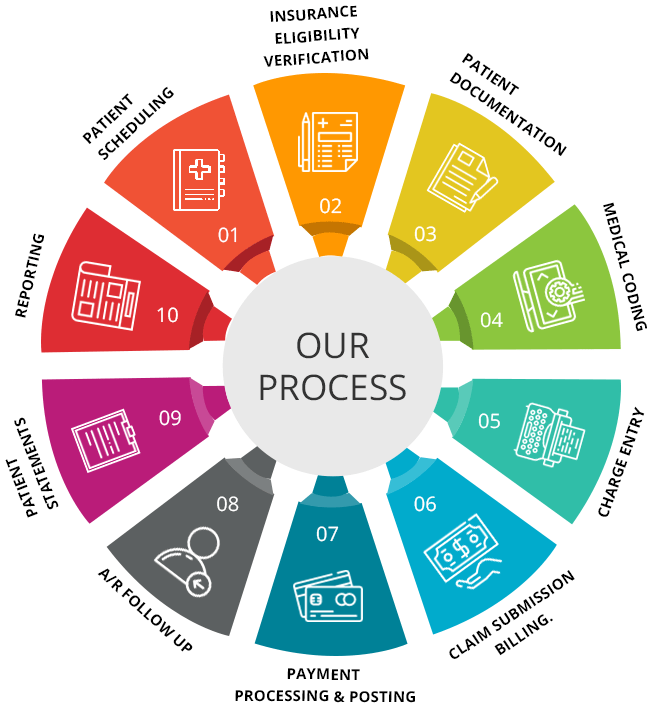
In this article, we will explore the different types of math skills required in the field of medical billing and coding. From basic arithmetic calculations to more complex formulas and statistics, we will delve into the specific areas of math that are crucial for success in this profession. Whether you are already working in the industry or considering a career in medical billing and coding, this article will provide