the field of medical billing and coding. Here’s a closer look at each of these additional considerations:
Understanding Medical Terminology
A crucial aspect of medical billing and coding is having a strong understanding of medical terminology. This knowledge allows coding professionals to accurately translate medical diagnoses, procedures, and treatments into the appropriate codes for reimbursement purposes. It is essential to invest time in learning and memorizing medical terms to ensure accurate and efficient coding.
Gaining Practical Experience
While theoretical knowledge is crucial, gaining practical experience is equally important in the field of medical billing and coding. Many programs offer opportunities for internships or externships, allowing students to apply their knowledge in a real-world setting. Actively seeking out practical experience through internships or volunteer positions can help strengthen skills and increase job prospects upon graduation.
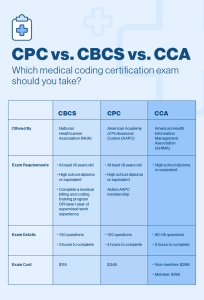
Certification and Continuing Education
Obtaining professional certifications can demonstrate your competency and dedication to the field of medical billing and coding. Organizations such as the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC) and the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA) offer certifications that validate proficiency in medical coding and billing. Continuing education through workshops, seminars, and online courses can also help stay updated with the latest industry trends, regulations, and coding practices.
Recommended Steps to Learn Medical Billing and Coding

Research and Evaluate Educational Programs
Begin by researching and evaluating different educational programs in medical billing and coding. Consider factors such as program duration, curriculum, accreditation, and delivery format (online or classroom-based). Compare programs based on your personal goals, preferences, and available resources.
Determine Program Duration and Format
Consider your time availability and commitments when choosing a program duration. Decide whether a shorter certificate program or a more comprehensive degree program aligns better with your career goals. Additionally, determine whether you prefer the structure of a traditional classroom setting or the flexibility of online learning.
Meet Prerequisites and Enroll in a Program
Ensure that you meet the prerequisites for the educational program you wish to pursue. Complete any necessary prerequisite courses or requirements before enrolling. Once you fulfill the prerequisites, submit your application and enroll in the chosen program.
Create a Study Plan and Schedule
To effectively learn medical billing and coding, create a study plan and schedule that allows for consistent and dedicated study time. Break down the curriculum into manageable chunks and allocate specific time slots for learning and practice. This structured approach can help you stay organized and focused throughout the program.
Develop Strong Study Habits
Developing strong study habits is crucial for efficient learning. Adopt strategies such as active reading, note-taking, and regular review of material. Engage in practice exercises and quizzes to reinforce learning. Utilize available resources, such as textbooks, online tutorials, and study guides, to supplement your understanding of the material.
Attend Classes and Participate Actively
If you are enrolled in a classroom-based program, attend classes regularly and actively participate in discussions and activities. Take advantage of the opportunity to interact with instructors and fellow students. Engage in group projects and practical assignments to gain hands-on experience.
Seek Hands-On Experience
While academic coursework provides a foundation, seek hands-on experience to further enhance your skills. Look for opportunities to shadow professionals in the field, participate in internships, or volunteer in healthcare settings. Practical experience can help apply theoretical knowledge, develop confidence, and gain exposure to different aspects of the industry.
Prepare for Certification Exams
If you plan to pursue professional certifications, prepare for the relevant exams. Utilize study materials provided by certification organizations and consider joining study groups or online forums to exchange knowledge and resources. Practice sample questions and take mock exams to assess your readiness.
Secure Employment or Internship Opportunities
Upon completing your educational program and obtaining any desired certifications, begin searching for employment or internship opportunities. Network with professionals in the field, attend job fairs, and leverage online job search platforms. Tailor your resume and cover letter to highlight relevant coursework, certifications, and practical experience.