valuable insights into the mathematical knowledge needed to excel in this field. So, let’s get started and discover the math behind medical billing and coding.

Mathematical Concepts in Medical Billing and Coding
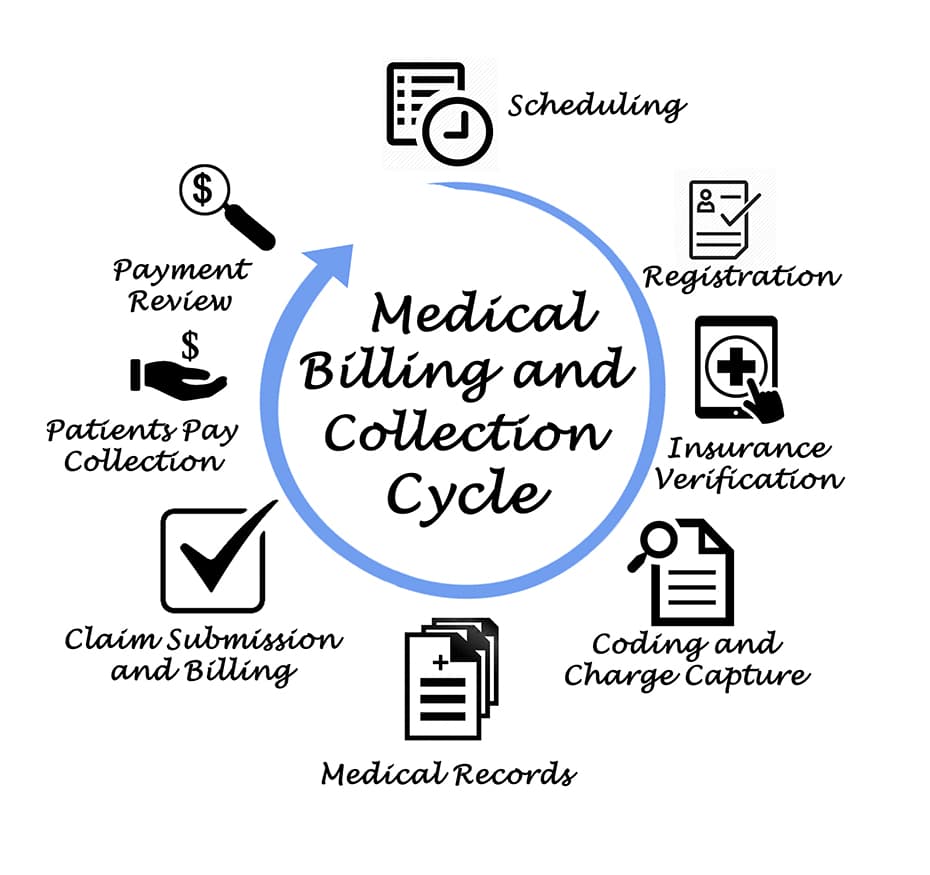
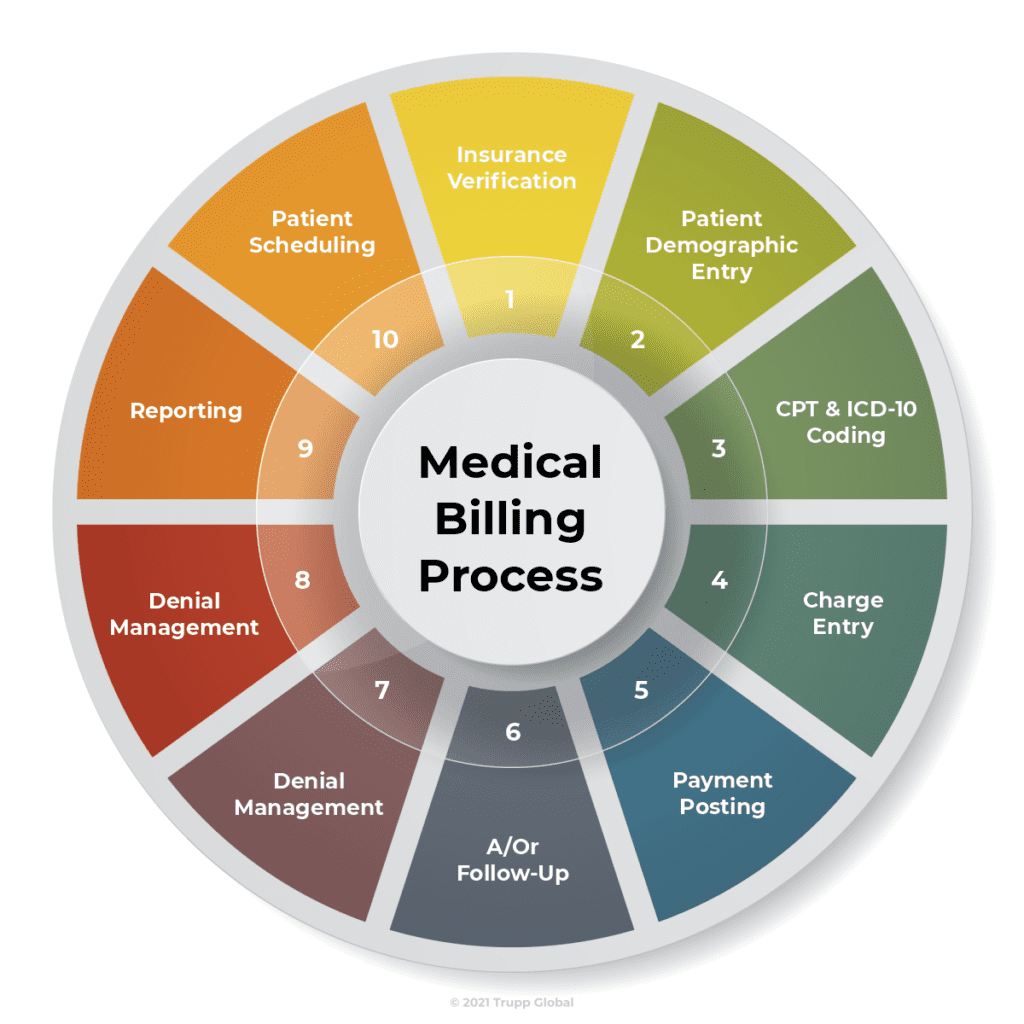
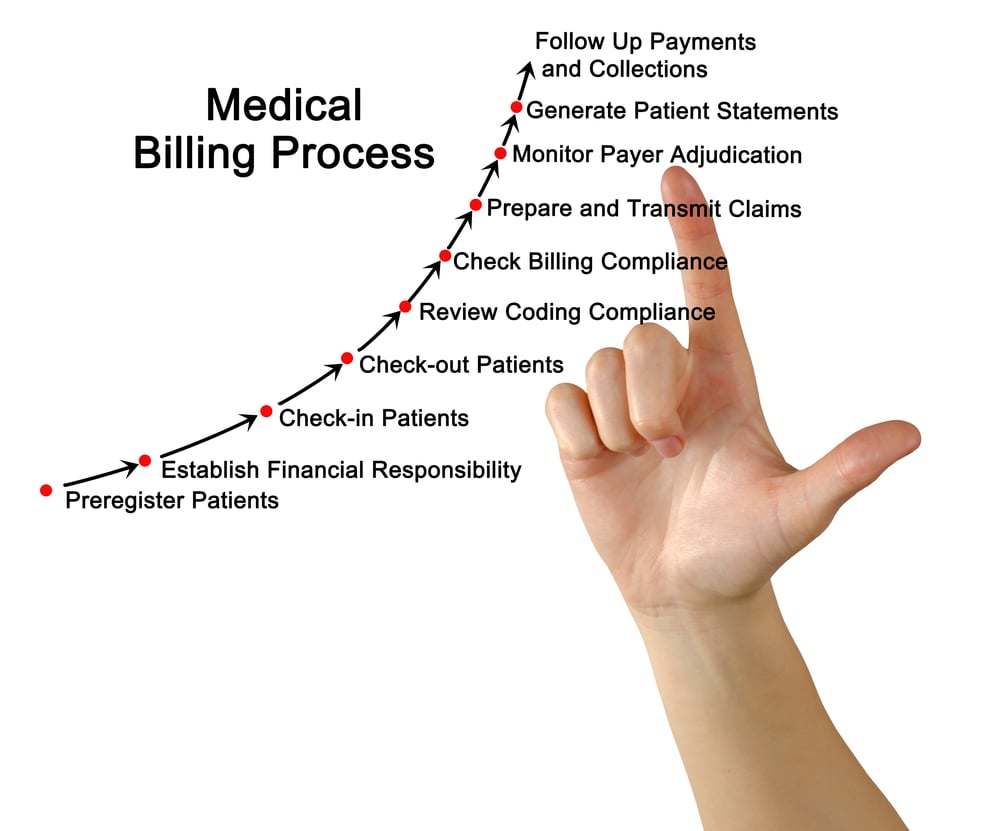
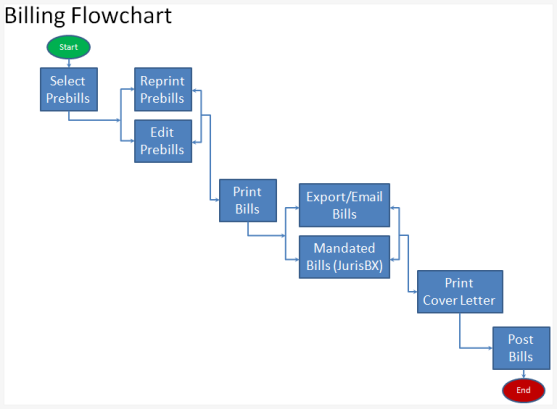
When it comes to the field of medical billing and coding, mathematical concepts play a crucial role in ensuring accuracy and efficiency in various aspects of the job. From arithmetic calculations to algebraic equations, understanding fractions and decimals to percentage calculations, mathematics is an integral part of the daily tasks performed by medical billing and coding professionals. In this article, we will explore the different mathematical concepts involved in medical billing and coding and how they are applied in practice.