Length of Time to Complete Medical Billing and Coding Programs

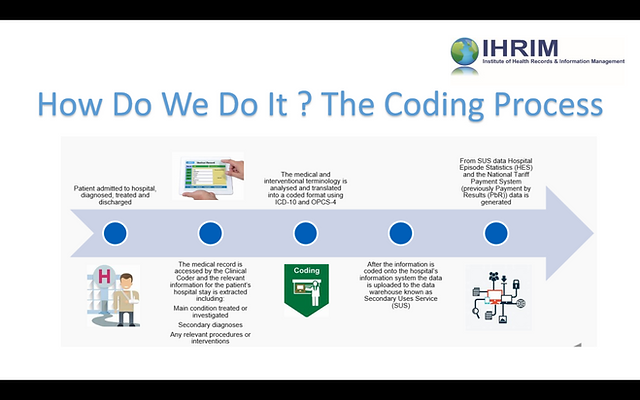
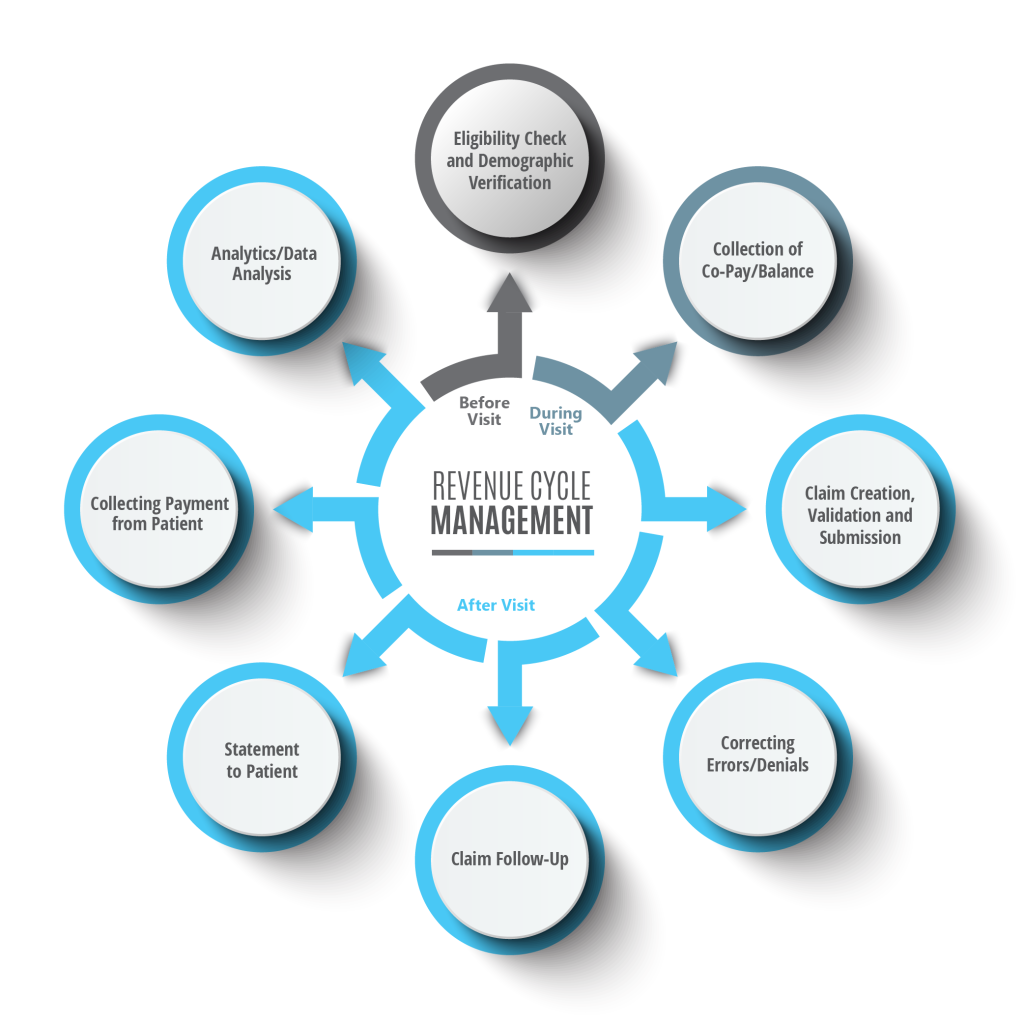
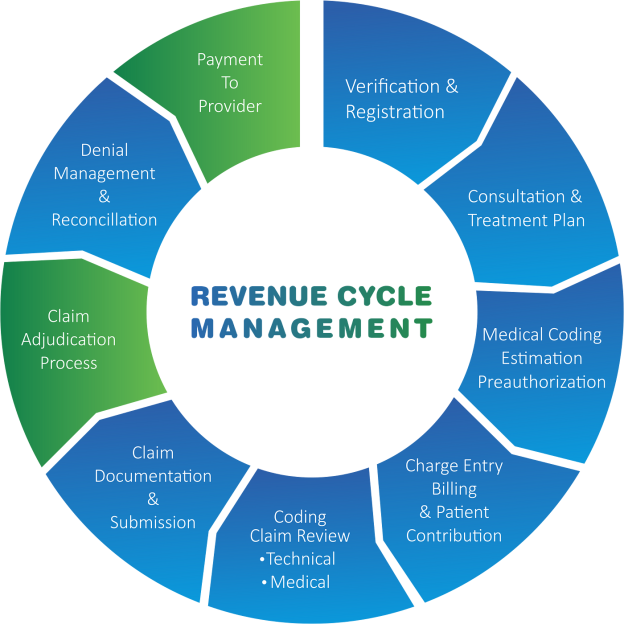