Arithmetic in Medical Billing
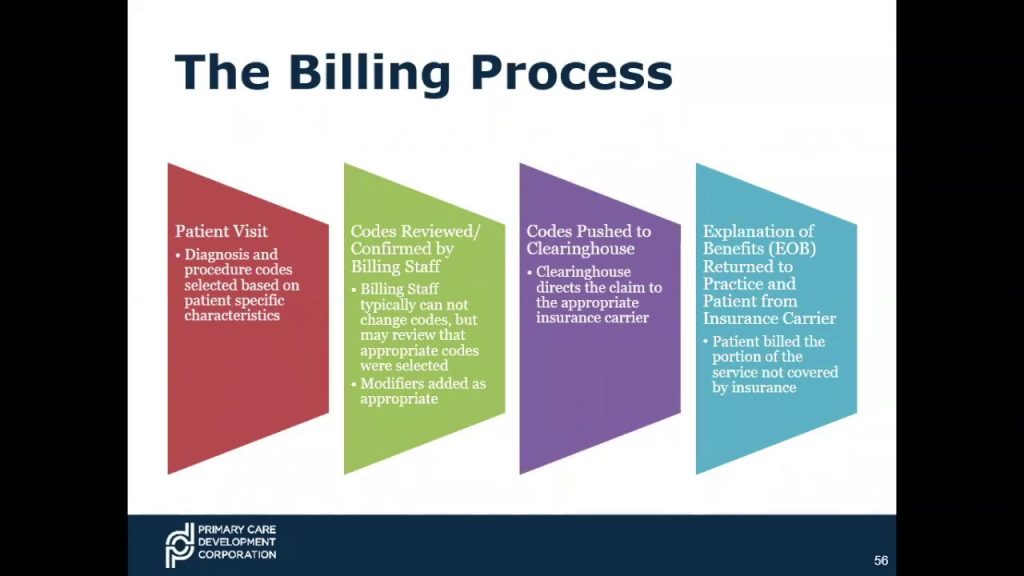
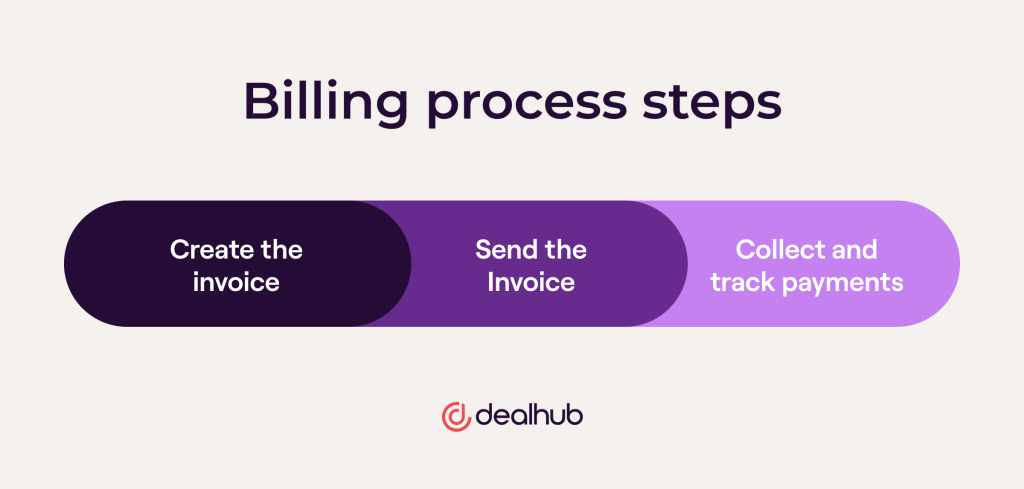
At its core, medical billing involves the process of calculating charges and creating invoices for medical services rendered to patients. This requires a strong foundation in arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Whether it’s determining the total cost of a medical procedure or calculating the remaining balance after insurance coverage, being proficient in arithmetic is essential for accurate billing.
Understanding Fractions and Decimals
Fractions and decimals are commonly encountered in medical billing and coding, especially when dealing with units of measurement and dosages of medication. For example, when calculating the amount of medication needed for a patient based on their weight, it may be necessary to work with fractions or decimals. Being able to convert between different forms of fractions and decimals, as well as perform calculations involving them, is crucial for ensuring the correct administration of medication and accurate documentation of dosages.
Percentage Calculations in Medical Coding
In medical coding, percentages are often used to determine the extent to which a patient’s condition may affect their overall health or the severity of a procedure. This information is then used to assign the appropriate codes for billing purposes. Understanding how to calculate percentages accurately is vital for ensuring that the correct codes are assigned, as errors in percentage calculations could lead to incorrect billing and potential legal and financial consequences.
Applying Algebraic Equations in Billing and Coding
While arithmetic calculations form the basis of most mathematical operations in medical billing and coding, there are instances where algebraic equations come into play. For example, when determining the cost of a procedure, factors such as time, complexity, and additional resources may need to be taken into account. By using algebraic equations, medical billing and coding professionals can accurately calculate the total cost and provide an itemized breakdown in the invoice.
Mathematical Terminology in Medical Billing and Coding
In addition to the various mathematical concepts, medical billing and coding also involve specific terminology and abbreviations that are used in conjunction with these mathematical principles. Understanding this terminology is crucial for effective communication and accurate documentation.
Medical Terminology and its Mathematical Components
Medical billing and coding professionals must be familiar with medical terminology, as it often includes mathematical components. For example, terms such as “milligram” (mg), “milliliter” (mL), and “microgram” (mcg) indicate specific measurements of medication. Familiarity with these terms and their mathematical meaning is essential for accurately documenting dosages and quantities in patient records.
Mathematical Symbols and Abbreviations Used in Medical Billing and Coding
In addition to medical terminology, there are various mathematical symbols and abbreviations used in medical billing and coding. For instance, the symbol “%” represents a percentage, while the symbols “+”, “-“, “×”, and “÷” correspond to addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, respectively. Understanding these symbols and their mathematical meanings is essential for correctly interpreting and calculating numerical information in medical documents and invoices.
Mathematical Applications in Medical Billing and Coding
Now that we have explored the mathematical concepts and terminology involved in medical billing and coding, let’s delve into the practical applications of these mathematical skills.
Medical Dosage Calculations
One of the critical areas where mathematical calculations come into play in medical billing and coding is medication dosage calculations. Medical billing and coding professionals need to accurately calculate the appropriate dosage of medication based on factors such as a patient’s weight, age, and medical condition. This requires a solid understanding of fractions, decimals, and ratios, as well as the ability to convert between different units of measurement. Accuracy in dosage calculations is crucial to ensure patient safety and comply with dosing guidelines.
Calculating Medical Charges and Insurance Claims
Another crucial aspect of medical billing and coding is calculating medical charges and insurance claims. By applying arithmetic calculations, percentage calculations, and algebraic equations, professionals in this field can determine the cost of medical procedures, factor in insurance coverage and deductibles, and generate accurate invoices for patients. Being able to perform these calculations accurately and efficiently is vital for ensuring timely and appropriate reimbursement, minimizing billing errors, and avoiding legal and financial issues.
Analyzing Medical Statistics
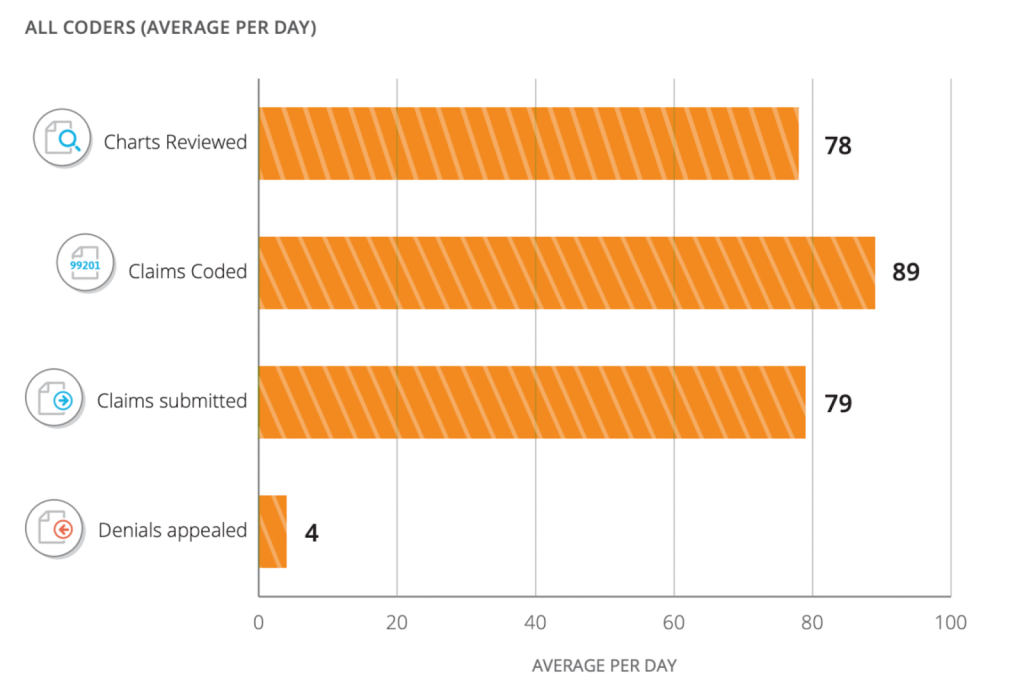
Medical billing and coding professionals are often involved in analyzing medical statistics to identify trends, patterns, and outcomes related to patient care and treatment. By applying statistical analysis techniques, mathematical calculations, and data interpretation, professionals can draw meaningful insights from medical data. This information can be used to improve patient care, identify areas of improvement, and make informed decisions regarding billing and coding practices.
Mathematics in Medical Coding
While we have primarily focused on the mathematical concepts involved in medical billing, it is essential to recognize the role of mathematics in medical coding as well.