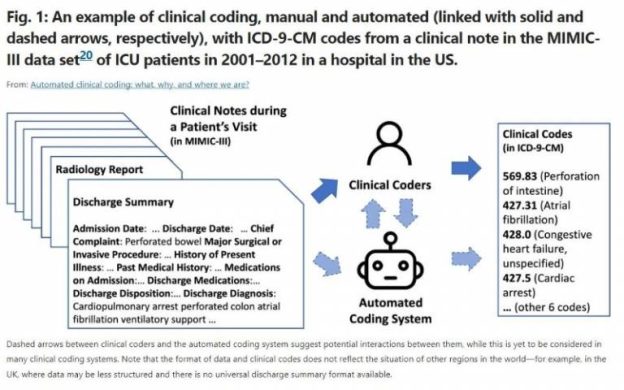
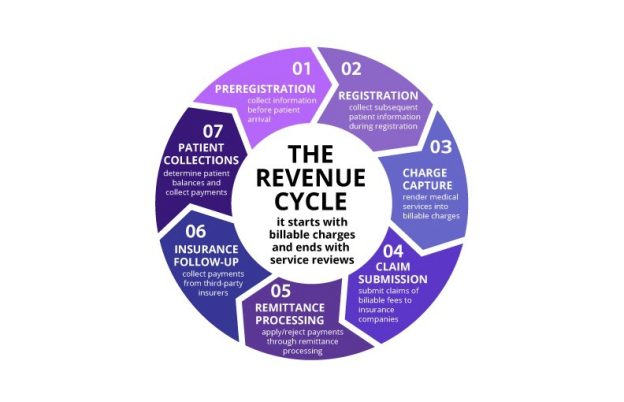
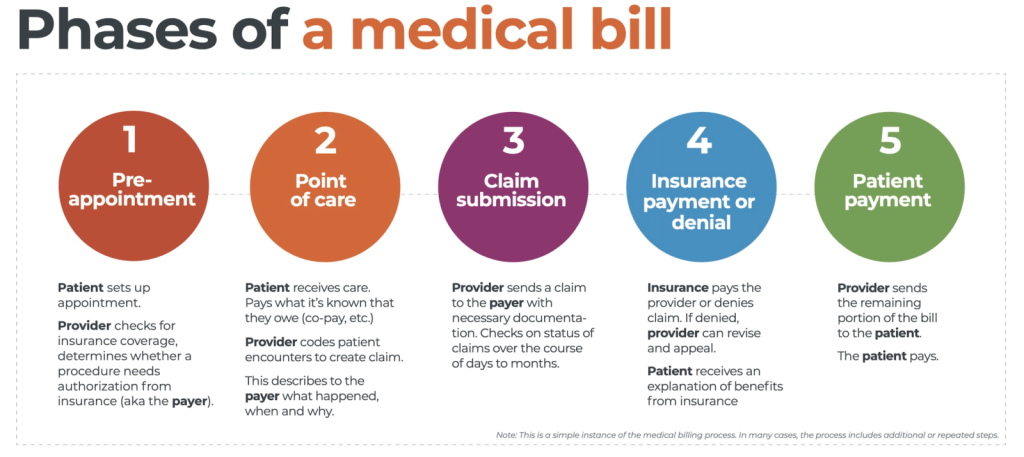
This image is property of image.isu.pub.