ICD-10 Coding and Numerical Classification
In medical coding, the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision (ICD-10) is the widely used system for categorizing and coding diseases, medical procedures, and other health-related conditions. The ICD-10 coding system relies on numerical codes that correspond to specific diagnoses and procedures. Medical coders need to accurately assign these codes based on medical records and documentation using their mathematical understanding to ensure precision and consistency in coding practices.
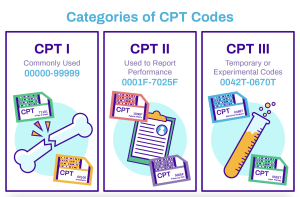
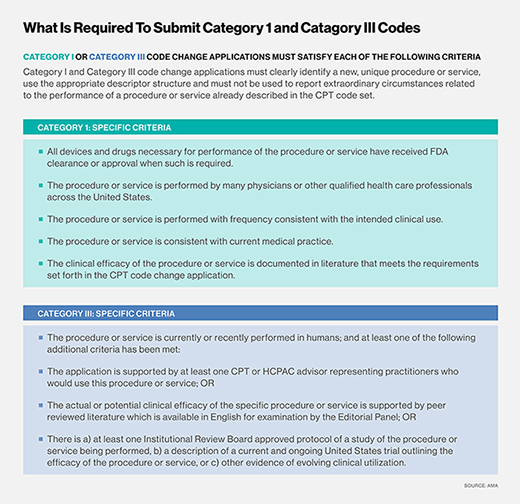
Using CPT Codes for Billing and Reimbursement
In addition to ICD-10 codes, medical billing and coding professionals also work with Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes. CPT codes are used to describe the services and procedures provided to patients. These codes contain both numerical and alphanumeric characters. Accurate coding using CPT codes is crucial for proper billing and reimbursement. Understanding the structure and meaning of these codes requires mathematical proficiency to ensure accurate documentation and communication of medical services provided.

Importance of Accuracy in Mathematical Calculations
Mathematical accuracy is of paramount importance in medical billing and coding due to the potential impact of errors on patient care, billing processes, and reimbursement.
Importance of Precision in Medical Billing and Coding
When it comes to medical billing and coding, precision is key. Errors in mathematical calculations can lead to incorrect invoices, inaccurate insurance claims, and potential financial loss for both patients and healthcare providers. Furthermore, precision ensures that medical records are accurately updated, allowing for continuity of care and appropriate treatment decisions. Therefore, it is crucial for medical billing and coding professionals to prioritize precision in all mathematical calculations.
Impact of Mathematical Errors on Patient Care and Billing
Mathematical errors in medical billing and coding can have severe consequences for patient care and billing processes. Errors such as incorrect dosages, incorrect procedure codes, or inaccurate insurance coverage information can lead to delayed or improper treatment, financial burden on patients, and legal issues for healthcare providers. By maintaining accuracy and attention to detail in mathematical calculations, medical billing and coding professionals can help ensure the smooth functioning of healthcare systems and the well-being of patients.
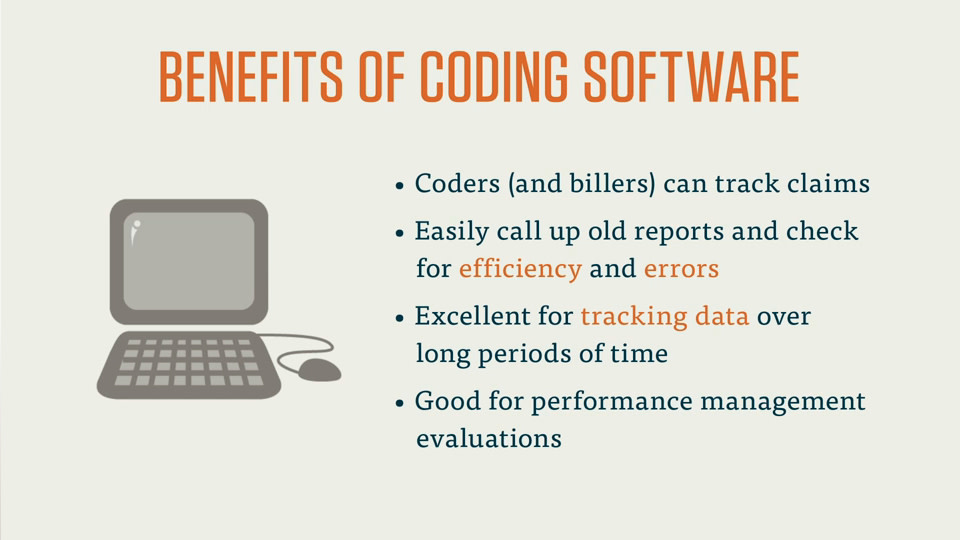
Technology and Automation in Mathematical Calculations
Advancements in technology have revolutionized mathematical calculations in the field of medical billing and coding. Software applications and electronic health records (EHRs) have greatly improved efficiency and accuracy in performing mathematical tasks.
Advancements in Software for Mathematical Calculations in Medical Billing and Coding
Software applications specifically designed for medical billing and coding have simplified and automated many mathematical calculations. These applications often include built-in calculators for performing arithmetic operations, converting units of measurement, and calculating percentages. By leveraging such software tools, medical billing and coding professionals can minimize manual errors and focus on more complex tasks that require critical thinking and analysis.
Integration of Mathematics with Electronic Health Records
The integration of mathematics with electronic health records (EHRs) has also enhanced the accuracy and efficiency of medical billing and coding. EHR systems can automatically populate demographic and clinical data, perform calculations, and generate standardized invoices based on established mathematical formulas and algorithms. This integration reduces the risk of human errors, streamlines billing processes, and ensures consistency in documentation and coding practices.

Educational Requirements for Mathematical Proficiency
To excel in the field of medical billing and coding, individuals need to possess the necessary skills and knowledge related to mathematics.
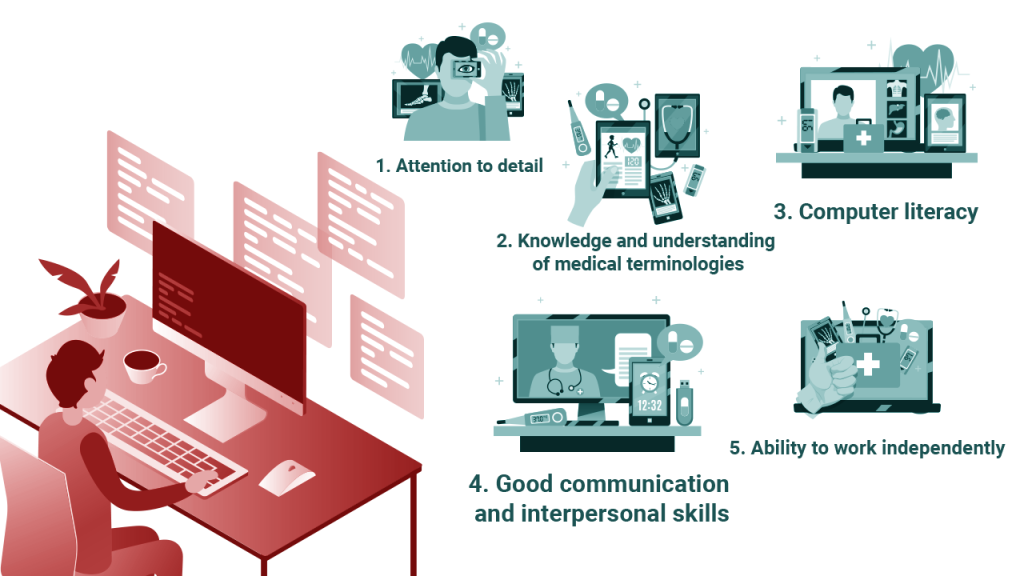
Skills and Knowledge Required for Medical Billing and Coding Professionals
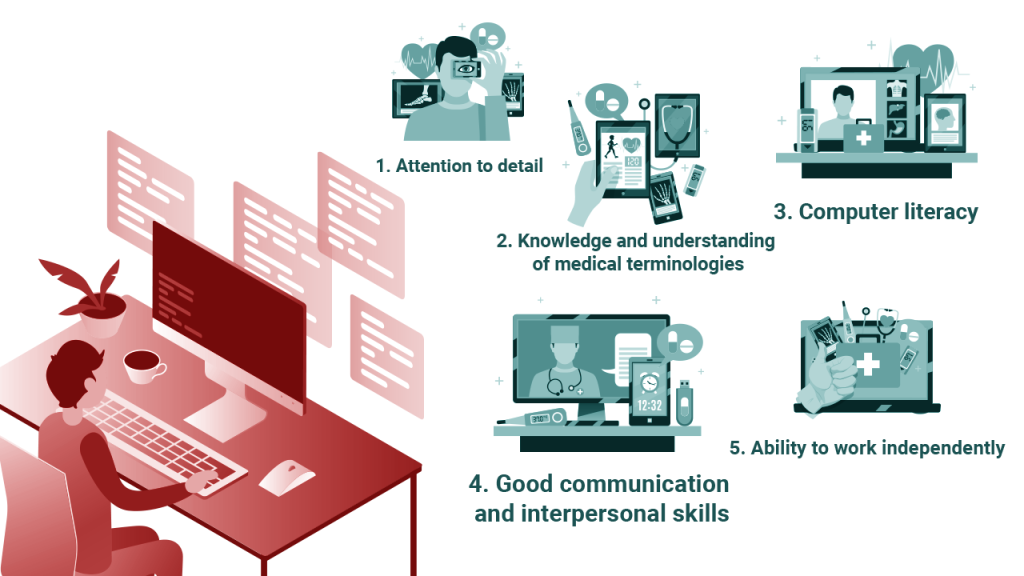
Medical billing and coding professionals need a solid foundation in arithmetic, fractions, decimals, algebra, and percentage calculations. They should also be well-versed in medical terminology, including mathematical components and numerical classifications. Proficiency in using mathematical symbols and abbreviations is crucial for accurate documentation and communication in this field. Additionally, individuals in this profession should be detail-oriented, possess strong analytical skills, and have the ability to interpret and analyze numerical data.