Certificate Program: 9 months to 1 year
The duration of a certificate program in medical billing and coding can vary between 9 months to 1 year, depending on the program and the intensity of the curriculum. Certificate programs often provide a concentrated and specialized education to quickly prepare individuals for entry-level positions in the field.
Associate Degree Program: 2 years
Associate degree programs in medical billing and coding typically take 2 years to complete. These programs offer a more comprehensive education, combining general education courses with specialized coursework. An associate degree can provide a broader understanding of healthcare administration and coding practices, opening up additional career opportunities beyond entry-level positions.
Bachelor’s Degree Program: 4 years
Bachelor’s degree programs in medical billing and coding generally take 4 years to complete. These programs offer a comprehensive education, covering a wide range of subjects related to healthcare administration, medical coding, and healthcare informatics. A bachelor’s degree can provide a more in-depth understanding of the field and potential for career advancement and leadership roles within the industry.
Factors Influencing Program Duration
Program duration in medical billing and coding can vary based on several factors, and individuals often have choices that influence the length of their educational journey. Here are some key factors that can impact the duration of a medical billing and coding program:
Part-Time vs. Full-Time Enrollment
The choice between part-time and full-time enrollment can significantly influence the duration of a medical billing and coding program. Full-time enrollment allows students to complete the program more quickly, as they are taking a higher course load each semester. Part-time enrollment, on the other hand, spreads out the coursework over a more extended period, accommodating individuals who have other commitments or responsibilities.
Online Programs vs. Traditional Classroom Programs
The format of the program, whether online or traditional classroom-based, can also impact the program duration. Online programs often offer more flexibility in terms of scheduling and pace of learning, allowing individuals to complete the program at their own pace. Traditional classroom programs follow a structured timetable and may have fewer scheduling flexibilities, potentially extending the program duration due to course availability and sequencing.
External Commitments and Responsibilities
Individuals with external commitments and responsibilities, such as work, family, or other educational pursuits, may require more time to complete a medical billing and coding program. Balancing these commitments alongside academic coursework can influence the program duration. It is important to consider the time and energy you can realistically allocate to your studies when planning for the program duration.
Importance of Personal Commitment and Dedication
In the realm of learning medical billing and coding, personal commitment and dedication serve as the bedrock for success. The journey to mastering this intricate field demands consistency, effective time management, and a willingness to seek support and mentorship. In this discussion, we’ll delve into the significance of these factors and how they contribute to a fruitful learning experience and a promising career in medical billing and coding. From regular practice to astute time management and the value of support networks, these elements are pivotal in shaping your path to proficiency in this vital healthcare disciplin
Consistency and Regular Practice
Consistency and regular practice are key factors in successfully learning medical billing and coding. Set aside dedicated study time each week and adhere to a consistent schedule. Regularly reviewing and practicing coding techniques, rules, and guidelines can help reinforce your understanding and retention of the material.
Time Management Skills
Developing effective time management skills is crucial to optimize the learning process. Prioritize your academic commitments and create a schedule that allows you to balance your studies with other responsibilities. Avoid procrastination and aim to complete assignments and readings well ahead of deadlines to minimize stress and ensure thorough comprehension.
Seeking Support and Mentorship
Seeking support from peers, instructors, or mentors can be invaluable when learning medical billing and coding. Engage in discussions, ask questions, and participate in study groups or forums to exchange knowledge and learn from others. Connecting with experienced professionals in the field can provide insights, guidance, and motivation throughout your learning journey.
In conclusion, the time required to learn medical billing and coding can vary based on several factors, including prior knowledge and experience, program duration, learning style, and personal dedication. Certificate programs typically offer a shorter duration, focusing on essential skills, while associate and bachelor’s degree programs provide a more comprehensive education. Understanding medical terminology, gaining practical experience, and pursuing professional certifications are additional considerations to enhance proficiency in the field. By following recommended steps, developing strong study habits, and seeking hands-on experience, you can minimize the time needed to acquire the necessary skills. Ultimately, personal commitment, consistency, and dedication are vital in determining the length of time required to learn medical billing and coding.