Training and Certification Programs in Mathematical Competence
To ensure competence in mathematical calculations, aspiring medical billing and coding professionals can pursue training and certification programs that focus on mathematics in healthcare. These programs provide comprehensive instruction in arithmetic, fractions, decimals, percentages, algebraic equations, and mathematical applications specific to medical billing and coding. By completing such programs, individuals can enhance their mathematical proficiency and increase their employability in this field.
Future Trends in Mathematical Applications in Medical Billing and Coding
As technology continues to evolve, the future of mathematical applications in medical billing and coding holds promising advancements that will further streamline processes and improve overall accuracy.
Emerging Technologies and Mathematical Innovations
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning have the potential to revolutionize mathematical calculations in medical billing and coding. These technologies can automate repetitive tasks, analyze large amounts of data, and identify patterns and trends that may be overlooked by manual processes. By leveraging AI and machine learning algorithms, healthcare providers can enhance the accuracy and efficiency of mathematical calculations and coding practices.
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Mathematical Calculations
Artificial intelligence has the capability to transform mathematical calculations in medical billing and coding by performing complex calculations, predicting billing outcomes, and ensuring compliance with coding standards. AI-powered systems can analyze medical records, identify discrepancies, and generate accurate billing codes and invoices. This technology has the potential to greatly reduce errors, improve workflow efficiency, and enhance overall patient care and reimbursement processes.

Ethical Considerations in Mathematical Decision Making
While mathematical calculations in medical billing and coding are essential for accurate documentation, billing, and coding practices, ethical considerations must also be taken into account.
Ensuring Fairness and Equity in Billing and Coding Practices
Mathematical decision making in medical billing and coding should prioritize fairness and equity. This includes ensuring that mathematical algorithms and calculations do not discriminate against certain groups based on factors such as race, gender, or socioeconomic status. Healthcare providers and policymakers must be vigilant in monitoring and addressing any biases or disparities that may arise from mathematical processes to ensure equitable access to healthcare services and fair billing practices.
Avoiding Bias and Discrimination in Mathematical Algorithms
Mathematical algorithms used in medical billing and coding should be designed with care to avoid any biases or discrimination. It is crucial for practitioners and developers to continuously evaluate and refine algorithms to minimize the risk of adverse outcomes and unfair treatment. Transparency in how mathematical algorithms are developed and applied is essential to gain the trust of patients, healthcare providers, and stakeholders in the healthcare industry.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mathematics plays a critical role in medical billing and coding. From arithmetic calculations to algebraic equations, understanding fractions and decimals to percentage calculations, professionals in this field rely on various mathematical concepts to ensure accuracy and precision. Medical billing and coding professionals must possess a strong foundation in mathematics, along with the ability to navigate complex terminologies, symbols, and abbreviations. The continuous development of technology and integration of mathematics with electronic health records will further enhance the speed and accuracy of mathematical calculations in this field. However, to ensure ethical and equitable practices, it is vital for professionals to remain vigilant and proactive in addressing any biases or discrimination that may arise from mathematical decision making. By staying updated with the latest advancements and continuously honing their mathematical skills, medical billing and coding professionals can provide efficient and accurate services, ultimately contributing to better patient care and well-functioning healthcare systems.